Apple: Efforts to profitability after the crush
- Increased spending on research and development.
- Consistent technological improvement of gadgets.
- Focus on high quality level.
- Involvement of customers in designing new technologies.
Apple allocated a significant amount of resources to its research activities at a time when most companies were limiting their expenditures on activities such as R&D. This provided the company with a greater ability to initiate new technology, which they included in their gadgets. Apple products could not be compared to any of the rival products in the market as it was original and incorporated great quality that competitor products lacked. This attracted consumers as they opted for products that would last longer and save them the trouble of buying new products after a short period.
- Introduction of new OS with flexible features.
- Building a single device with the features of many other devices.
- Locking device software.
Apple introduced an operating system that sought to provide more benefits to users as compared to other existing systems in the market. Because more users could still not afford the cost of buying separate devices, Apple incorporated the idea of designing a single product that would have multiple features, such as MP3 player, camera, browser, among many others. This augured well with the market as it was less costly to acquire an iPhone with all the features combined than acquiring separate devices that only performed a single tax. Apple also introduced the idea of locking its devices and software such that it would in turn become difficult for rival firms and non-consumers to enjoy its benefits. This increased the urge for buyers to acquire the devices so as to enjoy.


Hewlett-Packard: Efforts to profitability after the crush
- Consumer cash-back programs.
- Lay-off of 2% of the workforce.
- Acquired Electronic Data Services (EDS).
- Cutting 24,600 jobs at EDS (Savitz, 2012).
HP introduced a program in which it traded cash for old PC’s and other electronic devices, such as cameras, printers, and smart phones, from consumers. The program involved devices from all manufacturers, including HP’s rivals. HP’s program became popular because it came at a time when consumers had little cash to spend on such devices . It spurred PC upgrades from consumers who had opted to stay with old models because of the poor economy. HP also laid off about 6,000 of its workers in a bid to reduce expenditure and acquired another global IT firm, EDS, which consequently boosted the overall services revenue by close to 99%.

Unethical Practice: Apple
- Tax evasion tactics (RT, 2013).
- Unbearable working conditions in supplier companies.
- Anti-competitive behavior.
- Anti-trust issue (WRVO, 2013).
- Patent violation.
Apple has employed tax-evading tactics over the last four years that have seen the company shield close to $74 billion of its profits from being taxed. It has created several international subsidiaries that lawfully provide it with the loophole to evade taxes in the USA (WRVO, 2013). The company also employed cost cutting measures in 2011, which involved employing 500,000 workers in China to help in the manufacture of its devices. The working conditions were inhumane and there were increasing cases of suicide. In order to unfairly ward-off competition, Apple locked all its devices into its online software and music store iTunes. This saw the company create an unjust monopoly through the use of iTunes service. The company also altered its existing terms of service by denying Apple users the ability to use other programs that were not approved by the company. This saw such programs as Adobe Flash being disabled on all iPhone gadgets. Apple’s main competitor in the mobile phone industry, Samsung, has sued Apple of violating its patent rights in a move that is seen as an attempt by Apple to employ unorthodox means to win competition.

Unethical Practice: HP
Pretexting:
- Unethically obtaining private information concerning board members.
- Unethically obtaining private information about the media.
The HP board of directors was rocked by cases of top corporate secrets being leaked out to the public without the board’s approval. To curb the practice and determine who the culprit was, the senior members of the board, led by the chairperson, sanctioned the use of unethical pretexting methods. This saw private information of other board members as well as the media being unlawfully tracked.

