Introduction
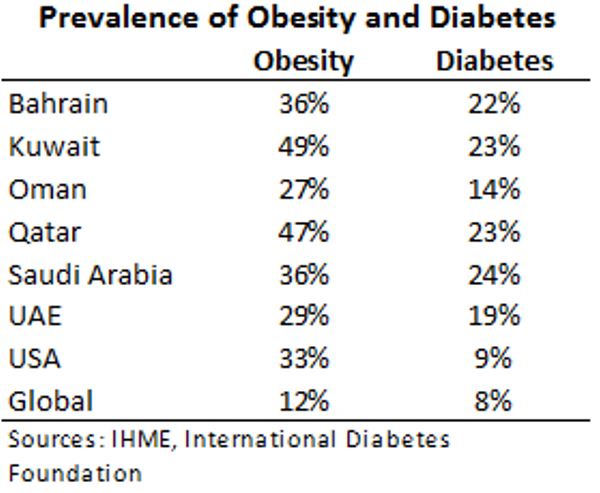
Diabetes and obesity are the diseases that are not only prevalent in the GCC countries, but globally. However, the issue with these two diseases in the GCC countries is their quick development within the population (The National 6). With diabetes and obesity being the major issues in the community, the solution to the issues is raising awareness and encouraging people to diagnose the problems as soon as any symptoms appear. As illustrated in Figure 1, by the year 2014 diabetes and obesity rates in the GCC countries have exceeded the ones in the USA.
What is Diabetes
Diabetes is an increase in the amount of sugar (or glucose) in the blood. The pancreas is gland in the upper part of the abdomen that is connected with the intestine. One of its main functions is releasing the digestive juices that are combined with food after leaving the stomach. The system is essential for digestion and absorption of food into the body, however, this part of the pancreas has nothing in common with diabetes. The pancreas also produces hormones that release straight into the blood. The most important of those is insulin, lack of which in the body can cause diabetes (Leslie et al. 11).
Obesity as a Disease
Obesity is a complicated disease, the development of which can be prevented by the changes in the person’s lifestyle. It is defined as a condition of excessive fat accumulation to the extent of the threat to the health. Despite this, the individuals that struggle with obesity can differ not only in the excess fat they store in the body but in the distribution of it. The further diseases and health risks associated with obesity are connected with the distribution of weight throughout the body (Seidell 17).
Diabetes in the UAE: the Nation at Risk
Among the MENA countries, the UAE has the highest diabetes rate (almost at 19 percent of the adult population). It was estimated that by the year 2020, 32 percent (68 million people) of UAE adult population will be faced with diabetes if the trends continue. According to the International Diabetes Federation, in 2015, the country was ranked 16th worldwide with over 19 percent of the UAE population battling with diabetes. Bad diets as well as inactive lifestyle contribute to the type two diabetes in the region. It has also become clear, that type two diabetes in tightly coined with increasing prevalence of obesity cases (Knowledge Action 4). The Figure 2 demonstrates the interconnection with types of diabetes and obesity as well as other factors.
