Introduction
The Department of Defense [herein referred to as DoD] is one of the United State’s largest and oldest government agency. Moreover, DoD is one of the indispensable agencies in the United States. Over the years, the DoD has undergone significant growth and evolution (The U.S Air Force, 2012). Provision of sufficient capability to the US military forces to deter war is one of the department’s core functions, and in the process, the security of the American people is certain. The DoD works in collaboration with other government agencies thus providing timely, accurate, and official information regarding the country’s defense operations, functions, and policies. To attain effectiveness and efficiency in maintaining the US’ sovereignty, the DoD ensures that the country’s military forces are well equipped with weapons. The government achieves this goal through a well-formulated defense acquisition program, which the Congress should endorse. In line with its mission, the DoD proposed to invest in F-22 Raptor project (Crane, 2009). The proposal came to picture for the first time in 1999 and from 1999 to 2009, the US government had procured 187 F-22’s (Gertler, 2009).
The objective of this paper is to develop a comprehensive understanding of a number of issues associated with the F-22 Raptor project. Some of the issues outlined in this research paper relate to the project’s mission, use, and purpose. The leading political forces affecting the project and the main supporters also feature in this paper. Considering that a significant amount of money will be required to implement the project, this paper explores the financial aspect of the project. Additionally, the paper illustrates the contemporary status of the project and finally outlines recommendations with regard to the project’s feasibility, costs, needs, and benefits.
Discussion
Mission of F-22 Raptor Project
Considering the rise in the rate of insecurity experienced today across the world due to issues like terrorism, the US DoD is committed towards ensuring that the country’s military forces attain a remarkable level of air dominance.
Investing in the F-22 Raptor project is a crucial step towards the country’s military forces attaining air dominance. The F-22 Raptor is the newest and most effective fighter aircraft. By investing in the F-22 Raptor project, the DoD intends to ensure that the US attains an exponential leap with regard to its Air Force’s war-fighting capabilities. The F-22 Raptor project intends to propel the country’s air dominance by incorporating a number of characteristics in the aircraft. Some of the F-22 Raptor features will include maneuverability, super-cruise, stealth, and improved supportability.
Purpose and use of the F-22 Raptor
The masterminds behind the project aim at improving the Air-Forces operational effectiveness by performing both air-to-ground and air-to-air missions. The US Air Force had been relying on YF-22 and YF-23, which were prototypes of the Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF). However, these fighter aircrafts had minimal air-to ground attack capability (Bolkcom & Chanlett-Avery, 2009). In an effort to improve its military’s air fighter superiority, the US government decided to improve on F-22’s air-to-ground attack capability. Therefore, by investing in F-22 Raptor project, the US DoD will be in line with the security needs of the 21st century (The U.S Air Force, 2012).
By investing in the project, the US DoD expects to achieve reliability in addition to developing a fighter aircraft whose cost of maintenance is minimal compared to any other fighter aircraft that has ever been in operation in the past. Upon completion of the project, the F-22 Raptor will be of use in a number of ways. For instance, the F-22 Raptor will “provide pilots with situational awareness because the aircraft is fitted with sensor fusions within the cockpit” (Gertler, 2009, Para. 11). Its sensor capability coupled with the fitted weapons will provide the first-kill opportunity to any threat. Moreover, “the fighter aircraft is fitted with sophisticated sensors, which enable the pilot to detect, identify, and shoot possible threats effectively before the enemy can detect it” (The U.S Air Force, 2012, Para. 8). The Air Force will use the F-22 Raptor in attacking surface targets. F-22 Raptor’s capability to conduct surface attacks will improve in the future by fitting it with eight small diameter bombs and upgraded radar.
Given that the F-22 Raptor has low-observable technologies, high lethality, and high survivability, it will be of great use in protecting key facilities and other assets across the US. The F-22 Raptor will ensure that the US Air Force can cope with the current and future threats. One of the factors that will enable the aircraft achieve this goal is that; it will be fitted with advanced flight control, a high thrust-to-weight ratio, and sophisticated F-22 aero-design. These aspects will allow the aircraft to outmaneuver both the current and projected aircrafts (The U.S Air Force, 2012).
Major political forces and adversaries affecting the project
Despite the F-22 Raptor performance capabilities, the project has been receiving mixed reactions from different parties. Some parties support the project while others criticize it, which has led to numerous controversies. The opposing sides have dragged the project and affected key decisions towards the fully commissioning of the project. The involved stakeholders have to converge at some point when commissioning projects of such importance like this one. Some of the parties supporting and criticizing the project are as follows:
Support for the project
The US Air Force is one of the parties that support the F-22 Raptor project. Its support arises from recognition that the F-22 Raptor is an exemplary aircraft with regard to air dominance and performance. The department cites the aircraft’s Performance Based Logistics (PBL), which is a unique innovative support approach. The PBL helps in the improvement of the aircraft’s readiness (Gertler, 2009). Support for the project also lies in the realization that the cost incurred by the taxpayers is low. Ultimately, the government should work towards cushioning taxpayers against exorbitant undertakings by pursuing affordable alternatives. The US Air Force seems to understand this aspect in its quest to push for the adoption of the F-22 Raptor project.
