Abstract
The conversion of innovative business ideas and concepts to provide customer-centric healthcare services based on a technology-driven business model is multidisciplinary. The model is customer-focused and provides the user with the ability and flexibility to use interactive web-based technology that is interoperable and reaches a wide span of audience, and market. The technology-driven business model provides customer-focused solutions to problems that remain effective and enduring with a cost-effective approach. That enables the use of virtual personal medical assistant services. However, the web-based business model is developed with salient issues in mind. These include providing the customer with the capability to manage his or her own health while creating a service provision environment focused on locking in the customer based on customer satisfaction. In addition, it is crucial to customize the application based on the user environment with a multicultural mindset as the services are hosted on the internet. The model represents a radical departure from the product-based to service-oriented business model by factoring transitional concepts to enable transition into a service-oriented enterprise. Thus, the transition is technology-enabled, based on the identification of opportunities, threats, and marketing principles.
Introduction
The purpose of the study is to design and develop a technology-driven business model that is customer-focused to address their medical needs and expectations while providing them with the ability to self-manage their personal health in a virtualized environment. The strategy is multidisciplinary and reflects on the needs of the patient and the success of the healthcare business in offering customer-focused services. To attain that purpose and goal, the model is defined by technology and market-oriented concepts to address the healthcare and insurance need of the customer based on the business model. It ultimately addresses the healthcare needs of the patient in the healthcare industry by engaging them in new and proactive ways to stimulate interest, loyalty, and commitment toward the use of the business model. Such loyalties, commitments, and interests ultimately generate financial growth for the service provider firm. However, toward the attainment of the purpose for setting up the model, a number of assumptions that include the capabilities associated with the interactive use of technology, business growth capabilities, readily available technology platforms, active involvement of the customer, and risks cannot impede the development and full implementation of the model.
On the other hand, thought it might be difficult to provide realistic estimates of the size of the industry, yet research shows its dynamism in growth and expansion as an underlying rationale to invest in the industry with projections on a positive return on investment, based on project appraisal concepts. However, the size of the current and proposed technology-driven, the growth rate, and the industry outlook provide, based on available literature to support the idea as an investment success. On the other hand, projections show the customer base to increase from the local market and international market as it is a web-based model, therefore, with well designed and developed features and other system requirements tailored to address industry needs, the direction of growth might be spontaneous once it is launched and not localized. The strategy draws on customer involvement in the development of products and services tailored and customized to address their needs in the industry. However, it is not possible to understand the needs of the customer except by conducting research and implementing other business-oriented approaches to attain the ultimate goal of understanding the customer to customize products and services to address the customer needs.
Business/Service Unit Strategy
Mission
Committed to the provision of personal health based on a technology-driven business model.
Vision
To be an excellent provider of healthcare cost-effective services that are long term.
Objectives
To identify technology-centered business models for growth and expansion.
To identify strategies for the organization to adopt in shifting from product-based to service-oriented business model.
To formulate service alignment and integration approaches unto the business model
Value statement
To provide healthcare service across different cultures while valuing their cultures, beliefs, and race.
The Strategy
One of the strategic approaches of addressing customer needs in self-management of personal health care using the virtual personal medical assistant service is for a firm to identify a business model that captures and translates customer needs into production rules appropriately interpreted using technology. Typically, the business model focuses on growth and expansion based on the customer-centric business goals of the firm. Empirical evidence provides a number of options to tailor to fit into the business models, which is descriptive and reflective of a technology-based business model that facilitates growth and expansion in the target market.
The proposed model for such growth and expansion is based on web-based technologies. That in part is due to the rapid expansion and growth in web-based technologies which can be adopted and integrated into the service provision industry in the provision of health care services to enable the customer to manage their own health. Web-based technologies adopt the concept of the internet due to capabilities and speeds associated with the internet to enable the re-engineering of health care service provision while facilitating its growth and expansion. Growth, expansion, technology, and customer focus constitute the underlying concepts of the business model to address the current study (Anderson, De Dreu, & Nijstad, 2004).
It is worth noting that the current approach of integrating technology into the healthcare system provides patients with the capability to manage their health care when integrated into devices that provide the patient with the connectivity and the services required to interact with the system. In addition to that, web-based technologies provide a platform for service providers in the business industry to reach a wider and growing audience. On the other hand, web-based technologies provide an environment for service providers to leverage existing business lines while enhancing the traditional services into new technology-based services.
One of the requirements of the service provision industry is the technological characteristics of web-based technology. It is crucial that the technology be characteristically real-time, be available to fulfill services requirements, be able to comprehend and synthesize spoken languages and provide appropriate answers to problems, able to understand the intention of the user, enable collaborative problem solving for the user, have a knowledge base, and enable the use of web-based technology-driven devices. The devices used in the industry in the provision of the services should be characteristically flexible to use and available at all times, not only to the professional offering the services, but available for the patient to comprehend the type of services offered on that model. In that case, the interests of the patient and the industry are worth accounting for (Allen, Byron, Dzikovska, Ferguson, Galescu & Stent, 2000).
Therefore, it shows a radical departure from the previous views that technology was only for professionals. However, based on the model that integrates web-based technologies into the provision of healthcare services, there is a radical shift from the reliance on professionals in the administration of services to the casual user of the technology. However, there is a significant demand for the use of technology in value addition to address the market needs, therefore facilitate growth and expansion in the service industry business.
Typically, the architecture of the web-based applications integrated into the business model in healthcare services provider is defined as an enterprise-oriented architecture. Typically, the architecture addresses industry needs by consolidating the healthcare service industry vertically while addressing the dynamic nature of the market and the evolving customer needs. Typically, the business model should integrate technology that constitutes a complex software stack and other business applications that support self-contained devices, which can be reused to address the healthcare needs of the patient (Shapiro & Posner, 1979).
Once such a business model is in place, it will provide the users and the business service providers with the ability to offer their services on a platform that affords flexibility and interoperability. It will also provide the organization with the flexibility to tailor its services into long-running business processes that span a wide and growing market segment, thus, fostering growth and expansion.
The motivation behind the model will be to provide the customer and the service provider with navigational capabilities. Navigational capabilities provide the person in need of healthcare service to navigate to the required services and link to semantic service details. Thus, the services offered on the technology designed with the underlying concepts should focus on the business in relation to its performance in terms of growth and expansion, the customer in relation to accessing services offered on that platform, and other crucial elements in the business model.
It is also critical to understand that accessing the market is also a crucial challenge. Typically, that is because the current approach used by the customer to search for services is by the use of keywords. Keywords provide the customer with the ability to access information based on the search results. Such approaches, however, are recommended for information domains that are tightly coupled and the search results are predictable. However, when services are provided on wide domains, there is the problem of transforming the search paradigm to an automatic intelligent centric paradigm. Typically, that calls for the exploitation of metadata and ontology-based searches, which span machine-readable presentations.
There is also the challenge of addressing the evolving environment where humans are replaced by computers. Although that is reflective of the changing trend in the service provision industry, where computers replace services and tasks, such a business model will require a complex network of computers and related infrastructure. Therefore, the underlying driver to the successful implementation of the business strategy is to understand comprehensibly the business needs of the customer, customer expectations, and the flexibility of the technology in addressing customer needs and expectations (Sheth, 1994).
Another underlying factor to consider when setting up such a technology-based business model in the service industry is the trust and assurances the customer gets from the use of such technologies in the provision of services in the healthcare service industry. The technology should reflect the expectations of the customer in relation to the obligations set at the service level. Here the customer is guaranteed of the services and their qualities, which are critically indefinable with a lot of risks and uncertainties. Thus, there is a need to understand and evaluate the services whether they correspond to the conditions of the prevailing business environment while addressing the need for quality.
