Abstract
The objective of the present paper is to review and discuss the present literature on the topic of using AI in medicine, the potential challenges and opportunities for its development, and the current applications. The stated goal is achieved through the method of a literature review, focusing on the academic sources published within the last five years.
As a result of this review, a better understanding of the current state of artificial intelligence in healthcare settings will be acquired. Additionally, the review will function as an analysis of the quality of the present body of literature on the subject. The present paper will be beneficial to medical professionals who aim to understand the impact of AI technology on the field and work towards improving the integration of smart technology in the medical field. No financial support or funding was utilized in the writing of this paper, and the author does not state any present financial interest.
Introduction
The growth and development of technology have moved at an unprecedented pace in the last few decades. With the advent of computers and the internet, an average person has gained access to a processing capacity that people from previous generations could envy. This development also meant that technology has begun a deep integration into the professional sphere, influencing a large variety of industries. Business, accounting, management, sales, production, manufacturing – all of these areas have practically been revolutionized by the use of modern technology. Among all others, however, it is crucial to note healthcare and medicine as fields most intimately connected with contemporary tech. The use of computers and various types of machinery have supported the creation of more effective medicine, diagnostics, treatment, and healthcare organization.
Technology can present a multitude of positive outcomes to the medical industry, enhancing the work effectiveness, optimizing processes and improving standards of care. Nowadays, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more prominent, with recognition algorithms and machine learning advancing at a rapid pace. The integration of AI into the healthcare industry has already started, with a number of programs being used for diagnosis purposes, drug development, and finding research candidates, among other things. The use and application of artificial intelligence into the healthcare sphere is a rather recent development, but a considerable body of research currently exists. To evaluate the current state of AI in the field of medicine, discuss potential applications and identify the contemporary challenges, a literature review will be conducted. An examination of available data can be effective in highlighting the common industry consensus on the effectiveness of this type of tech for medical purposes. First, the history of artificial intelligence will be discussed, further transitioning to the possible uses of AI and its future.
History of Artificial Intelligence in the Medical Sphere
The history of AI’s application in the medical field is complex, and can be channeled into separate discussions on the history of Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), as well as other forms of computer analysis. As discussed by Vivek Kaul et al., in their History of artificial intelligence in medicine (2020), the start of artificial intelligence discussions can be traced back to Alan Turing, one of the key figures in the development of computer science. Early on, it has been hypothesized that it is possible to engineer intelligent machines, potentially mimicking the functioning of the human brain. Significant advancement over the years has been made, moving on from simple algorithms to the performance that much more accurately copies the capabilities of human thinking. The AI in early stages of its development could not be effectively utilized for the medical industry, needing a more robust computing power and better algorithms. It is important to note that while AI and its use can often be regarded as a recent development, the field boasts considerable history and decades worth of legacy.
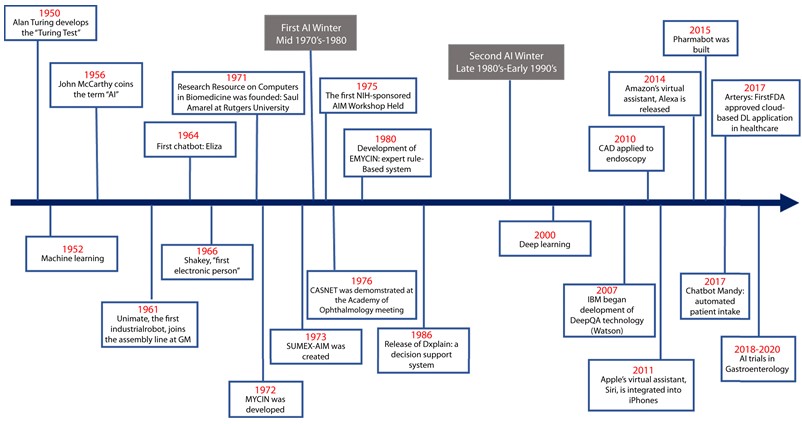
The development of technology has been most significant in the medical sphere. Influenced by the creation of Deep Learning algorithms, expanding the avenues of potential application (Kaul et al., 2020). Currently existing possibilities for the use of AI are bolstered by the development of neural networks and the constant improvement of recognition algorithms. Considering the history of the field’s development, it can be noted that advancement occurs at a continuously increasing pace, meaning that the use of Artificial Intelligence has a lot of untapped potential.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and Medicine
A number of potential applications of AI have currently been identified, mostly focusing on pattern recognition, optimization of medical processes and monitoring. Generally, this type of technology is a welcome change from traditional methods of healthcare provision and organization, as they allow for more patient autonomy while also increasing work efficiency (Briganti & Le Moine, 2020). As noted by Kaul et al., predictive models of AI can be utilized in medical diagnosis of disease, and possible future prevention (2020). Other authors have also had considerable discussions on the current uses of Artificial Intelligence. As brought up by Briganti & Le Moine, deep learning technology can be efficient in gathering and analyzing large amounts of digital data (2020). Information collected from smartphones, computers and monitoring equipment can all be categorized, analysed and presented for further medical use.
