General Information
- Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrinologic condition.
- It is characterized by an increased concentration of glucose in the blood (WHO, 2018).
- There are two main types of diabetes mellitus:
- Type 1 diabetes – the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (insulin deficiency);
- Type 2 diabetes – the insulin produced by the pancreas is ineffective (insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency).
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrinologic disease, which is characterized by increased blood glucose concentration. There are two main types of diabetes mellitus. Type 1 diabetes is associated with insulin deficiency. It occurs when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to promote a healthy breakdown of glucose. Type 2 diabetes is associated with insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. In this type of diabetes, insulin produced by the pancreas is ineffective, as the cells are resistant to it.

Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK, 2016), diabetes results in the following symptoms:
- polyuria (increased urination);
- fatigue;
- increased hunger and thirst;
- weight loss;
- blurred vision;
- numbness in the extremities;
- persistent sores.
The three main symptoms of diabetes are increased urination, or polyuria, persistent hunger, and increased thirst (NIDDK, 2016). Some patients also develop persistent ulcers. However, diabetes mellitus can also cause symptoms similar to other endocrinologic diseases, including fatigue, weight loss, numbness in the extremities, and blurred vision.

Causes of Diabetes Mellitus
The causes of diabetes vary by type:
- Type 1 diabetes is caused by autoimmune destruction of beta-cells in the pancreas (American Diabetes Association, 2014).
- Genetic predisposition and viral infections are the leading causes of this process (NIDDK, 2016).
- Type 2 diabetes develops due to hereditary factors, as well as obesity and physical inactivity.
The causes of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different. Type 1 diabetes is primarily genetic. It develops due to an autoimmune reaction, which leads to the destruction of beta-cells in the pancreas (American Diabetes Association, 2014). Viral infections and some environmental factors can also contribute to its development (NIDDK, 2016). Type 2 diabetes can be connected to genetic predisposition but is also influenced by body weight and physical inactivity.

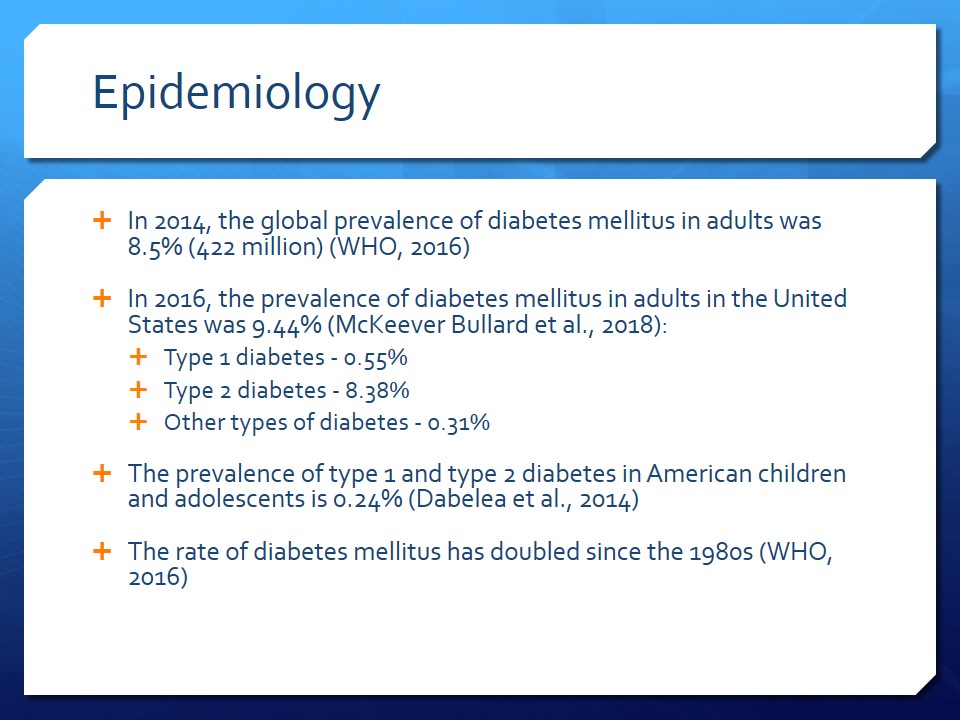
Epidemiology
- In 2014, the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus in adults was 8.5% (422 million) (WHO, 2016).
- In 2016, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in adults in the United States was 9.44% (McKeever Bullard et al., 2018):
- Type 1 diabetes – 0.55%;
- Type 2 diabetes – 8.38%;
- Other types of diabetes – 0.31%.
- The prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in American children and adolescents is 0.24% (Dabelea et al., 2014).
- The rate of diabetes mellitus has doubled since the 1980s (WHO, 2016).
According to the World Health Organization (2016), the prevalence of diabetes across the world was 8.5% in 2014. In the United States, 9.44% of adults had diabetes mellitus in 2016 (McKeever Bullard et al., 2018). Type 2 diabetes is the most common and affects 8.38% of the American population, while type 1 and other types are evident in 0.55% and 0.31%, respectively. Among American children and adolescents, the prevalence of diabetes is 0.24% (Dabelea et al., 2014). The WHO (2016) also states that the rates of all types of diabetes have doubled since the 1980s.
Risk Factors
Based on the current research, the risk factors for diabetes include:
- A family history of diabetes;
- Overweight and obesity;
- Physical inactivity;
- Insulin resistance or prediabetes;
- Diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, etc.);
- Hormonal diseases (Cushing’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism, etc.).
According to the NIDDK (2016), the main risk factors for diabetes are family history, excess weight or obesity, physical inactivity. Conditions such as insulin resistance or prediabetes also indicate a high risk for diabetes. In addition, diseases of the pancreas, as well as hormonal conditions, contribute to the development of diabetes mellitus.

