The connection between environmental, social, and economic spheres of life can be demonstrated through the lens of their intersection in different fields. One of them is agriculture, and its examination from the selected perspective seems reasonable in order to reveal the interrelation of the above concepts alongside the importance of sustainability. Therefore, this paper aims to analyze the link between the mentioned areas applied to the production process.
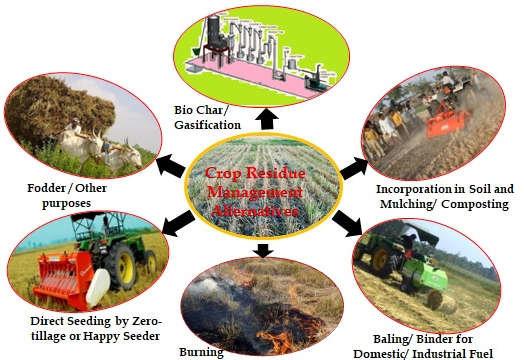
The primary source of information in this situation is the study of Chinese scholars intended to show the impact of crop residue and operations for its proper treatment. According to this article, the results of the assessment of regular procedures, including collection, transportation, and the subsequent conversion, imply the presence of environmental impacts (Zhang et al., 2021). They are connected to carbon emissions, which should be decreased in order to ensure the sustainability of this activity in the long run (Zhang et al., 2021). Meanwhile, the concerns are complemented by economic considerations, such as the costs of delivering them as well as energy utilization accompanying the process. In turn, the social aspect of this issue is the response of the population to their shifting living conditions under the influence of these practices.
To summarize, the performance of any operations in different fields, for instance, in agriculture, is a multi-faceted activity. It implies the intersection of economic, environmental, and social concerns while their resolution depends on the implementation of efficient policies aimed at reducing the negative impact. This outcome means that sustainability is crucial for addressing all the needs as per the above categories, and the importance of this task is complemented by the necessity to mitigate different risks.
Question: How can the enterprises involved in the process of crop residue management select a method which resolves all of the challenges of a social, economic, and environmental nature?
References
Singh, R., & Upadhyay, S. K. (2018). Ecofriendly management of paddy crop residues for sustainable environment and development.BioScience Research Bulletin, 34(2), 59-72.
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Liu, H., Zhao, G., Tian, Y., & Xie, K. (2021). Environmental, social, and economic assessment of energy utilization of crop residue in China. Frontiers in Energy, 15(2), 308-319.