Introduction
Poor leadership is known to destroy organizations’ credibility and may contribute to the company’s customers and stakeholders to move away. Mismanagement of the workforce can greatly affect the company’s working and environment and this definitely has an impact on the overall output.
Poor communication ways of a company affects the health of the workforce and this in turn affects employees’ commitment to the company’s vision.
Initial Analysis
Going by the ratings of the of the survey indicators, the company is facing serious management and leadership problems in its overall business operations in most of its branches across the three continents. Each country of operation has both a unique and a common problem that challenges its business operation and continuity.
These range from financial management, employee cutbacks, effective leadership, embracing new technology and workers development, culture clash to customer service. All the indicators are far below the national average and these damages the company’s reputation leaving the company to struggle to restore its reputation in the market and regain its market shares.
The survey indicators in comparison to other companies as well as the national standards were as in the table below.
From the survey indicators, it is clear that the overall trust in the company’s leadership and the way in which the leadership supports and demonstrates its understanding of the employees are far much below the employees’ expectations and also below what other employees from other organizations are getting from their leadership.
This implies that the employees do not feel valued by the company’s leadership and are less motivated to perform their duties. Development and training of the employees is poor and this affects their ability to work effectively and efficiently towards achieving the company’s vision and goals.
The leadership has not done much to enable them improve their technological and social skills which are very important in this business operation. This is because there is a disconnect between those in the company’s key leadership positions and the staff.
The forms of communication channels, structures and processes in the organization remain a barrier to effective communication across all the operating groups in the company. The monthly team briefings imply that not all team briefings are carried out. Besides, the quality of some of the communication is poor.
The company has a workforce which comprise of individuals from different cultures including the management team. They have English managers in the UK, American manager in the US, a Pakistani manager in India, an Indian department director among many other cultures. Although the diversity in culture is supposed to give the company an advantage, its diversity to some extent inhibits some operations in the company.
Organizational operations
The company’s organizational structure is centralized with the headquarters operating in London although sub headquarters are also in the countries of operations. There exists a director of the company’s operations in each country and each country branch has a specific departmental function.
The New York branch provides banking and insurance services; the Delhi branch supports customer service and is the company’s main call centre while the UK branches provide insurance and banking service as well as administrative functions to the company. However, management and leadership problems have rocked almost all the branches of operations.
UK
Stabilization of the business organization in the UK faces serious challenges and may be forced to close down its operations in some its branches in the country. The major challenges faced by the UK are how to improve its financial results, how to boost the morale of the staff and how to go about the uncertainties over job prospects. There are various reasons that can explain the problems experienced in the company.
First, there exist a clash of corporate cultures as well as operational styles between the former employees of the acquired banks and insurance companies and those of the company.
The company did not take into consideration the need to address the difference in company cultures that employees come with from their former organizations. Companies have unique systems of achieving their objectives and these needs to be properly integrated when these employees are incorporated in the company’s human resource.
Secondly, the second problem was as a result of the new IT technology that was introduced in the company two years ago that led to employee cutbacks as the company was also struggling to improve its financial output. The low satisfaction ratings especially on communication, strategic understanding, leadership and company culture are clear indication of how the management must have gone about employee lay offs.
Not much has been done to dispel fears among those who survived and to support those who were laid off. The communication on employee cutbacks did not address all thee employees’ expectations. Thus there are still remains uncertainties especially among employees concerning their future stay and job security in the company.
Besides, there are still uncertainties about the future of employees in company’s administrative offices in Bradford and Glasgow which are under review for closure. This is a major cause of employees’ low morale and motivation to perform optimally.
The employees are depressed by the announcement of the company’s announcement of potential redundancies and the divisional managers and supervisors have tried in vain to boost the employees’ morale to so as to ensure delivery of targets.
The UK top leadership team also experiences conflict of cultures. They embrace change without fully accepting the ideas of the change. This implies that they have not been enabled to accept these new programmes and ideas that are normally introduced in the company.
This also implies that decisions to adopt comprehensive programmes rest in the hands of senior managers only while the rest of the employees are supposed to embrace the ideas without much questions. This also implies that there exist differentiations among decision makers, programme users and implementers.
This in turn has caused the clashes between the sales director and the IT and finance director over their perception of command and rule. This situation is a clear indication of the bureaucratic rules regarding communication and procedures within the company’s branch in the country.
While the sales director favours a more flexible structures of operations and communication, the finance and the IT directors favours the bureaucratic structures which create red tapes to employees innovativeness as well as flow of information across all the operating groups.
