Introduction
The Glo-bus company has applied strategic business principles in all its levels of performance. This has played an imperative role in placing it in the position it currently holds in the camera business arena. Its managers at different stages of operation apply explicit managerial skills in association with ethical guidance in order to realize organizational goals and objectives. For this reason, the company is stabilized as far as return on investment is concerned.
This paper is meant to give a comprehensive discussion on ways in which the Glo-bus team made good use of the strategy principles to facilitate organizational growth exhibited by the company. The paper contains subtopics that will further explain the significance of the applied strategy principles in decision making and duty execution. Also included in the paper are addendum pages meant to provide vivid company data that represent company progress in terms of profits, growth, return on investment and many others.
Strategic plan
The company’s data, as indicated in the financial, marketing, production and planning information, are proof that it exists in times of great uncertainty. This is a situation that calls for unequivocal strategic planning that is very different to a linear, bureaucratic process. It, however, demands for a more target-instigated approach that is both innovative and comprehensive.
The purchase trends of both the multi-featured and entry-level cameras indicate that the products have a wide market amongst the youth. This is perhaps because of the fact that most youths would want to make some events in their lives memorable by storing pictures of the events.
The important realization that the youths are the biggest customers for this company forms the foundation of the strategic plan for this company. It strategizes to market its products on various media stations that are widely perceived as youthful in order to increase its sales and make profits for both its customers and shareholders. That notwithstanding, most of the burners aimed at marketing both the multi-featured and entry-level cameras are meant to be placed at areas that are most visited by the youth.
Such areas include shopping malls, movie outlets, shows and some parts of the streets like shopping centers. This strategy is projected to increase the levels of purchases by a considerable margin. The fact that the marketing strategies for both the multi-featured and entry-level cameras are similar puts the company in a favorable position to harness its resources and capture a wider market for its products.
Product and market strategy
Since the company’s sole objective is to increase its sales and market share, its management has formulated some strategies that are meant to spearhead its quest to capture a wider market. The company is targeting multi-store chains, online retailers and local camera shops to serve as its intermediary to reach clients. This is done with assistance from extensive marketing backed by explicit marketing skills of its managers. Additionally, technical support also plays an imperative role in the capturing of the projected markets.
The above mentioned strategies are aimed at capturing the markets of North America, Europe, Africa, the Latin America and Asia. The company has since come up with the projected retail demands of all the retail shops in the mentioned regions. It has also evaluated the units left in the retailer inventories and their projected orders. This is important in determining the next market places for the products offered by this company.
Production strategy
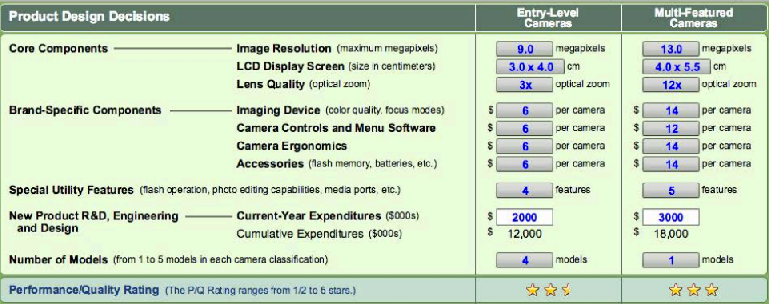
The company’s production strategies for both the multi-featured and entry-level cameras are aimed at providing the market with quality products that meet the unique preferences of clients and that conform to the projected budgets of expected clients. The production costs for both the multi-featured and entry-level cameras vary due to the variations in the quality, number and sizes of their components.
The production cost for multi-featured cameras is a little higher as compared to the production cost for entry-level cameras. This is an implication that multi-featured cameras are more expensive to purchase than entry-level cameras.