Medications: Metformin
- Class: biguanides.
- Widely used to treat type 2 diabetes.
- Supported by most clinical guidelines, including those of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology (Handelsman et al., 2015; Garber et al., 2018).
- Indications: type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, prediabetes, and high blood glucose.
- Side effects: bloating, diarrhea, anemia, anorexia, and lactic acidosis (Marín-Peñalver, Martín-Timón, Sevillano-Collantes, & del Cañizo-Gómez, 2016).
Metformin is the main type of diabetes medication, which is used to treat type 2 diabetes. The use of metformin is supported by most clinical guidelines, including those of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology (Handelsman et al., 2015; Garber et al., 2018). The critical indications for prescribing metformin are type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, prediabetes, and high blood glucose. The medication has a variety of gastrointestinal side effects (bloating, diarrhea) and may lead to anorexia, anemia, and lactic acidosis (Marín-Peñalver et al., 2016).

Medications: Rosiglitazone
- Class: thiazolidinediones (TZDs).
- TZDs work by directly reducing insulin resistance.
- Also recommended for use by the guidelines of the AACE and the American College of Endocrinology.
- Indications: type 2 diabetes, high blood glucose, and insulin resistance.
- Side effects: weight gain, increased risk of bone fracture, chronic edema, and heart failure (Marín-Peñalver et al., 2016).
Rosiglitazone belongs to the class of drugs called thiazolidinediones. These drugs are used in type 2 diabetes and are “the only antihyperglycemic agents to directly reduce insulin resistance” (Garber et al., 2018, p. 98). Rosiglitazone is recommended for use by the guidelines of the AACE and the American College of Endocrinology. Indications for rosiglitazone include type 2 diabetes, high blood glucose, and insulin resistance. Side effects may include weight gain and increased risk of bone fracture, chronic edema, and heart failure (Marín-Peñalver et al., 2016).

