Practicum Goal Statement
Nurse leaders and their leaders will:
- apply theory in practice;
- widen experience in conducting patient observation;
- improve the quality of shift reporting;
- understand the importance of accurate information exchange;
- be able to find approaches to enhance quality of patient care.

Project Objectives
- Nursing leadership will explain positive reasons for implementing routing bedside shift reporting for staff nurses;
- Leaders increase the number of patients receiving rounds and taking part in their care. Measurable percentage – 40 %;
- Nurses should demonstrate awareness of steps taken during observation, planning, and problem solving.

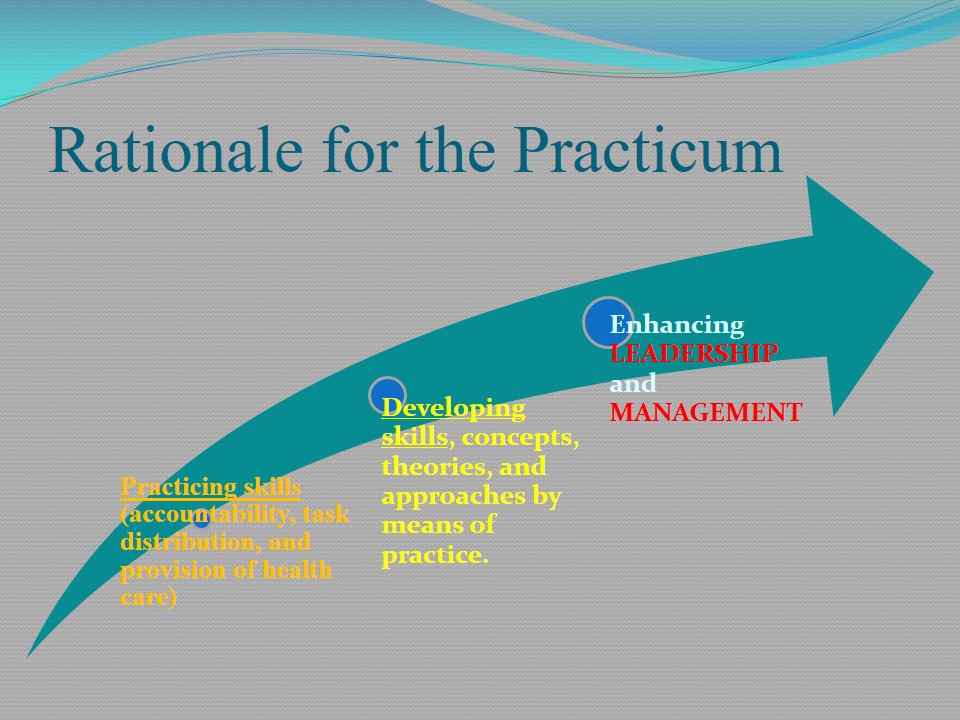
Rationale for the Practicum
- Practicing skills (accountability, task distribution, and provision of health care).
- Developing skills, concepts, theories, and approaches by means of practice.
- Enhancing LEADERSHIP and MANAGEMENT.
The main pillars of leadership and management involve evidence-based research and practice of receive theoretical knowledge. In their turn, constant practicing of simple procedures can provide a fresh insight into concepts and effective approaches to better treatment of patients. As a result of received experience, nurses can highlight the essentials of collaborative work, accountability through direct participation, equal distribution of tasks, and accurate information exchange.
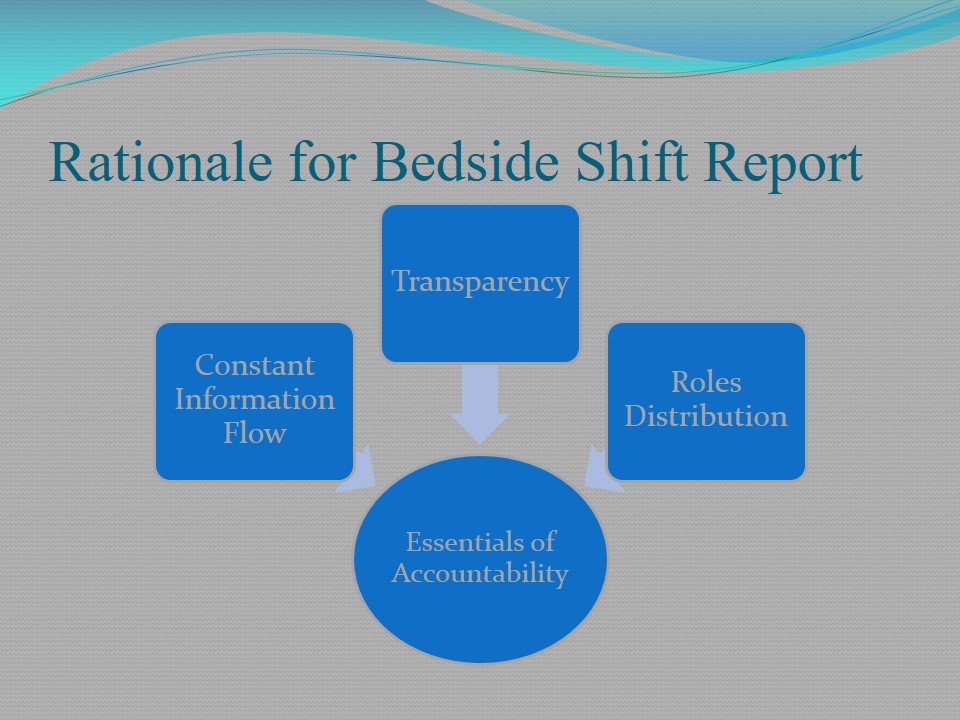
Rationale for Bedside Shift Report
- Essentials of Accountability:
- Constant Information Flow.
- Transparency.
- Roles Distribution.
The main purpose of bedside shift report lies in increasing accountability and developing trustful relations between patients and the nursing staff. Therefore, such components as constant information flow, transparency, and roles distribution are among the main ones to support accountability.
Practicum Methodology
- Preparation for Bedside Shift Report:
- Informing the participants about the goals and objectives of the practicum;
- Nurses will receive instructions on distribution of tasks and responsibilities;
- Introducing a training program to enhances nurses’ problem solving and decision making skills.
- Preparing patients for the Practicum:
- Patients should be warned about the steps and measures taken during the procedures;
- Principles and rules established by Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA);
- Ethical and legal concerns should also be known to the participants of the practicum.
- The Scope of Procedures:
- Nurse leaders and their subordinates will be informed about patients’ diseases and disorders. They will also have to conduct an observation;
- The participants will be split into two groups to encourage nurses reach the highest results and enhance the spirit of competition;
- Proper distribution of tasks and responsibilities should be carried out the team members to define their ability;
The training program will be introduced beforehand of nurses and patients’ informing about the general objectives and procedures involved into the practicum. During the training practicum, nurses should attend seminars and lectures during which they will have a possibility to view videos and presentations related to the actual process of bedside shift reports. In such a way, both nurses and their leaders will be able to enhance their competence and proficiency, as well as widen the understanding of what should be done during the practicum.
The purpose of HIPPA is “…improve the Medicare program under title XVII of the Social Security Act, the medicaid program under title XIX of such Act, and the efficiency and effectiveness of the health care system, by encouraging the development of a health information system through the establishment of standards and requirements for the electronic transmission of certain health information” (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, 1996).



