Introduction
Different environmental factors play a key responsibility in managers’ decisions and organisation’s success. Managers cannot avoid those factors. All the factors need to be analyzed so that managers can take decisions effectively. There are some factors, which cannot be controlled by manager, thus the controllable factors need much attention of the manager.
Background and Environmental Discussion on Qantas
As a result of recent collapse of airlines industry, Qantas Airlines takes few initiatives to change its environment. It is important because this is done to provide the firm with an explanation of the elements in society that straightforwardly affect the industry. Sometimes managers should take some measure to implement appropriate strategies to survive. In order to compete with other airlines industry and to ensure highest facilities for customer, Qantas is committed to alter its environment. Six key factors of environmental issue will be discussed here.
Political & Legal Factors
Politics is one of the most significant issue for Qantas and it has both hopeful and negative affect on success. Political factors in Australia effectively helped Qantas to formulate plans and policies.
Economic Factors
Qantas is experiencing an extremely competitive market as the government strengthens the security laws for internationally and domestically which has led to huge drop in passenger number. The recent increase in oil prices has been a threat for the aviation sector’s success.
Socio-Cultural
Qantas keeps relationship with various regional carriers. Oneworld Alliance is the philosophy that links the need for culture change and the long-term best interest. Qantas used union to increase market share and thus the company flourished.
Demographic
Air travel is must for individuals all over the world. As Australia is not much populated, sometimes Qantas has to attract customers aggressively. Now a day’s air travel is not much costly so Qantas can expect different aged customers.
Technological
By keeping Impulse airlines, which has changed into Jetstar, as a stand-alone unit, Qantas has been able to originate cost savings from using Impulse’s low-operating cost, all-economy class, and efficient staffing/labour practice. The modification in policy has enabled Qantas to apply some of its strategic learning’s from this low cost model develop Jetstar.
Global
Global factor constantly changes due to government interference and the incidents happening on a continuous basis. In spite of population of 20 million, Australia is number four in the world relating to domestic passenger-kilometres-performed. Though there were recent turmoil in the aviation industry of Australia, Qantas was able to increase its profit remarkably.
Task Environmental Analysis
Kotler, P., (2008) argued that task environmental analysis refers to the environment that is related to task completion. It is related to workers selection and training, procedure design etc. Qantas had to analyze this environments element to introduce Jetstar model. Qantas had to learn about its rivals policy and procedures so that Qantas can take competitive benefit. Based on this analysis it took a market segmentation policy.
This wide differentiation strategy includes “Pincer movement tactics”. As the market is becoming competitive day by day, each and every task requires to be completed accurately. Personnel are very important to maintain daily schedules of an airline. As the timing of the flights are really important, personnel need training to do their work within a short time. If Qantas can not fulfil its customers demand, then its customers will go to its rival and thus Qantas’s market share will abate.
Answer to the Question no 2. (A)
Major issues or problems: As a country Australia has involvement with high individualism is high where power detachment is small. It is well known that uncertainty prevention is more moderate and quality of life would be strong. As Qantas has the plan to expand its service over the world, its managers need to know about a country’s economic system because it has the potential to constrain decisions and actions. Other economic issues a manager might require to understand include currency exchange rates, inflation rates and diverse tax policies.
Gomez-Mejia (2007) said that the Economic environment consigns to the features those have an effect on consumer buying power as well as spending patterns where all the Nations to a great extent in their intensity and allocation of income. These countries offer few market opportunities. At the other intense are industrial economies, which constitute rich markets for many different kinds of goods. Marketers must pay close attention to major trends and consumer spending patterns both across and within their world markets. Australia has such an industrial economy.
In 2004, when aviation industry was suffering from losses, Qantas was the largely profitable airline, strategically well managed the main factors behind this success. Thompson, A. (2007) said that the Strategic management acts as set of managerial decisions as well as actions those settle on the long term performance of the organisation. It varies from Organisation to Organisation on how to well perform for the reason that there are differences in their strategies as well as dissimilarity among their competitive abilities. It is a significant assignment of managers as well as necessitates all the basic management purpose.
