Introduction
In the business context, the cultural differences experienced by international companies arise as a result of two main reasons. These relate to differences in corporate culture and national culture (Jackson & Schuler, 2001, p.131). According to Schuler, Jackson and Luo (2004, p.120), national culture affects operation of multinational companies in a number of ways.
On the other hand, cultural issues between organizations occur as a result of the difference in the corporate culture that a particular organization has developed. Corporate culture differences between organisations are evidenced by the diverse norms, beliefs, values and attitudes adopted by organizations (Dwivedi, 1995, p.9). Additionally, culture clash between organizations may arise from the difference in treatment of employees, decision making procedures and what each organization values (Carleton & Lineberry, 2004, p. 13). Additionally, difference in corporate culture between organizations may arise from difference in opinion regarding how the organization will implement its business strategies ( Erdogan, Liden & Kraimer, 2006, p.309). Other issues that lead into difference in corporate culture relate to differences in company mission, vision and philosophies (Carleton & Lineberry, 2004, p.13).
Cultural differences may result into failure of the firm undertaking the acquisition attaining the desired synergy. Existence of cultural difference in the new entity formed through mergers and acquisitions result into a high employee turnover. Additionally, it also results into a decline in the employees’ productivity with an approximate margin of 15% ( Gitelson, Bing & Laroche, 2000, p. 1).
This mainly occurs amongst the key executives. Cultural differences also lead to internal confusion and infighting within an organization (Carleton & Lineberry, 2004, p.13). To deal with cultural differences, most organizations which have adopted the concepts of internationalization and mergers and acquisitions are increasingly adopting various harmonization strategies. Additionally, organizations are also adopting due diligence the process of conducting mergers and acquisitions (Hewitt, 2009,p.2).
In an effort to attain international expansion objective, Kraft Foods which operates within the US food industry in Chicago acquired Cadbury which is based in Birmingham, UK. Kraft Foods deals with marketing of various food products such as snacks, cheese, grocery, convenient meals and beverages. The firm is ranked as the 2nd largest company in the US food industry. Cadbury deals with marketing of products such as gum, candy and chocolate. The firm is also ranked as the 2nd largest confectionary company in UK.
The two companies are characterized by different cultures. For example, Kraft Foods have incorporated aggressive management style. The firm has also integrated the concept of mergers and takeovers as its core goal to gain a high market share and to attain its financial performance goals. On the other hand, Cadbury has adopted a paternalistic leadership. Cadbury is mainly concerned with creation of a strong heritage and a loyal workforce. Cadbury goal is to gain strong brand awareness and to produce high quality products. This paper is aimed at evaluating the issues that need to be addressed in order to ensure effective integration of the two companies so as to attain future growth. The paper will also propose the management style, structure and reporting methods that will provide solution to the issues identified.
How cultural problems are addressed in order to attain integration and future organizational growth
In an effort to ensure effective integration and hence the future growth of the new entity resulting from a mergers and acquisition, management teams of firms involved in mergers and acquisition are incorporating different strategies (Stahl & Mendenhall, 2005, p. 30).To eliminate cultural problems, management teams of firms involved in merger and acquisition are increasingly conducting cultural assessment (Stahl & Mendenhall, 2005, p. 30). This entails comparing the culture of acquiring firm and that of the firm being acquired. The cultural assessment process entails evaluating issues such as company’s goals, objectives, mission, vision statements, core values, beliefs, norms, customer focus, employee empowerment policies and strategic direction for the two companies (Stahl & Mendenhall, 2005, p. 30).
Mergers and acquisitions between two companies result into extensive combination of the two firm’s operational strategies and organizational structures (Badrtalei & Bates, 2007, p. 303). The result is emergence of confusion amongst the employees regarding the culture to follow (Mercer, 2006, p.136). To ensure success of the new entity, management teams of firms involved in mergers and acquisitions are also conducting cultural integration or acculturation. Some of the acculturation strategies being incorporated include assimilation, integration, separation and de-culturation (Mercer, 2006, p. 136). Mercer (2006, p. 136) asserts that the objective of cultural integration is to develop a new culture.
Reason for the acquisition
Kraft Foods’ management team made the decision to acquire Cadbury so as to increase its presence in the global market hence its sales revenue (Waldie, 2009, para. 10). The decision was also aimed at increasing the firm’s market share in the global market from 20% to 26% (Waldie, 2009, para. 3). After the acquisition of Cadbury, Kraft Foods experienced an increment in its sales revenue with a margin of 26% to $ 11.9 billion (Fontevecchia, 2010, para. 1). Kraft Foods also intended to become the leader in the gum and candy business. The firm intended to achieve this by commanding 15% of the global market (Waldie, 2009, para. 11).