After a close monitoring of the viability of some in-house production units, the company has since outsourced some services that are not economically productive when done within the premises. However, there have been other services that are better produced within instead of being outsourced. This is a move for quality assurance as well as reduction of company expenses. These are decisions made after realizing how cheap or expensive it would be to outsource of locally produce some products and services.
The company intends to produce multi-featured cameras with an image resolution of 13.0 megapixels and entry-level cameras with an image resolution of 9.0 megapixels. The lens qualities of the two cameras are also expected to vary with multi-featured cameras having 12x while entry-level cameras having 3x optical zoom.
Other brand specific components like image devices, menu software, camera controls, camera ergonomics and accessories are also expected to differ with multi-featured cameras having advanced or more components and accessories as compared to entry-level cameras. Their special utility features are also supposed to vary considerably in the two cameras. All these are meant to meet every unique need of clients.
Compensation and labor strategy
It is important to note that employee motivation is the key to organizational success. Frustrated employees are bound to offer substandard services as a move against frustration and poor working environments. For this reason, the company has put in place compressive compensation plans for the sole purpose of employee motivation.
For instance, is has incentive bonus for employees. This is aimed at reducing the warranty claims. The company has also established other benefit packages for its employees in order to guarantee their full dedication to meeting organizational objectives.
In addition to compensation, the company has also put in place measures to stabilize its labor costs and other expenses related to labor like wages, employee training, bonuses and fringes. The company seems to be achieving its expected profit margins in relation to its production, market share, competition and other factors. This is the reason for the maintenance of the labor costs that aims at retaining the company’s expenses and income.
Corporate citizenship strategy
This is one of the most important parts of the company’s overall strategies. This is because it is the part that aims at making the company more acceptable and liked by the public through incorporating the special needs of the public into company’s strategic plans. It is only through this that the organization is able to create new and retain its existing customers. Additionally, this strategy ensures that employee-customer and product-customer relationships are ethical and acceptable.
Clients will only want to associate themselves with companies that look into their special demands in addition to transacting business with them. For this reason, the Glo-bus Company has put in place a few corporate citizenship strategies that aim at enhancing the relationship it has with its customers and the public at large.
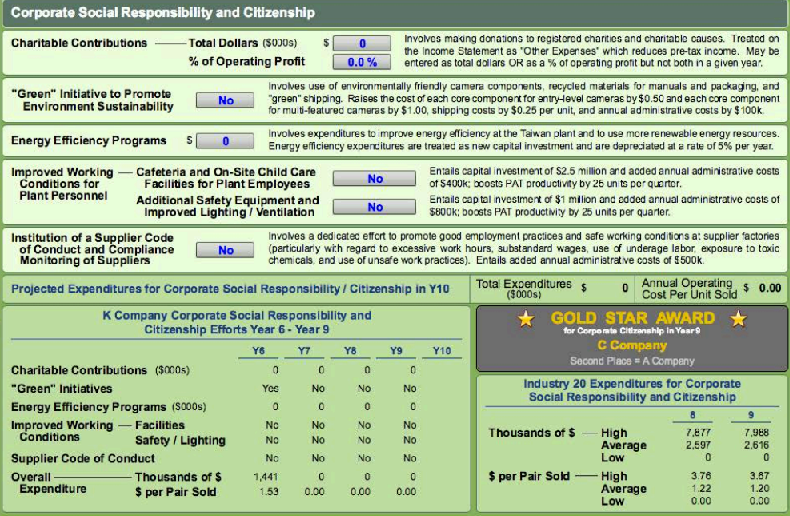
For instance, the company contributes to charities in a bid to woe more support from the public. This is a charge treated on its income statement. In addition to helping the public, this strategy plays an imperative role in reducing the pre-tax income of the company.
The company also engages in the “green” initiative to assist in the fight for environmental sustainability. This too is aimed at ensuring that the unique customer needs of environmental friendliness are met by the company. The company does this by the application of absolutely environmentally friendly components of the cameras sold by it. It also engages in the recycling of most of its packaging materials and ‘green’ shipping of its finished goods.
