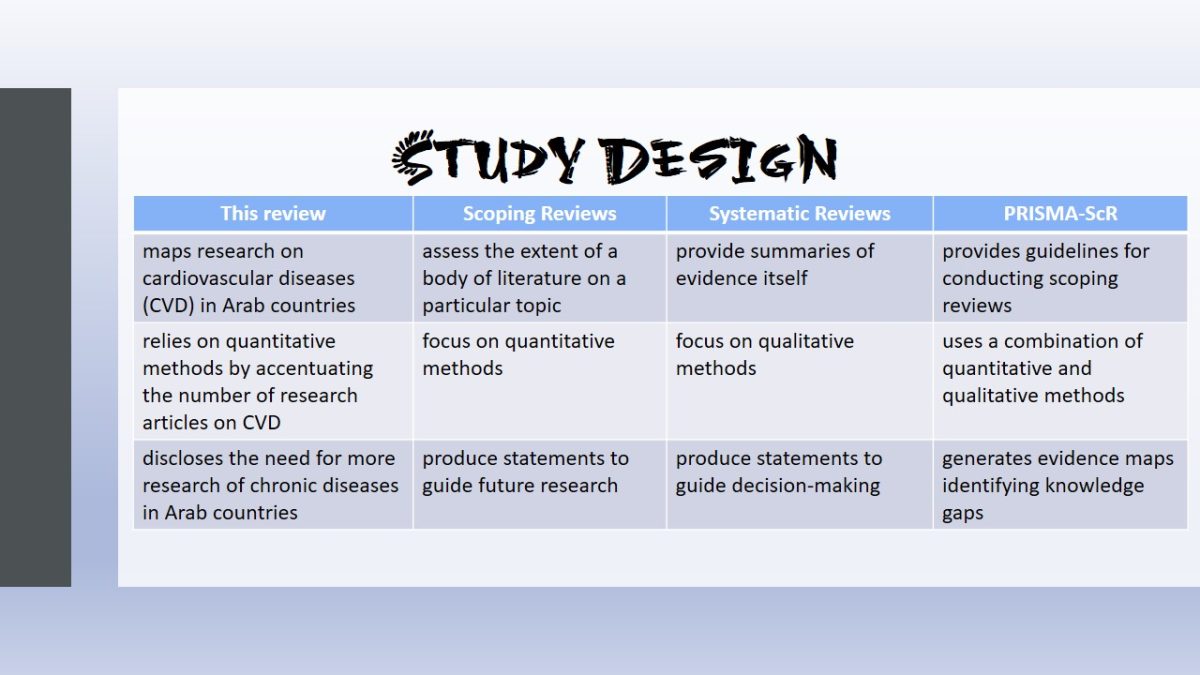
Study Design
Introduction
- CVDs and the potential impact it has on a global scale.
- 17.7 million people died from CVDs.
- Most cases tend to be limited to low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- 34.1 percent of deaths in the Mediterranean region.

Aim
Analyzing cardiovascular (CVD) research in Arab gaps to highlight:
- The existing opportunities.
- Gaps in literature.
- Which will be utilized to inform future research.

Methods
- Scoping review research methodology over four years, from 2012 to 2016.
- The review employed a 5-step mapping framework .