Other factors to consider in developing and implementing the business include user-based interactions. Web-based applications function on machine interactions with the customer and the application in a harmonious manner. When such functionality is not attained, there is a high probability of failure and diminishing market size, and poor growth and expansion forecasts. In addition to that, the underlying infrastructure supporting the web-based technology adds a lot of application logic which requires monitoring of business processes that demand workplace health, environmental conservation, and emissions of carbon dioxide to mention a few. Thus, it is critical to consider all these when designing and implementing the technology-based service provider of the business model with the view to integrating the capabilities to enable the customer to take control of the service provisions.
Evolving product-based organizations into service-oriented enterprises is a strategy that addresses the current business strategy. That is an approach to attain the mission and vision statements in the business model and attain the business objectives for the service provider firm. Typically, therefore, to integrate the concept of evolving product-based organizations into service-oriented enterprises draws on the evolving trends in the market today. The underlying principles of the proposed model provide a baseline for a radical shift from product-oriented to service-oriented enterprise. Thus, the model is a technology business based model that is based on the World Wide Web, and other interactive technology devices, which are designed to address customer needs in taking control of their health management. This should focus on the customer, the service industry, and the need for the organization to grow and expand (Teece, Pisano & Shuen, 1997).
It is crucial to note that clients want services that are delivered professionally and at cost-effectiveness to allow for growth and expansion by targeting large market segments. While cost is one of the underlying components when shifting from product-based to the service-based business model, is crucial to consider the underlying paradigm to adopt in the change strategy (Chaudhry, 2006).
One of the approaches is to differentiate products and services through the services offered on the current business model. Thus, that enables the organization to shift toward service-based enterprises by offering better and competitive services, while pricing the services to remain competitive. The firm uses its technical competency to shift toward the attainment of the new goals and shift to a service-based approach of offering services by exploiting the current and evolving technologies. These technologies are composed of components with their own standards and templates that need to be developed and made integral to the business firm in the provision of services. To attain the goal of shifting from product-based to service-oriented applications, there is a need for organizational managers to consider various issues. That is because a number of firms have taken into account such approaches and outperformed in the market.
Evolving the Business
The first approach is to start building the firm and shifting from the use of solid components and assets in shifting from product-based to service-based enterprises. One of the underlying facts about the mentioned approach is for the current firm to conduct market intelligence research, gather information, and gain knowledge about the customer base and their needs. It is important to note that superior knowledge of the customer is crucial for the design and development of a service industry that shifts from product-based to service-based architecture. The underlying platform, in this case, is technology, leading to the conclusion that technology plays a crucial role in the development of the enterprise.
Another crucial fact to consider in this case is the proximity of the customer to the services. Typically, the current model is web-based and access to services provided by any firm on the models is based on access to the internet and the use of applications that enable interaction between the computer and other devices used in offering services to the customer.
One process has been set and firms have acquired sufficient knowledge on the customers and identified the technology platform upon, which the services are to be offered, and the interactive devices to use, then the firm now shifts to setting up the services offered on the firm as separate units. The rationale for setting up the units as different units is to establish distinctive growth and expansion with the underlying principle of a service-oriented architecture. In addition to that, it inculcates a service-oriented culture in the growth path. At this point, the firm, the firm establishes product neutrality. It is crucial for the firm to establish a frontline or set up an innovative approach to delivery-focused services by the firm. It is also crucial at this point to integrate the use of professionals in offering the services tailored on technology-based platforms. While the evolution process continues, it is important for the firm to develop new skills and professionals for offering services and address the innovation of product to services offered by the firm. It is at this point that the firm rapidly grows and scales to capture a larger market share in the delivery and provision of services in the healthcare industry. Thus, the movement from the product-based to the service-based enterprise is attained by adopting both the technology-based model and the shift from product to the service-oriented business model.
The integration of and the aligning of goods, services, and solution strategies to the current technology-based business model enable the organization to attain the ultimate business service strategy. The integration of the goods, services, and solutions is based on the shift mentioned above where the organization concentrates on extensive gathering and combination of necessary skills and collaborating with other firms that offer certain services. These include technology firms that provide the infrastructure, identifying the range of customers with their needs, and rapidly evolving from the current to the next level in service provision.
Once the organization has shifted to the current approach of offering services, the firm has to seek highly qualified personnel with service-oriented expertise to offer highly specialized services. That enables the organization to evolve irrespective of the state in which it is.
Developing and managing services-goods portfolio becomes a crucial component in the attainment of the business unit strategy based on the management concepts developed based on the new and evolving requirements of the firm. It enables the firm to develop its products in the market based on the use of available technology infrastructure and other interactive technologies. It is a transformative strategy into a new service-oriented enterprise and there is a crucial requirement that it develops a portfolio by prioritizing the project and allocating resources such as expertise across the firm. To attain the unit business strategy by developing and managing a services-goods portfolio, it is crucial that the approach be characterized by optimizing the value of the project. That enables the management to ensure that the right balance between services and products offered by the service provider firm is balanced, aligning the portfolio strategy of the firm with the business unit strategy and the development of a services-goods portfolio. However, the use of web-based applications provides the underlying support for the organization to achieve portfolio development (Mandel, 1997).
In portfolio development, it is crucial to address the development of services and products and amalgamates the provision of services and products in a balanced approach while using the available technologies and platforms. Typically, one of the approaches is to determine the current project’s products net present value, and assign constrained resources to address the service provision and product development, evaluate the expected commercial value of the products and services, decision rate the undertaking, and address other developing needs in the products and services industry. Once all the elements in the strategy are attained, the firm shifts into the next strategy of globalization.
New or Enhanced Service Strategy
Mission
Dedicated to offering user-centric healthcare services to enable the customer to manage their personal health on web-based real-time intelligent applications by use of the virtual personal medical assistant in collaboration with well-skilled medical personnel.
Vision
To be an excellent customer-centric technology-based healthcare business model that factors modern technology to enable the customer to be responsible for their healthcare management.
Objectives
To design, develop, and implement a customer-centric technology-based business model for the provision of healthcare services.
To identify underlying technology requirements and business concepts to design, develop, and implement the business model.
To examine the security related issues and techniques to implement security associated with web-based applications.
Value statement
To provide healthcare service that reflects the needs and understanding of healthcare needs across different cultures, beliefs, and races.
Definition of Service Strategy
Services strategy is a service management approach for converting innovative ideas and concepts to provide cost-effective durable solutions to problems under controlled costs to create value and successfully seize upon existing opportunities in the provision of services.
Global aspects/international strategies
Globalizing a service organization’s culture across different countries is one of the approaches to be adopted by the firm in the healthcare service industry. One of the characterizing features that allow the firm to go global is the platform that it uses to provide services. Typically, the model adopted is web-based with the appropriate devices that allow for the interactive provision of automated services. Typically, the rationale is to provide healthcare services across a wide market segment to increase the customer base, increase, and sustain profits for the firm. Profits are crucial for the growth and sustained existence of a firm, as is the case of the current business. However, the current business is unique in that the customers are required to take control of their healthcare management based on the use of technologies. The current business model is the provision of healthcare services on web-based technologies with the internet and the underlying infrastructure support.