Medication: Insulins
- A class of drugs used to treat type 1 diabetes (Handelsman et al., 2015).
- It can also be used in combination with metformin in some patients with type 2 diabetes (Garber et al., 2018).
- The use of insulin in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus is consistent with guidelines of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology.
- Indications: glycemia in type 1 diabetes; symptomatic hyperglycemia or ineffective therapy in type 2 diabetes.
- Side effects: hypoglycemia, headaches, blurred vision, fatigue, and nausea.
Insulins are a class of drugs used to treat type 1 diabetes (Handelsman et al., 2015). They can also be used in combination with metformin in some patients with type 2 diabetes (Garber et al., 2018). The use of insulins in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus is consistent with guidelines of the AACE and the American College of Endocrinology. Insulins are indicated for glycemia in type 1 diabetes, as well as symptomatic hyperglycemia or ineffective therapy in type 2 diabetes. Patients treated with insulins may develop hypoglycemia, headaches, blurred vision, fatigue, and nausea.

Clinical Presentation of Diabetes Mellitus
- Symptoms of hyperglycemia: polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia.
- Plasma glucose concentration of ≥200 mg/dL 2 hours after a 75-g oral glucose load – this test is taken in the morning.
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) concentration ≥126 mg/dL (after at least 8 hours of fasting).
- Random (casual, non-fasting) plasma glucose concentration of ≥200 mg/dL.
- Hemoglobin A1C level ≥6.5% (Handelsman et al., 2015).
According to the guidelines of the AACE and the American College of Endocrinology, the clinical presentation of diabetes mellitus includes the symptoms of hyperglycemia and plasma glucose concentration of ≥200 mg/dL 2 hours after a 75-g oral glucose load after at least 8 hours of no caloric intake. Alternatively, clinical presentation of diabetes mellitus can include FPG concentration at or above 126 mg/dL, random glucose concentration at or above ≥200 mg/dL, or Hemoglobin A1C level at or above 6.5% (Handelsman et al., 2015).

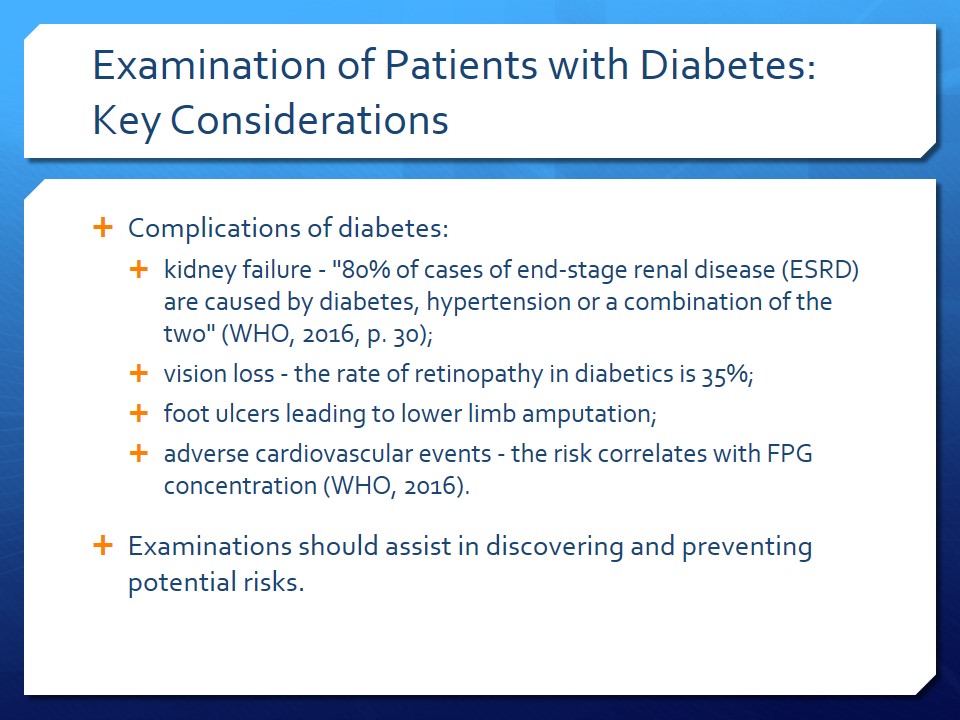
Examination of Patients with Diabetes: Key Considerations
- Complications of diabetes:
- kidney failure – “80% of cases of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are caused by diabetes, hypertension or a combination of the two” (WHO, 2016, p. 30);
- vision loss – the rate of retinopathy in diabetics is 35%;
- foot ulcers leading to lower limb amputation;
- adverse cardiovascular events – the risk correlates with FPG concentration (WHO, 2016).
- Examinations should assist in discovering and preventing potential risks.
Diabetes is associated with multiple health risks and complications, including kidney failure, vision loss, foot ulcers leading to lower limb amputation, and cardiovascular disease. For instance, as estimated by the WHO (2016), “80% of cases of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are caused by diabetes, hypertension or a combination of the two” (p. 30). Vision loss, foot ulcers, and adverse cardiovascular events are also prevalent among diabetics. Thus, examinations of patients with diabetes should be aimed to discover and prevent potential risks.
Examination of Patients with Diabetes: General
- General examination of patients with diabetes must include:
- weight;
- abdominal circumference;
- height;
- body mass index (BMI).
- Identify obesity and set weight goals if overweight/obese.
- Normal weight lowers the risk of adverse CV events (American Diabetes Association, 2016).
In patients with diabetes, excess weight contributes to the risk of adverse cardiovascular events (American Diabetes Association, 2016). Therefore, the general part of the examination serves to identify obesity and set weight loss goals if the patient is overweight or obese. The medical practitioner should collect measurements of weight, abdominal circumference, and height, and calculate the patient’s BMI.