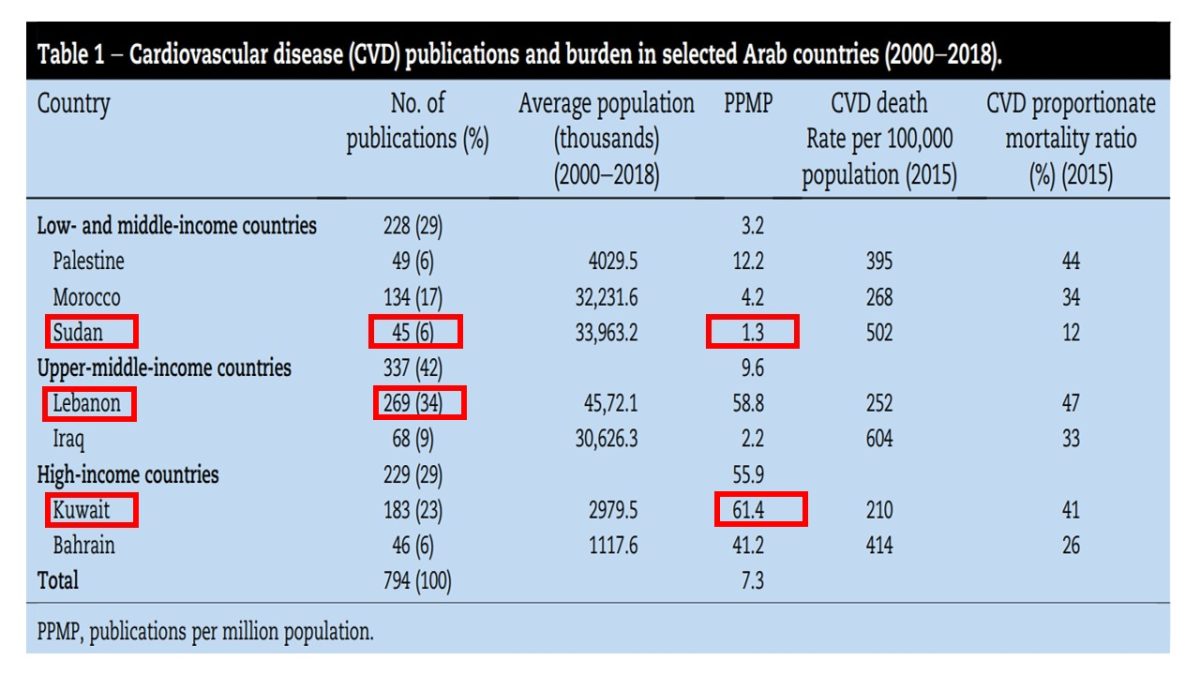
- Only seven countries were included due to the limit in the number of published research.
- collected from 794 articles.
- SPSS tool version 24 was used to analyze data.

Results
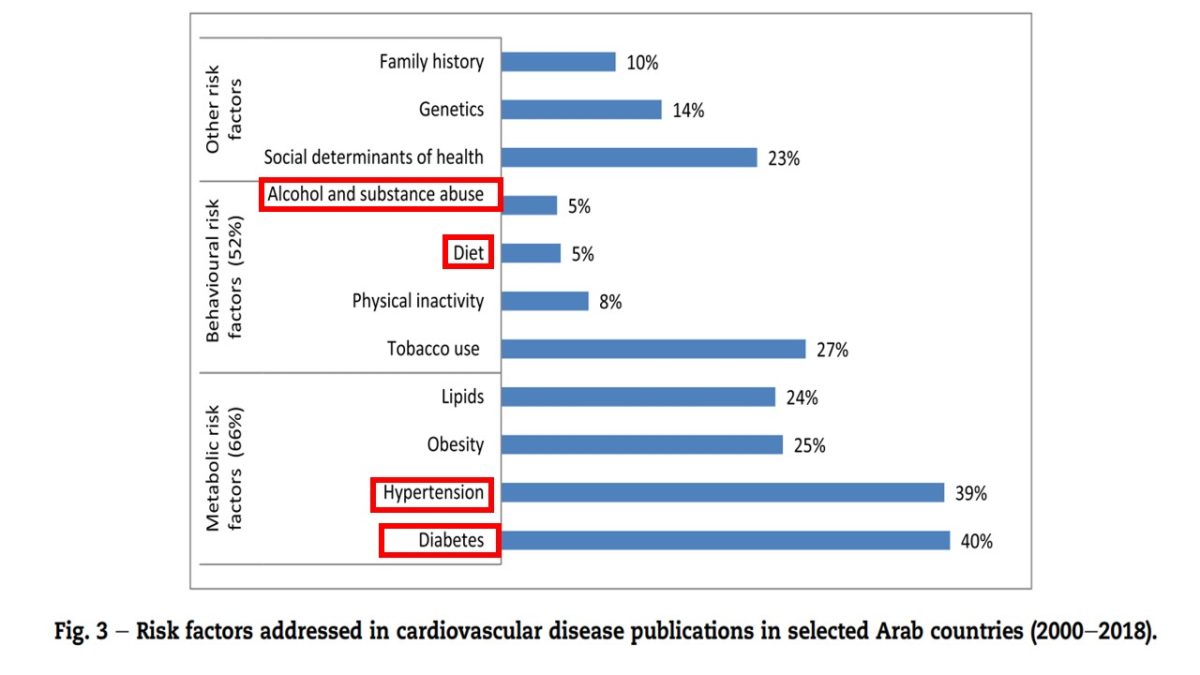
Discussion