However, there are a number of issues associated with globalization. These include strategies to globalize the firm across different cultures and market the services across the cultural divides. Salient issues to consider include identifying the salient features of different cultures in different countries, differentiating between culture and nationality and amalgamating the two into a single whole, evaluating and distinguishing between culture and competence, and endeavoring to understand the culture and social representations when designing the healthcare services offered on the internet technology. It is important to understand and establish the cultural dynamics of different audiences that the firm intends to offer healthcare services. In addition to that, the model should integrate the cultural mindset of different customers by considering the feelings of others. In addition to that, the model should factor the cultural assumptions of different nationalities and their values. Among the underlying factors to consider when marketing across cultures are the cultural feelings, the thinking, and actions of others and the reactions from such actions (Yip & Madsen, 1996).
Once the underlying cultural concepts have been developed, it is important to identify the consumer behavior across cultures and the influence culture has on the consumption of certain products and services. The model should focus on how the consumer behavior concepts can be applied in the models targeting a wide audience of consumers, ethnic-based consumptions, and the meaning associated with marketing as a means to deliver messages to customers (Woolliams & Trompenaars, n.d).
Other factors to consider include the ability to recognize different explicit cultural differences to ensure the strategy and model addresses the differences. Typically, that is because one might never be aware of informed of the implicit cultural differences that might prevail in cultures and within cultures. It is therefore important to factor in cultural differences when going into the global market to market healthcare products and services. It is crucial to different people and their backgrounds and their values and beliefs. That is because different customers have different ways of interpreting the world. However, different views by different customers might be divergent, thus, it becomes necessary at that stage to reconcile the opposing differences that might appear. It therefore should be an amalgamation of global branding that gives the customer a local touch.
In going into the international market to seek customers, it is critical to tailor the products and services to address ever-changing customer needs and behavior. In addition to that, the products, once on the web-based applications can be accessed globally, therefore, it becomes all too important to examine different issues such as the degree of involvement of the customer. In this case, the level of involvement of the customer is crucially important since it is a healthcare business model that allows the customer to take control and manage their healthcare based on technology. It is an automated approach where the customers use computerized devices to address their healthcare needs and take full control of it in consultation with experts (Allen, Ferguson & Stent, n.d).
Business Model Enhancements
The proposed model’s underlying concept is that it is web-based. However, the model, in view of globalization, cultural aspects, and the ever-changing business needs of customer behaviors, and the dynamic business environment, demands that the web-based model be enhanced to accommodate new and dynamic business trends in the healthcare service industry. One of the best approaches to enhancing the business model is to incorporate technologies that enhance interactive use. One such approach to enhance the business model is to integrate into the web-based business model a conversational system to enable the systems to interact with the customer and the service provider. Thus, from being a web-based with only simple features integrated into the web sites, into a conversational system that is a virtual personal medical assistant service (Allen, Ferguson & Stent, n.d). The virtual personal medical assistant service should integrate features that enable the user to interact with the system. It should also be easy to use and be affordable. That is also because different users hail from different economic backgrounds and different countries suffer from different economic hardships and levels of income (Ferguson et al., 2002).
The systems should be characterized such that can allow for the collaborative use of the applications in the web-based model. The architecture of the proposed model should appear as presented in fig 1below.
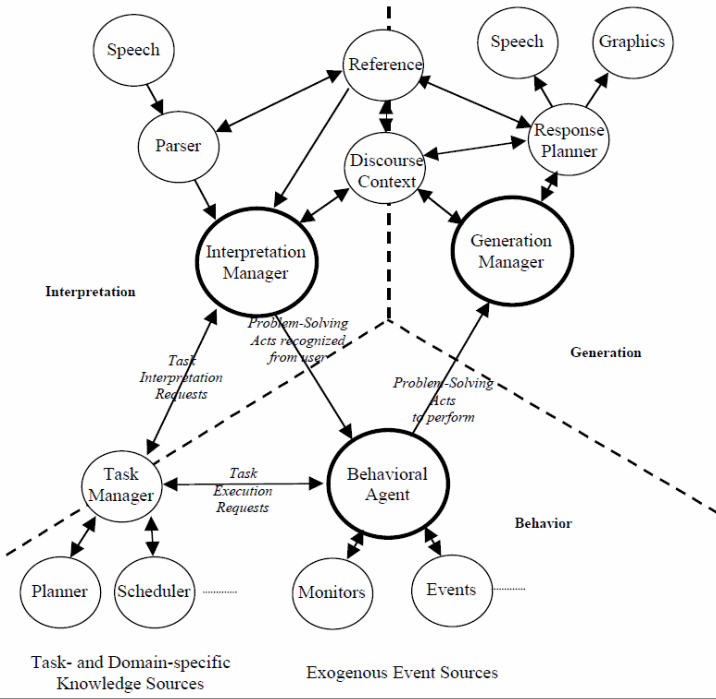
According to the above figure, a number of applications interactively play the role to provide healthcare consultancy services to the customer. Thus, an enhancement of the previous web-based model into a speech recognition application improves communication and capabilities in the provision of healthcare services to the customer. Typically, the enhanced system consists of components classified into three. These include the interpretation component that provides the user with the ability to start a dialogue with the system. On the other hand, there is the behavior component that provides the customer with the ability to negotiate their problems with the application, while the application considers various diagnostic approaches to solving the problem of the patient (Allen, Ferguson & Stent, n.d).
The goal is to design, develop, and integrate web-based applications that approach the performance of the human being in the provision of healthcare services while ensuring that the customer takes management of the healthcare services they are provided.
Therefore, the model is able to capture and use dialogue as a tool to communicate with the customer in the provision of services and is a unique characteristic integrated into the model to enable the patient, the doctor, and the application engages in a cooperative dialogue with the ultimate goal of providing the services to the customer (Allen, Ferguson & Stent, n.d).
It should also be convenient to provide the application across different hardware and software platforms to enable interactive use of the applications and ensure that the user is can acquire the services on different technology domains. It is crucial for successful provision of the services that the application be able to clearly interpret the content of user input, provide abilities to maintain the content of user discourse, enable the customer and the healthcare professional to provide appropriate plans for the content and enable the customer to manage their problems effectively (Allen, Ferguson & Stent, n.d).
It is critical to briefly discuss the system architecture that enables it to attain the ultimate goal of providing the customer with virtual healthcare services. In principle, the system consists of diverse information that enables the application to support and interpret anaphoric expressions, to support the acquisition of interpretations of input information for the expert and the patient to be engaged meaningfully, thus supporting ellipsis resolutions and provide further clarifications.
Thus, the main components in the architecture of the system to fulfill the ultimate goal of the application include the task manager, which performs tasks such as answering the queries of the customer and provides an interactive environment for the fulfillment of problem solutions. Another component is the generation manager. This component is used to perform content planning and addresses problem-solving of specific problems. It plans and captures the discourse and inputs and transforms the inputs to enable discourse contributions (Cohen & Oviatt,1995).
The behavioral agent provides an environment for solving behavioral problems associated with customer problems in the healthcare provisions. Typically, that is based on interpreting user utterances in relation to the problems presented by the customer using the interpretation manager. The agent makes other intelligent applications become aware of the problem to be solved and interactively provide a solution to the problem. The current application enhancement is to address business opportunities that arise from the use of technology in the provision of healthcare services to the customer and allow the customer to take control of their healthcare services.
Business Problem or Opportunity Being Address
The opportunities to address include the ability to address the need for the customer to manage their healthcare by use of technology based on the use of a virtual personal medical assistant service. It is a new industry requiring a shift from the product-based to the service-based approach. It is a new industry that is growing based on functionality, flexibility, and development, if new technologies are integrated into business models.