This capability of AI is especially relevant for the field with the move towards e-healthcare and virtual visits, as the amounts of information collected from patients start to increase dramatically. The application of deep learning for such purposes can be considered both cost-efficient and time-saving. Another prominent and possible application of modern machine intelligence in medicine includes the use of AI-powered diagnostic technology and tools (Briganti & Le Moine, 2020). Intelligent medical devices can perform their main functions and collect feedback without human intervention, meaning that the degree of patient freedom and comfort is significantly expanded.
On a connected note, another research paper has discussed the use of AI in a way not previously covered by other authors. Choi et al., present a model of using neural networks of AI in predicting clinical events and producing diagnosis (2016). Authors of the paper have developed a medical Doctor AI, inputting patient medical history data from EHS’s of over 260 thousand patients. The subsequent AI is capable of predicting medical diagnosis based on the person’s medical history and records (Choi et al, 2016). The capacity of neural networks to learn, adapt and utilize data provided to them gives medical professional an opportunity of using AI to further streamline the medical care process and decrease the time spent of finding the correct diagnosis.
Opportunities for Development
Taking into account the variety and nature of the current application for AI, the opportunities for its development are numerous. Continuing with the considerations on neural networks, their learning capacity and the ability to process data for further use presents a valuable asset to the medical industry. Development of learning AI that can integrate medical data, patient records and diagnostics tools as a way to improve healthcare delivery is a significant avenue for further study and growth. As noted by the researchers presenting Doctor AI, an intelligent neural network-powered system “not only mimics the predictive power of human doctors, but also provides diagnostic results that are clinically meaningful” (Choi et al, 2016). The future efforts of medical AI, as also noted in the paper, should be primarily aimed at improving the quality of medical diagnosis offered by the computer, as well as its ability to behave in a way similar to a real physician.
Another potential area for improvement is connected with the validity of AI as a method for advancing the field. Due to the particularly recent nature of the technology used in medical AI, it is noted that it is met with resistance (Briganti & Le Moine, 2020). The traditional methods of clinical evaluation and testing as not currently applied to AI to a sufficient extent, making their use less credible as a result. Researchers state that artificial technology can enter the field more thoroughly and be integrated into medical practice on a deeper level, on the condition of more testing being performed (Briganti & Le Moine, 2020). The validation of AI in the eyes of medical professionals and the accumulation of a bigger body of research is a valid area of development for the field.
Gilvary et al., (2019), identify better interpretability as an additional avenue for improvement and better integration of AI into medical processes. Interpretability in artificial intelligence refers to the clarity with which the decision-making process of an AI can be understood. A better interpretability of a learning system means that medical professionals can understand its “thought process”, make necessary adjustments or put the data presented by the computer into the necessary perspective. Gilvary et al., state that further development of this consideration is necessary to guide investigation and growth in the field (2019). The authors note the importance of diverse data sources into neural network learning as well, which is also a potential avenue for change. The inclusion of diverse data pools can be effective in limiting AI bias, increasing its predictive accuracy and expanding the potential application of artificial intelligence (Gilvary et al., 2019). Overall, a need to improve the processes by which the AI data is selected, contextualized and understood is evident, creating the potential for long-term development and growth.
