Acknowledgment
The following Project is the positive and diligent output of the clear and fair learning and understanding of the Purnell Model in the classroom. It indeed enables to apply all the classroom learning and understanding towards the real-life projects that are practical in approach. It further enhances the capability of the student to critically analyze different cultures based on the knowledge and indulgent from the Purnell model. The implication and implementation of the Purnell model on our choosing Culture, which will be explored and elaborated with all the knowledge gained and understanding, made during the course, further augment the research skills that would be helpful and useful in the courses or projects ahead in academics and practical life after the campus. As said earlier, it would not only help in the theoretically gained knowledge, in the class, to apply in the real world, but it would also help understand the knowledge of general aspect that is covered in each module of the Purnell Model throughout the course.
With all the helpful and fruitful guidance and instructions from the instructor, the selection of choosing a Culture became possible. It also became more helpful to apply all the module of Purnell Model to the selected Culture that would be discussed shortly. Hence, enables to apply all the theoretical and practical understanding of the Purnell Model cultural specifically.
Also, the literature review and the scholarly article research became possible via the understanding of general aspect knowledge in the classroom. Hence, we dedicate all the learning and outcome, in the form of this session long project, to the instruction without whom assistance and instructions, it would not have been possible.
Therefore, with all the best efforts, abilities and knowledge, this project is finally prepared to be submitted. The instructor indeed has put in a lot of efforts via contribution towards suggestion to the project. Hence, the instructor is welcomed and appreciated.
Introduction
The selection of a culture for the implementation of all the concepts and theory that are understood and learned in the classroom is the important stride in the preparation of this Session Long Project. In order to make a clear impression and clarification for the instructor, the Culture selection was subjected to desire of the student. Hence, it enables the student to choose a culture that not only completes their Session long project’s step, but also allows them to apply all the concepts, i.e. theoretical or general aspect knowledge, to the culture selected.
Also, it was important to choose a Culture that is clear and precise for the implementation of all the modules defined in the Purnell Model. A culture that has all the aspects defined in the Purnell Model, i.e. everything from the definition of its economy to the level of spirituality and daily life routines. Since, the modules of Purnell Model are the foundation for the selection of culture in the session long project, hence the choosing culture must be broaden and distinct in all those fields mentioned in the Purnell Model which is discussed and elaborated below with all the possible efforts and hard work in order to make it as much clear and understandable for the reader and instructor.
Moreover, the selection of a culture became more straightforward keeping in mind all the discussions and classroom activities regarding the understanding of Purnell Model and its implementations in real world. Hence, as per the theoretical and practices envision of the Model, the chosen culture is decisively elaborated and discussed individually with each construct or modules described in the Purnell Model.
Culture
After the clear understanding and thinking, inside and outside the classroom, the selection of “Chinese Culture” for the session long project becomes possible. Also, the selection of Chinese Culture is moreover considered after critically analyzing all twelve modules of the Purnell Model, and its cultural competence addendum.
The People’s Republic of China is the most ancient civilization of Asia spreading over a large portion of East Asia with Beijing as its Capital city located in the Northern part of China. The People’s Republic of China has a population of around 1.3 billion, among the highest populated countries of the world. Having a centric location in Asia, China has seen an enormous development in the last five decades, hence coping to be the world’s largest economy in the year 2020.
China is a multi-national and multi-religious country in the Asia with almost 55 different nationalities that resides in it which enjoys equal rights and privileges under the constitution of Republic of China (PRC, n.d).
Having a democratic process of electing rulers, China has its own Military Army. It has its own river and enjoys the shores of Pacific Ocean for trade. It has land routes for the purpose of trade and exchange of aids with Vietnam, Burma, Bhutan, India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran.
China also ensures the freedom to practice the religious and cultural practices of individuals as per protected in its Constitution for minorities where it is defined as freedom to practice religious norms and practices (U.S State, 2011).
China leaves no comparison in the advancement of technology and science. It has been world’s largest exporter of daily routines utilities all over the world. It has very stable economy that is expected to become the world’s largest economy by 2020. It has a perfect Legal System for Trade, Business and Operations with rights reserved for everyone including the minorities in its constitution. Hence, it seems to be a perfect selection of a country for the session long project to complete the SLP chart on the basis of Purnell Model.
Hence, due to the broad and widen scope of Chinese economy, infrastructure, medical facilities, preservation of human rights, practice of religious norms, High business regulations, refrain of bribery, and effective examples of perfect cross culture business exchanges.
Literature Review
For the session long project, following is the literature review that is successfully reviewed after an effort on research and guidance towards its accomplishment. It takes account of sources quoted in the reference section from across the globe over the internet and journals. The idea is the indulgent of the practical implementation of the Purnell Model with a specific scope of cultural competence. The literature review is also meeting point on the cultural competence of the Purnell Model just as briefed above, which is the core aspect of this session long project.
According to a paper “The Need for Advancement in the Conceptualization of Cultural Competence” published by (Gallegos, Tindall, & Gallegos, 2008), the Cultural Competence is the course of action by which people and society from different background, ethnics and origins are respected and greeted for all kinds of honor and respect they seek and deserve. And it means that respect and honor in a way that the person as individual, family and the society is protected from all negative occupation over their property, respect, honor and dignity.