For Qantas Strategic management has very significant for the reason that strategic management is able to make a differentiation in how healthy the organisational performs is. The most elementary queries concerning strategy should address why organisations do well and why they fail when they are pursuing with the same environmental conditions as well as they have unstable levels of performance. Studies of the factors that contribute to organisational performance have shown a positive relationship between strategic planning as well as performance. In other hand, it is found that the organisations those uses strategic management, positively they have highly developed levels of performance those make strategic management more attractive and important.
Another reason strategic management is important has to do with the fact that organisations of all types and sizes face continually changing situations. These siftings possibly will be lower organisational significant, nevertheless there are still changes with which managers would be obliged to cope with. As Qantas is a huge organisation it needs to be managed very well otherwise the resources will not earn profit for the organisation. Qantas followed strategic management procedure and thus it was able to cope with uncertain environments. Qantas followed the strategic management process to get superior performance.
The earliest step of strategic management course of action is to recognising the organisation’s up to date mission as well as objectives and strategies. Qantas set its mission, objectives and strategies based on current market situations. It’s also significant for the managers to determining the goals that at present in position and the strategies those are presently pursued. Every organisation has its own mission statement that states the principle intention of an organisation.
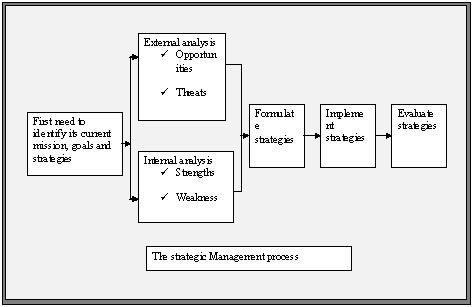
- The step 1 in strategic management process is external analysis. Manager in every organisation needs to do an external analysis. They need to know, for instance, what the competition is doing, what pending legislation might affect the organisation, or what the labour supply is like in locations where it operates. In analyzing the external environment, managers should examine both the specific and general environments to see what trends and changes are occurring. After analyzing the environment, managers need to assess what they have learned in terms of opportunities that the organisation and pose threats to another in the same industry because of their different resources and capabilities.
- Step 2 is internal analysis which leads to a clear assessment of the organisation’s resources (such as financial capital, technical expertise, skilled employees, experienced managers and so forth) and capabilities in performing the different functional activities (such as marketing, manufacturing, information systems, HRM and so forth).
- Step 3 refers to formulating strategies. Once the SWOT analysis is complete, managers need to develop and evaluate strategic alternatives and then select strategies that capitalize on the organisation’s strengths and exploit environmental opportunities or that correct the organisation’s weakness and buffer against threats.
- Step 4 refers implementing strategies. As soon as it would be completed to preparing strategies without any delay it must go for accomplishment. A strategy should be determined as good or better only when it goes for implementation. No matter how effectively an organisation has planned its strategies, it cannot succeed if the policies are not executed properly.
- Step 5 is evaluating results: The final step in the strategic management procedure is appraising results. How effectual would be the strategies. Is there any need for adjustment? If any, how long that is necessary. Geoff Dixon who is the CEO of Qantas made strategic adjustments to improve his company’s competitiveness in the information services industry. He did this subsequent to assessing the outcomes of preceding strategies and shaping that changes were needed.
The environment affects managers through the degree of environmental uncertainty that is present and through the various stakeholder relationships those are present between the organisation as well as its external constituencies.
Assessing environment uncertainty: it was the 2nd major issue related to Qantas. Qantas solved this issue by environmental uncertainty matrix. It is remarkable that all the environments are same. Most of them differ by what they call their measure of environmental vacillations; those are the level of change and level of complication within an organisation’s environment. The first of these dimensions is the degree of change. If the mechanism of an organisation’s environment changes repeatedly, that is addressed as dynamic environment. If change is minimal, we call it a stable one.
The stable environment would be that one where there are no presences of new competitors, a small number of technological step forward by existing competitors and modest action by the pressure groups to pressure that organisation as well as so forth. Probably the main environmental concern for Qantas is the increasing trend in oil price.
