Executive Summary
The adoption of sustainable development is one of the core aims of every organization operating in the current competitive environment. Anglo American PLC, which is a well-known mining company operating as the second-largest mining company in the industry, intends to embellish the rate of sustainability to retain its global position in the critical competitive mining environment. For this purpose, the company is engaged in the development and implementation of various strategical actions. Subsequently, in the under review report, an attempt is made to examine sustainability attainment for Anglo Americans in the future through water use and management through minimizing wastes. The report also exhibits the shareholders of Anglo American PLC and the initiative that the company has taken into account for the engagement of those stakeholders. Additionally, the effective usage of an external and internal accounting report has also been drafted accompanied by the relevant recommendations for the selected company.
Introduction
This report highlights the significant practices through which Anglo-Americans can attain long-term sustainability in water usage.
Water Use and Impact on the Mining Industry
Reducing water waste is the first priority of organizations to attain long-term sustainability in the mining industry. Sustainability can be achieved by modifying or installing water-efficient equipment and devices, and by fixing conductivity controllers on each water cooling tower. However, the most efficient technique to reduce water waste is to develop a water management plan (Norgate and Haque 2010, p. 271). This is summarised in the pie chart below.
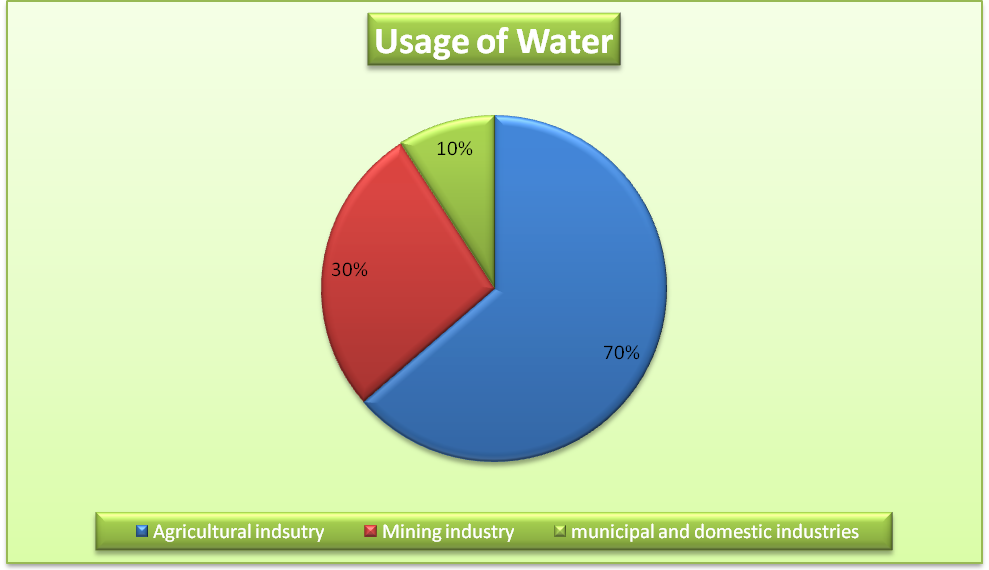
Graph 1 above shows the share of different industries in the use of water. Apparently, the Agriculture Industry is the leading in water usage at 70% followed by Mining Industry at 30% and Domestic Industry at 10% (Prior et al. 2012, p. 591).
The Anglo-American PLC
Anglo-American PLC is a multinational metal and mining corporation that was built in 1917 in Johannesburg, South Africa. In 1999, it was listed in London, United Kingdom. The company deals in producing metals such as diamonds, platinum, copper, nickel, iron ore and thermal and metallurgical coal. It operates in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. The company professes deep concern for corporate social responsibility and conducts business operations with respect to the environmental and human benefits (Northey et al. 2013, p. 119). At present, the company is the world’s largest producer of platinum.
