Background
Apple is faced with stiff competition in the Chinese smartphone market. In 2016, the company’s sales of smartphones in the country were substantially diminished by cheaper alternatives produced by companies like Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi among others (Hardwick). A recent report reveals that Apple Inc. took fifth place in total sales for the fourth fiscal quarter of 2016 with its 43.8 million units sold in China (Hardwick). In the same year, Huawei took first place with its 75.2 million units and was followed by Oppo and Vivo with 73.2 million units and 63.2 million units, respectively (Hardwick).
The numbers show that Apple drags behind in terms of year on year (YoY) sales in the Chinese market, which is a significant problem for the company. If the issue is not properly addressed by Apple’s management, Chinese competitors have a good chance of stealing the company’s market share in the country.
This paper aims to present a marketing analysis of Apple Inc. The report will address the problem of competition in the Chinese smartphone market and provide recommendations for its solution. The paper will also explore competition structure, economic factors, political factors, marketing mix strategies, and other elements of marketing analysis to substantiate a set of alternative solutions.
Overview of Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is a multinational company headquartered in Cupertino, California. The company specializes in the development and retail of consumer electronics, online services, and computer programs for its devices. Apple Inc. was created in 1977 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak—two college dropouts—and later became a producer of “one of the first highly successful commercially produced microcomputers in the market” (Yeung).
However, the company does not specialize in designing and manufacturing only computers. Instead, it concentrates on penetrating the consumer electronics market and produces mobile and music devices. Recently, Apple Inc. has started working on a project titled “Titan”, which aims to develop “an autonomous driving system” (“Apple Car”) that will explore the self-driving capabilities of modern electric vehicles.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Porter’s five forces analysis will help to get a differentiated perspective on Apple Inc.’s strengths and weaknesses within its industry. The analysis will examine the following forces that affect the company: industry competition, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of consumers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products (Yoffie and Baldwin).
Industry Competition
Apple Inc. faces a substantial level of competition in the industry. A recent review of the competition structure of the market environment suggests that the main competitors of the company are technological giants such as Google, Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., the Hewlett-Packard Company, Microsoft, Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi among others (Yoffie and Baldwin). Taking into consideration the fact that switching costs are relatively low, customers can easily buy products from rival firms, thereby diminishing Apple Inc.’s revenues.
Therefore, the market is represented by numerous companies that are willing to spend substantial capital on R&D to strengthen their market share position. Another threat for Apple Inc. is financial backing from the Chinese government that can decide to support its manufacturers.
The threat of New Entrants
It can be argued that there is no substantial threat emanating from new entrants to the marketplace. It has to do with the fact that the high costs of creating a firm within the industry serve as a natural barrier to competition. An entrant to the industry has to have a massive capital for R&D and manufacturing to develop its product portfolio.
Moreover, to attain a meaningful level of brand awareness, it is necessary to spend additional costs on marketing. Another challenge faced by new companies entering the marketplace is strong competition from already established brands.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is, arguably, not the key threat for Apple Inc. to consider because it is relatively weak within the industry sector. The industry is characterized by a significant amount of supply that diminishes the bargaining position of suppliers of components for consumer electronics.
Moreover, the level of competition within the electronics components industry is exceptionally high. Taking into consideration the fact that the switching costs that the company has to incur if it decides to change one supplier for another are comparatively low (Yoffie and Baldwin). Therefore, the suppliers are not willing to exert their bargaining power in order not to risk losing their major customers.
The Threat of Substitute Products
It can be argued that the threat of substitute products is not a substantial consideration for Apple Inc. because there are not many products that can serve as a direct substitute for devices produced by the company. Even though a landline telephone can be considered a substitute product for Apple Inc.’s iPhone, the market for such a proposition does not have significant future potential.
According to a recent report, “ten years ago, 9 in 10 households used to have an operational landline phone—now it’s just every second household” (Richter). Not only substitute products for Apple Inc.’s device are technological relics, but they also have extremely limited technical capabilities. Therefore, the threat of the company’s customers choosing alternative products is not an issue that has to be considered.
