Introduction
Nursing innovation and change management are critical for enhancing health, avoiding illnesses, identifying and mitigating risk factors, cultivating healthy lifestyle attitudes, and validating care and treatment approaches. The goal of healthcare innovation is to create better and more efficient health policies, systems, items, and technology, as well as services and distribution channels that benefit people. The specific nursing theory that will be encompassed in the paper is Kurt Lewin’s change management theory, whereas the theoretical framework is related to nursing and medication administrations and errors.
Nursing Framework
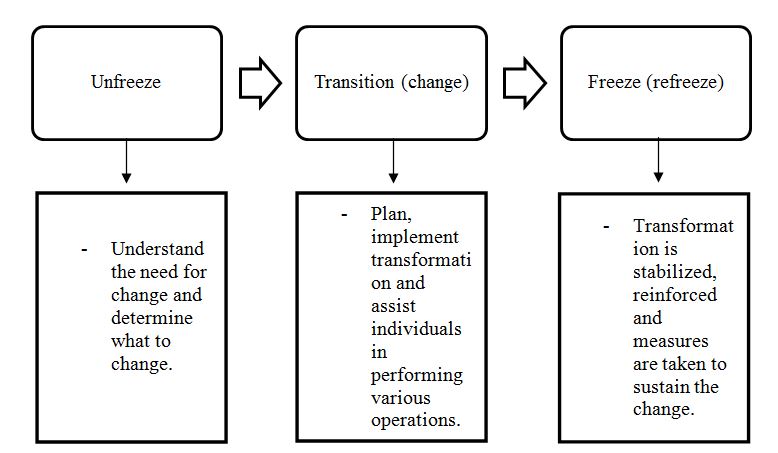
In the healthcare sector, change is a common phenomenon due to the rapidly changing medical and social environments. One of the developments caused by the information era is the digitalization and computerization of nursing networks and systems (Bozak, 2003). As a consequence, nurses’ opinions regarding technology and transformation in the workplace vary greatly (Bozak, 2003). The nurse practitioner or specialist must be aware of the elements that support and hinder change in order to efficiently transfer the healthcare personnel from one platform to another (Bozak, 2003). Nurses will need to devise strategies to help them go forward with the transformation. Kurt Lewin’s three-stage paradigm, often known as the structured concept of organizational development, is a fundamental notion that is still believed to be relevant. Lewin, a sociology professor and philosopher, proposed the three-stage hypothesis. In this approach, he highlighted unfreezing stage, transformation, or transition, and freeze, or refreeze phase, as a basic model for analyzing the process of organizational or institutional transformation. Change is a difficult transition for people or organization, and it is rarely straightforward. It requires numerous phases of shifts or misunderstandings before reaching a point of stability.
Framework Concepts
Concerning the analysis of the concepts within the framework, it is possible to emphasize several relevant notions. Firstly, the change framework should be ubiquitous since it is utilized by various healthcare specialists for multiple medical purposes. The first step in the theory is transition unfreezing, which is one of the most crucial phases in the overall change management plan. It entails cultivating a realization for relocating from one’s current normal routine and comfort zone to a converted condition, as well as enhancing people’s preparedness and willingness to change. The second step is also known as the transitional phase or the stage of real change execution. It entails a willingness to accept better ways of doing things and operating. The individuals are unfrozen at this point, and the real modification can be applied. People proceed from the phase of transition to a substantially more normal position, which is possible to be described as the stable equilibrium point during the last step, which is refreezing. The final step of refreezing occurs when individuals embrace or adapt new methods of working or transformation, integrate it as a part of their lives, and form new connections.
Relationship of Variables
Considering the relationship of variables within the framework, which is Kurt Lewin’s change management theory, it is compulsory to emphasize the factors that can change due to specific conditions and contexts. Variables in the input information can be generally included in one of the categories listed: individual characteristics and data of patients and personnel, equipment and methodology, or facility features. In addition, another set of variables related to the theoretical framework is medication errors. To prevent the harm induced by prescription and medication mistakes, a medication safety system of education can be devised and executed (Dennison, 2007). It may be inferred that robust administrative assistance and follow-up were required to create behavioral changes that could lead to a reduction in damage caused by prescription errors (Dennison, 2007). These variables are critical to analyzing the potential implications of Kurt Lewin’s change management theory in terms of nursing practice.
Nursing Framework Significance
Considering the significance of the chosen nursing framework, it is feasible to emphasize the necessity of implementing change in rapidly evolving medical conditions. In medical situations, executing a change among practice might cause depression or fear of rejection in nurses, resulting in unwillingness to change. Medication mistakes in healthcare facilities have terrible implications for both the patient and the nurse, but they may be dramatically minimized by implementing technology that enhances patient care. Kurt Lewin’s change theoretical framework can be used to help a large mental hospital implement bar-coded medication systems. Lewin’s theory can help organizations to identify how transformation impacts them, identify hurdles to effective implementation, and uncover conflicting forces that influence human behavior throughout change.
Conclusion
To summarize, due to the quickly changing medical and social contexts, change is a typical occurrence in the healthcare sector. The digitization and computerization of nursing networks and systems is one of the advancements brought about by the digital age. Kurt Lewin’s three-stage paradigm, sometimes known as the structured model of organizational growth, is a foundational concept that is still widely accepted. The change framework should be widely used since it is used by a variety of healthcare professionals for a variety of medical goals. Individual traits and statistics of patients and workers, equipment and methods, and facility features are only a few of the variables that may be found in the input data. Medication mistakes are also a collection of factors connected to the theoretical framework.
Reference
Bozak, M. G. (2003). Using Lewin’s force field analysis in implementing a nursing information system. Computers, Informatics, Nursing: CIN, 21(2), 80–87. Web.
Dennison, R. D. (2007). A medication safety education program to reduce the risk of harm caused by medication errors. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 38(4), 176–184. Web.