Holmes and Barsness focus on the problems related to the coronary artery disease and how it affects the human body. Moreover, the authors provide detailed information regarding the treatment and innovations in the sphere of diagnosis. Crowley offers insights concerning pathology and changes in the organism because of the disease.
Buja and Butany in their work Cardiovascular pathology examine the normal physiology and how it alters because of the coronary artery disease. They provide the reader with statistics and facts. Burke and Tavora are centered on describing pathology on cellular and organ levels because of coronary artery disease.
Methodology
In order to get deeper involved in the topic. The qualitative method of research is essential to be taken into consideration. To conduct appropriate research, the literature analysis seems to be the most suitable method to meet the fundamental objectives of the paper.
Pictures
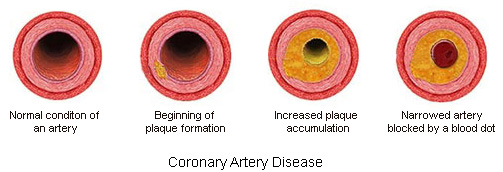
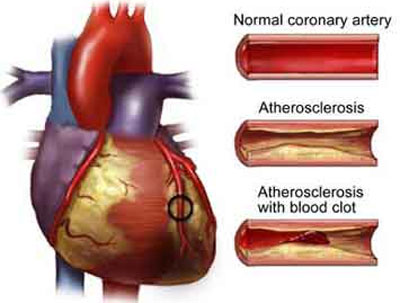
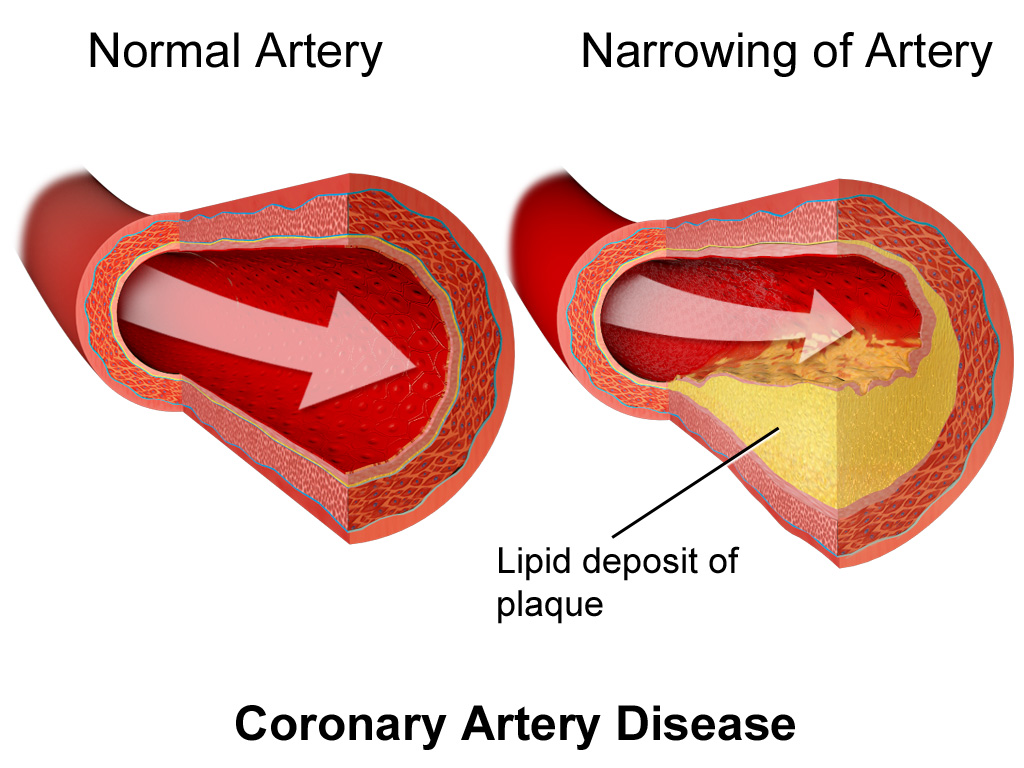
Risk Factors
The development of CAD may be spurred by a variety of factors. The key ones include hypertension, diabetes, obesity and, therefore, unhealthy diet, smoking, lack of physical activity, etc. (Rao et al., 2015).
As a rule, the approaches to treating the subject matter can be categorized based on the invasiveness level. For instance, there is a bypass surgery, which implies the maximum invasiveness, the minimally invasive treatment (i.e., stenting, coronary balloon angioplasty, and MICS CABG), and therapy. Although each of the three approaches mentioned above have their pros and cons, the surgery can be viewed as the most common and the most efficient tool in managing CAD.
Treatment Methods
Bypass Surgery
The beating heart surgery means that the process occurs while the heart is functioning under normal circumstances. The arrested heart surgery takes place after the heart is stopped. The artery is planted through the incision in the patient’s chest.
Minimally Invasive Treatment
MICS CABG presupposes making a small incision on the rib as opposed to a large one on the chest. In stenting, a stent is inserted into the artery to boost the bloodstream. Coronary balloon angioplasty helps make the artery wider to enhance the blood flow.
Outcomes
In the best-case scenario, the interventions mentioned above will cause a rapid drop in mortality rates and a rise in recovery rates among patients. As a study carried out by Rao et al. (2015) shows, in case of a timely provision of the corresponding healthcare measures, the patients are likely to face no further CVD issues. In other words, the substitute that they are provided with during the surgery, as well as the changes occurring to the artery after the therapy, is bound to affect the patient’s health positively.