The vision of the Anglo American PLC is to be a global leader in PGMs (Platinum Group Metals) and to deliver its operations in a value-driven and socially acceptable way. The company’s goal is to gain long-term sustainability for its organizational future through reducing water waste and by forging strong relations with its company stakeholders (Mudd 2008, p. 139). The number of employees that are currently working in the corporation is 135,000. In 2015, the company earned a net income of US$ 5.842 billion (Durand 2012, p. 31).
Corporate Social Investments by the Anglo American PLC
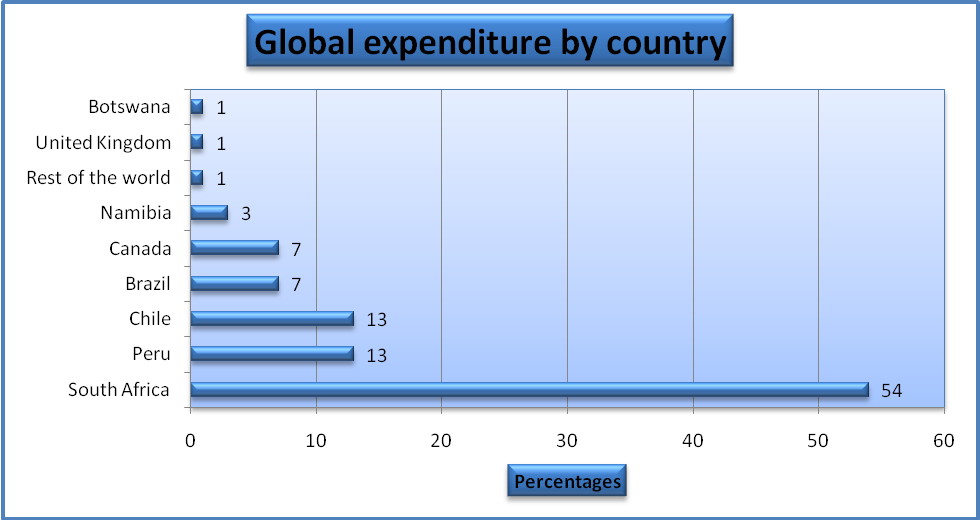
The total global investment made by Anglo-American Company amounted to $135,773 thousand. The graph below shows the allocation of the total investment for each country. South Africa was allocated the highest amount while Botswana had the least as indicated in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Global expenditure by the Anglo-American Company. (Source: Anglo American PLC 2014a).
This is summarised in bar graph 1 below.
The allocation of the total social investment to various activities within the company is summarized in table 2 below.
Table 2: Global expenditure by type at the company. (Source: Source: Anglo American PLC 2014a).
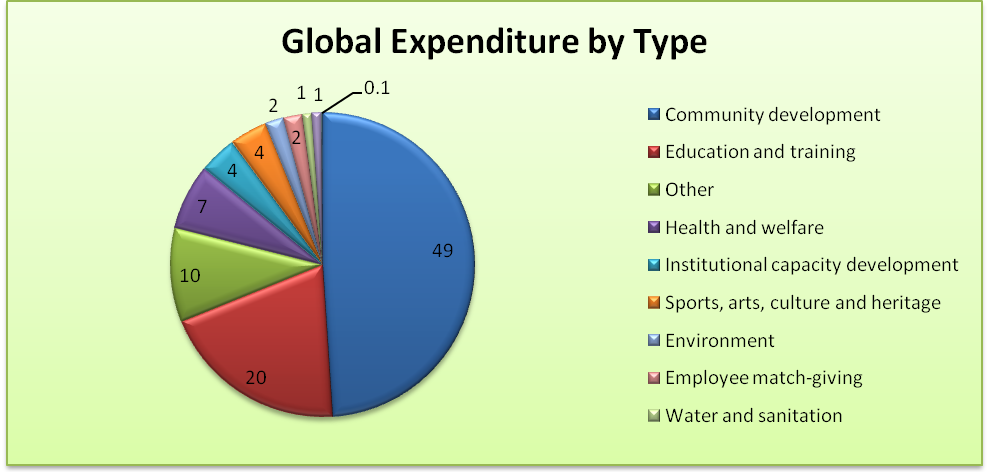
The data and the graph above show that community development was allocated the highest amount while energy and climate change had the least amount. Water and sanitation were only allocated 1% of the total expenditure.