Risk Factors
However, a number of risk factors associated with the use of the business model that integrates the use of web-based applications, which are enhanced with conversational systems are bound to be experienced. The risks can either be internal or external to the organization or target the customer. In addition to that, the risks might be related to the weaknesses associated with the use of technology in providing medical services to the customer. Such uncertainties are crucial since they can account for a significant percentage of customers to fail to use the technology in service provisions. Typically, these can either translate to financial or strategic risks besides being associated with the needs of the customer.
Other risks associated with the use of web-based applications and associated technologies are risks associated with the interdependencies of information systems, the risk associated with the security of applications such as intrusion into the privacy of the patient, problems associated with auditing the financial transactions on the technology-based business model, and other risks such as poor password control. In addition to that, it is crucial information integrity be maintained, services should be made available when needed, ensure that data transmission, transactions, and communication documents and applications be authentic and reliable. It is important that the business model be integrated with applications that support confidentiality in the integrity of information to ensure information is made available to the appropriate person. Other issues to consider include the utility of the system and able to identify potential threats and address them appropriately.
Creating and Maintaining A Service Culture
Creating and Maintaining a service culture within the new healthcare firm is one of the strategies that ensuring success. That is based on a number of paradigms that reflect the type of firm in the industry. Firms strive to maintain their position in the market; strive to gain a large customer base, endeavor in their business transactions to increase and sustain profits, and endeavor to enhance performance and gain a strong foothold on profits to sustain the performance of a firm (Jackson & López, 1999).
In view of the current healthcare services provision, it is important for organizations to create a culture for the provision of services within the industry to enable customers to benefit from such services. Among the approaches to adopt include ensuring that customer messages are tailored to be consistent and should be well defined to target the specific services offered by the firm. Another approach is to ensure that the message communicated to the customer reflects the mission and vision statements of the firm (Davis & Donald, 1997).
It is important for the upper management of the firm to be fully involved and provide support in creating a service culture in the firm. Management support for the creation and support of the service culture should identify the messages communicated across the firm and ensure there is a consistency of the message and meaning or content. However, there should be standards set by the management to create and enforce cultural competence in the healthcare firm.
The standard set includes ethics and values for the firm’s employees to function according to them and provide the professionals with values to adhere to. That enables conflict resolutions based on established standards, enabling the service provider to accommodate the views of others. It is also important to ensure that professional workers develop their own values to enable them to engage customers in a proactive manner to retrain them and create a better image of the firm. It also enables the service providers to develop a customer-tailored toward hearing the voice of the customer by appreciating the importance of working in a multicultural environment (Gibelman & Schervish, 1997).
Once the professional and other organizational employees become aware of themselves, it is crucial for them to develop sustainably cross-cultural knowledge by integrating the component of family systems, traditions, and other expressions in the service delivery environment. It is important for the management to equip their employees with cross-cultural skills to be able to handle people from different cultural backgrounds. However, there is also a need to integrate the entire aspect of service delivery by being trained and acquiring expertise on the use of technology in service delivery. In order to inculcate culture into the employee, there is a need to consider the educational qualifications of the employee and ensure competence in offering healthcare services on the web-based applications. Typically, therefore the process requirements for creating and maintaining a service culture to be used to reflect the above standards include CRM process requirements.
The CRM process requirements are detailed in diagram two shown below. Each of the elements in the process reflects the above descriptive approach of creating and integrating culture into the newly transformed healthcare service provider.
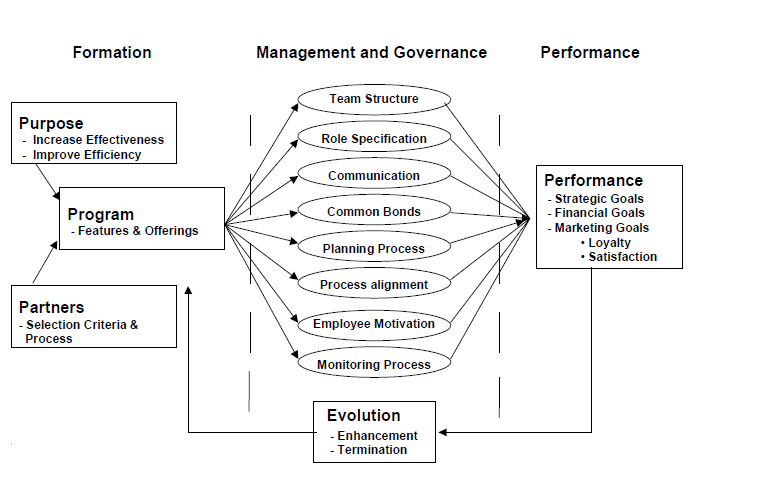
The model reflects the entire structure of the organization and the phases that are involved in the acquisition and interaction process of the service culture. The key areas include the formation stage in the process where the organization as a whole makes decisions to initiate cultural creation and integration activities. Typically, that focuses on the type of customers or a specific group of customers that can use the web-based services in the acquisition of healthcare services. It is at this stage that the firm identifies its customers and differentiates them in regard to the services each customer needs. Identifying and differentiating customers is an intensive marketing strategy that borrows from different fields including market intelligence information. Once the customers have been identified and differentiated, it then is the dusty of the professional and the marketers to develop services that are tailored to address the needs of the target customer who uses or is intended to use web-based applications in the acquisition of healthcare services (Lynch & Horton, 1999).
The elements constituted in the formation stage in the CRM process include the overall purpose of the system, approaches to increase effectiveness and efficiency such as integrating the enhanced applications such as conversational applications in the delivery of services. In addition to that, the formation phase program features are developed that enable the provision of healthcare services to enable the customer by focusing on customer needs and emerging market trends. In addition, the above elements it is crucial to factor collaborative issue of collaborating with others either in the market or on the use of technology. The partnership created with other players in the industry follows specific selection criteria for the collaborating parties and the services and functionalities of each of the applications. It is important to establish operational goals, be specific in their implementation, and streamline the operations in line with the business strategy of the current firm. Therefore, collaborating with other firms that [provide value addition to the current firm is crucial in a competitive playing field (Parvatiyar & Sheth, 2001).
It is critical to establish a management and governance structure that supports the implementation of the healthcare business in the current industry. That should be reflected in a team structure that works toward the attainment of organizational goals and objectives and enables the customer to be in charge of their healthcare management while being able to provide the required services in the healthcare service industry. Under the management structure, the roles specific to the tasks performed by each of the employees are defined and tailored toward attaining organizational efficiency and success. That is because customers want to meet effectiveness and efficiency in the acquisition of services. Thus, role specifications, communication strategies within the organization, the common bonds established between organizational employees, the customer, and the organization itself facilitate the provision of services in an effective and efficient manner and in relation to customer needs and expectations.
All the CRM processes are tailored to address performance to attain effectiveness and effectiveness in service delivery while ensuring that customer needs and expectations are kept in mind. Typically, the CRM process’ outcome is effectiveness and efficiency in the attainment of strategic goals of the firm, the attainment of financial goals, and the attainment of marketing goals.