The paper further defined the cultural competence as the combination of acts, mind-sets, conducts and procedures that ensure the effective cross cultural circumstances through organizations, health facilitation centers and experts in all the relevant fields that can fall within the twelve defined modules of the Purnell Model.
Moreover, the paper called a society or culture a culturally competent if it follows or belief in the following five assertions:
- The acceptance of diversity
- The evaluation of cultural component in a culture
- The vibrant change for cross-culture acceptance
- The widespread of cultural acquaintance, and;
- The start-up of value diversity plans within a culture
Also, Bhui defines the cultural competence as a perfect model for implementation if applied to the health sector. According to him, the model would promote decisively if taken to the education and health personnel training and development programs within an organization or health care system.
Bedell elaborated one term, for the perfect cultural competence and diversity acceptance culture, as words from cultures. The author uses the words as metaphor to describe the heal and harm or curse and cure for patients, if the model is used and implemented in the hospital sector or in health care system. The article further supports the use of healing words as an effective tool in the care and heals of a patient in any culture and hence symbolizing the language or words of a culture to be healing for cross cultural patients. Hence, the art of using language to bridge the cultural competency gap is a way that this paper analyzes.
The language, especially the words in any lingo, can bring a decisive and positive heal and cure to all cross-cultural patients, if, again, the model is implemented in the health sector.
The language barrier often becomes the cause of misunderstanding and discrimination in a culture especially when it comes to minorities and women. The paper concludes the inability or the barrier to translate the functions to the health officers in a culture often leads to misbelieve about that culture. Hence, criticizes the experts for the incomplete understanding of values and beliefs of a culture in order to completely transform the cultural competency.
Since, the Purnell Model has seen its implementation in health sector, so an inference from a document is also included here which was published in England in 2003 just after the World Health Organizations call the health centers around the world for the training and development program of health care staff around the world for incessant improvements in the health system.
The paper published by the National Institute for Mental Health (NIMH) proposed the ethnic discrimination via an ethnic equality improvement program in health service centers. The papers showed strong appeal towards the development of personnel at health facilitation centers for the reduction of ethnic and minorities’ discrimination.
Theoretical Framework
Culture
- Culture can be defined as a process of how a person or individual live in/as a group hence, it is also called a pattern of survival. Survival here means the passage of cultural package to the descendants.
- Every individual or society identified and differentiated through a culture.
- Every generation passes its values, beliefs, perceptions, ideas, norms and everything they possess to their next generation for the survival and the existence of a culture.
- Culture helps individual or a person to build a perception of things in surroundings. Culture provides an eye with built-in regulations to perceive the surroundings or world around the person with that vision.
- Culture helps individuals building in their fondness and likings, and it also helps individuals to make a sense of feeling of respect and honor for members and individuals of other cultures, and that respect and honor free from all differences of creed, cast, religion, ethnicity, etc.
Importance
The importance of culture becomes evident when applies to the health care system of a country or society, the consideration of health system again here is because of its soaring applications of Purnell Model. However, we can take the same examples from academic or research backgrounds because the acceptance of diversity or the development of new teaching in a culture breaks the old and bias concept teachings that discriminates between individual and societies for all the services and facilities that are common for all populous and locals. Hence, the culture empowers the locals and residents about their rights, their solutions for the problems and their faith in terms of rule of law and government.
Cultural Competence
The definition of Cultural Competence can be defined as the course of action where people from cross cultures are respected and greeted with all respect and honor. And it means that respect and honor in a way that the person as individual, family and the society is protected from all negative occupation over their property, respect, honor and dignity, as it is also defined in the introduction.
In the “The Need for Advancement in the Conceptualization of Cultural Competence” published by (Gallegos, n.d), it has been further defined the cultural competence as the combination of acts, mind-sets, conducts and procedures that ensure the effective cross cultural circumstances through organizations, health facilitation centers and experts in all the relevant fields that can fall within the twelve defined modules or sets or agenda of the Purnell Model.
The Cultural locale
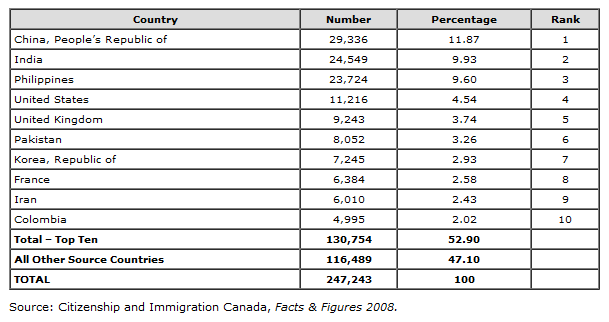
The definitions defined above about culture and the cultural competence leads to towards the point of giving room to diversity in a culture. For any culture to effectively implement and absorb the cross cultural mode or diversity in today’s modern and competitive world is very important. The world has become globalized and yet we have to compete every other country or individual for one’s personal and national interest at every platform. Hence, the aspect of diversity has now its root everywhere around the world. Refer to the Gallegos paper above; it stated that Canada has accommodated an excessive number of immigrants in the last 5 decades. The following chart shows the latest figures of foreign immigrants in Canada who succeeded in becoming her nationals as percent of the Canadian population.
Now, the discussion has reached on its point of elaborating and understanding those twelve constructs presented and published by Purnell Model for the effective cultural competence concept. There are twelve constructs related to different aspects of life and culture anywhere around the world. The implementation, utilization and applications can be seen in many real life departments, i.e. health care system, education system, research system, etc.
