Introduction
Dubai Metro is an automated rail network established by the Dubai Government to reduce traffic jam and congestion. It is one of the biggest Metro System in the world (Oxford Business Group, 2008). The system serves largely populated areas of Dubai, Sharjah, and Emirates. Even though it is in its inaugural years, the Metro System has handled a huge volume of passengers though the volumes have continually reduced. Dubai Metro has several lines, but only the green and red lines are operational. Before its construction, commuters used to spend considerable time on the road. Serco operates the system, and it is expected to transport 1.2 million people per day (Dubai Metro, 2013). However, the Dubai Metro has not been able to meet this target. In efforts to improve its volume of clients and meet challenges, the management has introduced various measures. Over the past few years, several feeder buses have been established.
The feeder buses are expected to improve linkages between the metro and other modes of transport. The Roads and Transport Authority has also established bus and taxi lay-bys to act as drop-off zones in each station. Regardless of these efforts, the Dubai Metro remains under-utilized. Therefore, there is a need to look for new ways to improve their services. The new ways have to be based on tangible research finding for them to be effective. However, it is crucial to note that the system has played a great role in reducing traffic jam. Dubai is one of the world’s renowned economic hubs. As both an administrative and economic centre, over 50% of Dubai residents own a motor vehicle. The combination of the high population and a large number of vehicles created a transport challenge to the administration. The government had to find ways to reduce traffic jam, which was substantially costly to the government and citizens. It is estimated that traffic jams lead to a loss of between DH 4.6 billion and DH 146 billion annually. This is how the Dubai Metro came about (Dubai Metro, 2013).
Reason for Implementing BPR
Reengineering of business processes is one of the most radical and effective methods of dealing with change. Reengineering is also effective in reducing costs and improving quality of service. A far-reaching method requires a thorough evaluation before a firm embarks on it to refine its processes. Many firms, unlike Dubai Metro, have tried and failed to carry out Business Process Reengineering successfully. The reason is that the process requires a lot of time, resources, and knowledge for successful implementation (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
At Dubai Metro, there have been changes to the processes carried out by management in the past. These changes were informed by previous needs and market assessment. Management has embarked on various strategies aimed at attracting passengers to the system. The Metro Station is fed by a network of buses, which makes it accessible to all. The Roads and Transport Authority has also established Lay-bys to act as drop-off zones at every station. The train now offers comfortable services such as air conditioning that were previously unavailable. However, it has not met the targeted volume of passengers. The system has faced various challenges since its launch. Some of the challenges include poor maintenances. Poor maintenances have a negatively affected provision of quality services by causing unprecedented delays. Accessibility is still a major challenge regardless of the feeder buses and lay-bys (Kutz, 2010). Understanding customers is a major requirement for any successful business. It is paramount to understand how clients view services provided by an organization or firm. Dubai Metro has therefore engaged customers in various platforms, including social media in an attempt to fill this gap (Kutz, 2010).
Advantages and Disadvantages of BPR
Currently, the economic environment is quite competitive and unpredictably dynamic. A firm has to review its operations, processes, and policies continue to align them with contemporary methods of doing business. Because of the dynamic nature of the business environment, a firm must embrace change if it is to survive or even maintain the same influence that it has in the industry. The need to meet changing and somewhat sophisticated consumer needs and to find cost-effective ways of operation has made Business Process Reengineering a necessity. The advantages of this process are far-reaching and quite essential. Business Process Reengineering is the essential rethinking and revamps of processes in a business to achieve an enhancement in current measures of operations strategy performance and strength such as cost, quality, and delivery.
There is no doubt that Dubai Metro has played a major role in improving public transport in the country. It offers a suitable solution to traffic jam by providing quick mass transport of people between major residential and commercial areas. It offers fast, convenient, and comfortable services to clients. Since its inauguration, the service has drastically reduced the time taken from/to the various destinations. Dubai Metro has received great government and municipality concern due to its strategic economic importance. Various efforts have been put in place aimed at improving its services. They include the establishment of feeder services and timely repair of trains. These efforts are not based on any tangible research finding or study. Therefore, they have had little impacts on improving the services of the metro. The expert understanding and proper implementation of Business Process Reengineering may harness information and data necessary for developing a customer-focused improvement of the services. This will enhance public transport. The information and data available will equally help in identifying areas in which the metro is performing, and those it needs to improve (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
The results from this study indicate that the majority of people rate the internal services of Dubai Metro highly. More than 90% of the respondents are sufficiently satisfied with communication during the journey, punctuality, and reliability of the services. However, only 24% were satisfied with the ticketing process. The respondents also rated external services highly. More than 90% of the respondents were very satisfied with personal and onboard security. In the study, 59% of the respondents very satisfied with the connectivity of metro services with other public transport modes. This is a low rating compared to other services. These data nuggets are critical in BPR (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
Critical Success Factors of BPR
The main aim of any Business Process Reengineering initiatives is to improve efficiency and effectiveness in the production, service, and sale processes. Also, reengineering is meant to enable a firm to keep abreast with modern technology and methods to remain relevant. Reengineering processes at Dubai Metro have been notably successful. This is because the company conducted thorough research on the change before attempting to institute any changes in its system. Dubai Metro is, therefore equipped with information that enables it to undertake redesign in areas where it is specifically required. Many firms do not achieve success in process redesign because they undertake change programs that are general to their industry instead of identifying their specific needs (Page, 2010).