Examination of Patients with Diabetes: Eyes
- Eye examination should include:
- visual activity check;
- eye examination for xanthelasmata, cataract or ophthalmoplegia;
- referral to an ophthalmologist for an annual dilated eye examination and/or a POC screening for retinopathy;
- These help to establish retinopathy and other visual impairments associated with diabetes.
- Annual eye examinations assist in preventing vision loss (Handelsman et al., 2015).
As diabetes is also connected with visual impairment and ophthalmologic conditions, it is essential to perform an eye examination. It should include a visual activity check and an inspection of the eye for pathological changes, such as xanthelasmata, cataract formation or ophthalmoplegia. In addition, it is necessary to refer the patient for an annual dilated eye examination and a POC screening for retinopathy. These steps can help in identifying an ophthalmologic condition early on, thus preventing vision loss and impairment (Handelsman et al., 2015).

Examination of Patients with Diabetes: Skin
- Skin examination should target ulcer prevention.
- Inspect the skin for ulcers, redness, or acanthosis nigricans;
- Assess foot deformities;
- In patients with type 1 diabetes, check injection sites for adverse reactions;
- Assessing skin conditions in patients with diabetes aids in preventing complications and determining adverse reactions to therapy (American Diabetes Association, 2016; Garber et al., 2018).
The key dermatologic risk for patients with diabetes is diabetic ulcers, which may lead to amputation. However, a detailed skin examination can also identify other conditions associated with diabetes. Firstly, the practitioner should inspect the skin for ulcers, redness, and acanthosis nigricans. Then, it is critical to assess the feet for deformities and check insulin injection sites for reactions. As noted by the American Diabetes Association (2016) and by Garber et al. (2018), assessing skin condition in patients with diabetes aids in preventing complications and determining adverse reactions to therapy.

