Introduction
The ISO 31000 is a set of standards that govern the implementation of the process of risk management across different organizational functions, projects, and other activities (Broadleaf Capital International, n.d.). Accordingly, these standards are designed to offer the best practices and guidelines to all activities related to risk management in an organization.
Here, the ISO 31000 standards guide the process of developing and sustaining different frameworks related to risk management as shown in figure 1 below. In figure 1, it is worth noting that the process of developing and sustaining a good risk management framework involves five major steps whose objectives include:
- Emphasis on continuous process improvement,
- Provision of comprehensive and acceptable standards of responsibility relative to risks, risk treatment duties, and risk controls,
- Alignment of all decision making processes to adequate consideration of the risks involved and application of the process of risk management within all organizational operations,
- Continuous communication within and without the organization,
- Continuous reporting of risks and the risk management tasks enacted, and
- Making risk management the center of all organizational management processes.
Figure 1
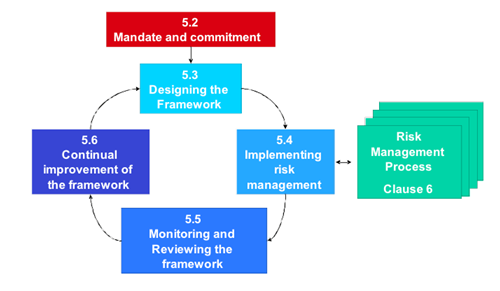
Source: (Broadleaf Capital International, n.d.).
Furthermore, the steps illustrated in figure 1 above play a pivotal role in the development and sustainability of a risk management framework such as the one described in figure 2 below.
Figure 2
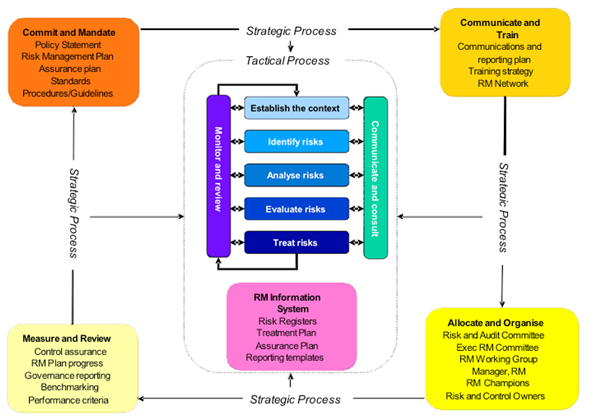
Source: (Broadleaf Capital International, n.d.).
Thus, the ISO 31000 standards provide different organizations with a practical framework in the examination of all the existing approaches required to develop and sustain a healthy risk management process (Broadleaf Capital International, n.d.).
As a result, this essay reviews the risk management methodology employed by AGL Energy. Additionally, the essay looks at how the process of risk management in AGL Energy is aligned to the ISO 31000 standards.
AGL Energy’s Risk Management Methodology
AGL Energy is a leading organization in the operation and development of renewable energy products such as hydro, wind, solar, geothermal, biomass, and landfill gases (AGL Energy Limited, 2011). In this line of business, AGL views risks as part of the internal and external functions of the organization, and thus it is committed to effective management of risks across all operating business environments.
Relative to ISO 31000 standards, risk management in AGL Energy is an inherent function of the management processes (AGL Energy Risk Policy, 2010). Consequently, the organization has developed an effective, fully structured, and consistent policy that describes the objectives and responsibilities of the management processes regarding risk management.
AGL Energy’s policy statement states that the organization is committed to entrenching effective risk management practices into all organizational functions, processes, and operations (AGL Energy Limited, 2011). This policy ensures that consistency, effectiveness, and accountability are maintained in decision making and management practices.
Therefore, the risk management policy within AGL Energy aims at promoting and integrating risk management in all business strategies, insurance, specialist risk functions, and general governance processes (AGL Energy Risk Policy, 2010). Additionally, the policy ensures consistent and transparent assessment and management practices across the organization.
Moreover, the policy recognizes the contribution of external factors and uncertainties in all business strategies and operations.
Finally, the policy enables the organization to take note that timely, effective, and accurate communication, review, reporting, and monitoring of risks entail timely warning mechanisms, provision of assurance to stakeholders, and provision of a sound platform for organizational growth (AGL Energy Risk Policy, 2010).
Furthermore, AGL Energy’s risk management policy sets out the responsibilities of the AGL Board, the Audit and Risk management Committees, the Group Audits, the Group Risk & Compliance Operations, the Management, and the Employees.
Here, the risk management policy sets out the risk management requirements, which include defining the accountabilities of all areas of business in risk management, developing and maintaining risk registers, regular review of risk registers, and conducting regular risk identification, risk assessment, and risk profiling processes.
As a result, AGL Energy’s risk management policy offers an effective framework, which guides organizational risk management relative to the provisions of ISO 31000.
Conclusion
This essay reviews the methodology employed by AGL Energy in the process of managing risks within its business operations. In addition, the essay looks at how the process of risk management in AGL is aligned to the ISO 31000 standards. From the discussions above, it is evident that risks form an integral part of all operations, functions, and processes carried out by different organizations.
As a result, there is the paramount need for these organizations to recognize the need to integrate the process of risk management into their internal and external operations. Moreover, the process of managing risks should be timely, regular, effective, and consistent with the ISO 31000 standards.
References
AGL Energy Limited. (2011). Company overview Web.
AGL Energy Risk Policy. (2010). Risk management policy. AGL Energy Limited Web.
Broadleaf Capital International. (n.d.). ISO 31000: strategic, enterprise and project risk management Web.