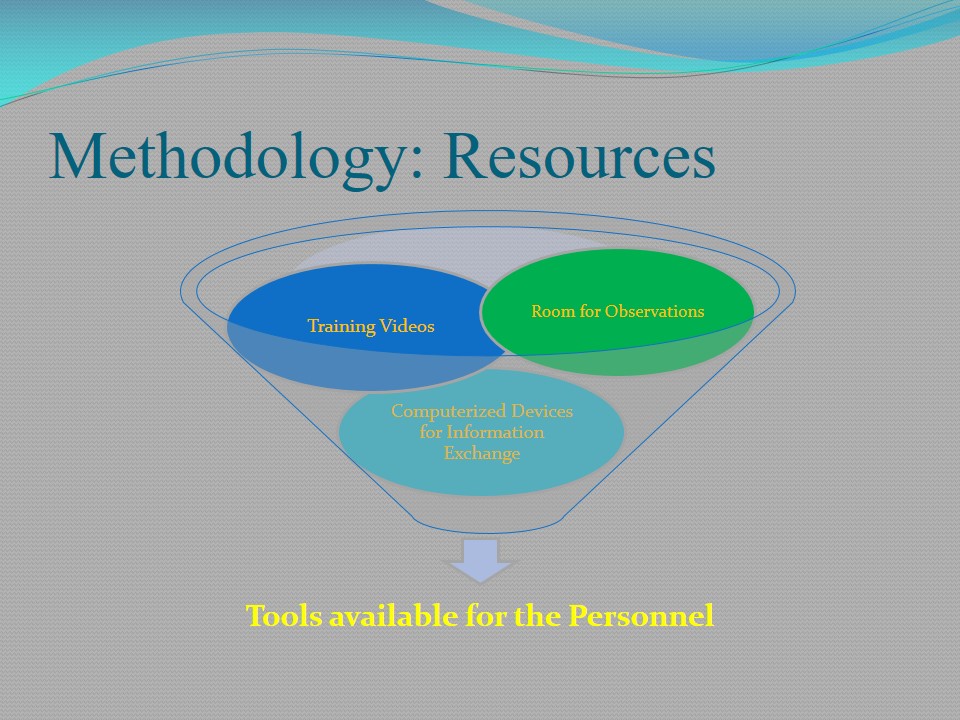
Methodology: Resources
Accurate allocation of resources, as well as managers’ responsibility for the availability of those, is essential for effective presentation of the Practicum Project. This is of particular concern to the shift handover. According to Philpin (2006), “in addition to the verbal handover at the end of each shift, each nurse would also write a full report in the nursing notes, which were kept in a black folder on the work surface next to the patient bed” (p. 90). Observational charts and note-taking are also among the techniques of information exchange that will ensure objectivity and accuracy.
Practicum Methodology: Introducing Three-Step Model
- Patient Observation.
- Problem Solving.
- Action Planning.
According to Dean (2009), nurses should take responsibility for the round the clock care because patient treatment that occur during their shifts have a potent influence on care that will be proceeded during the next shift. Hence, in order to avoid the challenges, a three-step model should introduced. It includes patient’s thorough observation, identification of the problem and searching for solutions, and action planning. Additionally, once the model is implemented, a survey will be conducted to evaluate the degree of patient satisfaction with the bedside shift reporting.