Also, the constructs must be defined in the light of the selection of a Culture, which is done before defining those constructs in order to have a clear understanding and analysis of that culture and of Purnell Model’s constructs as well which are briefly explained in the Purnell Model Section in the above pages.
Since, the selection of the culture is Chinese culture; therefore, the discussion of those twelve modes of Purnell Model would be about those aspects from the Chinese Culture. The elaboration and description of those constructs are divided as follows:
- Module I:
- The module one is based on the definition and analysis of culture of the basis of two constructs from the Purnell Model as highlighted below.
- “Overview/Heritage and;
- Communication” (Severstal, 2010).
- Module II:
- The module two again defines three constructs from the same Purnell Model provided inspected in the light of the selected culture. Those constructs to be discussed in this Module are:
- Family Roles and Organization
- Work Force Issues
- Biocultural Ecology
- The module two again defines three constructs from the same Purnell Model provided inspected in the light of the selected culture. Those constructs to be discussed in this Module are:
- Module III:
- The module three would be discussing the following three constructs as an integral part of the chosen culture i.e. analysis of the culture on these chosen constructs here:
- Pregnancy
- Nutrition
- High-risk Behaviors
- The module three would be discussing the following three constructs as an integral part of the chosen culture i.e. analysis of the culture on these chosen constructs here:
- Module IV:
- This module evaluates and understands two more constructs from the Purnell Model from the aspect of chosen culture. Those are:
- Death Rituals
- Spirituality
- This module evaluates and understands two more constructs from the Purnell Model from the aspect of chosen culture. Those are:
- Module V:
- This is the last module and discussion about the cultural overview and aspect with respect to the chosen culture on the following two more constructs from the Purnell Model. These two constructs also ends the mentioned model, i.e. the model concludes the constructs part by the elaboration of these points:
- Health-care Practices
- Health-care Practitioners
- However, the Purnell Model further divides these above mentioned constructs into more and more sub-constructs in order to have a deepen and widen understanding and analysis of the chosen culture so that the effectiveness and implementation of the cultural competence model remain the same in each chosen culture anywhere around the world and that too in any field or real life practice.
- This is the last module and discussion about the cultural overview and aspect with respect to the chosen culture on the following two more constructs from the Purnell Model. These two constructs also ends the mentioned model, i.e. the model concludes the constructs part by the elaboration of these points:
Module One
The first module of the session discusses and elaborates the understanding and implementation of two constructs in a culture that is subject to the choice, in this case, of a culture “Chinese Culture”.
These are as:
Overview/Heritage
This is the first constructs defined in the Purnell Model. As its name suggest, it is related to the understanding and general highlights and briefs about the country and culture, chosen for this session long project.
- This mode discusses the following points in regard to the Chinese Culture:
- Origin of the country/culture
- Residence aspect of the Culture
- Topography
- Economy of the Culture
- Politics
- Education
- Occupations in the Culture
The Chinese culture as defined in the brief intro about the selection of culture portion above is the old and ancient culture and civilization of the Asia. It has its root of civilization back 4000 years ago (History of China, 1995). The Republic of China had been the centre of wars for the rule on great empire by many warriors. This culture has seen invaders from different parts of the Asia, i.e. Mongol’s Era, Ming Dynasty among the popular ones.
After a long battle towards democratic and capitalist society, China had passed through many revolutions in the twentieth century that fueled a total change in the economic, social and political scene for years. The movement of May fourth and the nationalist party era are examples to name few of those revolutionary times. Hence, brought home these revolutions were the effective and sustainable land, social, political, and ideological reforms in every aspect of the modernized Chinese culture and country.
China in itself has been further dividing into nationalities and origin and language. There are almost around 54 Chinese origin different backgrounds of people living in China whom rights are very well protected under the constitution and law of Republic of China (Paulnoll, n.d).
Today, the total Chinese population has exceeded to 1.25 billion. Almost every 1 out of five lives in China. It constitutes the 20% of the world population. The densely populated province is the Sichuan Province, with population of almost 107 million people that is above the population of whole Nigeria in comparison. Hubei province populated locals almost the same in comparison with the whole population of the United Kingdom (UK) i.e. above 54 million (China’s Demographic, 2009) which later is analyzed that how the Chinese government has regulated laws to control the heavily increasing population.
The topography of the Republic of China is based on the mountainous and unequal distribution of land over the eastern part of the Asian Continent. Almost ten percent of its land covers the Hills in China with 33 percent, the largest in area or size is the estimate of the mountainous land (China Topography, 2007).
The economy of China is based on the fundamental principle of capitalism. But after the fall of last Qing Empire in China, the successor thronged the country towards communism and socialism. But after the death of the communist leader and the rule of communist party in China, leaders of that time made China a free-market and hence open doors to investors from capitalist societies and culture to come and invest in China. Hence, the Chinese economy soared during the 1980s’ and 1990s’ with a boom in every sector especially the energy and industrial sector of its economy took a huge stride forward towards a total development vision for china (Hays, 2008).
Political situation is China is more and more stable just after the last revolution that turned the Chinese economics towards capitalism. Today, People’s Republic of China has a democratic form of government. The National People’s Congress is the hub of all political, economical and social regulations and discussions.