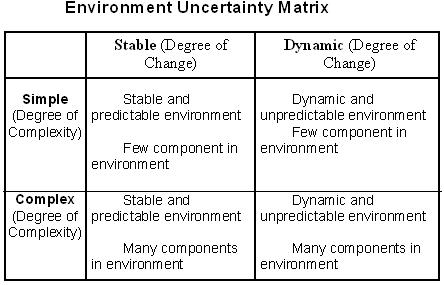
Qantas assumed that the airline industry is dynamic and thus it took steps to compete with its competitors. The third major issue is control stakeholder relations. Most of the Stakeholders stay within the external environment of the organisation but they can easily affect the organisational decisions as well as some actions may alter. To managing stakeholders is also a very important factor for every organisation and Qantas has been maintaining a sound and healthy relationship with its stakeholders through their effectual management.
Stakeholders should be given importance for the reason that it can guide to other organisation effects such as enhanced expectedness of the environmental challenges, further flourishing innovations, wider extent of trust in the midst of stakeholders and superior range of organisational flexibility to diminish the blow of change. It also influences the organisation performance An organisation’s customers, supplier, socio-political action groups, shareholders, competitors, governments, trade and industry associations, unions, communities, media and employees all together are called stakeholders
Answer to the Question no 2. (B)
The Reconciliation Action Plan was recently introduced in Qantas. The company is committed to give importance to indigenous people. Qantas helps the indigenous community by several ways such as recruitment, employee engagement and community activities. The Reconciliation Action Plan (RAP) has been initiated by Dixon, G., in November 2007. Qantas strives to bridge the gap among non native and aboriginal community by introducing the Reconciliation Action Plan.
For the existence of the RAP, there is a necessary combination and change within strategic planning of Qantas. Strategic planning is the process of maintaining and formulating a strategic fit connecting the organisation’s objectives as well as capabilities within its shifting marketing opportunities. It is concerned with defining clear mission of company, supporting goals setting, and healthy business portfolio designing as well as and harmonising serviceable strategies.
The mission statement of Qantas has to be altered for the reason of introducing of this new plan. Mission statement includes the organisation’s goals, which carry out in the better environment to achieve its success. The success of an organisation depends and deeply concerned on the management of that organisation. On every occasion there would be a change within the organisation and the mission statement positively uphold that necessary change. A successful company like Qantas asks some questions and carefully answers them. These questions would be query about what their business is and who the customers are.
Always the Mission statement would be market driven. Mission statement describes the business in provisions of fulfilling fundamental needs of customer. For example, mission statement of eBay’s states that ‘the world’s online marketplace. The Management always put its emphasis to avoid preparing its mission too short or too broad in length. As Qantas has started a plan for indigenous people, mission statement should contain the service presented to them. Also the mission should always fit with the market environment. The organisation should formulate its mission concerning with its distinguishing competencies. Another remarking criterion of mission statement is to be more motivating. The RAP will put additional responsibility to Qantas.
Answer to the Question no 3
Understanding organisational is significant because business performance greatly depends on understanding and responding to the environment. The external environment indicates to the power, politics or pressure which potentially affect business performance. The external environment is includes 2 components and these are specific and general component.
The specific environment includes those external forces that have a straight and instantaneous impact on managers’ decisions and acts and are directly relevant to the achievement of the organisation’s goals. Each organisations specific environment is unique and changes with conditions. The forces that make up the specific environment are customers, suppliers, competitors and pressure group.
Customers
Qantas has control large international market. As a result customer is significant factor for Qantas. Perceiving customers needs and responding them is the key to success. It’s the customers or client who absorbs the organisations output. This is true even for governmental organisation and other non for profit. Qantas always concern about customer’s interest to take any initiatives. Thus, it has created small cost model of airline. Customers taste can change or thy can become dissatisfied with the organisation’s products or service.
Suppliers
The forward and backward relationship with customers and suppliers is important to manage the company. Managers seek to ensure a steady flow of needed inputs at the lowest price available. Because these inputs represent uncertainties-that is their unavailability or delay can significantly reduce the organisation effectiveness.