Methodology Timescale

Practicum Project Outcomes: Formative Assessment
- Formative assessment:
- Seeks to define nurses’ ability to cope with patients’ situation and operate knowledge they receive during patient observation;
- Explores shift managers’ ability to give orders and monitor the overall procedure of the project;
- Defines nurses and managers’ ability to provide input in terms of their competence in evaluating patient needs, handling equipment, and assigning medicine.
- Expected outcomes imply:
- Advancing nursing competence;
- Enhancing decision making skills;
- Readiness of the nurses to be involved into project;
- Ability of nurses to produce effective bedside reporting.
All the participants involved into the Practicum will have to take an assessment test to define their readiness to be involved into practical assignment. They should be assessed in accordance with their ability to communication and make decisions with regard to time and space.


Practicum Project Outcomes: Summative Evaluation
- Summative Evaluation will involve:
- Analysis of shift managers’ understanding the essentials of leadership and management;
- Defining managers’ and nurses’ abilities to cope with critical situations;
- Assessment of managers’ ability to arrange resources and responsibilities among their subordinates;
- Identifying the level of nurses’ ability to face changes;
- Test accomplishment will reveal:
- Nurses’ communication skills before and after the project;
- Patients’ level of patient satisfaction through questionnaires;
- Analysis of patients’ appraisals, as well as outcomes of these appraisals for the organization in terms of safety and satisfaction.


Assessing Organizational Environment: Knowledge Management
- Knowledge Management within Practicum Perspective:
- Defining the gaps in communication and information flow;
- Understanding the essentials of handling acquired knowledge;
- Using practical knowledge to shape theoretical perspectives.

Assessing Organizational Environment: Human Resources Management
Lammintakanen et al. (2008) argue that efficiency of human resource management within a practical setting depends on the extent to which managers focus on human competency, effective communication, personal development, and reward and punishment scheme. All these components are inherent to successful accomplishment of the practicum. Therefore, it is important for top managers to implement human resources development into the health care practices so as to increase the quality of patient care and enhance the overall level of service delivery. In addition, in case one component is missing, serious problem can arise in terms of leadership and control of the working environment within an organization.

Assessing Organizational Environment: Patient Care
Benestante and Mitcham (2008): “Implementation of a strategy to conduct bedside shift reports can increase patients’ involvement in discussion and decisions about available treatment options, increase patient and staff satisfaction, promote teamwork”(p. 541).