Support for the project also comes from the government and contractors. The main contractors to the project include Boeing, United Technologies, Pratt & Whitney Corporation, and Lockheed Martin. Additionally, more than 1,000 suppliers located in more than 44 states also support the project (Gertler, 2009). The contractor-government partnership is significantly improving the project’s maturation. The contractors work as a team in an effort to achieve the project’s goal. The collaboration of the contractor teams has significantly contributed towards unprecedented cost sharing. Additionally, contractor teams also share their respective production capabilities and strengths.
Numerous pilots have also lauded the F-22 Raptor project citing its role in ensuring that the US is secure considering the increment in possible threats, especially from Asia-Pacific countries such as China (Gertler, 2009). To meet the country’s operational demands at a relatively low operational risk, most supporters of the project, especially the Air Force officials, argue that the US requires approximately 243 to 250 F-22s. A fleet of 187 F-22s would result in higher operational risks (Gertler, 2009). The project’s support from the aforementioned quarters is substantial towards the adoption of the project.
Politicians
Despite the commitment of the DoD to ensure that the country is secure by investing in more F-22s, the project has faced numerous challenges from politicians since its inception. A report released by the US Government Accountability Office showed that the cost of modernizing the fighter aircraft has risen to $ 11.7 to $ 5.4 billion (Lessig, 2012). Additionally, controversy with regard to the project hinges on the fact that the projected timeframe for its implementation will extend with approximately 7 years. This aspect is likely to increase the cost of the project. One of the greatest hurdles facing the project is that, it will be difficult for the Congress to approve the proposed budget to facilitate the procurement of additional F-22. The Congress is of the opinion that the 187 F-22s, which have already been procured, are sufficient for the country’s security if they work in collaboration with other tactical aircrafts (Gertler, 2009).
Funding the F-22 Raptor project would also lead in reduction of funds necessary to undertake other defense projects. According to Congress, the expected deficit after approving the purchase of more F-22s would create operational risk (Gertler, 2009). Therefore, the Obama administration deems it necessary to halt the procurement of more F-22s. As a result, the government has vowed that it will reject any proposal to increase the budget for procurement of the F-22s.
Analysts
Security analysts assert that F-22 does not have key installations to allow it respond effectively to small fleeting machines, which are the predominant elements in the contemporary seditious warfare. In comparison to other attack aircrafts such as F-35, helicopters, and UAVs, “the F-22 does not have laser targeting capabilities and built-in optics to enable it respond to such forms of insurgencies” (Defense Industry Daily, 2012, Para.16). Critics also fault the deployment of F-22 in ‘small wars’ and they base their argument on the assumption that high costs are involved in the purchase, operation, and maintenance of the F-22 Raptors. As a result, it beats economic logic to deploy F-22 Raptor fighter aircrafts in such ‘small wars’ scenarios (Defense Industry Daily, 2012).
Analysts are of the opinion that qualified weapons fitted within the F-22 Raptor fighter aircraft are limited. Analysts also fault F-22 Raptor by citing that its internally carried attack weapons are not fully functional and powerful. In a bid to improve the F-22 Raptor attack capability, analysts are of the view that it should be fitted with radar killing missiles such as the AGM-88 HARM/AARGM. However, analysts assert that the US government is currently not pursuing that option in its drawing board in an effort to develop the aircraft. F-22’s attack effectiveness also falls short given that it lacks some facilities such as ground-looking radar arrays. Additionally, critical facilities such as broader field side-looking radars are also lacking. Therefore, analysts are of the opinion that these facilities will not be fitted unless future Block 30 and Block 40 upgrades are fully funded (Defense Industry Daily, 2012).
Aviators
In most cases, military officers do not speak negatively regarding their services; however, several pilots have faulted the F-22 Raptor project. Two pilots within the US military, viz. Captain Joshua Wilson and Major Jeremy Gordon who chose to cease flying the F-22 Raptor, underscore this unusual criticism. The two pilots said that flying the F-22 Raptor could be dangerous to one’s health. In their criticism, they said they could experience disorientation and oxygen deprivation while flying the aircraft. The F-22 Raptor aviators are increasingly refusing to fly the aircraft due to its malfunction with regard to its oxygen system. In addition to their safety, the two pilots were also concerned about their long-term health (Defense Industry Daily, 2012).
Most of the F-22 Raptor aviators are of the opinion that investment in the fighter aircraft is a waste of taxpayers’ money for the cost of procuring an F-22 Raptor is significantly high. On May 2, 2012, the US Air Force received its last F-22 fighter aircraft from a previous order of 187 F-22-fighter aircrafts from Lockheed Martin. The aircraft cost the American taxpayers $ 79 billion. However, the projections for the total costs of procuring one F-22 Raptor amounts to $ 420 billion. The high cost of the F-22’s and their combat capability coupled with the dangers it poses to its pilots, make the project less appealing to most US taxpayers. Despite this understanding, supporters of the F-22 argue that the project will save taxpayers more than 35% of its support cost, which is equivalent to $ 14 billions during its lifetime (Defense Industry Daily, 2012).