Sustainability Issue Analysis
Water security strategy of Anglo American PLC for the attainment of sustainability
Anglo American PLC uses water throughout the sequential mining progression. The progression sequence includes extraction of metals and transportation, crushing, grinding and finally processing metals and minerals (Eskerod & Huemann 2013, p. 47). With this respect, Anglo American has adopted a water reduction strategy since 2011 in order to meet its water requirements and to attain sustainability for its organizational future. The water reduction strategy is called the Water Efficiency Target Tool (WETT). which represents the 10 years water-saving projection plan from 2011 to 2020. It is the corporate social investment project that enables the company to forecast the water demand for individual operations, set targets to reduce predicted water consumption, and establish water-saving projects to meet targets (James 2011, p. 45).
Before implementing the WETT, the company first tested it in all seven units of platinum production in South Africa. After earning a positive result in water saving, the company then implemented the strategy in other units operating in different global regions. With this investment, the company achieved a 21% improvement in water consumption in the first year of its implementation, which was the year 2011. Over time, the project has yielded more significant results saving 22% in 2013, which is equivalent to saving 30 million cubic meters of water. This equates to 126 billion glasses of water (Anglo American PLC 2014b). The results of the WETT are summarized in table 3 below.
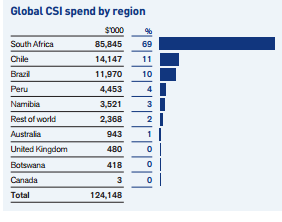
Table 3 above illustrates the amount of investment that the company made in order to save or use water efficiently. With the investment of $85,845 on WETT, the company had a water-saving rate of 69%, which is the highest in comparison to other regions (Prior et al. 2012, p. 579).
The company has also established Water Action Plans (WAP) in order to manage the distribution of water to all its manufacturing and production plants. These action plans were developed to face the situation of high risk and uncertainty of water supply from reservoirs. Through these plans, the company is managing the supply of adequate water with its efficient use to the project at Los Bronces in Chile and its rain-immunization program at Coal in Australia. These action plans also provide certain solutions and alternative techniques for securing water in times of extreme weather variability and storm conditions (Anglo American PLC 2014b). The company has invested US$ 100m in establishing a water recycling plant as part of the WAP. This plant cleans wastewater from underground mines and converts it into drinking water. Through this plant, the company fulfills 66% of its operational water requirements by re-using and recycling wastewater. This plant currently provides drinking water to 51,000 people with 21% of its water supply in the municipality community of Emalahleni. Consequently, it has decided to increase its investment to improve the capacity and efficiency of the plant in recycling water from 30 Ml to 50 Ml as summarised in graph 2 below.
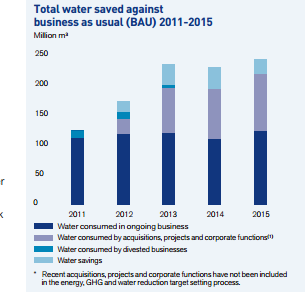
Graph 2 above represents the operational excellence of Anglo American from 2011 to 2015. It presents the company’s water-saving and water consumption processes side by side. The light blue region shows that the company is continuously improving its water-saving efforts through its water reclamation plant. In 2011, water security stood at only 4% while in 2012, the percentage rose to 9%. In 2013, the company secured 64% of its water and 68% in 2014. In 2015, the company recycled 80% of its water for drinking and re-using purposes (Anglo American PLC 2015).