SWOT Analysis
Exhibit 1 shows the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc., which is instrumental in developing adequate solutions for tackling the problem outlined in the previous sections of the paper.
Exhibit 1. SWOT analysis of Apple Inc.
Strengths
The company’s advertising capabilities can be considered one of it’s most significant strengths. According to Jurevicious, the company’s advertising budget was doubled in 2015 and reached US$1.8 billion (Jurevicious). However, it should be noted that Apple Inc.’s competitor Samsung Electronics spends even more on advertisement—US$3.4 billion in 2015 (Jurevicious). Apple Inc’s and Samsung Electronics’ advertising budgets represented 0.77 percent and 1.86 percent of the companies’ sales (Jurevicious).
Another key strength of the company is its network of distribution channels. Apple Inc. employs multiple channels for delivering its consumer electronics: direct sales force, brick-and-mortar stores, and online stores. Moreover, mobile carriers such as Verizon and T-Mobile among others are operating as third-party distributors for the company’s smartphones.
Brand recognition is the most important strength of the company. According to the rating of the world’s most valuable brands issued by Forbes, Apple Inc.’s brand is valued at US$145.3 billion (The World’s Most Valuable Brands). Sound financial performance is another strong point for the company. Apple Inc.’s profits increased by 27.94 percent in the period from 2012 to 2015 (Jurevicious).
Weaknesses
iPhone sales account for 66 percent of the company’s sales (Yoffie and Baldwin). Apple Inc.’s overdependence on the sales of its flagship product makes it vulnerable to its customers switching to smartphones offered by the company’s competitors. Another weakness of the tech company has to do with the fact that it is not presented by direct distribution channels in the third-largest smartphone market in the world—India.
At the moment, Apple Inc. distributes its products with the help of cellular network carriers and third-party retailers. Another weak point in the company’s modus operandi is its low levels of R&D spending as compared to other tech giants.
Currently, Apple Inc. spends only 3.4 percent of its revenues on R&D, which is nowhere enough to introduce innovations that are capable of disrupting the market (Yoffie and Baldwin). Incompatibility with other operating systems (OS) is a weakness that has to be addressed if the company is to gain a competitive advantage.
Opportunities
The production of healthcare-related wearable devices that can “monitor calorie intake, sugar and hydration levels, heart rate and blood pressure, as well as potentially diagnosing many illnesses or even infusing drugs through the skin” (Jurevicious) is an opportunity that cannot be missed by the company. Considering that the company produces a wearable gadget called Apple Watch, it already has the necessary experience and technical expertise for taking the market niche.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another opportunity that can be explored by Apple Inc. According to Norton, currently, there are more than 21 billion devices that are connected to the Internet. The author forecasts that this number will grow to 30 billion in 3 years (Norton).
The company should increase its presence in the mobile payments market if it is to gain a competitive advantage over its rivals. A recent article reveals that even though only 17 percent of the U.S. citizens regularly use mobile payments, the total value of transactions facilitated by the technology will be worth US$27 billion in 2017 (McHugh). Therefore, it is clear that the system for mobile payments developed by the company—Apple Pay—presents an enormous opportunity for the tech giant to establish itself on the market.
A recent trend of purchasing subscription-based software provides Apple Inc. with a chance to strengthen its ecosystem. As big businesses are increasingly opting for buying their software on the mobile enterprise app market over conventional licenses, the company has to develop its solution for targeting a new audience of customers.
Threats
The most significant threat for the company is an ever-increasing level of competition on the market. Companies like Microsoft, IBM, Dell, and HP among others engage in a direct rivalry with Apple Inc. in the sector of personal computing (Jurevicious). Other tech giants that include, but are not limited to, Google, Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., the Hewlett-Packard Company, Microsoft, Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi compete with other Apple Inc.’s gadgets such as tablets and smartphones.