With regard to attaining global expansion through acquisition, the acquisition of Cadbury by Kraft Foods was aimed at increasing its presences in the emerging markets. The acquisition was aimed at enhancing its sales revenue by increasing its distribution efficiency. This arises from the fact that the Cadbury has implemented an effective distribution system which entails distributing its products through convenient stores and petrol stations (Waldie, 2009, para. 13).
Cultural issues experienced as a result of Cadbury acquisition by Kraft Foods
As a result of the acquisition, Kraft Foods experienced a significant cultural shock. Acquisition of Cadbury by Kraft Foods resulted into an increment in the firm’s profit margin. However, Cadbury lost its British identity and hence the level of confidence amongst its employees which it had developed over the years. The acquisition was also faced by intense government pressure. This arose from the fact that the UK government was opposed to the takeover since it considered Cadbury an important component of the country’s economic growth (House of Commons, 2010, p. 2). This affected the companies operation which is evidenced by the large number of Cadbury’s employees who resigned. This led into an increment in the rate of employee turnover within the organization 6 months after the takeover. A high rate of employee turnover was mainly evident amongst the key staff (Bridge, 2010, para. 1). According to Bridge (2010, para.2), 120 managers out of the total 170 have quit working for Kraft Foods since it acquired Cadbury. One of the key employees who quit Kraft Foods is Mark Reckitt who was the firm’s Chief Strategy Officer (Human Capital Forum, 2010, para. 1).One of the factors that have led to this exodus is related to culture clash between the two companies (Bridge, 2010, para. 3).
After the acquisition of Cadbury, Kraft Foods experienced a number of culture integration problems. These problems were mainly evident in its emerging markets such as India (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 3). For example, the officials who were charged with the responsibility of ensuring successful integration of the two companies said that the process was increasingly becoming complex (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 3).
In an effort to attain effective integration, Kraft Foods formed an integration team.
Additionally, the integration officials were of the opinion that the integration process was hindered by differences in corporate culture between the two companies.
Prior to the acquisition, Kraft Foods was very bureaucratic in its decision making process (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 3). On the other hand, Cadbury was very fast in its decision making process. After the acquisition, the bureaucracy at Kraft Foods did not end. This is due to the fact that lower level managers have to consult from the top managers when making decisions such as those related to pricing and promotion (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 3).
In an effort to ensure effective cultural integration, Kraft Foods formed an integration team. The integration team was composed of management team members from the two companies. The team was charged with the responsibility of harmonizing the cultural differences between the two organizations (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 6). Additionally, the firm also integrated effective internal communication. The resultant effect is that Kraft Foods was able to strengthen and to create a mutual absorption of the various cultural traits that the management teams identified within the two companies. As a result of integrating cultural integration analysis, Kraft Foods was able to identify the cultural gaps that should be improved ( Vijayraghavan, 2011,para. 6).
Despite experiencing problems during the integration phase, Kraft Food acquisition of Cadbury was successful. This is evidenced by the increment in profitability that the firm experienced as a result of the acquisition. After the acquisition of Cadbury, Kraft Foods experienced an increment in its sales revenue with a margin of 26% to $ 11.9 billion (Fontevecchia, 2010, para. 1).
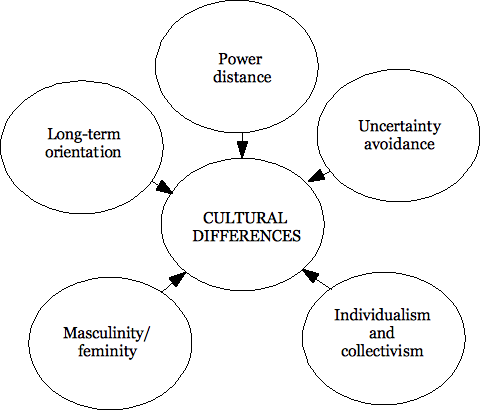
Hofstede’s cultural dimension theory
Power distance explains the degree of equality or inequality that exists amongst people within a certain society (Hofstede, 2001, p.2). Power distance can either be high or low. In the UK, power distance index is relatively low at 35 compared to that of the US which is 40. Therefore, there are minimal inequalities amongst the UK citizens compared to the US. Organisations that operate in such countries adopt decentralised organisational structure (Hofstede, 2001, p.3). Prior to its acquisition by Kraft Foods, Cadbury had adopted a decentralised organisational structure. This is evidenced by the fact that the subordinates had an opportunity to make decisions without inquiring from the executive (Vijayraghavan, 2011, para. 3). On the other hand, power distance within the Kraft Foods is relatively high. This is evidenced by the fact the bureaucratic decision making process. In an organization characterized by high power distance such as Kraft Foods, it is only the top management team which has the privilege of making or approving decisions (Hofstede, 2001, p. 17).