Competitors
It is quite natural that organistion has to compete with market players. Managers play vital role to avoid the competition by providing or implementing new plans. The relationship with competitors is antagonistic as it is using head to head advertisement and promotional activities. They represent an environmental force that manager must monitor and to which they must be prepared to respond.
Pressure groups: managers must recognize the special interest group that attempt to control the actions of organisations. As social and political attitudes change, so too does the power of pressure groups.
General environment: Any political socio cultural, demographic and other changes the business environment, increase or decreases the risk. Suppose if Government wants to hike up the oil price for political turmoil, which has adverse impact on the business. Recently UK has signed up the in the single European currency and this decision has serious influence on economy.
Changes in any of these areas usually do not have as large an impact as adjusts in the specific environment do but managers must consider them as they plan, organize, lead and control. Interest rates, inflation, changes in disposable income, stock market fluctuations and stage of the general business cycle are some of the economic factors that can affect management practices in an organisation.
Government can influence what organisations can and cannot do. Some legislation has important implications. Robbins S. P, (2007) emphasis that organisations waste lot of time and money to meet governmental regulations. EU regulation has forced Organisation to change their policy and hence the cost structure has been changed though the geographical location is limited to UK and EU. Other aspects such as Changes in the technological sector will impose a direct impact in the organisation or in overall business process. The transaction cost or information exchanging cost can be reduced as 24 hours call centre, internet facilities are establishing more.
Society, people, friends etc changes the economic conditions. Judge, A. T, (2008) argued that their behaviour, attitude, demand has a direct relationship with the business. For example, as workers have begun seeking more balance in their lives, organisations have had to change by offering family leave policies, more flexible work hours, and even on site child care facilities. As Qantas does business in other countries also, managers need to be familiar with those countries values and cultures and manage in ways that recognize and embrace those specific socio cultural aspects.
Robbins S. P, (2007) argued that employees comes from different area as a result manager should treat them in a different way. By the time, people enter an organisation, their cognitive structure the way they perceive and response to the world around them has been largely determined. This cognitive structure is shaped both by unique personal experiences and by the socializing influences of the person’s culture and it operates both at home and in the workplace. There are two kinds of environment and these are discussing the external and internal factors of the organisation. The internal factors can be found from microenvironment and it mainly concern competitors and suppliers.
On the other hand, Macro-environment influence the microenvironment. Managers have to take other company groups into account. Groups such as top management, finance, research and development, purchase etc. People are considered as most significant asset. As a result the organisation should focus customer’s interest when then consider environment of the organisation. Different studies have concluded that an organisation’s human resources can be a significant foundation of competitive benefit. In order to Achieving competitive success Human Resource Managers are ready, willing, and able to contribute to organisational goals; they work in the organisation and also known as personnel. Human resource forecasts predict an organisation’s future demand for employees.
It involves working with and through people and seeing them as partners, not just as costs to be minimised or avoided. In addition to their potential importance as part of organisational strategy and their contribution to competitive benefit, and organisational strategy and their contribution to competitive improvement, and organisation’s HRM practices have been found to have a significant impact on organisational performance. So manager has to look into many environmental factors to turn out to be successful.
Bibliography
Charnov, Bruce H. P. & Montana, J. (1993), Management, 2nd edition, Barrons Educational Series Inc, ISBN-10: 0812015495.
Chapter 3: Organizational Culture and Environment: The Constraints, (2008). Web.
DeConzo A. D & Robbins S. P, (2007), Fundamentals of Human Resources Management, 8th edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ISBN: 9812-53-171-8.
Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O.C. (2001), Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
Gomez-Mejia Luis, Balkin, David & Cardy, Robert, (2007), Managing Human Resource, 5th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 978-0135032749.
Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G., (2008), Principles of Marketing, Prentice Hall of India, 10th ed., New Delhi.
Robbins, S.P. & Judge, A. T, (2008), Organisational Behavior, 13th edition, Prentice-Hall, ISBN: 81-203-3-90-0.
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, India: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, 13th edition.