The term recovery is used to describe the part of the business cycle during which the enterprises of a country regain or surpass the previous levels of production as well as employment (Swart 175). As a rule, during this stage, the interest rates are relatively low (Swart 175).
The declining value of British bound is more likely to decrease the consumption of the goods imported to the United Kingdom. This trend makes foreign products less accessible to buyers. As a result, they are more likely to buy the products of local manufacturers. Nevertheless, this outcome is possible only if British producers are able to meet the demand. Moreover, they should be able to compete with foreign companies in terms of price and quality. If these requirements are not met, the value of imported goods may not decrease. In this case, people will need to reduce their consumption. It is the main adverse effect that should not be overlooked.
In turn, the declining productivity of the UK labor is more likely to result in the increasing growth of imports. There are two factors that should be considered. First, there will be a shortage of local goods, and British manufacturers may not fully meet the demand of consumers. Secondly, local companies will become less competitive, and foreign goods may be less expensive. It is one of the main factors that can contribute to the growing trade deficit of the United Kingdom.
Overall, there are several benefits of a weakening British pound. At first, one should mention that British products will be more accessible to foreign buyers (Hill 55). So, British exports can increase. However, in this case, much depends on the competitiveness of companies working in the United Kingdom. They should be able to erode the market share of their foreign rivals. One should note that the governments of different countries deliberately avoid the strengthening of their currencies (Authors 7). For instance, this policy has been adopted in China (Napoleoni 89). Overall, this strategy can be more applicable to countries in which the labor force is inexpensive. Yet, it does not necessarily benefit very advanced countries.
Additionally, the weakening of the British pound can lead to an increased inflow of tourists. They will find it easier to buy the services of British hotels or restaurants. Thus, one can speak about the increased cash flow into the country. This trend has been observed in various countries with a weak currency (Laws 346). Moreover, they do not want to increase the value of their currency to ensure the growth of the tourist industry. This is one of the details that should be singled out.
Furthermore, the weakening of the British pound can benefit local manufacturers. As it has been said before, foreign goods will be less affordable, and consumers may prefer local goods. Finally, the weakening of the local currency can increase the inflow of foreign investment into the country. So, one should not suppose that the declining value of the British pound leads only to adverse effects because this assumption is not accurate.
The depreciation of the British pound did not improve the UK’s balance of trade due to several reasons. At first, one should mention that the UK economy gradually moved away from the production of goods to the provision of services. Furthermore, it is important to speak about the increasing role of the construction and distribution industries. Therefore, the country has become more dependent on imports. This tendency can be illustrated with the help of this chart that highlights the key elements of the British economy.
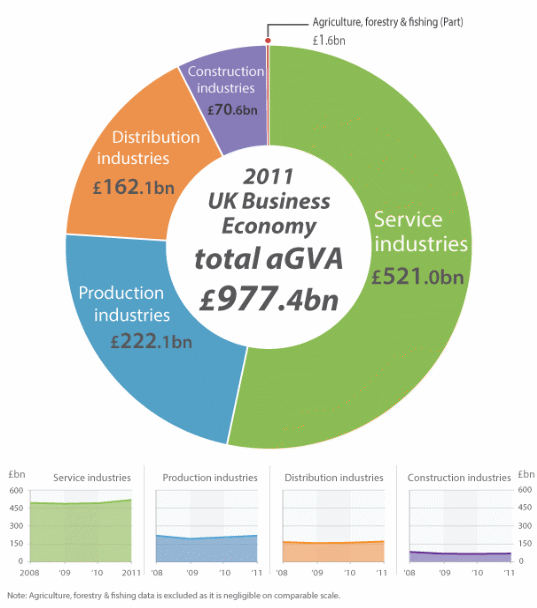
This chart suggests that the trade deficit of the country will not be reduced significantly, at least if one speaks about the exportation of goods. Yet, it is important to mention that the country exports services, rather than goods (Bowden 30; Hoffman 13). For example, the financial services industry plays an important role in the economy of the country. Furthermore, it serves clients from various countries. Overall, this trend has been observed in various developed countries. They are often called post-industrial economies in which the manufacturing sector does not play the main role (Tucker 227). Moreover, this tendency could be observed even before the recession that began in 2007 (OECD 21). These factors are necessary for explaining why the weakening of the British pound did not reduce the trade deficit (OECD 21).
The rising taxation and cuts in public spending can increase the trade deficit of the United Kingdom. In particular, local consumers will choose more affordable goods. In turn, it is quite possible that foreign goods will be more competitive in terms of price. These policies are more likely to slow down the economic recovery. Overall, these examples suggest that the competiveness of local businesses is the main factor that should be considered. Moreover, one should focus on the general tendencies within the economy which can be dominated by the service sector. These are the main details that should be distinguished.
Works Cited
Authers, John. Europe’s Financial Crisis: A Short Guide to How the Euro Fell Into Crisis and the Consequences for the World, New York: FT Press, 2012. Print.
Bowden, Rob. United Kingdom, London: Evans Brothers, 2005. Print.
Hill, John. International Business: Managing Globalization, New York: SAGE Publications, 2008. Print.
Hoffman, Kenneth. Services Marketing: Concepts, Strategies, & Cases, New York: Cengage Learning, 2010. Print.
Laws, Eric. Crisis Management in Tourism, New York: CABI, 2007. Print.
Napoleoni, Loretta. Terrorism and the Economy: How the War on Terror is Bankrupting the World, New York: Seven Stories Press, 2011. Print.
OECD. OECD Economic Surveys: United Kingdom 2011, New York: OECD Publishing, 2011. Print.
Office for National Statistics. Statistical Bulletin: Annual Business Survey, London: Office of National Statistics, 2011. Print.
Swart, Nico. Personal Financial Management, New York: Juta and Company, 2004. Print.
Tucker, Irving. Economics for Today, New York: Economics for Today, 2008. Print.