The study found that the process of ticketing is also a challenge to Dubai Metro services. To improve its ticketing process, the company can opt for e-ticketing. Mobile ticketing reduces queues witnessed during the process. It also reduces the number of employees required in the station. The government should also try providing unique services that are comfortable to attract self-employed individuals who seem not to have embraced the Dubai Metro. The following figure illustrates some of the critical success factors, along with customers’ ratings and perceptions. The management and the government, as the major players in the success of Dubai Metro, should critically analyze these factors and come up with sound solutions.
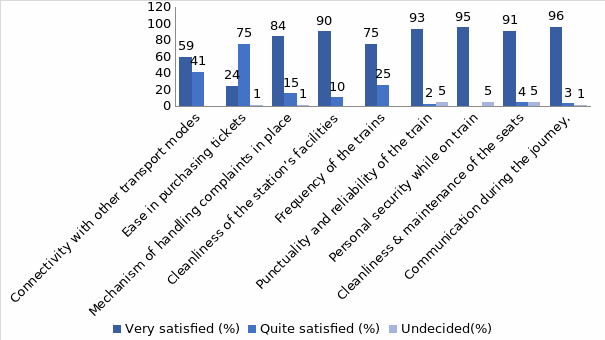
The following is an analysis of some of the factors and the writer’s insights into the data.
Public Transport Services
Use of private mode of transport is a major contributor to traffic jam. Most people prefer to use private transport because it is convenient and flexible. Public transport is associated with congestion and inconvenience. Although 65% of the respondents reported having used a train in the past one month, the flipside is that the majority were not happy with it at all.
Perceptions of Dubai Metro Services
The researcher assessed the perceptions of the public toward efficiency of Dubai Metro based on the frequency at which people used the service. It is expected that if people are comfortable with a service they will use it. The results indicate that 83% of the respondents use Dubai Metro services less than once per month, while 17% use the services once a month. This paints a grim picture, which the government and management should critically consider in change management and BPR.
Satisfaction to Internal Services
Internal services are the services that are dependent wholly on the operation of the metro. The internal services that were investigated included purchasing of tickets, punctuality, reliability, cleanliness and handling complains. In general, most respondents rated the internal services of Dubai Metro highly. The system scored highly in punctuality (93%), communication during the journey (96%) and cleanliness (91%). The process of ticketing was rated low compared to other services. Only 24% of the respondent felt that the process was very satisfying. There was no significant difference in women and men rating. The age also had no influence on individual rating of the services. Regardless of their nationality, the respondent portrayed a similar trend in their rating. This is a critical perception that management should look into carefully. The fact that the Dubai Metro scores quite well in the services that touch directly on customers but are considered noncore indicates that management is ignoring the basics. Hence, this is a critical success factor in Business Process Reengineering efforts at the Metro (Oxford Business Group, 2008).
External Services
External services involve the relationship between metro services with other modes of public transport. They represent factors outside Dubai Metro control but whose partnership is critical. Some of the external experiences the researcher investigated include connectivity and personal security. The respondents portrayed reduced excitement in the external services such as connectivity of the metro to other modes of transport (59%, very satisfied). Of the respondents, 75% felt that the frequency of the train was very good; 95 % of the respondents were very satisfied with onboard security, while 75% felt the same about personal security. These figures are essential in designing a process consistent with the aspirations of the ultimate consumer. Dubai Metro should consider greater partnerships with other operators to enhance service delivery and customer satisfaction. Doing this will ultimately make the Business Process Reengineering success (Christensen, 2011).
Change Management and Employees’ Resistance
Change management ensures that the change is implemented appropriately. When an organization’s employees are prepared for the process of change, the implementation of the change is much easy for the agents of change. The change also acquires visions that must be effectively communicated. Initiatives of change ought to be designed through making a feeling of necessity within the organization (Page, 2010).