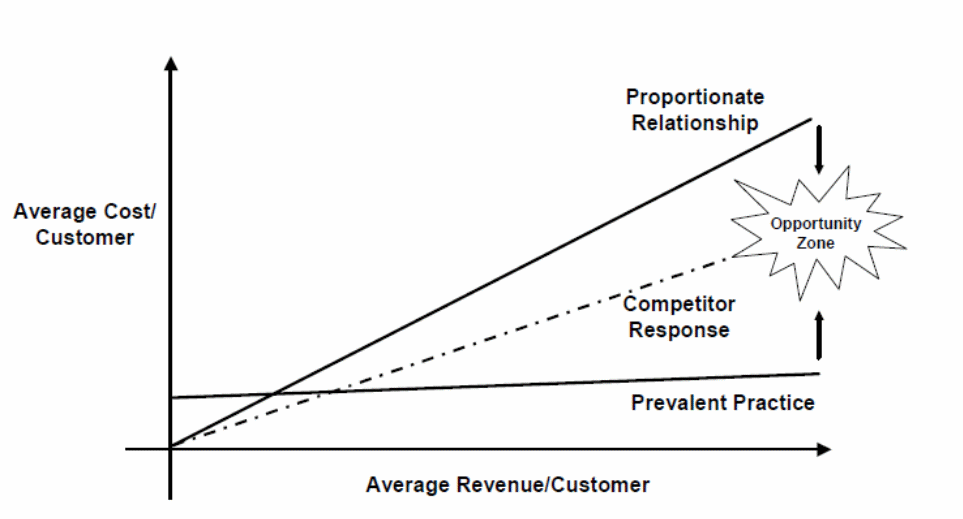
However, the type of model to implement in the current strategy should reflect the healthcare provisions and address the goals to enable the customer to attain a virtual personal medical assistant service and be in control of their healthcare management. There are variations in the models to adopt but after a thorough investigation of the models and their appropriateness in fitting into the technology-based business model. The factors to consider include opportunities, the cost of services and the cost of setting up the firm, average customer revenue while bearing in mind the business model is based on the internet, prevailing industry practices, and competitors, provides the underlying rationale to select a specific model as shown in figure three below.
However, it is critical to consider other issues as detailed in figure four below.
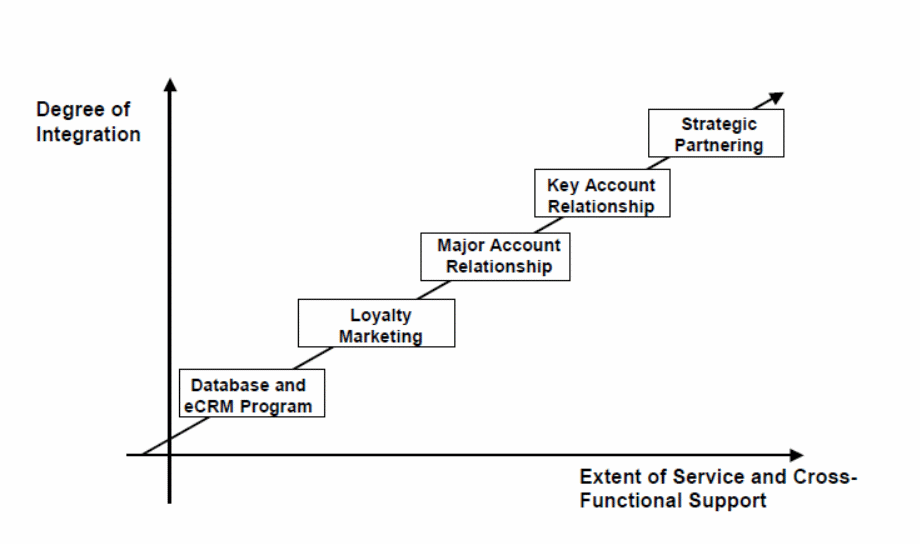
It is shown in the above figure the degree of integration of the applications into the web-based business model and the extent of services provisioned based on the business model. Typically, there should be integral components such as marketing, accounting, and strategic partnering among other components involved in the process.
Developing a service mind-set (in the service-focused organization) becomes crucial at this stage. That could be based on the shift from a product-based firm to a service-oriented enterprise. However, such development is highlighted in the above paper.
Keeping a service focus as an organization grows, matures, and changes become the approach that is adopted by an organization. It is critical to understand that the lifecycle of an organization is to grow, age and at times some organizations diminish and die out. It is critical that the management factors a strategy that maintains the organization at a level that does not threaten its growth, expansion, and sustainability to stay and retain its position in the market. It is therefore critical at this stage for the firm to identify suppliers and key alliances to sustain the business operation. That is especially the case as the firm keeps the focus on the provision of services while moving away from being product based.
Suppliers play a significant role in ensuring that the products and services reach the customer in a timely and appropriate manner. Suppliers integrated into the business model should be characterized by the ability to add value to the healthcare provision of services. That strategy is attained by value into the organizational service provisions, ensure and integrate value creation in the supply chain, and have the potential to create value in the provision of services to ensure a smooth and value-based transition from the product based to value-based approach in the provision of healthcare services (Spekman, 1988).
It is crucial for the supplier to integrate the concept of value creation by focusing on the direct value functions such as enhancing and sustaining profits, which is related directly to the direct revenue generation from the customer. In addition to that, it is crucial to focus and evaluate the volume of business generated by the customer as a volume function. In addition to that, the contractual agreement entered into with different suppliers and the healthcare enterprise. However, it is crucial to consider the indirect value function by focusing on the ability of the supplier to provide innovative services and products that address the current and changing needs of the customer, in addition to addressing different customer needs and expectations in different environments. In addition to that, the supplier should be concerned with the market function by accruing new customers. However, it is crucial that the supplier be constantly concerned with acquiring market intelligence reports to be kept constantly updated on the supply in product and service qualities in relation to dynamically changing market needs.
Sometimes customers might decide to concentrate their procurements on a particular supplier or through a linkage of other providers in the market with the intention to minimize the cost of products and services offered by a specific firm. It is crucial to note that when suppliers provide standard prices for their products, they are better placed to compete with others in the same industry. The potential to add value to the products and services they have to offer, based on a model that factors in the components of supplier efficiency functions, supplier network function, and supplier effectiveness, which is aggregated into the supplier value creation potential. In effect, that becomes supportive of the strategy to shift from a product-based to a service-based enterprise.
Alliances form the underlying component in the marketing of the healthcare provision firm. Strategic alliances determine the level of success of a firm and are based on the quality and competence of the parties involved in the business alliance. Competent alliances provide a way in which collaborations are done in working toward a common goal. Strong alliances provide the synergy needed in a competitive environment leading to higher revenue generations in a global environment. Typically, the goal of the alliance is to increase profits, the quality of services, and minimize the risks associated with investing in a technology-related business environment. Here the healthcare technology-based business strategically leads to the reduction of cost of doing business, enhances service provision, product development, and delivery. Alliances accommodate diversity, lead to the growth and expansion of the market, enhances and leads to market penetration, improves the position of the current firm in the domestic and global market, and enable a firm to concentrate on its core business without diversifying to other areas.
Professional Assessment for CR with Providers & Doctors
Identifying drivers of sustained new service success forms the underlying principle upon which the success of the current business thrives. Success in the provision of services is based on the professional competence of the doctor and the customer relationship with providers of healthcare services. Typically, the patient-doctor relationship and the relationship developed with the customer by the service provider play a significant and cumulative role in customer satisfaction which is key to increasing the customer-based and leading to customer satisfaction. Such a relationship is the underlying factor that forms the basis for modern contemporary ethics. Typically, that is driven by keeping and upholding the patient’s integrity and respecting the privacy of the patient (Shamdasani & Sheth, 1995).
However, the strengths and weaknesses associated with the business in view of the patient needs and expectations provide the rationale for evaluating the success of the business in the provision of healthcare services. Internally, the business will constitute well-trained and highly qualified personnel to offer the services and the business shifts from the product-based to the service-based enterprise. The use of technology to provide the services in combination with the highly qualified professionals is an internal strength to bank upon that makes the application upon which the services all more efficient and competitive. That leads to quality care, good coordination in the provision of services. It also provides a platform where the patient and the doctor are transparent to one another, services can be sustained, cover the private and public sector, and inculcates confidence in the customer. However, internal weaknesses include the use of technology when providing input, as applications are not as intelligent as human beings and can provide a wrong diagnosis for the patient. In addition to that, the lexical semantics required to reason out certain information might be difficult for the applications. Another weakness in the language that customers use is speaking about their medical conditions including metonymy where an application lacks the interpretation components to perform the interpretation. However, there are external strengths associated with the applications in the context of the provision of the healthcare business.