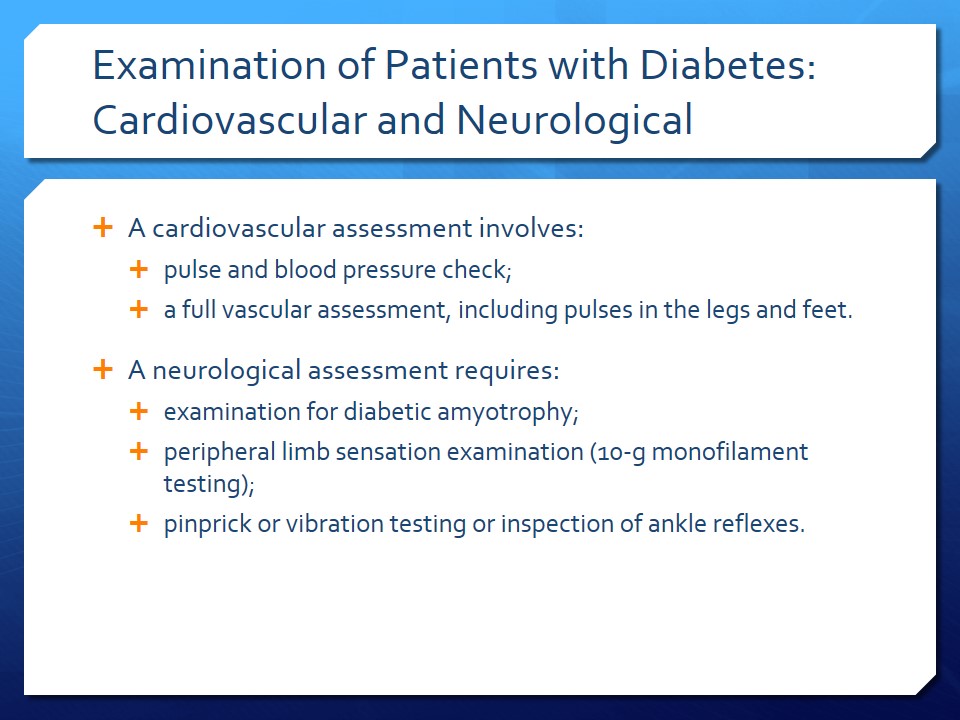
Examination of Patients with Diabetes: Cardiovascular and Neurological
- A cardiovascular assessment involves:
- pulse and blood pressure check;
- a full vascular assessment, including pulses in the legs and feet.
- A neurological assessment requires:
- examination for diabetic amyotrophy;
- peripheral limb sensation examination (10-g monofilament testing);
- pinprick or vibration testing or inspection of ankle reflexes.
In order to assess a diabetic patient for cardiovascular disease, it is crucial to perform a pulse and blood pressure check, as well as a full vascular assessment, including pulses in the legs and feet. A detailed neurological examination involves the evaluation of diabetic amyotrophy, peripheral limb sensation, and ankle reflexes. A thorough cardiovascular and neurological assessment of the patient could identify essential complications of diabetes, including heart failure, diabetic amyotrophy, and hypertension (American Diabetes Association, 2016).
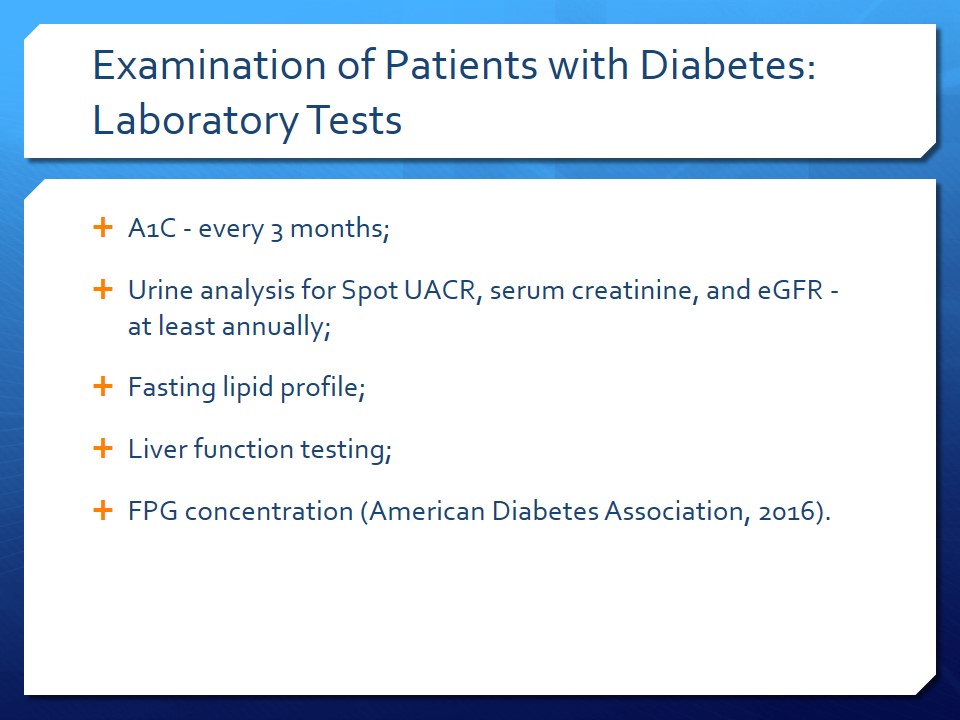
Examination of Patients with Diabetes: Laboratory Tests
- A1C – every 3 months;
- Urine analysis for Spot UACR, serum creatinine, and eGFR – at least annually;
- Fasting lipid profile;
- Liver function testing;
- FPG concentration (American Diabetes Association, 2016).
In the management of diabetes, monitoring the patient’s laboratory test results is critical to promoting positive outcomes. Laboratory tests could help to identify liver or kidney dysfunction, the risk of heart disease, and the effectiveness of the chosen diabetes treatment plan. Hemoglobin A1C testing is required every three months. Annual testing of urine for Spot UACR, serum creatinine, and eGFR is also advised (American Diabetes Association, 2016). Fasting lipid profile and liver function testing should be performed regularly to identify cardiovascular and hepatological risks. Finally, a test for FPG concentration should be done during every visit.
Patient Education
- Promote treatment compliance (Garber et al., 2018):
- discuss treatment options, side effects, and benefits;
- encourage reporting of side effects or health concerns.
- Facilitate healthy diet and lifestyle changes (American Diabetes Association, 2016):
- recommended physical activity: 50 minutes/3 days a week;
- explain carbohydrate counting, healthy eating choices, and portion control;
- establish weight loss objectives, if obese or overweight.
The two main goals of patient education in diabetes management are to promote treatment compliance and facilitate healthy lifestyle changes. Following the recommendations provided by Garber et al. (2018), medical practitioners should discuss treatment options, their side effects, and benefits and encourage patients to report any side effects or health concerns. A healthy lifestyle could also assist in the management of diabetes mellitus. In particular, practitioners should advise patients to engage in physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week (American Diabetes Association, 2016). They should also promote healthy eating habits by explaining carbohydrate counting, healthy eating choices, and portion control. Finally, if the patient is obese or overweight, it is vital to set healthy weight goals and discuss plans for weight loss.