USA
The US situation is a mix of management and leadership problems. The company’s debt levels have created serious dents in its performance and reputation in the financial markets. The attempts that have been made to rescue the company have not yielded much since the company still experiences declining revenues and loss of customers. The poor performance of the company has also contributed to the declining staff morale.
The declining staff morale has also been attributed by some compulsory redundancies in trying to salvage the business from the financial crisis that it is experiencing. Besides, the head of the business in the US demands loyalty from the staff and does not take perceived challenges positively. This implies that he is a barrier to employees’ innovativeness.
He makes decisions and expects everyone under him to embrace the idea as it is. However, it is obvious that the company’s overall manager in the US lacks the vision and the capacity to predict and analyse the anticipated outcome of some business activities which involve excessive risk-taking particularly lending services which has contributed to the business’ decline.
Besides, he does not accept new ideas and challenges to his authority easily and this seriously affects the staff’s motivation and morale to provide their best to the company. They feel les valued since their ideas can not be accommodated in the company’s business operations.
India
The company’s problems in its Delhi branches include personality and culture clashes, poor training and development and thus leading to overall low customer service and complaints from the customers. The volume of complains coming from a particular call centre has generated a lot of concerns. Apparently, the call centre is headed by an Indian UK born banker who helped establish the company’s operations in India.
Her role in the establishment of the company in India gives her good reputation at the headquarters in London. Seemingly, this might be the reason for their clash since she feels that she has more authority over her boss considering her past role and her relation with the head office. Secondly, employees in her department might not have been fully trained and enabled to accept and use the new technology.
The manager of the poor performing centre is a woman and as a woman, she concentrates more on her interest; which is to be liked by her staff, but not on the company’s interest. This implies that gender difference has an influence on the job performance since women’s negotiation skills are poor or limited.
Although the woman is aware of the complaints directed to her department about its performance, she does not initiate negotiations with her staff on the need to improve their performance. She would want to be the darling of her staff and therefore she feels that talking to her staff about their performance may not help become their favourite. She is therefore not as assertive as the other managers.
On the other hand, the Pakistani manager is not able to separate the problem from the Indian director. He confronts the woman but does very little to solve the problem, implying that he is not creative enough to provide solution options that help them generate mutual gain.
The problem has become worse since the Indian lady is not willing to compromise her stand hence worsening their interpersonal relationship making it difficult for them to collaborate in solving the problem.
Evaluating communicating channels
The ways of operations in most of the company’s branches is a clear indication of bureaucratic models communication and this remains a serious challenge to the company efforts to improve its financial services, boost the morale of the employees and achieve improved financial results.
There exist red tapes between the company’s top leadership, those in the management in the various levels of the organization and the other staff who deal directly with the customers.
The reason for the staff’s low morale in their various jobs is as a result of the poor communication of potential staff redundancies. The timing is poor and staff’s expectations are not fully addressed. The top leadership is not committed to having a face-to-face communication with the employees on some critical issues in the company branches.
This implies that there is no interpersonal touch between the staff and the management and this makes the staff feel that they have been excluded and disregarded.
The human resource managers do not communicate properly with the staff especially before and after the redundancy to address the uncertainties that exist among those who have survived so as to encourage and motivate them to work towards achieving the company’s vision.
Employees learn some important activities of the company through new letters, emails and through rumours. Such communication forms do not involve any interpersonal touch between the staff and management and have little positive influence on the workforce.
Applying communication solutions
It is important to understand that employees’ motivation is normally affected by interpersonal, intrapersonal and cultural communication factors. Therefore the company’s communication processes should comprise of carefully encoded statements and approaches that better help motivate the employees and remove barriers that exist between the employees and the leadership.
Addressing staff redundancy needs to involve a face-to-face communication between the management and the staff so that the staff feels included. Employees in an organization are always keen to know the company’s plan on the post redundancy period particularly concerning the support that would be given to those who will be laid off and the future of those who remain.
Those in the management and key leadership positions should involve a collaborative approach so as to collectively meet the needs of all employees in the company. They should cooperate among themselves and acknowledge the value of each person in the company. Some managers in the company and in particular, the head of operations in the US should be made to realise the need to accommodate ideas from the junior staffs.
He should also be ready to compromise his stand on some issues that affect the company. This would help integrate various creative ideas that may provide long term solutions to the company branch’s problems. The Indian lady manager and others also need to learn to be accommodative.