Hence, the republican China entitles every one of its resident rights towards total free and quality education. Education in China is compulsory for everyone till 9 years, i.e. until the completion of a nine year education by every child by state owned and ran schools and institutions. The ministry of Education is responsible for the maintenance of quality education and standards at the public universities in China (Index-China, 2009). Their primary motto is to bring all competent and intellect students to the mainstream development process of China.
The China has shown a high development growth in every sector, i.e. development in the agriculture, energy, education, industry, coal and gas, technology, military, art and many others. Hence, gives path to every individual in every aspect of life to groom and develop.
Communication
The communication in any culture or society is the important aspect to analyze thoroughly because all means of trade and talk is via the understanding of the local people’s attitude, their daily life routine and their manner to do a business or their way to deal with any kind of sudden situation. For the understanding of Cultural competence model in Purnell Model, following points will be elaboration below for the understanding of communication modes in Chinese culture.
- Languages spoken in China;
- Dialects;
- Tone;
- Personal Space;
- Eye contact;
- Gestures;
- Greetings;
- Time;
- Touch;
- Names.
The national language of China is the modern standard mandarin Chinese, but there are few other languages that are spoken in many large provinces in China. Other languages include Cantonese, Taiwanese and others (Learn Chinese, n.d). The Chinese, therefore, is spoken with a variety in parts of China, i.e. on the basis of regional specification with Mandarin as the standard one to be spoken by large part of China. Others are Wu, Yeu, Hakka and others (Spoken Chinese, n.d).
Chinese are very soft and calm people. They have a very polite way of talking and dealing in every aspect of life. In Business or dealing, they prefer not to use the word “No”. For them, it’s a bad omen while their “may be” or “some other time” reply indirectly can be inferred as a “No” (Kwintessential, n.d).
Personal Space is viewed as a belonging to all in Chinese Culture. People can be seen jostling for space in train, crowded at the ticket counter irrespective of the thought of personal spaces as a right of every other individual. While a good eye-contact can result in good impression in deals or businesses in China. People prefer to have a good eye-contact. In contrast, they never mind if the speaker is not having a proper eye-contact with the listeners or the audience, they don’t call it a weakness.
The Chinese welcome the guest with a bow and a gentle handshake. Their handshake is covered by the left hand as a sign of hospitality for the guest. The Chinese people are very kind in their nature as they send delegates to welcome their guests from abroad and organize a meal in their respect.
Chinese people are very punctual of their time. In any business deal or trade, the guest must reach at the venue before the Chinese host (China, 2008). Chinese usually have their day meals very early in the day as compared to meal timings in the Western culture.
Chinese don’t like touching much. Usually, they have a “guanxi” principle that says the relationship between the guest and a Chinese host must be built before any kind of deal and if this relationship is successful in terms of honesty and hospitality, and then the deal is signed or moves forward.
Mostly, Chinese people have their surnames first in their name. And it is preferable to call a Chinese by his surname with a title before, i.e. Wang, Chen are single syllable surname example while names can be wangling, liming, etc.
Module II
Module two for the session long project covers the following three constructs from the Purnell Model which are further sub divided into sub constructs which we will define and elaborate in the following headings.
Family Roles and Organization
The Chinese people, even in the highly technological and modernized world, follow the tradition method of handling and maintain the family roles with the utmost integrity and honesty. The parents in China are very conscious of the future of their children. The regulation of only child in a family by the Chinese government in order to control the perpetually increasing population for the reason of national sustainable growth of economic and industrial sector brought excessive privileges to the families in the rural areas especially when the only first child is a girl. The parents engage themselves in a healthy and mature relationship in the only first marriage for the better future of their only child. Father is the head of the family and child affairs. Parents are respected by children with utmost respect and integrity.
Therefore, the family’s elder who often happens to be a man, i.e. father or husband, is responsible for the bread and butter of the family. He holds the responsibility of child’s education and personal care expenses as well as of the whole family. Women are entitled with the responsibility of caring and nurturing the child and the family, most of the time (Chinese Symbols, 2004).
Hence, the Chinese people are family oriented people. They tend to keep the family and relations together at any cost. As for the role of the extended family in Chinese culture, any Chinese family would seek help or any kind of assistance, first, from the immediate and extended family (Shapir, n.d).
Workforce Issues
The role of both genders in the development and uprising of the Chinese economy is evident from the current enhancement and expansion in the infrastructure, booming economy, rising industries and improving agriculture in China.
The industrialization and privatization in China brought enormous resources in the form of capital, investors and human resource to China. And China on the other hand, welcomed them all with all its hospitality without any discrimination on the basis of origin or development (Thornton, 2005).
The strategy that the Chinese government has been adopting for the past three decades, to cater the effects and challenges from its capitalist and globalization policy is the major factor of its rapid economic growth. They intend to play a vigorous role with good conversation and communication with the globe, but it all based on protecting the autonomy of China at all front (Keping, n.d). This way, the diverse workforce was accommodated in the progress of a developed China very effectively and the autonomy status remained untouched by external forces as well.
The language barrier has been one of the biggest challenges for a diverse group to integrate in the Chinese culture. According to the U.S. State Department, Chinese Mandarin (a classification of Chinese language) is among the world’s five most difficult languages (others include Korean, Japanese, Cantonese and Arabic) (Ramzy, 2006).