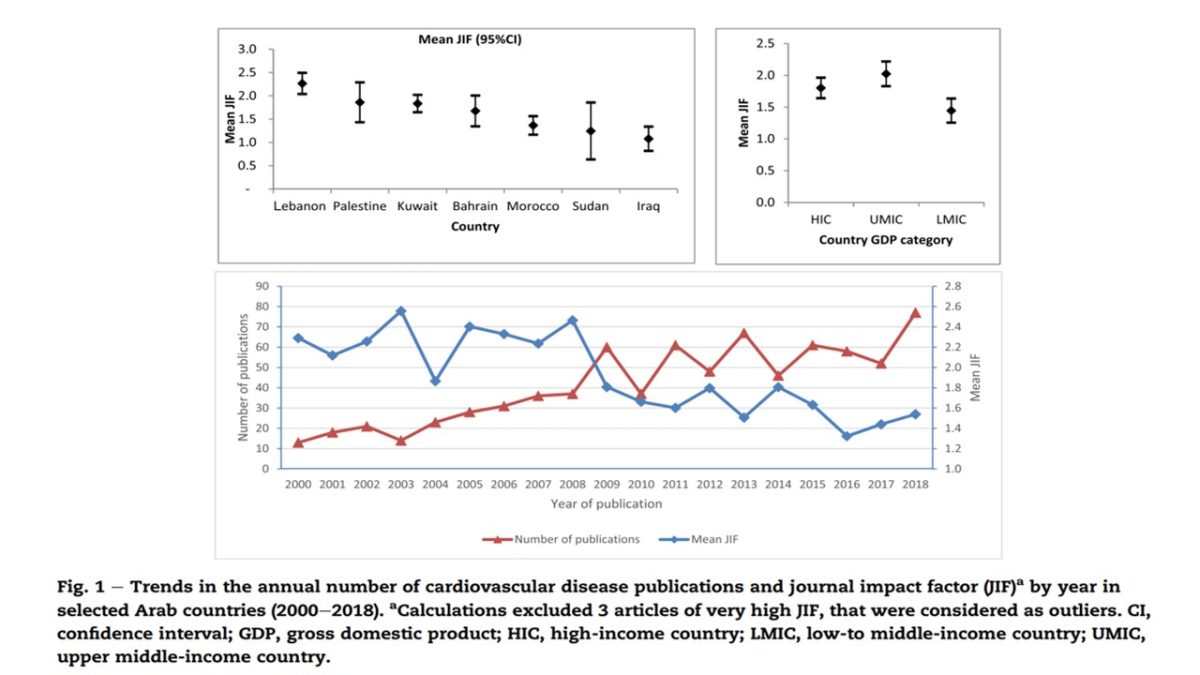
- Most publications were published in low impact JIF , with the lowest being in Iraq and Sudan.
- The scarcity in the publication was linked to:
- the availability of funding opportunities;
- individual and institutional resources.
