Unemployment problem is rising in most parts of the world. Economic crisis and spiraling prices, in an age of cost cut and job cuts, unemployment is on the rise. Similar case has been noted in Spain where the unemployment rate has reached a 15-year high (Brat, 2011).
The article discussed in the essay was published in Wall Street Journal in October 2011 (Brat, 2011). The article used for the essay is an online version of the printed newspaper. The aim of the paper is to summarize the article on unemployment and establish a connection between the article and the economic theories unemployment.
The article reports the increase of unemployment rate in Spain and the situation it has created for the unemployed people. Spain’s government spending has reduced greatly that has reduced the unemployment benefit given to the employed families. However, due to building pressure from international financial organizations to reduce budget deficit, the government was compelled to reduce its spending that subsequently reduced the unemployment benefits.
One main reason cited in the article for this 15-year high unemployment situation is due to three-year-old economic crisis that has left a high unemployment rate in Spain. In order to face the situation Spanish government has decided to boost up spending on job development. However, this may rise to increasing cuts in many areas, especially when the Euro zone is trying to reduce the spiraling debt situation.
The unemployment situation in Spain has become so dire that food assistance has to be increased. Many people are homeless, are moving to shelters, and have no money for food. The unemployment benefits are drying up for many and they are still unable to attain jobs. In such a situation, what economic reforms must be undertaken by the government that would bring forth a possible solution to the problem of unemployment in the country?
The Spanish unemployment demonstrates a job cut situation due to shrinking economic growth and recession. As the economic crisis has been looming over the country for almost 3 years, there has been a lack of economic growth and spiraling prices i.e. increasing inflation raises the rate of unemployment in the economy.
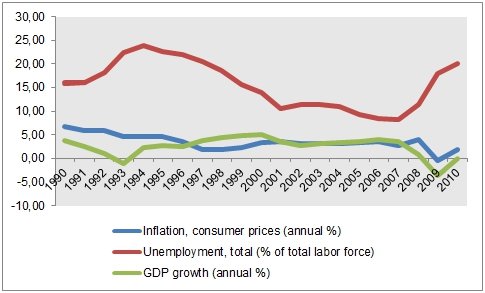
Figure 1: 20 year data on GDP growth, Unemployment rate, and Inflation in Spain. Source World Bank Databank (World Bank, 2011)
Figure 1 shows that the unemployment rate, GDP growth and inflation in Spain since 1990 through 2010. For the last 20 years unemployment rate is found to have a similar trend as the of inflation and GDP growth. In other words, as there is a decline in GDP growth, there is an increase in unemployment rate as is observed in 1993, 2002, and then again in 2009.
The figure shows that there is a continuous rise in unemployment rate since 2007 and it has reached the highest in 2010, supporting the observations in the article. Economic crisis in Spain is evident as there is a continuous decline in GDP growth in the country since 2007. This demonstrates that unemployment rate as a negative relation with GDP growth.
When the latter declines, the former increases and vice versa. This supports the argument put forth by Keynes that due to lack of economic growth, there is a decline in aggregate demand in the economy, which therefore, declines demand for labor, thus creating unemployment. Rise in inflation increases the cost of production that induces a decline in production, which in turn reduces labor requirement, therefore increasing unemployment. This is what has happened in Spain.
References
Brat, I. (2011, October 29). Benefits Run Out for Spain’s Jobless. Retrieved from The Wall Street Journal: https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424052970204505304577003864242042958
World Bank. (2011, November). World Development Indicators and Global Development Finance. Retrieved from World Bank Databank: https://databank.worldbank.org/data/home.aspx