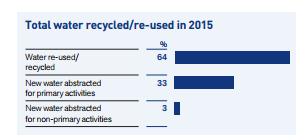
In the year 2015, the Anglo American PLC invested in New Integrated Water Technology in order to save and use water more efficiently. Through this technology system, the company brought new and advanced ways to save water including evaporation control and haul road dust suppression methods. These methods assist in several processes for water security as summarised in Graph 5 (Durand 2012, p. 29). Examples of the usefulness of these technologies can be seen in how, in the year 2016, they have facilitated Los Bronces in Chile and the rain-immunization program at Coal in Australia to control evaporation from water reservoir plants on the sites and, with the use of thickeners, recover water from slime dams. This technology led to recycling up to 64% of water in 2015 with 33% of water abstracted from primary activities and 3% of water abstracted from non-primary activities (Amit & Zott 2012, p. 41).
To further improve the water abstraction process through primary and non-primary resources, Anglo-Americans organized an Innovation Open Forum by Name Future Smart in the year 2015 with the aim to reduce water dependency by the company. It was a four-day event attended by several water specialists from different industries. They provided numerous useful and constructive methods and techniques to eliminate the dependency of the mining industry on water resources. They also provided guidance for the use of technology to attain this noble purpose and contributed ideas to start new water-saving projects for 2017 onwards (Anglo American PLC 2014b).
Water Consumption and Sustainability at the Anglo-American PLC
The consumption of water at the Anglo American PLCE over the last dour years is summarised in table 4 below.

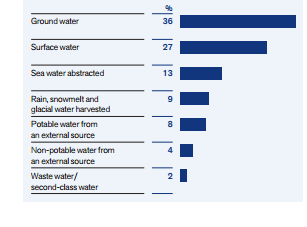
Table 4 above shows the water consumption activities of Anglo-American mining companies from the year 2011 to 2015. There is the apparent decline in water usage from 195.88 million cubic meters in the year 2011 to just 124.14 million cubic meters in the year 2015. The percentage of water re-used/recycled increased from 64% in the year 2011 to 70% in the year 2015. As indicated in Graph 6, the company has estimated an extraction of 36% of the water from a groundwater source, 27% from a surface water source and 13% from seawater. In addition, the company will be able to abstract 9% water from the sources of rain and snowmelt from glaciers. Furthermore, the company will abstract 8% potable water and 4% non-potable water from external sources (Hodgkinson et al. 2014, p. 1669).
Stakeholder Identification (Key Stakeholders Group)
Stakeholders refer to any individual or group of people that have an interest in the loss or profit of an organization. Moreover, in the opinion of Eskerod and Huemann, (2013, p. 44), stakeholders are an individual or a group that can affect and be affected by organizational decisions, successes or failures. As affirmed by Wang, Liu, and Mingers, (2015, p. 569), for every organization that intends to attain a sustainable market position, pleasing the organizational stakeholders is one of the core interests along with responsibility. As has been clearly demonstrated by the Anglo-American sustainability report of 2015, the main visionary aspects of Anglo-American involve the motive of developing a constructive association with their stakeholders, based on the foundation of mutual respect, authenticity, and trust as summarized in figure 3 below.
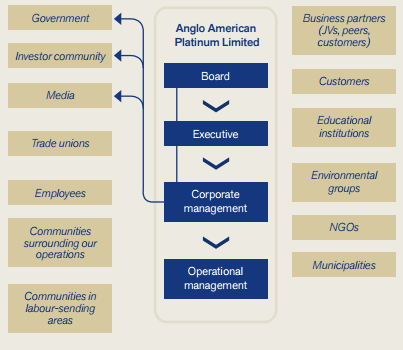
Figure 3 above depicts the list of all stakeholders of Anglo American including both primary and secondary stakeholders of the firm. Thus, in regards to the above figure, it can be seen that the main stakeholders of the company incorporate investors who invest an amount of capital to assist the business operations without any major hurdles. The second group of stakeholders is the employees, who without their cooperation and efficient work the company cannot move toward success. Additionally, any action of the company in terms of policies or rules and regulations can affect the employees. The other stakeholders are trade unions and customers. As per the sustainability development report of Anglo American PLC (2014a), the management of Anglo has declared their shareholders as a part of their primary stakeholders. The report further reveals that the other business peers of the organization such as the business partners are also under the consideration of the management, as they play a pivotal role in contributing constructively to the advanced business initiatives that further aid in enhancing the collective interest of the entire business.