Practicum Outcomes: Scholarly Products
- Improvement of information share between patients and nurses.
- Individualized Intervention Planning.
- Greater adherence to goals and outcomes.
According to Caruso (2007), planning and implementing stage is always a challenging process both for patients agreeing to participate in the shift report and for nurses who face problems with accurate information distribution and delivery. Hence, “Nurse-to-nurse bedside report is described as a strategy that includes the patient in the reporting process and is an innovative alternative to traditional shift report” (Caruso, 2007, p. 17). The above-presented outcomes are congruent with the evidence presented by Caruso (2007) in terms of information processing and intervention planning.
Practicum Scholarly Products: Active Patients’ Participation
Bedside Shift Report revealed that patient are willing to react to nurses’ concerns, as well as to respond to the changes that need to be introduced. They are ready to communicate because they are aware of the objectives and goals of communication.
Anderson and Manquino (2006) bedside shift report has a great number of benefits for nurses to build and develop favorable relationships with their managers and other nursing staff, which can increase patient satisfaction. As a result, health care team can also provide a better ground for patients who can receive options in terms of communication and involvement into their treatment. As a result, change from taped reporting to bedside reporting is a step forward toward increased quality of care.

Practicum Outcomes: Team Working Essentials
- 50 % of nurses taking part in the Practicum did not experience challenges in front of changes and difficult situations;
- One shift was totally disarranged because of the failure of the manager to make decisions and organize a strict model for problem solving;
- Despite the problems, most of managers and nurses were satisfied with the change process and the overall outcomes of patient observation.