Moreover, the language barriers within the regional divisions in China are very well handled by the government through various local and international organizations, i.e. these programs include various vocational trainings, training programs for rural population etc. Once, it was observed that the low paid and low standard jobs were only for people from rural China as it happened after the capitalism took over the whole country. The Chinese government intervened and stopped the over flowing displacement of population to the rural areas via the advent of various programs and incentives for the rural population.
The source said, the dialect barrier widened when the foreign investment flew in the region with rural population, with no access to high school due to high tuition fees, were halted and provided with jobs of just low salary or standards. But as mentioned, the government initiatives did improve the widen gap of rural and urban immigration along with especial perks to the rural population (Wang, 2004).
Unlike the West with individualistic culture, the China has been the centre of the collectivist culture since years. Therefore, any final or ultimate decision in reached upon by the mutual agreement of all the members in the group or team. Issues are resolved with harmony and talks. Hence, the relationship between supervisor and employee is not the same as it is in the West. Chinese workplace tends to respect the senior staff and employees for their lifelong commitments with that organization or firm (Kwok, Au, & Ho, 2005).
Biocultural Ecology
The Biocultural ecology refers to the differences in the cultural and racial backgrounds within a territory. This includes the regular practices that are distinct in a particular group within a culture, i.e. a sub-culture with a culture. Also, the differences can be of the color, genetics, etc.
With reference to the Chinese culture, which is the chosen culture for this SLP, China does accommodate different cultures within its whole territory. As defined earlier, there are more than 54 various ethnicities recognized by the Constitution of China whereas there are several others are derivative of them (Wu, 2006). Each national has common and equal rights that are defined in the charter of Human Rights with equal access to all the facilities being provided in the country.
Furthermore, China has been doing its best to use the diversity of ethnics in the best favors of the country and its traditions by initiating various diversity ethnic programs, training and educational programs etc. The source, mentioned above, also says that due to weak financial backgrounds, many students from minority ethnics couldn’t perform up to their potential. Hence, the Chinese government is taking the initiative to empower the minorities as possible as they can be in order to have sustainable and tolerable region.
It has been estimated that the 93.3 percent of the Chinese population belongs to the Han genetics i.e. almost the entire population of china is the derivation of the Han culture and background while the other small remaining fraction constitute the other 55% minorities in China (Tan, n.d).
Also, the HIV/AIDS and HIV/STD, are the most communicable diseases in China which is the also a major problem for the Chinese government to prevent its population from. Other major diseases include strokes, tuberculosis, cancer, breath problems, heart problems etc (US-China Life Style, 2010).
Module III
The module three discusses the following three headings i.e. three sub constructs as per described in the Purnell Model. These sub constructs are mostly related to the nourishment and health topics for the analysis on Chinese culture.
High-Risk Behaviors
The high risk behavior is the use of drugs and medicines for pleasure. That includes the use of alcohol, drugs, etc. In order to understand the implementation of the cultural competence model to avoid any cultural clash in serving the social and humanitarian duties to the cross cultural people, this sub construct may be amongst the most understanding one. It analyzed the behavior of locals within a culture based on their daily routine activities. Sometimes this behavior is referring due to lack of physical activities. This sub constructs also includes the sexual practices particularly with risk high due to AIDS/HIV.
To compare, China has the highest rate of HIV/AIDS infected patients and ranked first in the fastest spread of HIV/AIDS within China (Chan, Yang, Li, Stoove, & Reidpath, 2009). The same source indicates the rate of around 20 thousand deaths a year due to HIV/AIDS and around 700 thousand are reported to have been the infected of this disease. It further says that the HIV/AIDS infected are ashamed of their infection and link that with the homosexuals.
Tobacco, on the other hand, is also the wide spreading addiction among the Chinese people. Around 30 percent of the cigarettes, produced around the world, are consumed by the Chinese people while this figure is an approximate population of the USA. Also, China is the largest producer of cigarettes (Smoking, 2001). Tobacco addiction kills around 1 million people, a year, in China (Wong, 2011).
The drinking pattern of alcohol varies in the Chinese culture due to cultural norms where men are preferred to drink alcohol while women keep themselves restricted to bear or wine. In 1996, the per capita consumption of alcohol in China was 5.17 annually. According to a WHO report, average of 2.118 million people die in China due to alcohol addiction, says report in 1990 (Wiley, 2008).
Use of recreational drugs has been a big problem for the Chinese government (BBC, 2009). According to the site quoted, government has rounded off around 1.2 million recreational drug addicts in China. Moreover, 40 tones of drugs was confiscated during a raid back in December 2009 in the Xinhua state, as per sited by the source, which worth around 2.6 million dollars.
For a healthy and successful life, Chinese belief in the physical activities is the same as of every other nation. Chinese people have their own way of doing physical activities that includes the world known Martial Arts exercises, i.e. “Tan Chi Chuan” to one of the many martial arts practices (Wu S. , n.d). Besides, the use of bicycles and walking is seen very common in the urban regions of the country while people in rural areas are seen to practice the walking art regularly and efficiently (Hu & Yu, n.d).
Nutrition
Nutrition refers to the ample supply of the food in a culture. It includes the choices for food items, the quality of those food items and healthy substances. The poor rich gap still exist in China where the urban areas are the focus of development while ignoring the rural or agricultural areas causing a poor rich gap among them.
But the Chinese government has been busy bridging this gap with the help of rations support programs to make assurance of social equality among every national (Times Online, 2005). The undernourishment in China has fallen to 9% which indeed is the success of equal social reforms (Balfour, 2009).