Android devices produced by these companies put pressure on Apple Inc.’s sales. Moreover, iTunes, iBook Store, and Apple Music revenues are also dwindling due to ever-increasing Android OS usage. Another threat that might substantially undermine the company’s success is the increasing U.S. dollar exchange rate. Taking into consideration the fact that approximately 65 percent of Apple Inc.’s revenues are coming from overseas, it is fairly reasonable to assume that the upcoming rise in the exchange rate will diminish the company’s revenues when they are converted to U.S. dollars (Yoffie and Baldwin). Patent wars present another threat to the company.
Intense competition among tech giants of the industry translates into continuous efforts to pursue legal redress concerning intellectual property. In 2010, the company was engaged in litigations against major Android manufacturers such as Samsung (Yoffie and Baldwin). The industry is associated with a high incidence rate of patent infringement lawsuits because tech products are “made of multiple parts and use software with thousands of lines of code that may have already been patented by another company” (Jurevicious).
Alternative Solutions
This section of the paper will provide a set of alternative solutions for resolving the problem outlined in the previous sections.
Fresh Marketing Vision
To tackle the problem of competition, Apple Inc. has to develop a fresh marketing vision. It can be argued that the company, has not been sufficiently innovative and trend-setting for a few years. Even advertising campaigns for Apple devices are less innovative than they were in 2011 (Gianatasio). According to Gianatasio, the average Ace score measuring consumer perception of the company’s advertising efforts has decreased from 614 points in 2011 to only 554 points in 2013 (Gianatasio).
When compared to its competitor Samsung, Apple Inc. is outpaced by almost 50 points (Gianatasio). Taking into consideration the nature of a competitive marketplace, Apple Inc. has to reconsider its marketing strategy to regain its momentum. The obvious advantage of this alternative is its ability to refresh the company’s marketing approach. However, it is also associated with a downside of shifting marketing focus.
Expansion of Supply Chain
By expanding its supply chain, the company will be able to maximize its profit margins, thereby strengthening its position in the marketplace. Overdependence on GT Advanced Technologies prevented Apple Inc. from equipping the iPhone 6 and 6 Plus devices with sapphire displays in 2014 (Dormehl). The company has already announced that is going to include Compal Electronics and Wistron into its supply chain (Dormehl). This move will help Apple Inc. to retain its gross margins.
The diversification of the supply chain is an obvious advantage of the strategy and the step that has to be taken if the company is to gain a competitive advantage over its rivals. The strategy has a downside of cutting ties with existing partners.
Price Reduction
The price reduction is a viable alternative helping the company to boost its sales in both smartphone and tablet segments. According to Sparks, iPhone prices reach as high as US$949. It means that it is not likely that Apple Inc.’s sales will substantially grow in the first fiscal quarter of 2017. Exhibit 2 shows a year-over-year comparison of the company’s gross profit margins.
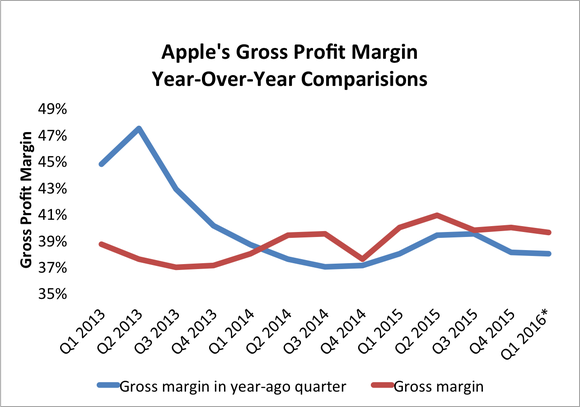
It is clear from the exhibit that gross profit margin comparisons for 2013 did not bode well for the company. Drastic reduction in gross profit margin can be attributed to the excessively high cost of iPad Mini as well as the cost of the initial production of the iPhone 5 (Sparks).
Even though Apple Inc.’s gross profit margin is on the rise since 2013, the company has to consider reducing the price of some of its products to tackle the problem of competition outlined in the previous sections of the paper. However, despite the obvious benefits of maximizing the gross profit margin, it is clear that the strategy may change the company’s market niche.