References
American Diabetes Association. (2014). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 37(1), S81-S90.
American Diabetes Association. (2016). Standards of medical care in diabetes—2015 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes: A Publication of the American Diabetes Association, 34(1), 3-21.
Dabelea, D., Mayer-Davis, E. J., Saydah, S., Imperatore, G., Linder, B., Divers, J., … Hamman, R. F. (2014). Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA, 311(17), 1778-1786.
Garber, A. J., Abrahamson, M. J., Barzilay, J. I., Blonde, L., Bloomgarden, Z. T., Bush, M. A., … Umpierrez, G. E. (2018). Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm–2018 executive summary. Endocrine Practice, 24(1), 91-120.
Handelsman, Y., Bloomgarden, Z. T., Grunberger, G., Umpierrez, G., Zimmerman, R. S., Bailey, T. S., … Zangeneh, F. (2015). American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology– Clinical practice guidelines for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan–2015. Endocrine Practice, 21(s1), 1-87.
Marín-Peñalver, J. J., Martín-Timón, I., Sevillano-Collantes, C., & del Cañizo-Gómez, F. J. (2016). Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World Journal of Diabetes, 7(17), 354-395.
McKeever Bullard, K. M., Cowie, C. C., Lessem, S. E., Saydah, S. H., Menke, A., Geiss, L. S., … Imperatore, G. (2018). Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes in adults by diabetes type—United States, 2016. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 67(12), 359-361.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2016). Symptoms & causes of diabetes. Web.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2018). Diabetes mellitus: Fact sheet N°138. Web.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2016). Global report on diabetes. Web.