Change in Consumer Demand Trends: Apple
- Apple revolutionized the smart phone idea, thereby increasing demand for its products.
- The iPod revolutionized portable music idea.
- The iPad revolutionized mobile computing (Deffree, 2008).
Apple initiated a revolution during the crash period through the introduction of the iPhone, iPod, and iPad. These new technological ideas influenced consumer demands as more users wanted to own a piece of Apple’s technology. The influence in consumer trends saw other device manufacturers, such as Samsung and Nokia, begin to concentrate on the manufacture of their own versions of smart phones and iPads in order to address the demand.
- Consumers increasingly went for faster computing devices.
- Demand for mobile devices with large storage increased.
- Consumers are seeking for Apps that would help them with every day tasks.
Apple introduced faster computing devices which have consequently seen the market consider speed as one of the main features before buying devices. The smart phone revolution initiated by Apple also incorporated the use of microchips which have boosted the storage capacities of the mobile computing capacities. Demand is currently on devices that have the capacity to store large content and external files. Mobile applications have also increasingly become the norm as consumers seek to download applications with interesting and complex capabilities.
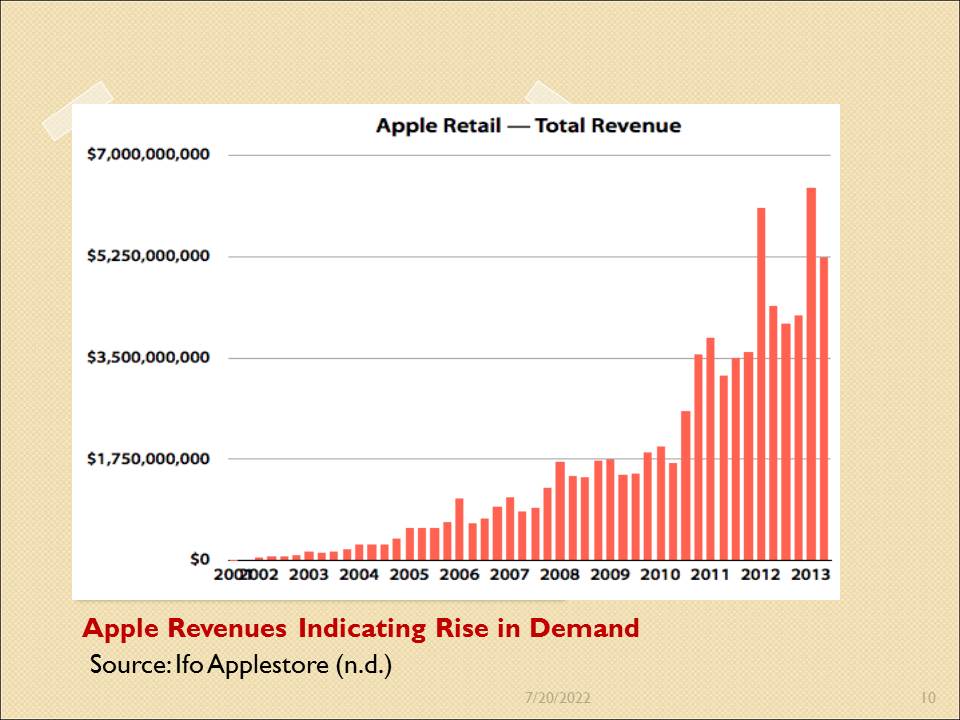
Apple Revenues Indicating Rise in Demand
Apple’s revenues have been on the rise since 2010, following the easing up of the global financial crisis. In the second and third quarters of 2011, the company’s revenues surpassed the $ 3.5 billion mark for the first time. The third quarter of 2012 saw the company’s revenues surpass the $ 5.25 billion mark, which indicates a continuous rise in consumer demand trends after the crash (Ifo Applestore, n.d.).
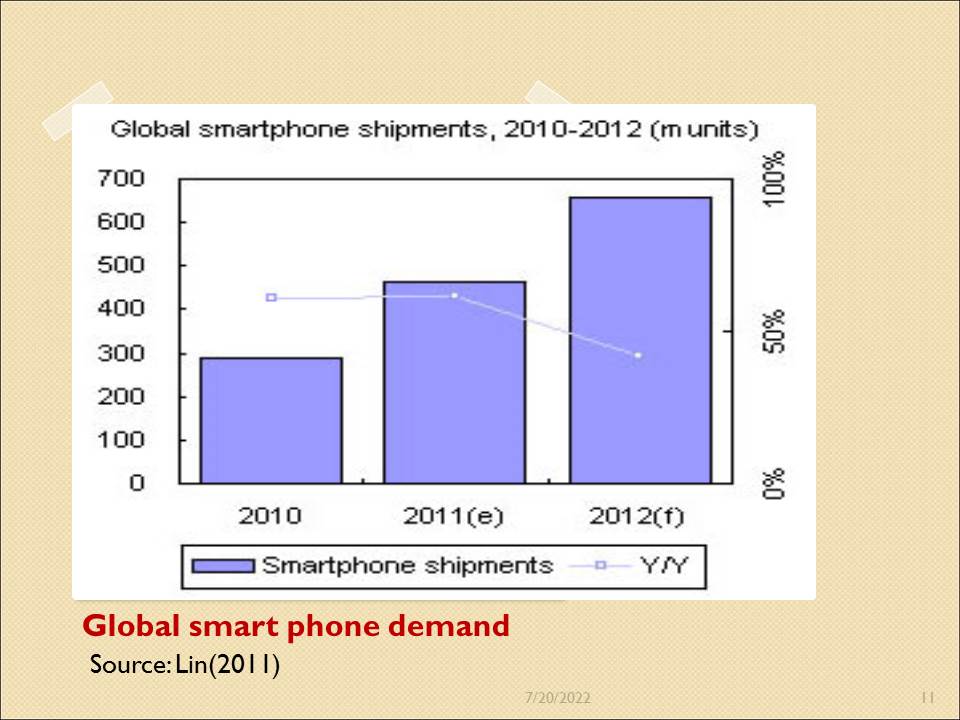
Global smart phone demand
The smart phone sector has been one of Apple’s strongest since 2009. The graph shows how the market trends have consequently been in favor of smart phones, with the demand increasing each year especially after the end of the crash in 2010 (Lin, 2011).
Change in Consumer Demand Trends: HP
- Increasing demand for laptops and decrease in desktop demand.
- Shift in demand for servers from branded to no-name hardware.
HP’s core business of manufacturing desktop PCs has suffered immensely as the market trend shifts towards laptops. HP’s other strong business area of selling servers has suffered as large internet companies Google and Facebook have opted to manufacture their own server machines through the help of Chinese manufacturers. Other small scale users have also expressed dissatisfaction with the costly HP servers and could soon change their options once they find other viable alternatives.