Ethical Challenges
The general challenges faced in the field of medical AI can be separated into categories depending on their nature, including technical issues, ethical, and legal considerations. All of the aforementioned areas are important to discuss, as Artificial Intelligence and its facets are currently underexplored.
Ethics in medicine is an ever-present consideration, stemming from the need for doctors to ensure a proper standard of care for their patients and prioritize their health, prosperity, autonomy and wellness. With the application of AI in the field, ethical issues were inevitably created, due to the self-regulating and artificial nature of computer intelligence. With the increased reliance on automation, algorithms and data analysis, it is necessary to continuously uphold moral standards of human care. First ethical avenue to discuss comes from the question of informed consent. As outlined by Gerke et al., consent is a crucial part of regular patient care, and its extension into AI is currently underexplored (2020). In a regular care setting, medical professionals have an obligation to disclose the intricacies of medical procedures, their effects and potential risks to the patients to proceed with the treatment. Considering the complex nature of AI in medicine, the authors propose a necessity to apply the informed consent framework to artificial intelligence. It is noted that the actual need for this procedure is yet unclear and demands further research, however.
The second important ethical avenue to discuss is safety. With AI algorithms being used as a way to provide diagnosis and analyse patient data, questions of medical errors and harmful treatment inevitably arise. Given the intricate nature of patient care, and the degree of danger that comes with medical treatment, it is necessary to ensure that artificial intelligence is safe for its primary recipients. The need to avoid medical errors in the diagnosis process, as well as provide doctors with the most correct recommendations is what primary fuels the questions of safety in AI application.
Another potential topic for exploration of AI ethics concerns bias. While the notion of “Artificial Intelligence” presupposes a level of intelligent thought on the part of a computer system, the AI is unable to think in the same way as a human being can. The AI predominantly analyses a particular existing pool of data to arrive at conclusions and perform operations. The reliance on training data means an AI is susceptible to selection bias. If the information provided to the artificial intelligence is unable to fully reflect the medical realities, the program will not be able to provide meaningful or fair results. This problem becomes much more apparent and critical when one considers the potential for discrimination. As outlined by Gerke et al., several real-world examples of AI bias already exist, resulting in ethnic and racial discrepancies for results (2020). Datasets used to train AI need to be both diverse and high-quality, to produce results that have a positive effect on a clinical setting.
Conclusion
To conclude, it should again be noted that the field of AI is currently still in the process of development, which presents its unique opportunities and challenges for the medical industry. The history of the field starts around the 1950’s with the creation of first computing technology and programming. The steadily quickening development of AI contributed to its integration into a variety of industries, ranging from producing to accounting. The use of artificial intelligence in medicine is by comparison even more modern, but the growth of neural networks and analysis algorithms has contributed to a steady supply of new tech. AI gives medical professionals a capacity to analyse large amounts of data, aggregating information collected from virtual health applications and monitoring devices. Deep learning algorithms and neural networks can access medical data to provide diagnostic recommendations, making the work of doctors more efficient. A number of development opportunities exist in the field, ranging from better interpretability of AI thought process and the use of neural networks to improved validity of computed intelligence as a method of patient support. While the potential of artificial intelligence is growing exponentially, professionals of the medical field have raised ethical considerations, especially concerning fairness, safety and informed consent. Most reviewed sources highlight and state the need to increase the available body of research, which appears to be a significant problem for truly understanding the role AI plays in medicine.
References
Briganti, G., & Le Moine, O. (2020). Artificial intelligence in medicine: Today and tomorrow.Frontiers in Medicine, 7.
Choi, E., Bahadori, M.T., Schuetz, A., Stewart, W.F. & Sun, J.. (2016). Doctor AI: Predicting Clinical Events via Recurrent Neural Networks. Proceedings of the 1st Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research 56:301-318.
Gerke, S., Minssen, T., & Cohen, G. (2020). Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven healthcare. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare, 295–336.
Gilvary, C., Madhukar, N., Elkhader, J., & Elemento, O. (2019). The missing pieces of artificial intelligence in medicine.Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 40(8), 555–564.
Kaul, V., Enslin, S., & Gross, S. A. (2020). History of artificial intelligence in medicine.Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 92(4), 807–812.