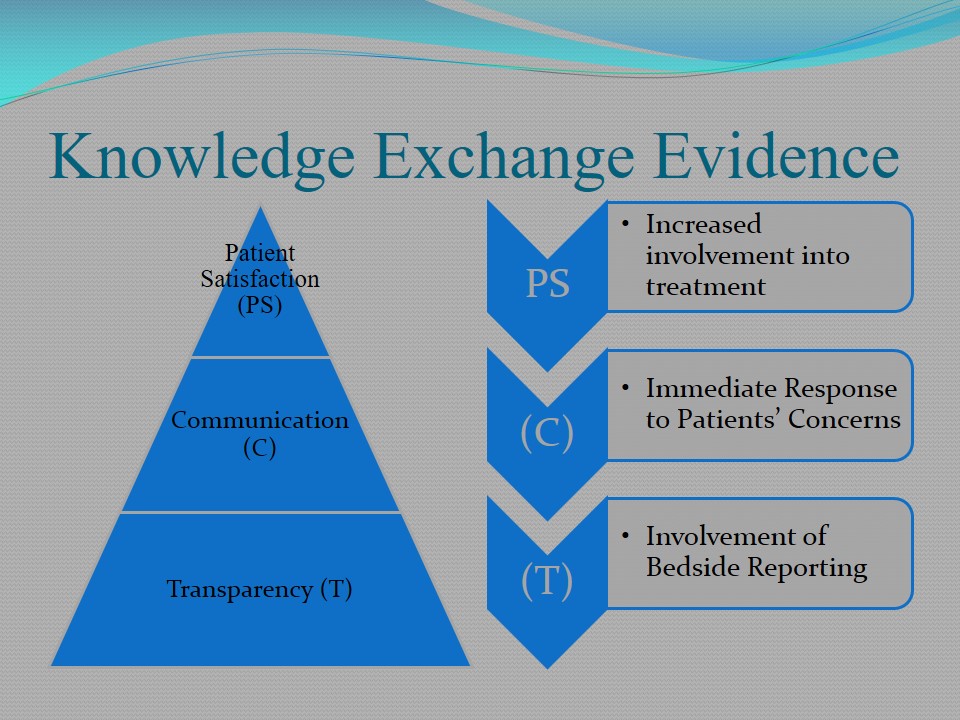
Knowledge Exchange Evidence
- Patient Satisfaction (PS)-
- Increased involvement into treatment.
- Communication (C)-
- Immediate Response to Patients’ Concerns.
- Transparency (T)-
- Involvement of Bedside Reporting.
Patients should be aware of all the procedures, measures, and problems related to their physical and mental state. The main task of a nurse is to inform their clients about possible difficulties, contingencies, and critical situation so that a patient is ready to face challenges. Therefore, transparency is the key to successful communication and increased level of patient satisfaction.
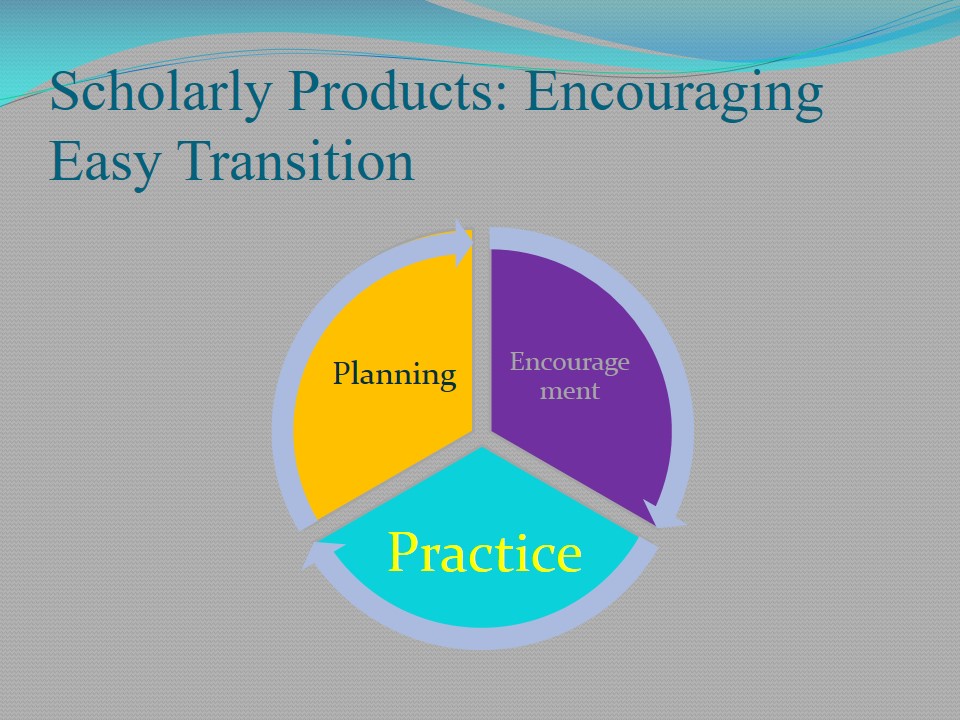
Scholarly Products: Encouraging Easy Transition
- Planning.
- Encouragement.
- Practice.
Facing changes during bedside shift reporting is often difficult for the nursing staff and their patients. Therefore, before nurses introduce any changes, they should inform their shift managers about those changes. The latter should work out a consistent plan and inform patient about the intervention. The patients, in turn, should provide their official consent and inform the nurses. Practice and planning should be supported by encouragement on the part of nurses and shift managers.
Scholarly Products: Adherence to Patient Safety Standards
Standard: LD.03.01.01.: “Leaders create and maintain a culture of safety and quality throughout the [organization]” (Joint Commission Perspectives, 2012, p. 1).
A4: “Leaders develop a code of conduct that defines acceptable behavior and behaviors that undermine a culture of safety” (Joint Commission Perspectives, 2012, p. 1).
A5: “Leaders create and implement a process for managing behaviors that undermine a culture of safety” (Joint Commission Perspectives, 2012, p. 1).

Ethical and Legal Concerns
- Each nurse was aware of the possibility to decline the experiment because of personal ethical and legal outlooks.
- All nurses accepted the rules and principles of the procedures;
- Patients were notified about possible threats, as well as the presence of HIPAA standards;
- Top managers to take legal and ethical responsibilities both for nurses and patients.
Consideration of ethical concerns can be regarded as a mandatory condition for conducting the Practicum because it involves a number of nuances related to human behavior. Therefore, all these moral and ethical codes should be carefully considered because proceeding with the Practicum.

Scholarly Products: Record Forms
- Bedside Shift Reporting:
- Increases patient safety;
- Enhances accountability;
- Introduces higher quality standards;
- Improves information transparency
- Traditional form of Reporting:
- Patient safety is under the threat because of subjective reporting;
- Lack of responsibility;
- Lack of information exchange between shift managers.