She should be accommodative and also ready to compromise her ambitions for the benefit of the company. This would help revitalize her relationship with her overall manager.
The company needs to assess the effectiveness of its communication. This would enable the company deliver messages which have clarity and most importantly deliver information which best match the medium of communication used in each case (Thomas and Kilman 2001, 4).
This means that the company has to undertake a survey to determine the employees’ communication preference so as to use medium which best communicates the message.
It is also important to apply an all-interactive channel of communication that helps interact with all the members of staff, the directors, the customers as well as other stakeholders. The communication model below shows an ideal all-interactive model of communication.
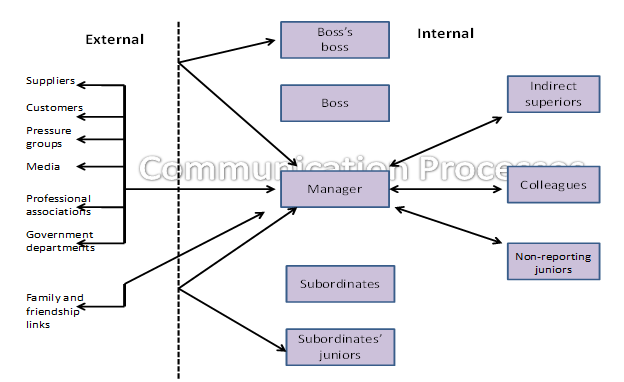
(Extracted from class lecture notes, 2010)
Recommendations
The company’s leadership has to learn to acknowledge its employees as a way of motivating them. It is also important to enable the target employees during a programme implementation especially anew to technology accept and use the new technology. This should also include those who would provide support systems to those who will use the programmes directly.
Learning outcomes
Poor management makes those in key leadership positions in the company to become less motivated to perform their duties efficiently and effectively (Ray 2002). This creates a poor working environment that may lead to interpersonal wars as well as petty disputes (Vazquez 2006, 5).
Continuity and prosperity of business organizations rely on effective and efficient leadership and management. Leadership skills are needed to ensure that the management is able to focus on anticipated crisis in business and be able to develop effective solutions to the problems.
Good management is important in managing the workforce and the company’s resources in order to realise the company’s vision. Therefore effective and efficient leadership have to apply proper communication ways and have to develop an understanding of the needs of the workforce as well as strategic understanding of the company.
It is also important to build the target employees abilities to use the programs as well as the employees’ acceptance of and involvement in the program. In this case building the targeted employees involve both those supposed to use the programme directly as well as those who would support the program since it is most likely that these groups at some point may overlap.
During the implementation process, the targeted employees should be made to be psychologically and behaviuorally prepared (Townsley 2005, 12). This implies that the organizational policies and structures also need to be able to support the program.
Indicators of leadership in the organization
The first one is the flexibility of the working environment to promote employees’ creativity without being incapacitated by the red tape. The sense of responsibility in the organization as well as the levels of standards set by employees in the organization is also key indicators of leadership in an organization (Pfeiffer 2010, 3).
Other important indicators of leadership include how clear the mission and values of the organization are to the employees and how accurate the performance feedbacks about the employees operations are. Finally, another key indicator of leadership is the level of commitment towards achieving the common goal of the organization.
Communication Review
As a result of such organizational activities as training, planning, and job specialization, there is no synchronized and coordinated promotion of the employees to suit various work shifts, departments, and locations. This implies that comprehensive programs meant to benefit the whole organization such as workforce motivation, improved services are not collective
The management team should understand factors that cause behavior change in their employees. It is therefore important not to underestimate the effect of the media on employees’ perception as well as their contributions to causes and solutions to problems in an organization. It is therefore important to involve communications with persuasive and at the same time assertive messages.
It is import to ensure message consistency particularly in its language, structure and theme; which gives room for employees’ improvement as well as motivation from the messages communicated to employees.
The purpose of highlighting certain words in a message should be aimed at suggesting the uniqueness of the message but should enable the intended audience the sophisticated aspects of the information which may include long-term attributes of the message (Gerrans, Smith and Whale 2009, 21).
Communication Crisis Management Plan
The company needs to set its change indicators to meet these targets in comparison to the other companies and the national averages. These indicators should be achieved within a period of two to three years if the company makes important and effective changes to its leadership and management approach.
The company has to develop better communication ways that would enable it put damage control measures on its reputation, financial safety and employee turnover as well as employee’s job satisfaction and optimum output for the company. The company needs to reorganize and restructure its leadership so as to build a working environment of trust among staffs and the leadership.