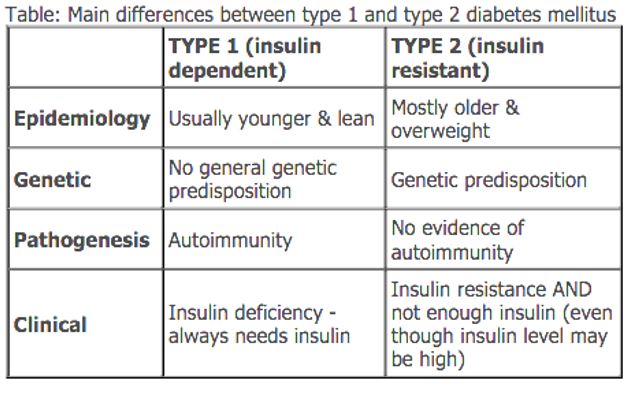
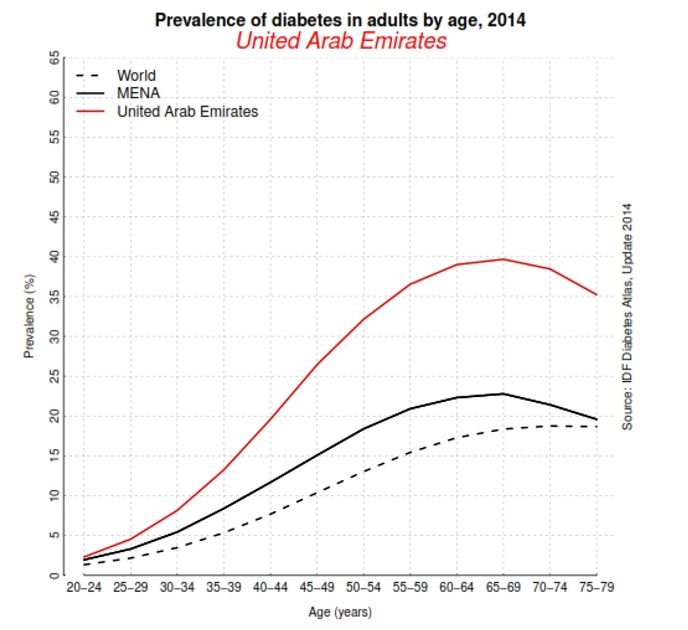
The UAE has significant risks factors of diabetes, including the prevalence of high-calorie diets and reduced physical activity. Moreover, almost 36% of the UAE population is obese, which is one of the contributing components of diabetes. In addition, there is also clinical evidence that the Arab population has a genetic predisposition towards resisting insulin production in the body. The combination of hot climate, sedentary lifestyle with the genetic predisposition may be one of the main contributors to a large number of individuals that suffer from diabetes (Booz Allen Hamilton 10). The Figure 3 shows the UAE diabetes statistics for the year 2014.
Obesity in the GCC Countries
The population of the GCC region was ranked as being among the fattest populations in the world. According to the UN report, almost half of adults can be classified as obese. The study conducted by the State of Food and Agriculture concluded that the rates of obesity in the countries could cost the global economy over forty-seven trillion dollars in the next two decades if the trends don’t change for better. This is connected with the lack of labor productivity in the region as well as costs that go towards treating the diseases coined with obesity, such as heart disease and diabetes. The statistics in the region for the year 2015 are the following: Kuwait is at almost 43%of obese adult population, Saudi Arabia with 35%, followed by the UAE at 34% and Qatar at 33% (Arabian Business 3).
Conclusion
To conclude, obesity and diabetes are the underlying health problems that are very prevalent in the GCC countries. Thus, these diseases require a lot of expenses that go towards diagnosing and treating, as well as they affect the overall economy of the countries due to lack of labor productivity. It was estimated that one out of 4 adults (20 to 79 years old) in GCC countries live with diabetes, with a similar percentage of individuals that suffer from obesity (Gulf News 6). A reasonable solution in preventing these diseases is awareness and advertising the healthy lifestyle. Given the fact that the Arab population is predisposed to diabetes, each individual should monitor the health in order to diagnose the diseases in the early stages.
References
Arabian Business, “GCC states named among world’s most obese”. Arabian Business Online. 2013. Web.
Booz Allen Hamilton. Exploring the Growing Challenge of Diabetes across the GCC and within the United Arab Emirates. 2012.
“Differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes” n.d. Web.
Gulf News, “Diabetes growing rapidly in GCC region”. Gulf News Online. 2014. Web.
Knowledge Action. Diabetes Facts. n.d. Web.
Leslie, David, Cecilia Lansang, Simon Coppack and Laurence Kennedy. Diabetes. Clinician’s Desk Reference. Somerset, UK: Manson Publishing. 2012. Print.
“Prevalence of Diabetes in adults by age, UAE” n.d. Web.
“Prevalence of Obesity and Diabetes in GCC countries” n.d. Web.
Seidell, Jacob. “Prevalence and trends in adult obesity on affluent countries.” Obesity Epidemiology. 2nd ed. 2010. Ed. David Crawford, Robert W. Jeffery, Kylie Ball and Johannes Brug. Oxford, NY: Oxford University Press. 17-26. Print.
The National, “Special report: Obesity rate in the UAE double the world average”. The National Online. 2015. Web.