The most important question for an organization planning for a change is whether their employees are ready to accept the change. The perception of the employees towards the efforts for change, which takes place in the organization, is a vital factor readiness for change. Managing and leading the change need the leaders of Dubai Metro to have the learning capability to adapt and learn from the changes. In this procedure, the learning process of the organizations is promoted within an environment of mutual trust and openness, which permits individuals to accept changes and experiment without feeling threatened (Page, 2010).
Today’s subordinates remain highly limited about having a “voice” in decisions affecting their organizations. This notion leads to a discussion of the motivational needs of subordinates and their influence on the ultimate job performance. Subordinates often experience fear, anxiety, and even animosity in the face of imminent change. Therefore, experts and industry pundits posit that organizations should plan for subordinate resistance to change. To combat subordinate fear, they suggest that change initiatives be conducted incrementally in a well-planned format. Diversity in race, ethnicity, and nationality should be considered in terms of their effectiveness and cohesiveness in multi-cultural groups and teams (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
At Dubai Metro, there was little resistance from employees. The whole organization was in tandem in terms of what needed to be done to grow business that was evidently under threat. The management took critical steps to ensure the ticketing was improved along with other operational areas. However, there was little resistance from a group of employees. They perceived the introduction of e-ticketing as a management’s ploy to cut them loose. Hence, they would frustrate the effort, but the management was quick to quell their fears (Page, 2010).
Revival and turnaround processes are subject to mistrust among the new and already existing forces. Instilling trust is crucial, though regarded as a long-term process. The CEO had to let others trust him before gaining trust. Hence, trust should start from the top down. Additionally, it is crucial to eliminate barriers to trust and instil a culture of openness. For example, departments should share progress, setbacks, milestones, and suggestions to encourage holistic growth. While undertaking organizational and strategic changes, the stakeholders may feel threatened. This leads to resistance to change and the possibility of a flop. Hence, necessary respect should be extended to employees (especially) because they are at the epicentre of the much-needed turnaround. Additionally, new management (in case there is one) should respect shareholders, immediate social environment, and members of the supply chain, which includes customers. This eases the whole process (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
Use of External Experts/Consultants
The Dubai Metro hires experts in the policy formulation and problem identification but majorly implements the findings. An observation such as the fact that a considerable number of people (65%) use train transport is interesting and should be analyzed well. The analysis leads to the indication that people use alternative modes of transport for daily transport other than Dubai Metro’s services (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
The research indicates that the public of Dubai has had a good experience with the Dubai Metro. Employed people mostly use their services. It is also worth noting that most of the respondents are Philippians. Their perceptions of the services are greatly positive. They are satisfied with the majority of its services, such as communication, cleanliness, and personal security. Regardless of the major efforts, to improve the connectivity of the metro to other modes of transport, a huge proportion of the public still are not very satisfied. Majority of the respondents use the services less than once in a month. This shows that the Dubai Metro is still not a popular mode of public transport. Hence, more expert and consultative approach is relevant to improve operations in the BPR endeavour (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
Management is the process through which resources in an organization are engaged for the ultimate realization of strategies and goals. Though there are management principles applicable universally, different scenarios call for a personalized input. This is what differentiates success from failure. Sometimes, strategies and directions emanate from personal experience, expertise, and sometimes sheer intelligent guesses. The latter is what should be sharp, visionary, and organization-centric. At the Dubai Metro, not all decisions need to be based on critical expert and consultants’ opinions. Rather, the management may play a crucial role in the realization of a successful BPR (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
Summary
The major challenge that hinders optimized utilization of Dubai Metro remains to be its connectivity with other modes of transport. Management should channel a lot of effort to improve this connectivity. The government should hasten the completion of subsidiary trains. Apart from improving connectivity, the government and management can offer reduced or subsidized charges to clients. It can also carry out a massive campaign aimed at publicizing the services. Despite respondents showing a relatively high rating of services offered, the numbers of clients remain low. Therefore, a comprehensive study should be conducted to identify reasons for the under-utilization of the metro’s services. The study should address other aspects such as costing, marketing, competition, and location of Dubai Metro relative to other modes of transport. Business Process Reengineering is also at the centre of a possible revamp at Dubai Metro. The management needs to hire consultants and experts in a concerted endeavour to improve the uptake of services at the metro. The study paints a relatively grim picture of most of the processes, and it will take a lot of employee motivation to accept change (Jeston & Nelis, 2008).
Reference List
Christensen, S 2011, Frommers Dubai, John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey.
Dubai Metro, 2013, Dubai Metro. Web.
Jeston, J, & Nelis, J 2008, Business Process Management, Elsevier, London.
Kutz, D 2010, Contemporary Marketing, Cengage Learning, Stamford, CT.
Oxford Business Group, 2008, The Report: Dubai 2008, Oxford business Group, London.
Page, S 2010, The Process of Business Process improvement, Amacom Publishers, New York.