Abstract
The proposed study aims at establishing if there is a relationship between dust events and respiratory diseases in United Arabs Emirates. This is will help bring to light the prevalence rate of respiratory diseases in the region as well equip relevant stakeholders with vital information concerning dust and its effects on human health.
Existing literatures draw association between dust storms and respiratory diseases. Mixed research approach will be used in the study. Both questionnaires and records from hospitals will provide the researcher with the desired data. Before the study begins, the researcher will get approval from Independent Regulation Board from the collage as well as obtain informed consent from the subjects.
Introduction and problem statement
The study seeks to establish the association between respiratory diseases and dust events in the United Arab Emirates. It is worth noting that UAE is in a region where dust storms occur regularly. Ideally dust is composed of very tiny solid particles floating in the air. This is capable of getting past the lung’s natural defense and build up resulting in serious health complications (Qiu, Zou & Zhan, 2006). Scholars have tried to link dust events and incidences of respiratory diseases.
Research shows that when an individual is exposed to air pollutants, they are at higher risk of contracting respiratory related illnesses for instance asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer as well as allergies. Since UAE is in a dry region, the greatest pollutant is dust caused by wind and storms.
This poses a great danger particularly to children, teenagers, infants, asthmatic individuals, pregnant women, healthy adults who exercise vigorously in the fields, people suffering from cardiovascular diseases and the elderly in the society. In the United States of America, a study carried out in 6 cities considered to be the most polluted by dust concluded that residents from these cities were at higher risk of being hospitalized as a result of respiratory illnesses.
Similarly majority died due to lung cancer as compared to others residing in cities that are less polluted. Additionally children in these areas were 5 times more likely to suffer from low lung functions. It is worth noting that dust events can worsen health conditions of people who suffer from respiratory related diseases (Host et al., 2008).
World Health Organization has shown that chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a global health issue and is one of the major causes of chronic morbidity and mortality in the entire world (Kanatani et al., 2010).
It is ranked sixth as a leading cause of death globally. Since it is one of the respiratory diseases caused by air pollution, it is estimated that it will continue causing death as well as increase prevalence of respiratory diseases in the coming years (Brunekreef & Forsberg, 2005).
Significance of the study
The proposed study is of importance as it will evaluate whether or not the relationship between dust events and respiratory diseases exists. The findings will be significant to various stakeholders such as institutions of higher learning, individuals, health organization, and ministry of public health among others.
It is worth noting that the findings will make those individuals who thought there was no relationship between dust events and respiratory diseases think twice and take necessary preventive measures. Similarly, health sector in UAE will embark on a campaign to educate people on how to avoid being victims of dust events related diseases.
Similarly the government will develop policies aimed at reducing dust events particularly those caused by human activities. This will help reduce the frequency of dust events. Not carrying out this research will clearly depict that the association between respiratory diseases and dust events in the UAE will not be brought to light. This will mean that there will be no action taken to save the lives of the vulnerable population.
Scope of the study
The scope of the study is to establish the relationship between respiratory diseases and dust events in the UAE. Similarly issues relating to the types of respiratory disease individuals suffer from, prevalence rate and how best to curb the situation are all of interests in this study. Based on this, recommendations will be brought forth to help guide the relevant bodies on the way forward in dealing with the menace. The study will take place in the UAE.
Aims and objectives and research questions
The aim of the study is to investigate the association between dust events in UAE and respiratory diseases. The specific objectives are;
- To find out the association between respiratory diseases and dust events among the UAE population.
- To establish the prevalence rate of respiratory diseases in UAE.
- To establish the strategies that can be adopted to curb respiratory diseases in the UAE.
Research questions
- Is there a relationship between respiratory diseases and dust events among the UAE population?
- What is the prevalence rate of respiratory diseases in UAE?
- What strategies can be adopted to curb respiratory diseases in the UAE?
Literature review
Most of the Asian part is either arid or semi arid. This has made the soils dry and loose; this coupled with the fact that winds are more prevalent makes it possible for dust to be carried out from the ground and deposited elsewhere resulting in air pollution. In Middle East the Shamala winds originate from Turkey, Iraq as well as Saudi Arabia. As the wind gain momentum across the Gulf of Arabia dust are kicked up.
Numerous studies have linked dust events and the high rate of respiratory diseases. In one study carried out by Kwon, et al., 2002 investigating the effect of Asian dust on daily deaths in South Korea between 1995 and 1998. He established that the relationship between dust events and deaths from heart diseases was strong.
Additionally individuals suffering from respiratory diseases are susceptible to dust events in Asia. Similarly another study carried out in Taipei revealed that there was a higher specificity in associating dust effects with respiratory deaths.
It is worth noting that a study carried out by Lei, et al., 2004 using rat model examined the inflammation markers in the lung as well as peripheral blood after the animals were exposed to dust storms particles. The outcomes revealed that dust has the potential of increasing lung inflammation as well as injury in pulmonary vein in those rats deemed to be hypersensitive (Peng et al., 2008).
According to Chen et al., 2004 dust events tend to impaired human visibility leading to accidents. Biologists have shown that people who live in areas prone to dust events breathe in particles which float in air. Luckily not all these particles get their way through human nose. However smaller particles usually get their way through the nose reaching the lungs. Human respiratory systems have cilia and mucus which help trap dust.
In case dusty air reaches the alveoli it is the responsibility of macrophages to remove the dust. Additionally lungs can produce protein to neutralize dusty air. In situations where the dust escapes all these mechanism of purifying air, then there are a number of diseases man will suffer from depending on whether the dust is organic or inorganic (Kanatani et al., 2010). For instance inorganic dust leads to asbestosis, silicosis, coal pneumoconiosis among others.