Pathology at Cellular, Organ, and Systemic Levels
Cells are the basic structural and functional elements of the tissues, organs and body as a whole. For the performance of its functions, cells support its own homeostasis, exercise metabolism and energy implementing the genetic information; transmit this information to offspring directly or indirectly. First and foremost, it should be stressed that the cell can function on four different levels, namely the following ones:
- Normal level of functioning, homeostasis;
- The cell adjusts to the life in changing conditions, adaptation;
- The cell can die in case its adaptation conditions were exceeded, necrosis;
- In addition, the cell can die because of apoptosis (Burke & Tavora, 2011).
The coronary artery disease is characterized with the mismatch between the amount of oxygen and nutrients needed for cells and the delivery of these components by coronary arteries. It consequently leads to the not appropriate functioning of the heart that can result in myocardial infarction or can be lethal for the patient. In the last case, the process occurs with an impressive speed and cells of the heart muscles do not have enough time to go through all the stages of ischemia and necrosis (Burke & Tavora, 2011). However, it should be stressed that the disease affects not only the functioning of the cells but the work of the organs as well. As a matter of fact, in the vast majority of health problems related to the heart caused by pathologies, the primary issue is poor circulation (Crowley, 2010). It consequently leads to the decrease of blood flow in the aorta. The problem is also related to the venous blood stagnation in a number of organs (Holmes & Barsness, 2012). The stagnation influences the way the organs function causing pathology. The cardiac insufficiency leads to an increase in circulating blood; however, the blood velocity occurs too slowly (Buja & Butany, 2016). This process can occur suddenly or be chronic. Coronary artery disease is a pathological phenomenon that characterized by cessation or decrease in the intensity of coronary blood flow that leads to the acute oxygen starvation of the brain as well as deficiency of essential nutrients (Crowley, 2010).
Homeostasis
It is worth highlighting that homeostasis is possible due to the function of organ systems. In order to get deeper involved in the issue, the definition of the word should be taken into consideration. Homeostasis is a set of coordinated reactions that ensure the maintenance or restoration of the internal environment of the body. The human body adapts to ever-changing environmental conditions; however, the internal environment remains constant, and its rates vary within very narrow limits. Therefore, a person can live in a variety of environments. Some physiological parameters are adjusted delicately and carefully, for example, body temperature, blood pressure, glucose, gases, salts of calcium ions in the blood acid-base balance, blood volume, its osmotic pressure, appetite, and other (Buja & Butany, 2016).
There are two main systems that the brain uses to maintain homeostasis, among them are the following ones, namely the autonomic and endocrine. The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is focused on maintaining a constant internal environment of the organism, which is carried out by changing the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system. It is controlled by the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus is controlled by the cerebral cortex (Buja & Butany, 2016). The endocrine system controls the function of all organs and systems by hormones. Moreover, the endocrine system is controlled by the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The cardiovascular system is vital for homeostasis and provides constant circulation of blood in a closed system of blood vessels. Blood carries to the cells substrates, which are required for their normal operation and evacuate their waste products. These substances go through the capillaries in the interstitial (extracellular) fluid.
The cardiovascular system, along with the nervous and endocrine systems, combines the activity of individual organs and organ systems in the entire organism. There are a lot of functions that the cardiovascular system performs, namely the transportation of metabolic waste products to the kidneys, lungs, and skin; gases transportation from the lungs to the tissues and vice versa, the transfer of thermal energy delivery to the tissue and organs of protective substances and hormones. The life is possible due to the work of heart that every second provides cells with nutrients and oxygen getting rid of unnecessary and harmful products of metabolism (Holmes & Barsness, 2012). The most common cause of death because of diseases of the heart and blood vessels is considered to be coronary insufficiency. It can be explained based on the fact that the heart and the blood vessels are damaged equally. This phenomenon is called sudden cardiac death. All the symptoms of this disease are complex, but the main and most important is believed to be angina pectoris.
The Altering of Normal Physiology in the Pathological Condition
A healthy body is able to resist disease, recover, and compensate the damages or stress, but when the organism is experiencing the disease, this ability is absent. In order for the human body to maintain the internal environment, the cardiovascular system should function appropriately. The cardiovascular system is an important transportation center. In case, the system does not function appropriately there is a risk that homeostasis will be affected as well.
In the pathological condition, the normal physiology is altered. The coronary blood flow of a healthy person is about 250 ml per minute. However, because of pathology, the intensity of coronary blood flow can increase in 15-20 times. With the development of the destructive process in the vascular wall, the blood flow slows down; blood vessels lose their elasticity, the ability to respond to the load. Coagulation homeostasis becomes activated.
References
Buja, L., & Butany, J. (2016). Cardiovascular pathology. Waltham, MA: Academic Press.
Burke, A., & Tavora, F. (2011). Practical cardiovascular pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Crowley, L. (2010). An introduction to human disease: Pathology and pathophysiology correlations. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett.
Holmes, D., & Barsness, G. (2012). Coronary Artery Disease: New approaches without traditional revascularization. Rochester, MN: Springer Verlag London.
Rao, M., Xavier, D., Devi, P., Sigamani, A., Faruqui, A.,… & Pais, P. (2015). Prevalence, treatments and outcomes of coronary artery disease in Indians: A systematic review. Indian Heart Journal, 30(15), 1-9.