Justification of the Selection of Three Stakeholders
The three major stakeholders that have been selected from Figure 3 include partners, governments, and consumers. However, each stakeholder belongs to either the primary or secondary domain of stakeholder and has a direct or indirect influence on the performance, growth, and development of the organization. The three selected stakeholders are considered as key influencers, as they exert a direct influence and can be directly influenced by the decision, success or failure of Anglo American PLC. As an international mining company, it is subjected to the intense pressure of governmental regulation at both the local and the international levels. Furthermore, as Anglo American is a stock exchange listed company due to its worldwide excellent performance, they are also bound to follow the regulations and legislations of the United Kingdom (Anglo American PLC 2014b).
According to Amit and Zott (2012, p. 41), every organization operating in the market intends to please their customers by providing excellent products or services as compared to their competitors. Thus, the share of success or failure is also highly dependent on the customers of an organization, which pinpoints them as important stockholders. The third main group of stakeholders that has been selected is that of the partners. The reason behind selecting them over others is that partners are the ones who have invested capital in the business and can suffer badly in the case of the organization’s failure. However, after keenly appraising the Annual report of Anglo American PLC (2015), it has been affirmed that due to the intense importance of the three selected stakeholders the management of Anglo has embedded stakeholder engagement as a major part of their core values, policies and organizational strategies. For this purpose, in order to evaluate their engagement with stakeholders, and to cope with any inadequacies, Anglo American PLC has currently developed an advanced stakeholder policy. According to this revised policy, the stakeholder engagement process is based on four key phases, as illustrated in figure 4 below.
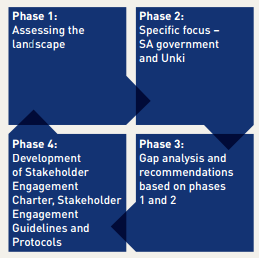
In light of Figure 4 above, the first phase of engagement is assessing the landscape that incorporates the identification of stakeholders in terms of registration of stakeholders’ issues, list down the Amplat’s and the in-depth evaluation of policies. The second phase integrates the attainment of the understanding of all the governmental regulations, legal legislations and the identification of regulations that impact the involvement of Amplats. Under the third phase, the pre-designated team alleviates the risk of stakeholder fatigue and confusion due to the intervention of Amplats; while in the fourth phase the managerial team develops the appropriate measures to deal with the evaluated gaps and stakeholder issues.
Internal Accounting Report
Table 5: Internal Accounting Report of Anglo American PLC. (Source: Anglo American PLC 2014b).
Table 5 above exhibits the internal accounting report of Anglo American PLC, based on both the financial as well as the non-financial informational aspects. The report shows that the total revenue that was generated by the company amounted to $27,073million in 2014. The operating profit was low at $138 million. The company made a loss of $1,524 million. Further, the amount of loss that can be attributed to the shareholders was $2,513 million. The results in the income statement show that the company was not profitable in the year 2014. The statement of financial position shows that the assets amounted to $66,010 million. The total liabilities were $33,833 while equity amounted to $32,177. Thus, liabilities exceeded equity by a small margin. The business was able to generate positive cash flow from operating activities amounting to $6,111 million. Cash flow was used in both investing and financing activities. Thus, at the end of the year, the net cash flow that used in the business amounted to $841 million. The total capital investments made by the company during the year amounted to $6,018 million. It is worth mentioning that the primary objective of any business is to generate profit and maximize earnings for the shareholder. Since the company made a loss in the year 2014, it is advisable that the company reduces financial allocation to corporate social investment. The total ratio of water consumed in 2014 was 100%. In 2014, Anglo paid 1,298 $ million in tax.