Thus, which constitutes an external analysis, which is the competitive analysis of the service provider in terms of opportunities and threats available in the target market. Opportunities include a number of customers who might not have been reached there before and had access to the new approach of providing services to the patient. Typically, such patients can be anywhere in the world and can be accessed on web-based applications, therefore enabling them access to medical services at a fraction of the original cost that could otherwise have not been accessible before. Such opportunities can be exploited as this could a first-mover approach to accessing the market. In addition to that, the uniqueness of the products and services offered and the use of technology provides strength associated with the current business model. Typically, the quality of services provided includes the use of well-qualified medical Practitioners and doctors, and the use of technology to provide quality healthcare services is an additional strength. Other strengths associated with the current approach include the use of technology and the availability of sufficient resources based on the partnering approach of working collaboratively toward a common goal.
However, the current business model is tailored to address any external threats that might be experienced in its growth and expansion. That includes threats of new entrants into the industry. While it is difficult to address the issue, it is worth noting that establishing and creating customer loyalty, creating goodwill among the customers, and collaborating with other service providers is a strategy that enables the current firm to address the threats of new entrants. Establishing the use of market intelligence reports and continuous monitoring of market trends enables the firm to gain information and strategize to address the issue of threats of new entrants into the industry.
Aggressive marketing of the services provided based on the proposed business model targeting different market segments and tailoring products to address each market segment needs is a strategy to enable the customers to develop a positive attitude toward the firm. Customers can be discounted on services if a customer brings another customer to be provided the services, thus, enabling their purchasing power to play a significant role in the growth and expansion of the firm. Typically, the size or number of customers a customer brings determines the discount level. It is crucial for the firm, as a competitive advantage be flexible and have the abilities to adjust to the cost of changing business with dynamic business needs, be sensitive to price changes, and evaluate the number of customers to determine its position in the market in relation to the buyer powers.
In addition to that, suppliers that the firm collaborates with should be evaluated to provide information about the sustainability of their services while ensuring that their pricing is always evaluated to determine the best prices that translate to the costs incurred in service provision. It should be within the ability of the firm to address new entrants threats and the substitutes they have to offer so the firm tailors its prof=ducts to address the substitutions in terms of cost, quality, and other product characteristics to fight off new entrants. In addition to that, the firm should identify the number of competitors in the industry and provide differentiated products and services that address the needs and expectations of the customers. The entire approach could be summed in Porter’s five forces that include evaluating the threats of new entrants, the buyer’s powers, competitive rivalry, and the threat of substitutes. However, it is important for the management and the marketing department of the firm to consider other market analysis options and identify the best strategy to use in penetrating the market and gaining a competitive position.
While using Porter’s five forces to evaluate the market and position it, the firm should also consider using the Ansoff Matrix, which requires that, the firm evaluate the risks associated with conducting business on web-based applications and the lifecycle of the services provided based on the business model. Typically, the current business model is an enterprise that is shifting from a product-based to a service-based enterprise that requires a detailed analysis of the business. One of the strategies that the firm should adopt associated with the Ansoff Matrix is to consider the number and type of products the firm was offering and the new products or services that the firm intends to shift.
Typically, there is a need for the proposed business to penetrate into the market by considering attracting new customers who have not had any loyalty to other service providers, and the strategy to execute that task is based solely on market intelligence reports and the management of the firm. Once that is identified, the current firm penetrates the market by attacking already players in the industry by adjusting any of the marketing components such as prices or tailoring the services to sound and look superior to the services offered by the competitors. On the other hand, the firm can embark on identifying different places and tailoring the services to suit each of the paces the services are to be offered. It is also crucial to consider strategies to be integrated into the creation of the business model where healthcare services are offered on web-based applications while enabling the customer to be in control of the management of their healthcare services.
Market analysis and demand include identifying the consumers of the services and products offered in the firm by identifying the needs of the customers and identifying new customers interested and who can use the services in different ways from the ways offered by the competitors. One of the approaches is to geographically, and demographically, identify the target market, and establishing their tastes and prevalence. It is also crucial to develop different services tailored to address different market needs in the identified markets.
The target market should be patients from different social and economic backgrounds and novice and trained uses of the electronically computerized devices and other diverse social backgrounds.
Service Design
The stages of the service design are reflective of the proposed business model and involve integrating “design thinking” into service practices, processes, and systems. In an endeavor to integrate the design thinking into the processes business practices, the management, designers, and developers of the current business models should identify and design and develop and applications that translate the thinking of the developers of the business model into the elements that define a service and service quality. Typically, that is managed by considering the quality of services to be offered as the first phase in the design and development process. Here the central idea of the services to be offered on the web-based applications is considered and the design of the applications considered. Quality should be experienced in the process of seeking a service and during the time the service is being offered (Sparks, 1994).
The next phase in the design process is to ensure the concept of service intensity is reflected and build into the proposed business model. Typically, that is in relation to the number and type of services to offer on the application based on market research and other market intelligence reports accumulated during the market analysis phase. Service intensity, therefore, should reflect issues such as the time it takes to offer a specific service, relative evaluation of the services offered, usability, enjoy-ability, and responsiveness in the provision of the services to the target customer.
It should be important for the service provider to consider, in the current business models the concept of service variability. Service variability includes customizing services to address the varied needs of the customers. It is important to realize that this stage enables the service provider to provide the customer with the ability to take control and manage the provision of the services. It empowers them to make decisions that address their needs while placing the service provider in a position of creating an image in the customer about customized services that address their needs. Typically, the model should at this phase be designed to address any additional problems that might arise during the service provision period.
However, it is important to borrow other concepts that have successfully been applied in the industry and that keep evolving with changing industry needs and business trends. That includes identifying preliminary requirements for integrating multidisciplinary design teams in the business model with different mindsets. Typically, the design is a computer to person interaction with the human being acting as a facilitator of the services offered on the web-based business model. The teams involved in the design should be ready to listen and learn from each other and be proactive in creating a model that captures different user needs and healthcare provisions. In addition to that, the team should work toward the attainment of organizational goals and objectives and toward the vision of the organization. There should be measures in place to reduce biasness in a particular direction while enabling a movement toward the next phase.
An enhanced system should capture and integrate functionalities that allow for information flow between different services offered on the business model, therefore avoiding situations of cracks occurring in the information flow process. Typically, good information flow allows managers, organizational employees, and the customer to track the actual movement of their services and products for the ultimate benefit to the organization. There should also be integrated capabilities in the applications to enable the customer to interact with the applications in relation to user needs and expectations. Thus, there should be models developed, as a final phase, to address the situation mention above. The final phase requires that the design be implemented based on user-centered interfaces. Though the above approach enables the organization to improve its performance and the productivity of the employees and other service providers in general, it is crucial to consider the fact that business organizations are dynamic and require innovative productivity and innovation to underlie the provision of services (Sawhney, Wolcott & Arroniz, 2006).