This would also enable reforming of mindsets so as to overcome personality and cultural clashes that have been experienced in the company’s branches in India, the US and the UK. Since human resource is the key driving force to the company’s prosperity, it is important to make, quick, wise and bold steps that would enable the company effect change in its operations and overcome its problems.
The company needs to learn from its current and past crisis to effectively effect changes that would help it overcome its leadership and management problems. It should adapt to communication ways that motivate the employees. This would help organization attract its customers.
Considering that the managers and other employees are from diverse cultural backgrounds, it is therefore important to incorporate language in the company’s mission statement and its core values. It is also important to include language in its mission statement.
This would enable integration of different cultures in the organization so as to develop a common organizational culture that would benefit the organization and the staff working in the company. The company should adopt communication ways that consider the communication environment and is able to foster the organization’s cultural growth and development.
It is also important to create leadership networks which comprise of employees who can act as the company’s ambassadors. This involves training employees on leadership as well as presentation skills so as to represent the company in the various company functional departments.
It is also important to develop affinity group programmes and clubs for specific operating groups so as to leverage communication channels; both formal and informal channels aimed at promoting social networks (DiCioccio, Rubin and Westmyer 1998, 16).
The company also needs to create marketing and communication plans that enable it leverage its communication channels and also enables the organizations target audience receive the organization’s important messages on its services and other programs as well as its current activities.
The organization’s management needs to be transparent with information to all the functional groups in the company. This will motivate employees to perform better.
Human resource managers have to quell the fears about employees’ concerns. The managers have to set directions, motivate and engage employees in the company’s operations.
The managers need to ensure frequent communication with the employees so as to ensure that employees work towards achieving a common goal (Anderson and Weltz 1989, 313). Managers also need to explain the new rules and policy guidelines and more importantly, help connect the employees with the leadership in the organization.
The management should be honest and transparent to the employees and communicate to them about what the company’s is going through (Fisher, Rayner and Belgard 1995, 26). This would enable employees reduce uncertainties and even turnover intentions since the employees become mentally prepared on a potential employee cutbacks (Pfeiffer 2010, 3).
They are also able to understand how the layoff is bound to affect their lives. Employees also get to understand the procedures that the company will apply in effecting layoffs. Managers and leaders in the organization have to support the employees’ transition and retention. It is also important for managers to move from using the word “it” or “they “and move to using the word “we” (Bryan, Laura, and Megan 2008, 4).
Conclusion
The leadership and management crisis in this company calls for the top management and the directors of the company to carefully re-examine its human resource and adjust its internal organization so as to enable its workforce to effectively respond to the company’s vision.
Effective management and leadership that ensures healthy communication ways would enable employees in the company acquire a shared belief and a common organizational culture that would create collective capabilities to execute their roles so as to successful achieve the company’s goals.
An all interactive communication model in the company would motivate and boost the morale of the employees and would enable them understand their value to the company. This would revitalize their commitment to the company and the need for optimum output.
Reference List
Anderson, E. and Weltz, B., 1989, Determinants of continuity in conventional industrial channel dyads. Marketing science, Vol. 8, No. 4. New York: Institute of Management Science. p. 313.
Bryan J. W, Laura A. L, and Megan A. L., 2008, Using organization theory to understand the determinants of effective implementation of worksite health promotion programs. London: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, p. 6.
DiCioccio, R. L, Rubin, R. B, and Westmyer,S. A 1998, Appropriateness and effectiveness of communication channels in competent interpersonal communication. Journal of Communication, Vol. 48. P. 16
Fisher, K., Rayner, S., Belgard, W., (1995). Tips for teams: A ready reference for solving common team problems. New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc. p 26.
Gerrans, P., Smith, M, and Whale, J., 2009, Communicating with superannuation fund members in good and bad times. Joondalup: The Australian Institute of Superannuation Trustees
Pfeiffer, G. J., 2010, Questions and answers with George Pfeiffer, MSE, FAWP. Washington, D. C.: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Washington, D.C. Medical Wellness Advisors. p. 3
Ray, C., 2002, Effects of poor management. New York: Helium Inc.
Thomas, K. W, and Kilman, R. H, 2001, Thomas-Kilmann conflict mode instrument. Consulting Psychologist Press, Inc. p.9
Townsley, C., 2005, Resolving conflict in work teams. Huddleston: R.V. Armstrong Associates, p. 12
Vazquez, L., 2006, How bad leadership spoils good planning. New York: Urban Insight, Inc. p. 5