Individualism dimension is concerned with the extent to which a particular society supports interpersonal relationships, individual or collective achievement (Galpin & Herndon, 2003, p.34). A high individualism score within a particular country is an indicator that that country values individualism. As a result, the relationships that are established are weak. Individualism score in the UK is 89 while that of the US is 91. As a result of the individualism characteristic, organisations in the UK lay minimal emphasis on loyalty compared to US firms (Hofstede, 2001, p.22). However, Cadbury is unique in that it has adopted creation of family atmosphere and a loyal workforce within its corporate culture. On the other hand, in a collectivist culture employees expect their employers to do a lot for them (Kerr & Slocum, 2005, p. 130).This is evidenced by the fact that Kraft Foods mainly emphasizes on giving its employees material rewards.
Masculinity dimension is related to allocation of roles between the two genders. In an organisation characterised by a high degree of masculinity, most of the assertive roles are assigned to the males (Hofstede, 2001, p. 22). The US has a low masculinity score at 62 while that of UK is 66. This is evidenced by the fact that Kraft Foods is led by a female Irene Rosenfeld (PR Newswire, 2011, para. 1).
Uncertainty avoidance index refer to the extent to which individuals feel threatened by uncertainty (Gertsen, Torp & Soderberg, 2004, p.56). The US has a low uncertainty avoidance index at 46 points compared to UK which has 35. The low uncertainty avoidance index in UK depicts the risk taking characteristic of the UK firms. For example, Cadbury consented to the acquisition bid by Kraft Foods which led to enormous change within the organisation. On the other hand, long-term goals entail the values that are integrated in order to attain future success. In it operation, Kraft Foods have adopted the concept of merger and acquisition as a strategy to attain its future success (Hofstede, 2001, p. 22).
Conclusion
The analysis above has illustrated the sources of cultural difference in cross-border mergers and acquisitions. These differences emanate from existence of differences in national culture and corporate culture. National culture differences emanate from firms belonging to different countries while corporate culture arise from differences in culture that the firm has developed in its operation.
If cultural differences are not well managed in the process of undertaking a merger and acquisition, they can result into failure to attain the desired synergy. This arises from the fact that the merger may be fail. Additionally, cultural differences can also result into a decline in the employees productivity due to increment in stress and hence a decline in the firm’s productivity.
In an effort to attain its profit maximization objective, Kraft Foods acquired Cadbury. The acquisition was also aimed at enabling the firm to increase its presence in the global market by venturing into emerging economies. The acquisition gave Kraft Foods an opportunity to expand its operations into emerging economies.
In its acquisition process, Kraft Foods experienced a number of cultural issues. For example, the firm experienced an increment in the rate of employee turnover. The firm also lost its identity as a British company in addition to conflict between the UK and the US management teams during the integration process. The resultant effect was an increment in the degree of complexity during the integration process.
However, through formation of an integration team and incorporation of effective communication, Kraft Foods acquisition of Cadbury was very successful as evidenced by the resulting increment in its sales revenue.
The report has also illustrated the different cultural dimensions that exist between countries. This has been achieved by incorporation of Hofstede’s cultural dimension theory. The five dimensions are analyzed with reference to organizational context specifically Kraft Foods and Cadbury.
Recommendations
To ensure success of the merger, Kraft Foods should consider the following recommendations.
- The firm should adopt a democratic management style. This will contribute towards creation of an environment where employees are able to express their opinions regarding the firm’s operation. The resultant effect will be elimination of conflicts.
- The firm should also consider adopting a decentralized organizational structure so as to eliminate bureaucracies that may limit integration of change within the organization. This will improve the effectiveness with which the organization responds to changes in the external environment.
- Kraft Food’s management team should also incorporate an open communication channel so as to enhance flow of information between the lower level employees and the executive.