In Chinese culture, the food is divided over hot and cold nature of the nutrition i.e. a Chinese name of yin for cold food products while yang is for hot products. The former includes the use of fruits and vegetables while the latter constitutes the meat, fluids and other baked items (Shapir, China, n.d).
The choice of food also varies across the north and east regions of the China. The former region prefers flour items, i.e. bread while the latter region have a culture of rice and spaghettis, said the source mentioned in the above paragraph. Vegetables come all along in each region with each meal.
According to traditional ritual, liquids are frequently used in each meal because it keeps the system warm and workable. Moreover, self discipline manners of exercising the traditional and religious spiritual powers are believed to be the secret for good health in Chinese culture. A person is characterized as weak on the basis of his weak emotional control over daily life matters i.e. sickness, failure in exams etc.
Pregnancy
The pregnancy sub construct is the discussion of pregnancy and childbirth procedures and practices within a culture. The procedures can be the control of birth, safety in pregnancy and birth giving procedures, etc.
The China has implemented the one-child policy in the country for cutting down the heavily increasing population of the most populous country on the earth. The one-child family is given special privileges that includes the quality housing for the family, long office leaves for the mother, cash perks, etc (Population Control Programs, n.d).
After the democratic process took its root in china, many reforms regarding modern day pregnancy and fertility were taken. To break the old tradition, the sperm banks were opened. To make the mother literate about the child-birth, many programs were initiated to make mothers aware about child and pregnancy procedures which are further enhance up-to-date (Inhorn & Balen, 2002).
Also, the Chinese have a very spiritual belief of child birth in their culture. They respect the mother and the family for the new comer in their family circle. It can be elaborated clearly by quoting a belief of theirs to mothers that mothers should not scorn or criticize any one near her as the child may inherit the qualities of that person being criticize.
Moreover, during the birth or delivery of a child in a Chinese culture, father must not be present in the delivery room. However, the father has the privilege to give his child the first bath after the delivery. Silence is asked to be maintained while giving birth because shouting or crying is considered as a negative omen for the child (HAWCC, n.d).
According to the same source mentioned in the above paragraph, the post-par-tum is also practiced in China which can be defined as the post child delivery time. The mother is taken special care with exemptions from workload, household works and others. Special food and hygienic care is maintained for the post-par-tum mother.
Module IV
The fourth module is the two sub-construct combination from the Purnell Model and is discussed as follows with respect to the chosen culture, i.e. Chinese Culture.
Death Rituals
The death rituals is the process of seeing and honoring a dead person in a culture. It can be the burial process and practices. The China has the Cremation old tradition which is now very rare seen to be practiced. Since, most of the population in China is Buddhist; they prefer to bury the body for the respect and honor of the dead (China Culture, 2003).
In traditional Chinese culture, man is the head of the family and is responsible for all the celebrations of the family. Hence, the occurrence of a death in a family is informed in the neighborhood and relatives via door-to-door knee down culture that is the son goes door-to-door and knocks at the door and knees down; the neighbors or relatives themselves understand that a death has happened in the family. Then, the neighbors have to cry upon seeing the man or son while placing the hand over his face (Simmons, 1999).
Moreover, there exists two views for the funeral ceremony in a Chinese culture; one claims the ceremony to be continued for continuous of 49 days while the other claims for it to be limited to 10 days. In the former form of funeral ceremony, the cost is met by the daughter or female head in the family while the elder son or man must be present in the funeral. In the latter form of ceremony, the funeral is for 10 days based on the burial to take place (Funerals, n.d).
Spirituality
The China has been the hub of soul and spiritual for centuries. Chinese people believe in the joy and calm of a Hormonal and Peaceful world around them. The symbol of Yin-Yang is its example among many symbols of spirituality (Chinese Spirituality, n.d). Also, China has been traditionally and activity the center of religious tolerance. Many religions exercise their practices and rituals independently and progressively within the Chinese culture and enjoy the equal rights under the Chinese democratic constitution. These religions include Confucianism, Daoism, Buddhism, Christianity and Islam to highlight the few (Religion in China, n.d).
While the same link shed lights on the concept of spirituality in Chinese culture. It says that the expression of spirituality through the art of painting and poetry has long been part of the traditional Chinese culture. Also, the religious influences of Buddhism and Daoism have been enormous in defining spirituality via the stated arts. Moreover, the symbol of Yin-Yang, as mentioned in the headline of this topic, is also the sign of long ago existence of spirituality in the Chinese culture.
Meaning of Life
The Chinese view on the meaning of life is evident from the following lines that says that the individual must be devoted in search for peace, happiness and joy to be created so that these can not only be enjoyed, but also can also prevail and save them for next generations to come (D u x i u, n.d).
Use of Prayers
China is a country where many religions are practiced and acknowledged constitutionally. These religions include Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Taoism etc. Many of the behaviors in the Taoism and Buddhism in China are directed by the philosophy of Confucianism, i.e. the belief of controlling a behavior. Hence, Buddhism falls in line with the beliefs of Taoism and Confucianism that’s why most of the Chinese, i.e. almost 65 percent of them, believe that they are Buddhist. Hence, these people visit special services, religious rituals, and pay visit to the temple regularly.
Islam, on the other hand, is also accepted and practiced by around four million Chinese, brought in China by Asian Traders back centuries ago. These people offer regular prayers in Mosques and celebrate religious occasions together. Christianity is also practiced in China where worship and prayers are said in Chinese or English languages (Liu, 2001).