Productivity and innovation are considered as being key in placing the organization in a competitive position with other rivals. That calls for a conceptual framework to adhere to in the design and development process constituting the12 dimensions of innovation. The 12 dimensions of innovation include offering where the firm will consider what services are available for offer to address customer needs and expectations that add value to the customer, platforms that provide the capabilities for the customer to appreciably use and enjoy the series offered by the firm. That includes applications that can be used and that is portable or address changing market environment (Sawhney, Wolcott & Arroniz, 2006). It is crucial as the third dimension of innovation to consider the solutions that are developed, customized, and integrated into the application to address diverse customer problems.
The applications or business model should focus on the customer experience. Customer experience focuses on developing an application and a business model that considers what customers experience in terms of seeing, feeling, hearing, and other experiences a customer experiences while interacting with the applications. Another dimension when designing and developing the business model to consider is the customer. Typically, the business model should reflect an approach ad be easily customized to address changing customer needs and expectations. On the other hand, the application should incorporate the next dimension of value capture. Value capture considers approaches the firm intends to use in accepting payments and recapture the value it has created. In addition to that, the company should develop a pricing system that factors and is reflective of the target market and customer expectations.
The next phase in the 12 dimensions is processes. Processes need to be redesigned based on market trends, the need to enhance efficiency and growth, and the need to offer quality services in the healthcare provider industry. It is important for the company to restructure itself in the pursuit of offering high quality and efficient services. Therefore, as another dimension, the firm could require to be organized toward the attainment of the stated objective (Sawhney, Wolcott & Arroniz, 2006).
The supply chain is a component that needs to be considered in the design and development process, as it is a crucial factor in organizing the movement of products and services to the target customer. A good supply chain can stream the flow and access of information to enhance collaboration and reinforce the presence of the firm. Presence is a typical component in the innovation process that demands that the channels used in the supply chain to be well defined and provide ready access to the market and the target customer for the firm in delivering their product and service offerings.
However, it is crucial to consider the other concept in the innovation dimension. Typically, networking provides the firm with a competitive advantage through which many of the services and products can be offered to the customer (Moller & Torronen, 2003). Networking increases the value of the firm and its products while creating its goodwill in the market. The firm’s presence can be reinforced through branding. Branding as another strategy provides the firm with the symbols and other marks that make its name known among its customers in a creative way. However, it is crucial for the firm to develop dynamically in relation to the dynamic changes in the business environment. It is therefore the embrace a design that reflects the dynamic nature of changing business needs and customer behavior (Sheth & Parvatiyar, 1992).
Designing dynamic and flexible services across economic cycles, maturity stages, and market segments is a practical component to consider in the growth and development of the firm. The economic cycles to consider include identifying the best strategies to best engage customers and employees in collaborative service design while using the using service design to influence the behavior of people within service systems. On the other hand, that calls for a template upon which service visualization through blueprinting could be done.
Functional Strategies
One of the functional strategies to adopt in the current business model is a marketing strategy that addresses local and international customers. Marketing is a challenging task for a service or a product to be accepted into the market. Therefore, the marketing strategy should be reflective of the current market, market opportunities, threats, demographic trends, income levels of the target market, availability of technology and support infrastructure, and other priority areas. Therefore, the strategy focuses on the price of the services offered, the quality of the services, features such as the well-qualified experts and personnel, warranties, and returns. The strategy also focuses on promoting the series by offerings such as free consultations, establishing good public relations, and directly selling to the customer using concepts such as social media. In addition to that, the channels used include the internet and other social networking sites, and other popular sites.
Innovative service marketing will constitute establishing a network of service providers such as doctors and the effectiveness of the applications in the provision of services, ensuring there is a flexible workflow between the patient, the doctor, and the applications (Chu-Carroll & Carberry, 1998). Providing functionalities to allow for global outsourcing to ensure the best of expertise are integrated into the business model, and stimulating continuous innovation provide another innovative approach to service delivery. It is therefore possible to experience benefits that include broad differentiation in the market place, increase client loyalty. Increased client loyalty includes approaches of locking in clients by innovatively providing them with easier buying processes and real-time communication between the client and the service provider. That is likely to make customers stay with the current service provider. Another characteristic of such services is the ease with which clients can access information, buy, and access the services provided based on the proposed business model. Then, that leads to increased speed into the market, improved utilization of the infrastructure and other resources, lower risks associated with the business model, higher access speeds to the market, and a strong brand name (Sparks, 1994).
Positioning the service in the competitive global market is another strategy that the firm employs to gain access to the market and position itself and gain a significant share of the market. Positioning will include identifying market segments, developing the profiles of each of the segments, developing strategies for penetrating each segment, and developing a marketing mix for each of the segments. It is crucial to embrace the concept of a value proposition. The value proposition approach will include a list of benefits to offer the customer. In addition to that, the benefits will have to be credible, thus attracting the customer. In the value proposition approach, the services provided based on the current business model will include differentiating the services at favorable points thus, providing an edge against competitors. In addition to that, customer intimacy, deeply understanding customer needs, inculcating excellence in the provision of services based on thoughts of best value, and integrating uniqueness in product development and creativity in the provision of services, while shifting from the product-based to the service-based enterprise.
Data analysis will constitute using statistical packages and financial packages to analyze data that has been collected from the customer, the market in for of market intelligence data, and the financial performance of the firm. That could be a functional strategy to evaluate the performance of the firm, the market position of the firm, and other issues associated with the growth and expansion of the firm.
Educating customers is another functional approach to implementing the marketing strategy. That can be attained with web-based applications such as social networking sites and other forums that a customer can be reached. That enables the firm to be aware of their rights, features, and other benefits associated with the consumption of the services.
Customer satisfaction and loyalty provide the key to locking in customers and gaining a stronger customer base. In addition to that, the approach is likely to cause a sustained consumption of services with the net effect of creating sustained revenue, based on the firm. However, there should be a strategic partnership between the firm and other firms to attain an effective and efficient delivery of services and a wide customer base (Shani & Chalasani, 1992).
Strategic partnerships will include identifying firms to collaborate with to create and add value to the services provided on the firm in addition to other benefits likely to accrue from such partnerships. However, communication should be the key to effective collaboration.
The communication strategy should include sharing of information across the organization, communicating with the patient in a clear and appropriate manner that facilitates understanding, and establishing communication channels with no impediments to the enabling communication between different departments and individuals (Shapiro, 1988).
A co-creating strategy for enhancing service experience are approaches that will constitute sharing between the partners while keeping in focus the customer needs and expectations. The results will be a functional organization that has a strong financial base.
Financial
Appropriate financial analysis packages will be selected to conduct a profit and Loss analysis for the first three years of offering services. However, that will depend on the initial investment, the cost of doing business, and accruing profits. The pricing strategy has a significant impact on the revenue generated from the business.
Revenue projections will be done using automated software to generate figures that enable managers to make both short-term and long-term decisions. In addition to that, these applications will be used to make expense forecasts, which need not be done manually, and the profit loss account. However, all these projections will depend on the pricing strategy of the services offered by the firm. Pricing analysis will also depend on a number of issues that include the business environment, competitor pricing for similar services, demographic trends, costs incurred in offering the services, and a myriad of other marketing items before settling on the final price. Typically, that will also relate to the value of the services offered by the firm.
That leads to service valuation based on customer response and feedback, repeat customers, customer base, the value of the services in terms of content, and other salient features that
Execution/Operations
The customer service strategy will include identifying the customer experiences across the web-based technology and managing the customer experience across complex and diverse offerings, touchpoints, and customers. These include interactive use of applications and the technology and other features that are customized to provide the ability to interact with the devices. However, it is crucial to start by defining the customer’s role and developing methods for motivation customer contributions to enhance service success and loyalty. That could include identifying the motivating factors that compel customers to seek the services offered based on the technology-based business model. That is attained by distributing services through physical and electronic channels. These are typically done on web-based applications and the need to drive customer/service collaboration through technology that is reflected in the web-based application. However, there is a need to consider intellectual property rights based on international standards (Matheson, Poesio & Traum, 2000).