External Accounting Report
Table 6: External Accounting Report. (Source: Anglo American PLC 2014a).
Table 6 above shows the external accounting report of Anglo American PLC, including financial information regarding social welfare, safety, human resources and divested business aspects. In light of this report, it has been estimated that in the year 2014 the number of work-related loss of lives was 2, while CSI expenditure that year was nearly 124.1 Million. Furthermore, the full-time employee average was approximately 96,630. Notwithstanding, the company had to endure an approximately 124.1$million CSI expenditure.
Table 7: External Accounting Non-Financial Strategic Report. (Source: Anglo American PLC 2015).
Table 7 above, shows the external accounting non-financial aspect of the report that affirmed the latest initiatives of Anglo American PLC, which the company has designed in order to engage the main stakeholders of the company.
Attainment of Sustainability by Anglo American in Light of Internal and External Report
With respect to the above discussion of the under review report, it has already been acknowledged that the attainment of sustainability is an important aim of every organization that intends to secure a strengthened position in the current competitive environment. Similarly, Anglo American Plc is also engaged in making possible efforts for attaining long-term sustainability. As asserted by their CEO, Sir John Parker, the entire mining industry has faced a period of exceptional challenges. Additionally, the rapid downturn was putting intense pressure on all the companies operating in the industry to develop and implement such advanced initiatives that can aid them in sustaining an effective position in the critical market. Yet, with respect to the above-represented internal and external accounting reports, it has been analyzed that one of the major facets that can assist the Anglo-American organization to attain strengthened long-term sustainability is reducing the consumption of water or increasing the ratio of recycled water.
In the above report, it has been clearly mentioned that the total use of recycled water was approximately 59% which further translates into a reduction of new water consumption costs. Undoubtedly, due to natural uncertainties that mine sites experience, there can be hurdles regarding the inflow of water. In such situations, the use of recycled water can help the organization by saving time as well as cost. Apart from recycling water, the value of water consumption for non-primary use was nearly 3%, which is beneficial for the successful attainment of sustainability for the company. Moreover, by implementing health and safety strategies, the organisation was able to decrease the rate of workplace injuries and death, resulting in further improving the market reputation of the organisation and enhancing the trust of stakeholders.
The increase in CSI and CSR activities boosted the probability of long-term suitability for the organisation. A study conducted by Kennedy, (2013, p. 54) revealed that organisations that intend to be involved in CSI activities gain more rapid success when compared to those that do not participate in the CSI domain. The study further emphasized that CSI activity involvement of an organisation builds public trust. Along with this aspect, another major initiative that can add precious value to the organisation is the engagement of shareholders and the strengthened association of the company and shareholders.
From the findings, it has been evaluated that the company is involved in shareholder engagement approaches. In terms of government, the company has utilized an engagement channel of face-to-face meetings and participation in intergovernmental processes. For customer engagement, Anglo American has implemented the approach of direct business engagement. As for partners, engagement in the decisional processes has been implemented, thus, increasing the contribution and cooperation of organizational partners. This shareholder engagement technique can boost sustainability for the organization since a strong association with shareholders reveals a positive impact on the sustainable development of an organization. Apparently, the analysis indicates that the Anglo American PLC has successful water usage sustainability strategies such as WETT and WAP. The internal and external accounting reports suggest that the company is geared towards sustainable financial health.
Recommendations
Based on the findings of the report, the Anglo-American should adopt the following techniques and methods to attain long-term sustainability for its organizational future.