Individual Strength
Chinese culture, as described in the above pages, is collectivist society as a whole, i.e. groups or members together are considered as good omen for work, family and social life. Hence, family relationships and strong workplace bonds are considered very important. Yet, individuals such as seniors at workplace and elders at home and society are respected in a very different way unlike the Western culture. Therefore, the collective strength of a social or workplace group is considered much more efficient and effective than that of individuals’ work and efforts (Xu, Xie, Lin, Xia, & Liu, 2007).
Module V
The fifth and the last module for this project is also the sub-construct combination from the Purnell Model discussed in the light of the selected culture that is Chinese Culture.
Health-Care Practices
Focus on Health Care
Chinese health system is distributed into rural and urban facilitation centers yet giving quality on both sides. China has been long engaged in preventing the population from many diseases, i.e. HIV/AIDS with the cooperation of International health institutions and organizations. The major programs include preventing of HIV/AIDS and Hepatitis (Zhang & Li D, 1996). The government supports and funds all these programs for a balance society vision both in rural and as well as in urban cities and parts.
Transplantation
The transplantation started way back in 1960s in China while, until the time when changes increased in the procedures for transplantation, in 2006, around 11 thousand organs were transplanted (TheLancet, 2008).
Traditional Practices
The traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is still in use and practice by many health care practitioners. According to the Health system reform in China link mentioned above, the TCM is still the best old healing system and is integral part of the Chinese healthcare system. It includes the herbal medicines, massage, physical exercises, etc.
Responsibility for health and Self Medication
The Chinese people believe in the self-medication as they have immense believe in their own traditional medical system of using bio products for cure. Around 52 percent of the Chinese people do not go for the treatment at first phase. They rely on sitting at home and doing the tradition cure by themselves, i.e. self medication (WSMI, n.d). In 2004, around 50 percent of the Chinese population was surveyed and observed to be exhibiting the activities for good healthcare by following the tradition medical system, i.e. doing exercise, body examination etc, said the above mentioned link.
Magico Religious beliefs
The folk culture in the Chinese religious stream adds the concept of divine or supreme sole worship and praise. The Chinese people subjected their local warriors or leaders as heroes and started worshiping them whenever a natural calamity or disaster occurred. If the things turn out well and good in favor of the locals, these people then build worship houses for those heroes who were praised and consider them as their gods.
Moreover, Chinese people pay tribute via immense respect to their elders and ancestors and believe in the life hereafter. This is because they believe that by paying respect to the ancestors’ spirits, they would be bestowed all equal benefits in the life hereafter and also to keep those souls happy so to avoid any natural calamity via doing any disgrace to them (Lin, 2001).
Rehabilitation and Chronicity
Chinese people believe in the philosophy of controlling the emotions by themselves, i.e. the belief of Confucianism of controlling the behavior via spiritual and religious practices. The physical rehabilitation in Chinese practices involves the use of traditional massage, Tai Chi exercises which are considered as therapies for relaxation. Traditional Chinese herbal medicines and practices are still useful in physical and mental rehabilitation in China (Dahong, 1991).
Barriers
Among many barriers to the health care and medical system to work efficiently in China, a few includes:
- Poor infrastructure.
- Inaccessibility of poor to the health care units.
- Soaring drug prices.
- Bribery.
Pain, Sick and Mental Health
In the traditional Chinese Culture, pain and sickness is considered the outcome of bad and unreligious deeds by a person. The patient doesn’t want everyone around him to get troubled because of him (Pain, n.d).
Moreover, around 17.6 percent of Chinese adults suffer mental illness or irregular behavior. This trend is considered the repercussion of the economical breakthrough and development from early 70s. Therefore, many of the patients don’t consult the doctor due to the social teasing for visiting the mental institute. Another reason is that the mental health services are too costly in China (Yanhai, 2011).
Health Care Practitioners
After the fall of communism in late 70s’ in China, it abolished the tradition medical and health system in 80s’. And brought remarkable changes to enhance the medical system to the most digital and technological one. It secures the services of paramedics and doctors via its three tier medical system. It divides doctors and practitioners in three fields. The general or primary physician takes care of daily care of citizens. If the case turns serious, it is then referred to the junior doctor who then refers to the specialist or the senior doctor in case of high emergency again (Karvounis, 2008). Also, most of the hospitals in China are owned by the government, hence the doctors work on a permanent salary with incentive of bonus upon the condition of bringing more returns in terms of profits and improvements to the hospital.
Conclusion
Achieving the tolerance and the cross cultural diversity within a culture is what every country and culture around the world is busy in with. Globalization is the term we use to define the world as a global village, which in terms do mean the acceptance and forbearance of multiplicity. This could benefit cultures and countries in a lot of way, i.e. from the development of basic agriculture and social infrastructure to the development and creation of space shuttles and digital technology.
In the light of the discussion and interpretation of the Purnell Model above, the selected culture for the session long project, i.e. China does accommodate the five modules discussed above. China has a long history of civilization and culture. It has more than 150 languages spoken within it across many provinces. It has its own mode of communication, i.e. communication in terms of family, society or global and international business adequate. The family and society culture is very family oriented. People tend to stick with one job for the rest of their lives. Father heads the family and earns the bread and butter though women do earn their earnings based on family culture as defined in the family roles sub construct above.