Service-Based Revenues
Another strategy for dealing with the problem of competition is the increase of service-based revenues. It is arguably the most promising growth vector that has to be considered by the company. In the 2016 fiscal year, the company derived US$19.9 billion from various services ranging from Apple Music to Apple Pay (Heisler).
As of 2016, the company had more than 1 billion active devices across the world (Heisler). It means that the tech giant has a substantial base of active users that can provide stable revenue streams. In the future, Apple Inc. can increase its service-based revenues by expanding a range of services it offers to its transacting customers. This strategy has no disadvantages.
Acquiring Netflix
Buying Netflix is a solution for Apple Inc.’s competitive struggles. If the company is willing to increase its service revenues, it should consider acquiring the entertainment technology company. According to a recent article, Netflix is responsible for a surge in customer spending in the App Store (Balakrishnan). The article reveals that a 130 percent increase in service revenues might be indicative of a promising trend that has to be explored by the company (Balakrishnan).
Therefore, Apple Inc. has to use some of its US$240 billion in cash for the major acquisition to sell digital content, thereby gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace. This alternative strategy is associated with a downside of Apple Inc. not having end-to-end control of the product created by other companies. Another disadvantage of acquiring Netflix is the dilution of the company’s earnings due to the necessity to issue debt for buying the entertainment technology giant.
Recommendation
The acquisition of Netflix is a move that can provide Apple Inc. with additional revenue streams. Having increased its service revenues, the company will be able to spend more money on R&D, thereby outperforming its competitors in terms of innovation and cutting-edge technology. Moreover, as have been mentioned above, the company spends less on marketing than its direct competitor, Samsung, thus losing a significant share of potential customers.
At its current market value, Netflix is worth US$150 billion, which is within the financial reach of Apple Inc. (Ingram). It can be argued that by acquiring the entertainment giant, the company will be able to reap the benefits of positive stock effects. However, to so, Apple Inc. will have to introduce an effective model of moving Netflix customers to its platform. Currently, Netflix has more than 80 million subscribers around the world; therefore, by opting for this alternative strategy, Apple Inc. will be able to boost the growth of its revenues.
Conclusion
The marketing analysis of Apple Inc. showed that the company is faced with a substantial level of competition from technological giants such as Google, Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., the Hewlett-Packard Company, Microsoft, Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, and Xiaomi among others. These companies are threatening to diminish Apple Inc.’s revenues. To address this problem, the company has to acquire Netflix, thereby diversifying its revenue streams and gaining a competitive edge.
Works Cited
“Apple Car.”Macrumors, Web.
Balakrishnan, Anita. “Here’s the Best Argument for Apple Buying Netflix.”CNBC, Web.
Dormehl, Luke. “Apple Broadens its Supply Chain to Maximize Profit Margins.”Cult of Mac, Web.
Gianatasio, David. “Apple Needs a Fresh Marketing Vision, and we Have Some Ideas.”Adweek, Web.
Hardwick, Tim. “Apple Loses Fourth Place to Xiaomi in Booming China Smartphone Market.”Macrumors, Web.
Heisler, Yoni. “Apple’s Growth Strategy is Hiding in Plain Sight.” BGR, Web.
Ingram, Mathew. “Five Reasons Why Apple Should Buy Netflix and Five Reasons why it Won’t.” Fortune, Web.
Jurevicious, Ovidijus. “Apple SWOT Analysis.” Strategic Management Insight, Web.
McHugh, Robert. “Apple Pay slices the Mobile Payments Market Again.” Mobile Payments Today, Web.
Norton, Sam. “Internet of Things Market to Reach $1.7 Trillion by 2020.” WJS, Web.
Richter, Felix. “Landline Phones are a Dying Breed.” Statista, Web.
Sparks, Daniel. “How Much More Can Apple Inc.’s Gross Margin Improve.”The Motley Fool, Web.
“The World’s Most Valuable Brands.” Forbes, Web.
Yeung, Natalie. “The Marketing Strategy of Apple: A Concise Analysis.” Verison Daily, Web.
Yoffie, David, and Eric Baldwin. “Apple Inc. in 2015.” Harvard Business Review, Web.