Focusing on stakeholder benefits and water-saving activities
The company should focus on stakeholder benefits and water-saving activities in order to achieve a culture of sustainability for the organization. Likewise, by extending its relations with stakeholders, it should achieve favorable results in strategic missions. For instance, the company’s CSR and SEA activities should reflect the interests of stakeholders (James 2011, p. 404). At the same time, the company should promote the use of primary activities, like dust suppression, for purifying water for drinking purposes. Additionally, future company strategies should acknowledge their corporate social responsibility and social and environmental accountability through organizing staff training events concerning the control and management of water. In my opinion, water specialists could be invited to train employees on how to use advanced technologies for water saving, as well as initiate more water security projects in the coming years.
Long-term budget plan for water-securing activities
The company should initiate a 10 years budget plan for water securing activities as this will help in utilizing and managing the assets and power in the most positive and beneficial way. In order to attain water security, the company should fix and install water-saving machines and equipment. It is critical for the company to follow governmental regulations to guarantee a peaceful business environment. The Anglo American PLC should reinvent its technologies to prevent water wastage and water contamination(Wang et al. 2015, p. 581). In my opinion, this will go a long way towards pleasing its customers. Lastly, the Anglo American PLC should maintain monthly reporting because this will facilitate accurate forecasting of the water action plans for the upcoming projects to guarantee sustainability in water usage, reuse, and conservation.
Conclusion
From the above analysis, it is apparent that Anglo American PLC has the strong market position and sustainable strategies for reducing water wastage. The company has integrated the key stakeholders in its operational sustainability strategies through its current four-phase engagement models. The report has also presented the significance of internal and external accounting reports as carrying valuable data on the financial soundness of different sustainability initiatives. Apparently, the Anglo American PLC has managed to achieve its short-term goal of reducing water wastage in mining and improving water reuse/recycling. For instance, since the introduction of the WETT and WAP strategies, the company has managed to reduce water usage by about 25% and increase recycling/reuse by 70%.
Reference List
Amit, R. and Zott, C. (2012) ‘Creating value through business model innovation’, MIT Sloan Management Review, 53(3), 41-42.
Anglo American PLC (2014a) Anglo American plc Annual Report. Web.
Anglo American PLC (2014b) Anglo American plc Sustainability Development Report. Web.
Anglo American PLC (2015) Anglo American plc Sustainability Report. Web.
Durand, J.F. (2012) ‘The impact of gold mining on the Witwatersrand on the rivers and karst system of Gauteng and North West Province, South Africa’, Journal of African Earth Sciences, 68(3), 24-43.
Eskerod, P. and Huemann, M. (2013) ‘Sustainable development and project stakeholder management: what standards say’, International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 6(1), 36-50.
Hodgkinson, J.H., Hobday, A.J. and Pinkard, E.A. (2014) ‘Climate adaptation in Australia’s resource-extraction industries: ready or not?’, Regional environmental change, 14(4), 1663-1678.
James, L.A. (2011) ‘Contrasting geomorphic impacts of pre-and post-Columbian land-use changes in Anglo America’, Physical Geography, 32(5), 399-422.
Kennedy, G. (2013) Anglo-American strategic relations and the far East, 1933-1939: Imperial crossroads. Abingdon: Routledge.
Mudd, G.M. (2008) ‘Sustainability reporting and water resources: a preliminary assessment of embodied water and sustainable mining’, Mine Water and the Environment, 27(3), 136-144.
Norgate, T. and Haque, N. (2010) ‘Energy and greenhouse gas impacts of mining and mineral processing operations’, Journal of Cleaner Production,18(3), 266-274.
Northey, S., Haque, N. and Mudd, G. (2013) ‘Using sustainability reporting to assess the environmental footprint of copper mining’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 40(3), pp.118-128.
Prior, T., Giurco, D., Mudd, G., Mason, L. and Behrisch, J. (2012) Resource depletion, peak minerals and the implications for sustainable resource management. Global Environmental Change, 22(3), pp.577-587.
Wang, W., Liu, W. and Mingers, J. (2015) ‘A systemic method for organisational stakeholder identification and analysis using Soft Systems Methodology (SSM)’, European Journal of Operational Research, 246(2), 562-574.