On the other hand, organic dust results in farmers’ lung, sewage sludge disease among others. It is worth noting that particles which are less than 10 microns in diameter might contain dust, smoke, silica, soot enter human lung and cause these problems. Interestingly dust events can impair animals’ health, corrode buildings as well as impair growth in vegetation (Husar et al., 2001).
According to Abdelkarim et al., 2011 changes in weather conditions which are characterized with dust events exacerbate chronic lung diseases particularly in those individuals deemed to be suffering from asthma. A study on children suffering from respiratory diseases in this region showed that the prevalence rate among children aged between 6 and 19 years stood at 13.0% (Choi et al., 2011).
Asthma in the region has been known to be responsible for higher morbidity rate as well as high rate of absenteeism in schools. Other causes of respiratory diseases in this region include cigarette smoking, genetic history of illnesses such as asthma, low birth weights among others (Wang et al., 1997). It is worth noting that the relationship between dust events and respiratory diseases in UAE is not well documented.
Methodology
Mixed research approach will be used to guide the study. Thus both qualitative and quantitative methods of data collection will be utilized. Data which show the number of patients suffering from respiratory diseases will be collected from health care centers and hospitals in UAE.
As suggested by Beiske, 2002 this will allow the study to have exact number of individuals who sought medical attention as a result of suffering from respiratory diseases. It will also allow me to establish the prevalence rate of respiratory disease in the region (Ko et al., 2007).
Additionally questionnaires will be distributed to patients who are in hospitals or have recently been discharged. Questionnaire covers a large population at a time as they would be distributed to different participants at a time and be collected later or at the same day depending on the willingness of the respondent in addressing the questions, due to it being standardized they are more objective, data collected from questionnaire are easy to analyze, due to familiarity with the tool, respondents will not be apprehensive, it is also very cost effective compared to face to face interviews and the tool also reduces bias (Robson, 2007).
According to Malig & Ostro, 2009 the major problem with questionnaires as a tool of data collection is that there is tendency of respondents to forget vital information, they may answers the questions superficially when it is a long one, to counter this I will develop a short but very inclusive questionnaire, due to standardization, there is no room for explanation incase respondents misinterpret or do not understand the questions. The collected data will be analyzed using SPSS version 12.0. Both descriptive and inferential statistics will be done.
Ethical issue
Before starting the study, I will seek approval from the University’s Independent Regulation Board. Similarly I will seek personal informed consent from the participants (Robson, 2007).
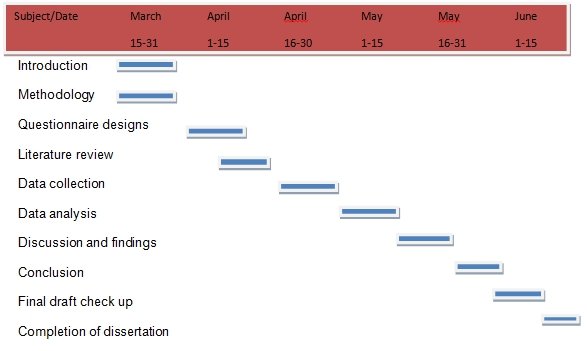
Study time line
References
Abdelkarim, W. et al., (2011). Respiratory disorders in the Middle East: A review. Respirology, 16(5): 755–766.
Beiske, B. (2002). Research methods: Uses and limitations of questionnaires, interviews, and case studies. Manchester: University of Manchester Publishers.
Brunekreef, B. & Forsberg, B. (2005). Epidemiological evidence of effects of coarse airborne particles on health. Eur. Respir. J., 26(1), 309–18.
Chen, Y. et al., 2004. Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily mortality in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ Res., 95(3), 151–155.
Choi, H, et al. (2011). Asian dust storm particles induce a broad toxicological transcriptional program in human epidermal keratinocytes. Toxicol. Lett., 200(1), 92–99.
Host, S, et al. (2008). Short-term associations between fine and coarse particles and hospital admissions for cardio-respiratory diseases in six French cities. Occup. Environ. Med., 65(1), 544–51.
Husar, B. et al. (2001). Asian dust events of April 1998. J. Geophys. Res., 106(2), 18317-18330.
Kanatani, K. et al. (2010). Desert-dust exposure is associated with increased risk of asthma hospitalization in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 182(2), 1475–1481.
Ko, F. et al. (2007). Temporal relationship between air pollutants and hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Hong Kong. Thorax, 62(1), 779–784.
Kwon, H. et al., (2002). Effects of the Asian dust events on daily mortality in Seoul, Korea. Environ Res Sec A., 90(1), 1–5.
Lei, Y. (2004). Effects of Asian dust event particles on in ammation markers in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary hypertensive rats. Environ Res., 95(2), 71–76.
Malig, J. & Ostro, D. (2009). Coarse particles and mortality: evidence from a multi-city study in California. Occup. Environ. Med., 66(4), 832–839.
Peng, D. et al. (2008). Coarse particulate matter air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases among Medicare patients. JAMA, 299(22), 2172–2179.
Qiu, Z., Zou, K. & Zhan, C. (2006). Research on impact of dust event frequency on atmosphere visibility variance: a case study of typical weather stations locating in the dust route to Beijing. Environ. Sci., 27(1), 1046–51.
Robson, C. (2007). How to do a research project: A guide for undergraduate students. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
Wang, X. et al., 1997. Respiratory impairments due to dust exposure: a comparative study among workers exposed to silica, asbestos, and coalmine dust. Am J Ind Med., 31(1), 495-502.