Financial aspect of the project
Estimated total cost of the program
The F-22 is one of the most expensive fighter aircrafts ever developed. Since its inception, intense criticisms on the cost of the F-22 raptor project have come up form different quarters especially the critics of the project. The cost of acquiring one F-22 fighter aircraft is approximately $ 412 billions and the total cost of the project is roughly $64.5 billions (Gertler, 2009). Some of the cost items that constitute the total cost of the project include the military construction cost ($650 million), cost of research and development ($30.4 billion), and procurement cost ($33.5 billion) (Gertler, 2009). Of the total estimated cost of the program, the US government has disbursed more than $62 billion by the end of 2009 financial year. From 2002, the budget for the acquisition of the F-22 has been on an upward and the downward trend as illustrated by the graph below
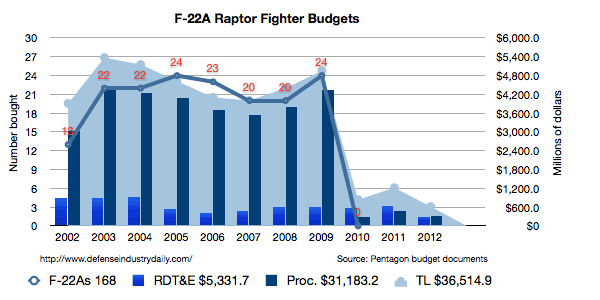
By 31 December 2007, the estimated total Program Acquisition Unit Cost for the 183 F-22 Raptor program was $ 350.8 millions. Additionally, the Average Unit Procurement Cost was $191.6 millions. Since its inauguration, “the cost of the project has been based on legislated limits with regard to the total engineering and manufacturing cost” (Crane, 2009, Para.8). The F-22 raptor project is one of the US defense programs whose priorities are relatively high. Its significance to the US government hinges on the rise in the level of security threats in the contemporary world. Investing in this project will significantly improve the probability of the US countering various security threats such as terrorism.
Current status of the project
Despite its importance, the US government intends to halt the F-22 Raptor project (Defense Industry Daily, 2012). One of the factors that have pushed the government to arrive at this conclusion relates to the high cost of the project. Currently, the US government and consequently the department of defense is experiencing current money crunch. The high cost of the project coupled with the F-22 raptor’s lack of sufficient combat utility is compelling the US government to consider reducing the cost of the project with a margin of $3.5 billion annually (Crane, 2009).
Conclusion
Findings of the research conducted reveal that the F-22 raptor project is an indispensable element in safeguarding the US security. Investing in F-22 raptor would significantly improve the US military capabilities with regard to air dominance. This observation hinges on the fact that the F-22 raptor fighter aircraft is one of the most effective fighter aircrafts, with regard to air-to-ground and air-to-air attack in the 21st century. Investing in the F-22 raptor project will contribute towards improved protection of the United States’ sovereignty.
The project receives mixed reactions from different parties. Some parties support the project while others intensely criticize it. Some of the parties that support the project include the government-contractor teams and the US Air Force. On the other hand, politicians are of the view that investing in the project is a waste of taxpayers’ money. As a result, politicians would consider halting the project. On the other hand, analysts doubt the effectiveness of the F-22 in countering insecurity. Some of the issues they cite relate to the aircraft’s minimal efficacy in “small wars” and limited weapon set.
In addition, aviators within the military are also faulting the project citing health and safety concerns of the aircraft. Since its inception, the US government has been committed towards ensuring the implementation of the 187 F-22 projects. As a result, the government has disbursed substantial funds towards the project. However, due to the high cost involved in completing the project, the US government has made a decision to halt the project.
Recommendations
The involved parties should consider the following recommendations with regard to the F-22 raptor project.
- Considering the ever-rising rate of insecurity, investing in the F-22 raptor should qualify as important and achievable government expenditure. Therefore, the US government should consider funding the F-22 raptor project because the project will significantly improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the Air Force in combating insecurity incidences such as terrorism.
- To ensure that the project does not fail, the US government should allocate a substantial amount of money in its defense budget for the procurement and maintenance of the F-22s.
- Given the hard economic times in the contemporary US, the government should consider formulating cost-minimization models with specific reference to the project. This move will reduce expenditure on the taxpayers’ money. However, reducing the total cost of the project should not compromise on the quality of the F-22.
- The government should adjust the schedule within which to implement the F-22 project. This adjustment will safeguard the government against a rise in the cost of project due to of unforeseen dynamics such as inflation.
Reference List
Bolkcom, C., & Chanlett-Avery, E. (2009). Potential F-22 Raptor export to Japan. Web.
Crane, D. (2009). F-22 Raptor program cancellation: Will we learn from it? Web.
Defense Industry Daily. (2012). The F-22 Raptor: Program and events. Web.
Gertler, J. (2009). Air Force F-22 fighter program: Background and issues For congress. Web.
Lessig, H. (2012). F-22 pilots who voiced concerns about raptor are willing To fly again. Daily Press, p.32.
The U.S Air Force. (2012). F-22 Raptor. (2012). Web.