Introduction
Online shopping is increasingly gaining currency among customers, not only in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) but also globally. As demonstrated in the literature, the application of technology-based online services has achieved tremendous growth in recent years due to the wide penetration of the Internet and its capacity as a channel of information and commerce (Behjati & Othaman, 2012).
A survey conducted in 2010 by MasterCard Worldwide showed that the proportion of customers in the UAE using web-based channels to conduct their shopping had increased from 29% in 2009 to 42% in 2010 (Middle East Company News, 2011).
There are several convergent factors that impact consumer buying behavior for individuals to either shop online or continue resisting this type of buying. In an attempt to identify these factors, the present study uses a mixed-methods methodology to show the importance of online shopping and how this concept has changed consumer habits on shopping in the UAE.
Literature Review
Available literature demonstrates that customers with tight work-related schedules cite convenience as their main reason for switching from traditional shopping to online shopping (Kapur, 2012). At the click of the mouse, these customers can use the Internet to make online purchases and then have the goods delivered at their doorstep.
Findings from a recent MasterCard survey on online shopping demonstrates a surge in customers who now prefer to shop online in UAE, with the growth being led by individuals within the age group of 25-44 years (Middle East Company News, 2011). The age factor demonstrates that within the general population, working customers are more likely to do online shopping than unemployed people.
As demonstrated by Behjati & Othaman (2012), “the perceived reliability and notion of trust on the Internet is the basis for customer involvement in online shopping” (p. 306-307). Other customers have cited cost savings, cost control, and time savings as the basis for their involvement in online shopping (Kapur, 2012). However, according to this particular author, some customers who would like to use online shopping desist from doing so due to complaints that online products are priced higher than what big retail outlets offer.
Extant literature demonstrates that “the UAE is fast emerging as the most attractive retail destination worldwide on its concrete fundamentals of a strong economy, growing the middle-class population, surging consumer confidence, and increasing domestic consumption” (RNCOS, 2011 para. 1). These fundamentals have been cited in Behjati & Othaman (2012) as the main drivers of online shopping. Hence it is expected that more UAE consumers will switch from traditional shopping to online platforms.
Data
A mixed method (quantitative and qualitative) was used to collect primary data to show the importance of online shopping and how this concept has changed consumer habits on shopping within the UAE context.
In the quantitative paradigm, a survey instrument was used to collect data on 29 participants. Data analysis using the SPSS computer program shows that almost two-thirds (65.5%) of the participants are female and 20(69%) are students, while the rest work in various occupations. 9(31%) of the participants earn a monthly income of between 1000 and 5000, 12 (41%) have an income of between 5001 and 10000, and 8(27.6%) earn an income of over 10000.
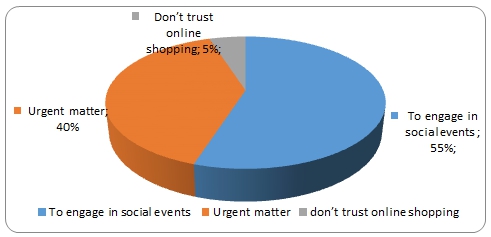
8 (27.6%) of the participants say they prefer physical shopping, 7(24.1%) prefer online shopping, and 14(48.3%) prefer both forms of shopping. The figure below shows the reasons why participants prefer to do physical shopping (data values include participants who say they prefer both shopping styles).
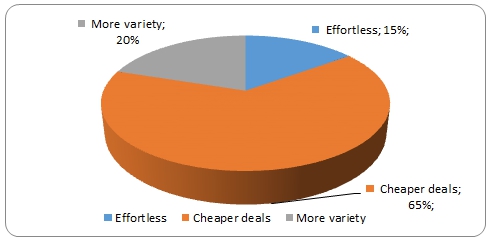
The next figure demonstrates why participants prefer to do online shopping (data values include participants who say they prefer both shopping styles)
It is insightful to note that only 11(37.9%) of participants sampled in the study posses a credit card. When asked their preferred payment method, 2(6/9%) of the participants say they prefer to pay via credit card, 9(31%) prefer online banking service, and 18(62.1%) prefer cash on delivery service.
In the qualitative paradigm, the researcher interviewed one participant about their preference for online and physical shopping, and if they thought online shopping would overcome physical shopping. The participant said that busy schedule, ease of finding products online, home delivery, and availability of many online shops were the main reasons for preferring online shopping over physical shopping.
In the second item, the participant said online shopping would take time to overcome physical shopping due to its limitation in socializing and lack of capacity to know what items best suit an individual before making a purchase.
Analysis
The findings of this study reinforce previous studies that found more consumers are switching from traditional shopping to online shopping due to convenience and cost considerations.
Behjati & Othaman (2010) cited perceived reliability and notion of trust as the main reasons for customer involvement in online shopping, while Kapur (2012) cited cost savings, cost control, time and energy savings as the main driving force for consumers’ involvement. However, this study comes up with other motivating factors for online shopping in terms of effortless shopping and the capacity for online platforms to provide more variety.
Previous research conducted by MasterCard Worldwide showed an increasing number of consumers using online channels to do their shopping in the UAE (Middle East Company News, 200). This finding has been reinforced by this study because, cumulatively, seven in ten people prefer to do online shopping or can comfortably mix online shopping with physical shopping.
Additionally, this study demonstrates that customers are increasingly trusting online shopping as only a small proportion of participants say they prefer physical shopping due to lack of trust in online shopping. These observations show online shopping has become an important facet in consumers’ life within the UAE context. The notion of trusting online channels to do shopping demonstrates a shift in consumer behavior.
An important finding in this study is that a sizeable number of consumers prefer to use physical shopping due to the capacity it provides in enabling individuals to socialize (e.g., engaging in social events, dining in restaurants as they shop, etc.).
This finding has not been assessed in previous studies and therefore, requires online shopping marketers to come up with strategies and approaches that will enhance consumer experience as individuals shop online. The lack of satisfying consumer shopping experience may be the reason why some people feel that online shopping will take some time to surmount physical shopping.
Conclusion
This study shows that online shopping is increasingly becoming popular in UAE and that it has changed consumer behaviors owing to factors such as increased trust in online buying, effortless buying, looking out for cheaper deals, and facilitating choice.
However, as the findings demonstrate, more research needs to be done to change customer perceptions on the use of credit cards to pay for products as most customers still prefer to pay using the cash-on-delivery approach. Increased uptake of electronic payment methods is fundamental in enabling a successful takeoff of online shopping. Additionally, more research needs to be done to ensure customers who prefer to do online shopping receive satisfaction from experience.
References
Behjati, S., & Othaman, S.N. (2012). What drives consumers’ online shopping? Conceptual review of online shopping attributes investigated in previous studies. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(12), 297-311. Web.
Kapur, S. (2012). Moms beat the heat with online grocery shopping.
Middle East Company News. (2011). MasterCard survey reveals jump in online shopping in the UAE in 2010. Web.
RNCOS. (2011). Online retailing driving the UAE retail Industry [Press release].