- Geopolitical factors also affected the publication of CVD research;
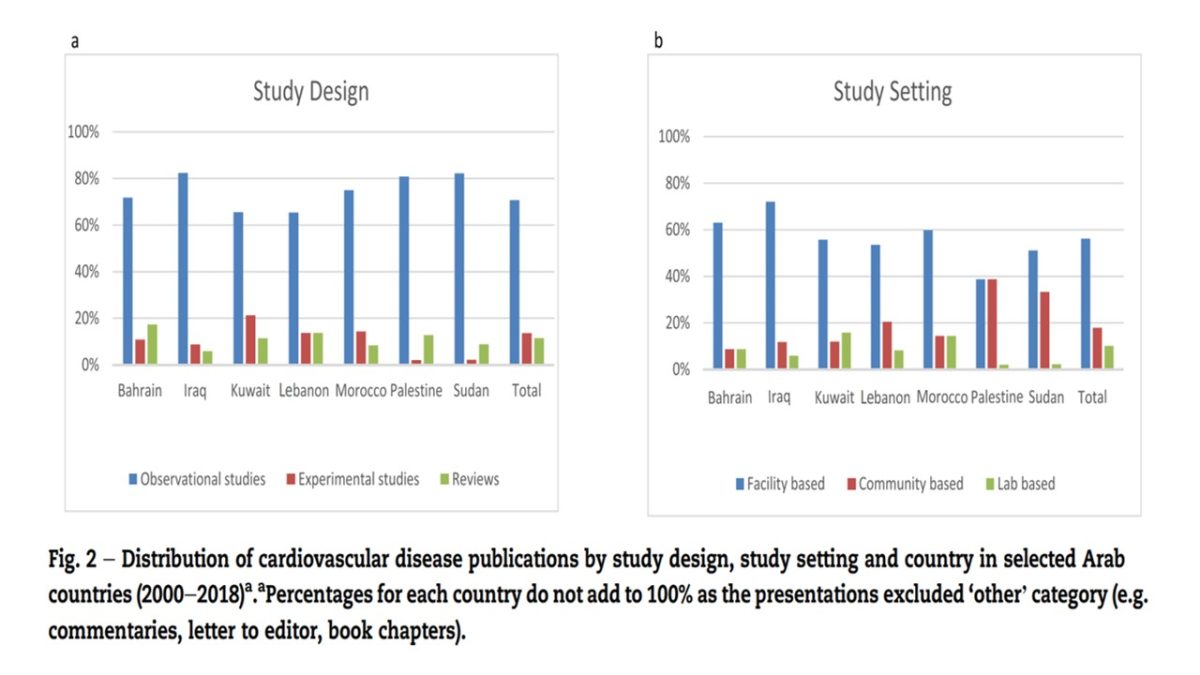
- Challenges associated with the production of high-quality research involve:
- selecting proper study design;
- analytical strategy;
- available evidence;
- study settings.
- Despite an increase in CVD publication, high-level evidence through proper testing designs and hypotheses is lacking.
- More research in Arab countries focuses on quantity over quality of research.

Conclusion
- There is a need for further research on political support from policymakers.
- The study recommends that funding bodies need to focus on research priorities in specific sections.
- Research communities are also essential in improving research investment.