Another important strategy that is meant to improve the wellbeing of both the company’s clients and employees is the application of energy-efficient programs. The company endeavors to use more energy-efficient and renewable sources of energy in its productions. This is treated by the company as new capital investment. In addition to that, the company has also invested a lot in improving the actual working conditions for its employees.
This has been done through establishing a cafeteria and child care outlets for its employees. It has also invested in safe equipments for its employees. All these are aimed at enhancing the faith locals have on the company in order to boost business relationships. The company, on the other hand, stands a chance of gaining a lot from the strategies as projected in the picture below.
Financial strategy
The financial strategies for the company revolve around the settling of outstanding loans, equity to shareholders and the projected purchase and sales of company shares. The company aims at reducing its credits tremendously. Additionally, it allows for an estimated 5000 shares to be sold this year with a maximum of 825 shares to be retired. That notwithstanding, the company has tried to improve the projected earnings per share of its shareholders as a move to escalate and stabilize its profit margins.
These strategies conform to the overall strategic plans. This is because they are aimed at increasing the profitability realized by both the clients and shareholders of the company. The increased number of shares to be sold by the end of this year not only adds revenue to the company but also serves as a marketing strategy. The youths that buy shares with the company initiate a business relationship whereby they not only become shareholders but also loyal customers to the company.
Competition
Despite the fact that the company has maneuvered the setbacks associated with fluctuating demands and counterfeit products in the market, the competition is still stiff and stunning. Amongst every other competitor that shares the market with Glo-bus Company, Sony still remains the biggest threat.
It is astonishing how Sony is still the company to beat in terms of market capture after so many years of stiff competition. Even though this is true, our company’s strategies are closing in on Sony and it is undoubtedly true that the margin has reduced significantly.
An explicit evaluation of the market has revealed that Sony enjoys an outstanding loyalty from customers across the globe. This may be driven by the fact that it was one of the earliest in the market of such products. Additionally, the loyalty amongst customers may also be brought about by the fact that people have had a notion that Sony products are the only legitimate electronics and that others are mere counterfeits. Even though this notion is gradually changing after people have tried other products, there is still a lot to be done.
Glo-bus company has countered the competition from Sony by coming up with superior quality cameras in both models (multi-featured and entry-level cameras). This is because all the two models produced by the company face the same competition. Their prices are also favorable as opposed to Sony products that take advantage of their popularity to hike their prices. As the margin between these two companies continue to reduce, it is certain that the difference will soon be negligible.
Strategy evaluation
For a long time, Glo-bus Company had been operation without comprehensive employee compensation plans and overtime allowances. This was done during its early years of inception. Even though duties were carried out well by employees, it was noted that they were not giving their best to the company. This then brought about the incorporation of employee compensation plans and allowances in the company’s strategies. Just as projected, this strategy bore unimaginable fruits.
Employee compensation and allowances motivated the workers to not only meet organizational goals but also exceed the projections of managers. After the inception of this strategy, employees would then work long overtime hours hence yielding a lot for the company. Therefore, it was not only the company that benefited from this. Employees benefited too. The results of these changes were absolutely positive since they played an important part in improving the productivity and enhancing the image of the company.
Our strategy for the next two years is based on ethical and social responsibilities to our clients and the public at large. Despite the fact that there are already underway projects to this effect, the company is not stopping at that. We are intending to establish a close and mutually beneficial relationship with the clients and other members of the public.
This is not only a move to show the company’s ethical and social responsibility to the public but also a marketing strategy. It is undoubtedly true that more people will get to know about the company through this and will hence want to do business with us.
Conclusion
In conclusion, therefore, Glo-bus Company is doing fairly well as far as the achievement of goals and objectives is concerned. The company has managed to maintain a high range of both client and stakeholder satisfaction amidst the stiff competition from other related companies. It has maintained high quality products in the wave of counterfeit cameras that have affected the market prices tremendously.