Delivery options for the services will include using electronic devices and through interactions with other collaborators to reach the customer and provide the appropriate services and an excellent supply chain in collaboration with the available technology. On the other hand, distribution internationally will be based on online tools to track the delivery of the products or services offered based on the business model.
The service package will be designed to address the customer needs, experience, taste, expectations, brand, and other features that support the positioning of the business based on the business model.
Technology
Technology to use
Detail of technology, which will be used for service, has had its architecture discussed in section 4.3, which looks in detail on the business model enhancement. However, the technology will be supported on the internet, as it will be web-based. In addition to that, the technology is characteristically portable across platforms to allow interoperability and allow other devices to be used.
Leveraging technology to advance service
As technology advances with new applications and new features added, it could be important to innovatively build business models for new service technologies (e.g., smart services, cloud computing) that can be used in conjunction with the new trend in technology. The crucial factor is to leverage technology and keep abreast with the evolving trends. Therefore there could be a strong need to accelerate the adoption and acceptance of new, service-oriented technologies into the business model to consistently maintain the market position and trend. However, it is crucial to capture and deliver service-oriented information for real-time decision-making. That is based on capturing real-time information to process the information and influence decision-making. However, the devices used have to factor in the mobility of the user of the services, thus, it is crucial to strategize approaches of enabling and accelerating mobile commerce and productivity for consumers and employees. Typically, that is based on the concept of e-commerce, which is not discussed in this paper.
There is a need to ensure online privacy and security of information and assets to protect service consumers, employees, companies, and society from unauthorized access to private information. That is attained by implementing security policies and adopting and integrating technologies that enable the firm to safely keep information in its confines by ensuring information integrity. However, there is a need to integrate the use of a service paradigm to drive innovation to higher organizational levels in relation to performance and service provision. That is attained by enabling agility and integration through service-oriented architecture and service platforms. These platforms include the internet and the use of web-based applications.
Implementation Strategy
The rollout strategy will take into consideration the purpose of the system, typically, to make services available to the customer based on a business model that integrates interactive use of technology. The firm will prepare the new system for acceptance, implementation, and validate the system functionality before full deployment. Typically, validation yields test data on the functionality and acceptance of the system, before full deployment for the system to undergo the lifecycle phases of system deployment. The implementation team draws expertise from different disciplines with distinct roles of the personnel to play. These include the system analyst, application developer, project manager, data modeler, technical support among other players. However, the transition of the system into full ownership depends on the development approach used. There should also be training sessions in the use of the system (Wilson, 1995).
Measuring and Optimizing the Value of Service
Measuring the value and return on investment from service for the services provided on the firm include using traditional methods measures of (ROI, ROE, shareholder equity, market share, product profitability). Typically, these are investment appraisals that the management of the firm should consider in evaluating the success of the firm (Srivastava, Shervani & Fahey, 1988). That could be based on cyclic measuring and analysis of the economic indicators that include time lags, capital spending, financial dividends, and price-earnings ratios. That could also include cash flow per share, asset value, and equity management. That could also include the cyclic fluctuations in the current business model.
However, it is crucial to engage in creating and enhancing tools for capturing the value in use for services and communicating value to customers and throughout the firm. Typically, that communication strategy is based on the objectives, the mission statement, strategy, and vision of the firm. The tools to use include moving averages, examining the average demand and supply for the services based on market intelligence reports and the analysis of available data, and use of time series techniques. However, it is important to consider the usefulness of indicators based on the economic cycles in the industry. It is therefore critical to integrate service value and the costs of service delivery into joint optimization models. These are the models that allow the designer and developer of the current model to innovatively move the firm forward in the provision of services with value addition being key to the services. It is therefore critical to identify the role and integrate the customers, employees, and technology for value optimization by defining and new metrics, which include customer satisfaction, customer profitability, customer, lifetime value into the provision of services (Storbacka, 2000).
Risk Management in Service Development and Design
Risk management in service design could be based on the need to manage the risks at earlier stages in the design process to either seek different options to avoid the risks or integrate strategies to avert or minimize their occurrence and potential impact on the business. The ultimate goal is to improve the operational efficiency of the business in the provision of healthcare services, support accountability, and enhances productivity and performance. These risks can be external or internal to the current business model. Typically, these risks span financial risks, foreign exchange risks, and credit risks. Other risks in the industry can be strategic that includes customer changes and customer behavior, industry variations, and changes in demand patterns. However, it is also crucial to consider internally driven risks such as recruitment and supply chain risks, which include operational risks, and hazard risks. Hazard risks include regulation risks, cultural risks since the business model captures a diversity of people from different environments, and management risks. Other externally driven risks include hazards, which include environmental risks, risks associated with natural events, and supplier risks.
The management in the proposed business model should identify the use of a risk management strategy to conduct a risk assessment associated with the current business models and healthcare business industry. Typically, the risk management strategy should enable the firm to add value to the provision of services. Thus, a risk assessment should be conducted against established standards based on the choice of the firm. However, it is recommended that risk management be conducted and implemented against international standards since the firm is international in nature. However, the framework against which the risk management is to be implemented includes conducting risk identification activities based on knowledge on the market environment, established operational objectives, and evaluating critical success factors and threats and opportunities associated with the business and as identified above.
Each of the risks identified translates the process into risk identification where each of the identified risks is presented in a structured manner and a tabular form. In the tabular for, the risk description should consist of scope of the risks, the risk attributes, collaborators, risk quantification, risk treatment and control measures to manage the risks, potential to improve on the risk management strategy and formulation of strategies and policies to address the risks. The next phase in the risk management process will include risk estimation, where the risks are quantified, and the probability of their occurrence evaluated and expressed. In relation to the threats and opportunities, the risks can be low, medium, or high. Then, a risk evaluation is done, followed by risk reporting, making decisions to address the risks, followed by risk treatment, and gradually risk reporting and risk monitoring.
The Challenge: Government regulations and policies
Governments have their own policies and regulations’, therefore doing business in such an environment presents significant challenges such as allowing controlled access to the internet, the platform that enables the use of web-based applications. Therefore, the firm will have to be objective in designing applications that conform to the policies of each government or at least a significant number of countries. In addition to that, conducting business in a stable or unstable political environment will constitute issues to consider when implementing the business model.
The demographic environment will constitute the population distribution and characteristics to consider when setting up the business to reflect the needs of each of the demographic segments. On the other hand, digital data security will constitute applying web-based measures to implement the security, authenticity, and data integrity and availability to authorized users. That can be done by defining data security policies and measures such as access privileges, authentication, and authorization, and other related measures.
The social environment will be considered in the design, as it constitutes the environment that defines the market. It is crucial to consider the six traditional.
Conclusions / Recommendations
The projection to provide web-based healthcare services on a technology-based business model is multidisciplinary and challenging. It is a viable idea based on the growing abilities that new software releases of software application stacks provide. However, salient issues to consider that draw across different disciplines include underlying infrastructure, business-related concepts, security issues, and a return on investment to reduce the risk of incurring loss and other pitfalls. However, it is recommended that comparative studies and market intelligence research be conducted to provide the project initiators with the best options to adopt in this new venture, to minimize the risks associated with shifting the business from the product-based to a service-based customer-centric enterprise. It is crucial to identify the demographic and national trends in the availability, adoption, and use of technology and interactive devices.