China welcomes workforce and employees from abroad too. The changing domestic culture of growth and development based on the concept of capitalism indeed enhance the domestic growth and improves the infrastructure in China as defined in the workforce module above.
It has a birth control system in its territory with the concept of bringing social equality among the nationals. It’s also taking measures to control the HIV/AIDS spread in the country while it has successfully overcome the hunger discrimination by initiating the self aid programs in the country hence got rid from international assistance.
Hence, the selected culture has all the basic roots that can spur the cross cultural competence model within it. Hence, the possibility to implement Purnell Model would be successful in a country like China where people have tolerance and acceptance of diversity and see each other as family to work and corporate with. Therefore, it’s giving life to a literate territory of love, peace and harmony.
References
Balfour, F. (2009). Hunger Scorecard: China Improves, India Deteriorates. Web.
BBC. (2009). China arrests 85 in drugs raids. Web.
Chan, K. Y., Yang, Y., Li, Z.-r., Stoove, M. A., & Reidpath, D. D. (2009). Web.
China Culture. (2003). Chinese Funeral Customs. Web.
China Topography. (2007). Web.
Chinese Cultural Studies: Concise Political History of China. (1995). Web.
Chinese Spirituality. (n.d). Web.
Chinese Symbols. (2004). Chinese Family Culture. Web.
Culture: China Changing Culture and Etiquette. (2008). Web.
D u x i u, C. h. (n.d). The True Meaning of Life. Web.
Dahong, Z. M. (1991). Rehabilitation in China. The Western Journal of Medicine , 154 (5).
Gallegos, J. S., Tindall, C., & Gallegos, S. A. (2008). The Need for Advancement in the Conceptualization of Cultural Competence. ASW , 9 (1).
General Information of the People’s Republic of China (PRC). (n.d). Web.
HAWCC. (n.d). Chinese Cultural Beliefs. Web.
Hays, J. (2008). Early Economic History in China. Web.
Hu, G., & Yu, Z. (n.d). Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in China pp. 203-218. Web.
Index-China. (2009). Science and Education. Web.
Inhorn, M. C., & Balen, F. V. (2002). Infertility around the globe: new thinking on childlessness, gender, and reproductive technologies. California: University of California Press.
Issues and Trends in China’s Demographic History. (2009). Web.
Karvounis, N. (2008). China’s Health Care System. Web.
Keping, Y. (n.d). Globalization and Autonomy in China. Web.
Kwintessential. (n.d). China – Language, Culture, Customs and Etiquette. Web.
Kwok, C.-K., Au, W. T., & Ho, C. M. (2005). Normative Controls and Self-Reported Counterproductive Behavior in the Workplace in China. Applied Psychology: An International Review , 54 (4), 456-475.
Learn Chinese. (n.d). Web.
Lin, A. (2001, September). Exploring Sources of Life Meaning Among Chinese. Web.
Liu, G. Z. (2001). Chinese Culture and Disability: Information for U.S. Service Providers. Web.
MedicineNet. (2004). Definition of Postpartum. Web.
Pain. (n.d). Web.
Paulnoll. (n.d). Chinese Nationalities and Their Populations. Web.
Personal Ceremonies: Funerals. (n.d). Web.
Population Control Programs. (n.d). Web.
PubMed. (1996). Health care delivery system and major health issues in China. Web.
Purnell, L. (2002). The Purnell Model for Cultural Competence. Web.
Ramzy, A. (2006). Language Barriers. Web.
Religion in China. (n.d). Web.
Severstal. (2010). Heritage and Achievements. Web.
Shapir, M. E. (n.d). China. Asian Culture Brief , 2 (2).
Simmons, S. (1999). Multicultural Interview – Grief in the Chinese Culture. Web.
Smoking ‘will kill one third of young Chinese men’. (2001). Web.
Spoken Chinese. (n.d). Web.
Tan, J. (n.d). Genetic relationship of populations in China. Web.
The Purnell Model for Cultural Competence. (n.d). Web.
TheLancet. (2008). Government policy and organ transplantation in China. Web.
Thornton, G. (2005). The China Vision: Opportunities and Challenges for U.S. Manufacturers. Web.
Times Online. (2005). China wins war on hunger after 25 years of UN aid. Web.
U.S State. (2011). Background Note: China. Web.
US-China Life Style. (2010). Web.
Vaughn, F. (n.d). Community Health based on Purnell’s Model. Web.
Wang, J. (2004). Workforce Education and Development Systems in the People’s Republic of China. In J. W. Rojewski, International perspectives on workforce education and development (p. 67). IAP.
Wiley. (2008). Abstract. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 1141 (1).
Wong, G. (2011). Anti-Smoking Push Not Enough To Fight China’s Tobacco Addiction. Web.
WSMI. (n.d). Responsible Self-Care and Self-Medication. Web.
Wu, S. (n.d). Tai Ji Quan. Web.
Wu, X. (2006). The impact of Ethnic Identity on student achievment in China: A meta analysis. Web.
Xu, A., Xie, X., Lin, W., Xia, Y., & Liu, D. (2007). Child, Youth, and Family Studies, Department of Faculty Publications of Child, Youth and Family Studies. Web.
Yanhai, W. (2011). The Madness of China’s Mental Health System. Web.
Zhang, K., & Li D, L. M. (1996). Health care delivery system and major health issues in China. Web.