Personal experience of working in a multi-cultural team
During the study on the acquisition of Cadbury and Kraft Foods, I was a part of a presentation group which was composed of team members from different countries. Being a part of this group was of great benefit. This is due to the fact that I was able to appreciate the importance of teamwork. The group was able to complete the task successful. This was achieved by allocating tasks to individuals in accordance with their skills. Additionally, the team was very successful in completing the task due to the synergy that arose from the association.
Being a member of a multi-cultural team also gave me an opportunity to appreciate cultural diversity. This is due to the fact that I was able to understand how national culture influences individuals in executing their duties. For example, I understood the diversity that existed with regard to culture amongst different countries. For example, I noted that some of the team members value some aspects more than others. For example, some of the team members valued working individually while others were more concerned with attaining the group’s objectives as a team. As a result, there were instances when conflicts arose due to differences of opinion. However, the differences were resolved through consultation amongst the team members. This resulted into the team reaching an amicable solution.
Additionally, I also noted that some of the team members were more concerned with attaining the long term goals while others were concerned with short term goals.
Working as a team enabled me to appreciate the need for organizations conducting a cultural analysis prior to venturing into mergers and acquisition. Conducting a cultural analysis enhances one’s knowledge regarding the probability of the merger and acquisition succeeding. This arises from the fact that one is able to determine the degree of cultural fit between the team members. If the degree of cultural fit is minimal, then the probability of the partnership succeeding is low. This arises from the conflicts that might arise as a result of cultural differences.
I also appreciated the importance of conducting cultural integration analysis in the process of entering into any form of cross-border partnership. To achieve this, it is paramount for one to ensure due diligence. Due diligence entails taking into consideration the other parties priorities. Conducting a due diligence process increases ones understanding of the priorities of the partners. Due diligence can be achieved by evaluating the partners’ values, beliefs, norms and attitude. This will aid in minimizing conflicts that might arise due to failure of respecting the other parties’ culture. Therefore, this study has been very important in my career. This arises from the fact that I will be able to deal with the cultural challenges that arise within organizations as a business student considering the high rate of globalization.
Reference List
Badrtalei, J., & Bates, D. L., 2007. Effect of organizational cultures on mergers and acquisitions: The case of DaimlerChrysler. International Journal of Management. Vol. 24, issue 3, pp. 303–317.
Bridge, S., 2010. The big meltdown at core of Cadbury. (Online). Web.
Carleton, R.J. & Lineberry, C.S, 2004. Achieving post-merger success: A stakeholder’s guide to cultural due diligence, assessment and integration. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Dwivedi, R.K., 1995. Organizational culture and performance. London: MD Publication Pvt. Ltd.
Erdogan, B., Liden, R., & Kraimer, M., 2006. Justice and leader-member exchange: The moderating role of organizational culture. Academy of Management Journal. Issue 49, pp. 395-406.
Fontevecchia, A. , 2011. Kraft profit drop but sales jump on Cadbury buy. Web.
Galpin, T.J. & Herndon, M., 2003. To complete guide to mergers and acquisition: Process to support mergers and acquisition. New York: Jossey-Bass.
Gertsen, M.C., Torp, J.E. & Soderberg, A.M., 2004. Cultural dimensions of International mergers and acquisitions. Sydney: Prentice Hall
Gitelson, G., Bing, J.W & Laroche, L., 2004. The impact of culture on mergers and acquisitions: New York: ITAP International Incorporation.
Hewitt, R., 2009. M&A transaction and the human capital key to success. Global report. New York: Hewitt Associates.
Hofstede, G., 2001. Culture’s consequences: Comparing values , behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
House of Commons., 2010. Mergers, acquisition and takeovers: The takeover of Cadbury by Kraft. Web.
Human Capital Forum., 2010. Kraft hit by talent exodus. Web.
Kerr, J., & Slocum, J., 2007. Managing corporate culture through reward system. Academy of Management Executive. Vol. 19, issue 3, pp. 130-138.
Mercer, A., 2006. The impact of culture on M&A: Doing something about it. Washington: Mercer Transatlantic Survey.
Schuler, R., & Jackson, S., 2001. Cultural diversity in cross border alliances. New York: Cengage.
Schuler, R., Jackson, S., & Luo, Y., 2004. Managing human resources in cross border alliances. New York: Routledge.
Stahl, G.K. & Mendenhall, M.E., 2005. Mergers and acquisition: Managing culture and human resource. New Jersey: Sage.
Vijayraghavan, K., 2011. Cadbury-Kraft not as sweet as chocolate. Web.
Waldie, P., 2009. Why Kraft wants Cadbury secrets. Web.