In some occasions, however, the company was compelled to vary its prices considerably as a move to provide favorable market prices for its products after sales were affected by the corrupted market of counterfeit products. It is a result of explicit managerial skills of the top managers of the company that it has maneuvered all the tribulations and tides of setbacks. We can note, therefore, that Glo-bus company will withstand may other future setbacks and competition.
Lessons learned
There are quite a number of lessons learnt from the strategy principles applied in this company. For instance, the competition offers a lot to learn form. We have since noted that it is important to establish the strategies used by competitors in order to come up with own viable strategies. We have also learnt that the success of a business organization is entirely dependent on absolute satisfaction on both the clients and shareholders of the company.
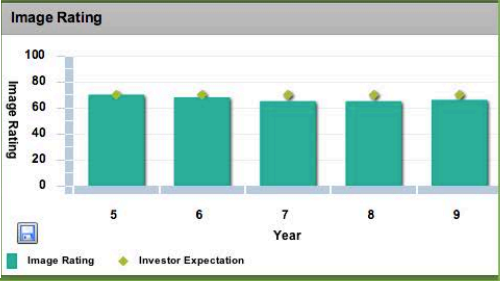
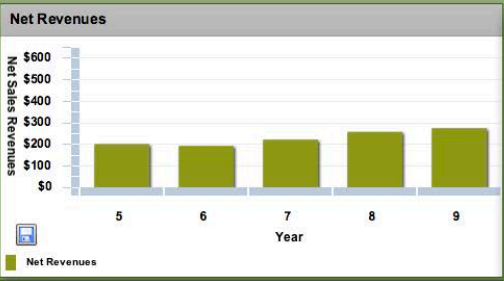
Performance results graphs
The following are performance graphs that represent net revenues, earnings per share, return on equity, stock process, credit rating and image rating of Glo-bus Company for the last five years.
Net revenues
Earnings per share
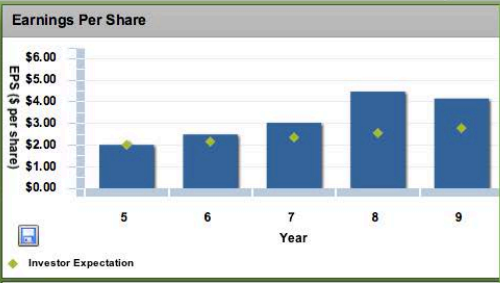
Return on equity
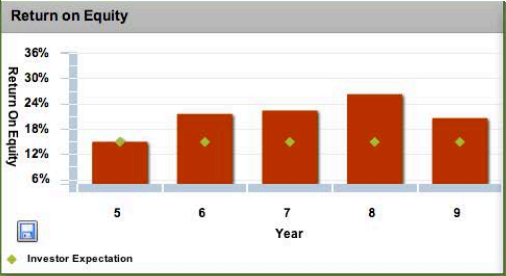
Stock price
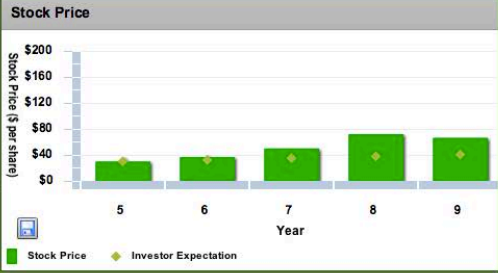
Credit rating
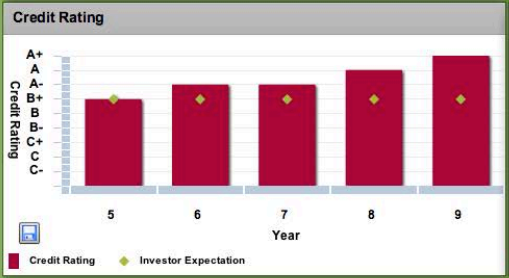
Image rating