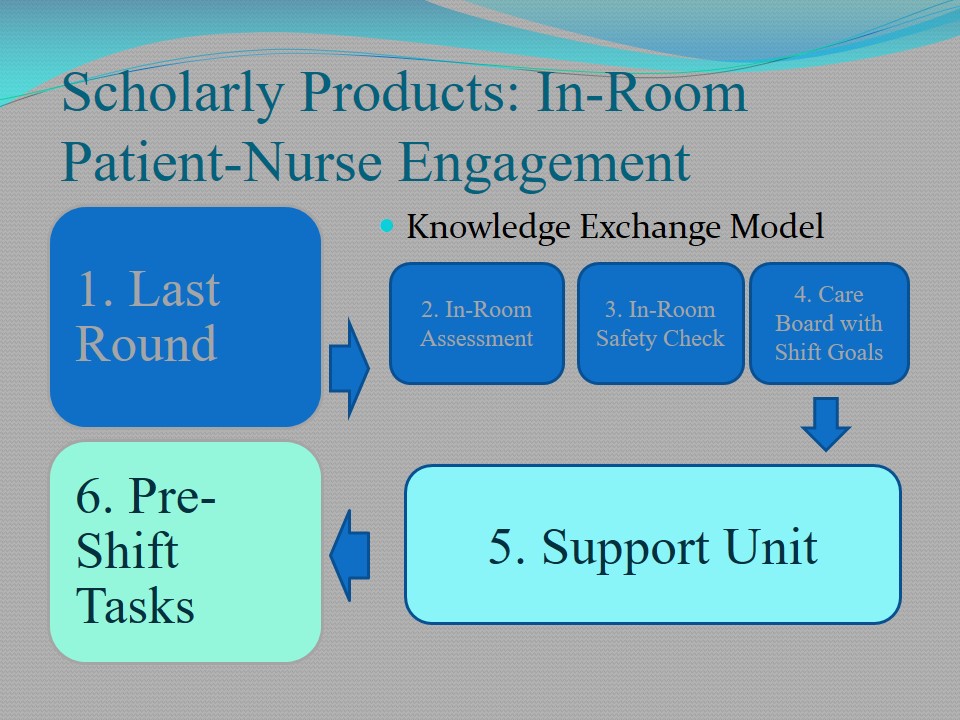
Scholarly Products: In-Room Patient-Nurse Engagement
Knowledge Exchange Model:
- Last Round.
- In-Room Assessment.
- In-Room Safety Check.
- Care Board with Shift Goals.
- Support Unit.
- Pre-Shift Tasks.
The presented Knowledge Exchange Model has allowed the nurses to highlight the sequence of importance procedures and principles that should be implemented in the course of the Practicum.
Practicum: Important Findings
- The Practicum has identified the benefits of teamwork, which allows nurses to define their duties and responsibilities;
- It has widened nurses’ experience in establishing real-to-life communication and facing patients’ complaints;
- Increasing the level of nurses’ availability for patient to get support and advice from;
- Understanding the matter of information sensitivity and confidentiality is increased during bedside shift report;
- Nurses are able to make instant decisions in case of emergency;
- Nurses are aware of the prioritization of patient treatment and care;
- Patients’ level of anxiety is decreased because the decisions are made in their presence;
- Improves accountability and awareness of shift managers;
- Encourages planning and exact intervention steps.


Practicum Conclusions
- The Practicum is aimed at learning the essential of leadership and management and increasing accountability of the shift involved into the bedside shift reporting.
- Knowledge exchange models have been developed during the practicum that have increased patients’ level of satisfaction and nurses’ ability to resist changes;
- Shift reporting was divided between two shifts with one manager and 2 nurses in each, which has increased competition and motivation.
Reference List
Anderson, C.D., Mangino, R.R. (2006). Nurse Shift Report, Who Says You Can’t Talk in Front of the Patient? Nursing Administration Quarterly. 30(2). 112-122.
Benestante, J., & Mitcham, G. (2008). Bedside shift report: a patient safety initiative. Oncology Nursing Forum, 35(3), 541.
Caruso, E.M. (2007). The Evolution of Nurse-to-Nurse Bedside Report on a Medical-Surgical Cardiology Unit. MedSurg Nursing. 17-22.
Dean, P. J. (2009). Nurse-to-nurse caring begins with shift-to-shift report. International Journal for Human Caring, 13(2), 22-26.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (1996). Public Law. Web.
Joint Commission Perspectives. (2012). Leadership Standard Clarified to Address Behaviors That Undermine a Safety Culture. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. 32(1), 1.
Lammintakanen, J., Kivinen, T., & Kinnunen, J. (2008). Human resource development in nursing: views of nurse managers and nursing staff. Journal Of Nursing Management, 16(5), 556-564.
Philpin, S. (2006). ‘Handing over’: transmission of information between nurses in an intensive therapy unit. Nursing In Critical Care, 11(2), 86-93.