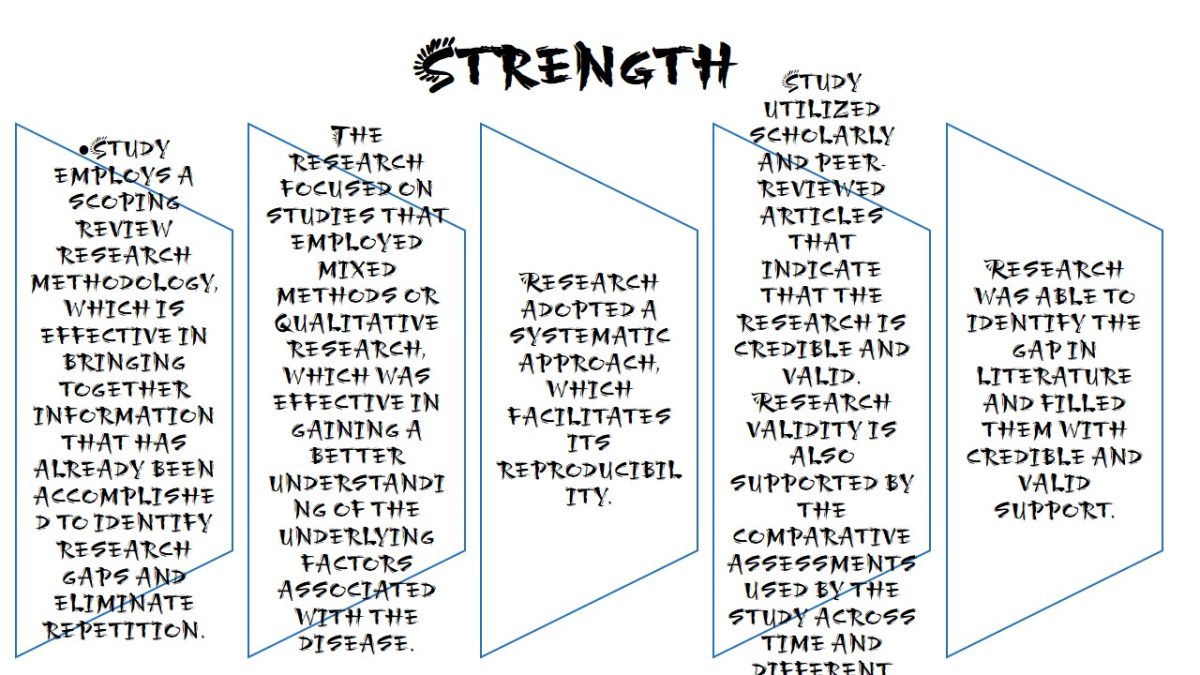
Strength
- Study employs a scoping review research methodology, which is effective in bringing together information that has already been accomplished to identify research gaps and eliminate repetition.
- The research focused on studies that employed mixed methods or qualitative research, which was effective in gaining a better understanding of the underlying factors associated with the disease.
- Research adopted a systematic approach, which facilitates its reproducibility.
- Study utilized scholarly and peer-reviewed articles that indicate that the research is credible and valid. Research validity is also supported by the comparative assessments used by the study across time and different nations.
- Research was able to identify the gap in literature and filled them with credible and valid support.
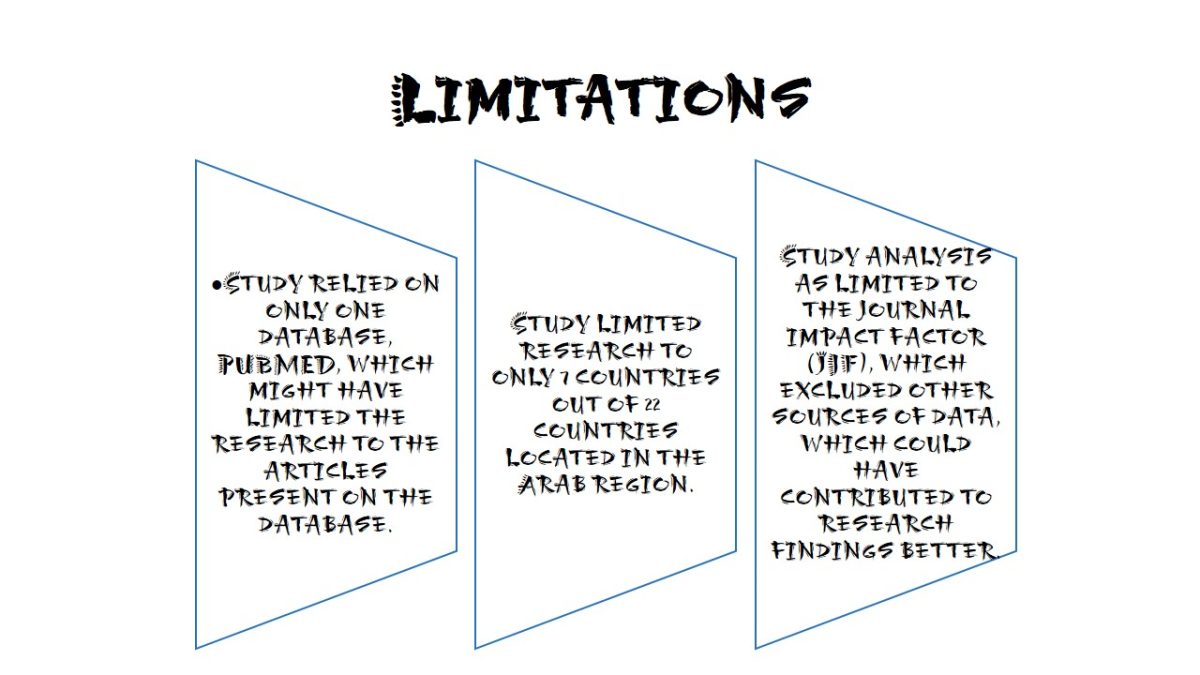
Limitations
- Study relied on only one database, PUBMED, which might have limited the research to the articles present on the database.
- Study limited research to only 7 countries out of 22 countries located in the Arab region.
- Study analysis as limited to the journal impact factor (JIF), which excluded other sources of data, which could have contributed to research findings better.
Critical Appraisal
- Did the study address a clearly focused issue?
- Yes. Evidenced through the selected supporting material and the research conclusion. The study concluded by addressing research objectives, which included identifying large gaps in literature based on the themes and methods used by other studies.
- Was the cohort recruited in an acceptable way?
- Yes. Data collection was done appropriately and acceptably. The study collected articles published or are in the plan of being published on the subject matter.
- Was the exposure accurately measured to minimize bias?
- Yes. Despite the inclusion of data from only seven out of twenty-two countries, the study adopted methods that aim to reduce bias.
- Have the authors identified all important confounding factors?
- Yes. The study analyzed all the significant confounding factors associated with cardiovascular diseases, the number of publications, and the disease’s geographical distribution in the Arab countries.