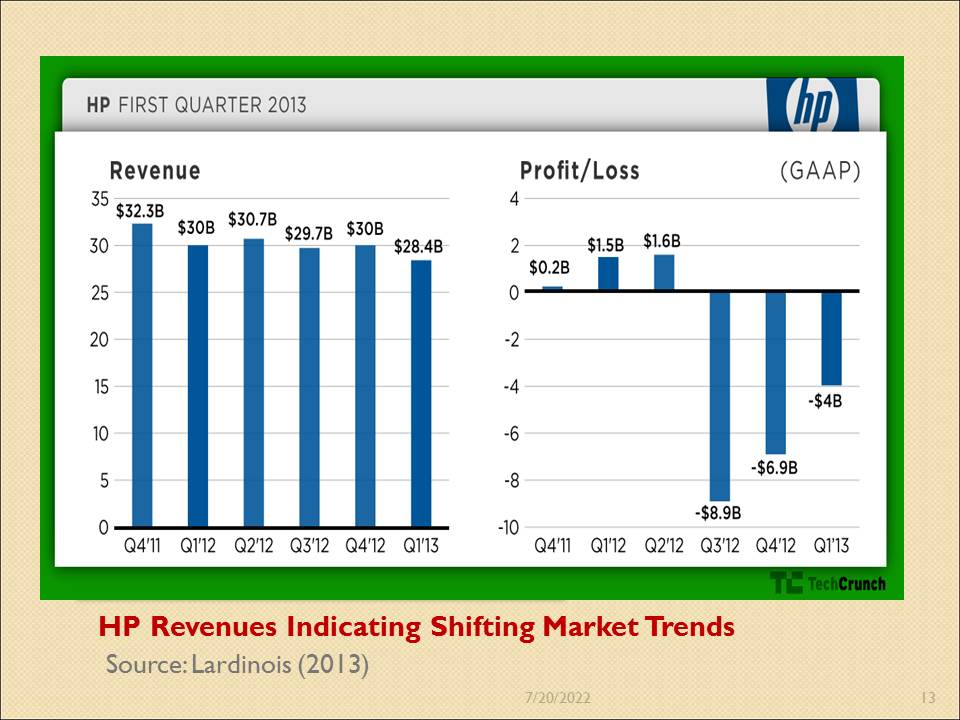
HP Revenues Indicating Shifting Market Trends
From the third quarter of 2011, HP has on average registered negative growth as the company struggles with changing market trends. The first quarter for 2013 gas seen the company register its lowest revenue amount since September 2011, posting only $28.4 billion. While profit figures increased in the first and second quarters of 2012, HP has consistently been making losses since then, with the first quarter of 2013 recording -$4 billion in losses (Lardinois, 2013).
Leveraging Strategies for MNCs in Quest to Make Profits
Segmentation according to specific customer needs:
- Purchasing power;
- Quantity;
- Demographics;
- Firmagraphics.
Segmenting the market allows the MNC to group its customers according to their specific needs such that it may be easier for the company to address each of the segments closely. Segmentation may be according to buyers’ power of purchasing, their quantity of purchase, according to their demographics, and according to the specific characteristics of the organization.
Appoint an executive customer champion:
- Representative of comprehensive customer views.
- Influence changes across divisions to reflect customer preferences.
- Customer intelligence progression.
The organization must have an executive officer who has powers to spearhead customer actions as well as influence action within the organization. The executive customer champion will act as the representative of customer needs in the organization. MNC’s operate in different markets where the preferences and characteristics vary. Thus, each market must have a powerful executive officer whose roles specifically involves representing the market’s wishes and preferences within the organization.
Orchestrate customer experience:
- Constant communication with customers.
- Design customer experience.
The MNC must be able to constantly keep in touch with its customers to be able to determine the individual feelings. Customer tastes and preferences are temporary and are bound to change with changing external business environment. To understand the customer experience closely, constant communications must be done through various avenues and a design of the experience undertaken to establish greater solutions.
Make data actionable:
- Regular customer surveys.
- Prioritization of issues.
- Partnering with customers to seek solutions.
A lot of data collected about the market and its preferences must be implemented accordingly. Sometimes the MNC may be forced to work closely with the customers in order to find important solutions that will help them maintain and serve the growing customer demand.




References
Deffree, S. (2008). iPhone spurs touch-screen market growth. Electronic News (10616624), 54(11), 18-18.
Ifo Applestore (n.d.). Yearly & quarterly financial result. Web.
Lardinois, F. (2013). HP beats expectations with revenue of $28.36B, $1.2B earnings and EPS of $0.82 for Q1 2013. Web.
Lin, L. (2013). Global smartphone industry, 2012 forecast. Web.
RT (2013). Apple accused of $74bn US tax evasion. Web.
Savitz, E. (2012). HP now sees 29,000 job cuts in restructuring plan. Forbes.com. Web.
WRVO. (2013). Apple, tech giants and an industrial-age tax code. Web.