- Have they taken account of the confounding factors in the design and/or analysis?
- Yes. It analyzed the mean JIF in the selected nations, the GDP, and the related CVD trends. It also examined the study design and study setting adopted by the different JIFs in different countries.
- Was the follow up of the subjects complete enough?
- No, there was no follow-up of subjects. Researchers employed a scoping review methodology that does not involve dealing with subjects. Therefore, they could not do a follow-up.
- How precise are the results?
- It is not clear if the results are precis. At one point, it can be deduced that the study results were accurate following the use of the confidence interval (CI) tool. However, the study failed to address some of the appropriate risk factors as they relate to CVD.
- Can the results be applied to the local population?
- No, results cannot be applied to the local population. The research’s target audience is researchers, research bodies, scientific scholars, and medical research fraternity.
- Do the results of this study fit with other available evidence?
- It is not clear if the results fit with other available evidence. The research is unique because no published reviews are covering the concepts argued and analyzed in the study.
- Were all important outcomes considered?
- No, the authors of the research consciously chose to limit their sampling to PubMed. The review would have been more comprehensive, if it had included articles from other search engines, like Ovid, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Scopus. The inclusion of articles from these databases would also help provide information on more countries, as the original research covered only 7 out of 22 countries in the Arab region.
- Are the benefits worth the harms and costs?
- Yes, the majority of risks are associated with poor execution of the research process. Proper selection of research questions would help compose an appropriate design and choose the right methods. Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality and Arab countries are not an exception. Therefore, more research into the development of chronic CVD diseases should be conducted despite the publication in low-impact journals.



