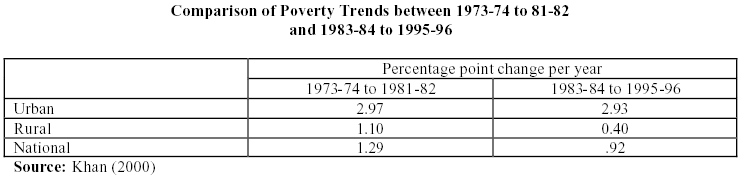Introduction
Economic development is a dynamic process of productive activity by which the livelihood of a geographic area uplifts to a superior stage. In another words economic development is an energetic process by which per-capita income of a county or region increases. Positive interaction of economic forces brings different changes both in social life and in macroeconomic factors in relation to time and place. As a consequence of gradual growth people’s income, savings, investment and employment opportunity increases and ultimately national income raises. There are too many indicators of economic development.
Mostly it is measured by the national income. In a particular time frame the total quality of goods and services including balance of payment, FDI, foreign loan and aids are included in national income. National income may not always indicate economic development reasoning that some time increase in price may increase national income. The primary conditions of economic development are as development of Production Organization, Population growth, national resource, capital accumulation, specialization of productive force, efficiency of resources, and technological development.
This report would go for analysis the problems of economic development of a developing country and Bangladesh has been taken as an instance or model of a developing country. The report should be organized with country profile of Bangladesh & development records, its major developmental challenges, strategies for economic development and recommendation.
Country Profile & development records of Bangladesh
Background
Bangladesh lies in GMT+6 hours time zone within 20°34′ and 26°38′ North Latitude and 88°01′ and 92°42′ East Longitude with an area of 147,570 sq. kilometers. India has bordered Bangladesh on east west and north side and Myanmar stands southeast corner when Bay of Bengal completely south coast. Almost 85% area of the country is plain level field with rivers such as Padma, Meghna, Jamuna and rest covered with hills and forests. The world’s largest mangrove forest Sundarbans stands in the southwestern coast of Bangladesh. The world’s longest sea beach situated at Cox’s Bazer of Bangladesh.
Historical context
The civilization of Bangladesh belongs about 5000 years as a part of Indian sub continent. The country was under British colonial rule for 200 years. In 1947 after fall of British emporium in Indian subcontinent, Bangladesh was a part of Pakistan named as East Pakistan. Through a long bloodshed and nine months liberation war Bangladesh achieved independence.
Population profile
By birth, Bangladesh is a secular county with a well-defined population of 150 millions. There are ethic groups such as Hinduism, Muslim, Buddhism, and Christianity. The country is a significant of peaceful coexistence co all ethic groups. The country’s-
- Per Capita GDP US$ 456 (2005-06 Fiscal year)
- GNI US$ 482 (2005-06 Fiscal year)
- GDP rate of growth 6.71% (US$ 63.4 billion in 2005-2006 Fiscal year)
- Sectoral share of GDP (2005-06 Fiscal year)
- Agriculture 21.77%
- Industry 29.01%
- Service sector 49.22%
- Population 150.03 million
- Literacy 62.66%
- Annual Export/Import US$ 10.5 billion (2005-06 Fiscal year) (EPB, 2008).
Geo-political issues
Geographic location of Bangladesh is very important for South Asian Political Economy. Bangladesh is a member of South Asian Regional Cooperation (SARC) It has well framed neighboring relation with all the countries, though there are some geo-political conflicts with Pakistan and India. The country practices multi party democracy with a parliamentary form of government. The county has a Modern Armed Force. From its birth to till last thirty-six years,
Bangladesh Army has killed to elected presidents and ruled at least four times military intervention. For its geographic importance donor agencies and so called development partners like USA and European Union has linkage with frequent military intervention that introduced corruption in the society and its politics. Two major political Bangladesh Awami League & BNP are also involved in this scandal. Therefore, people are turning to the politically left.
The Human Development Index of Bangladesh
The Human Development Index is a combination of three measures of human improvement such as living an extended healthy life, literacy rate, and well-mannered standard of living. The HDI lies beyond GDP as a wider classification of well-being.
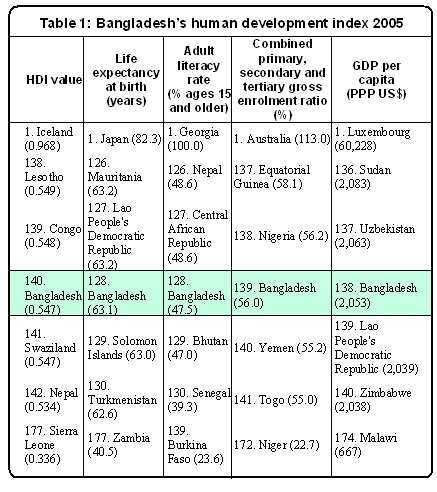
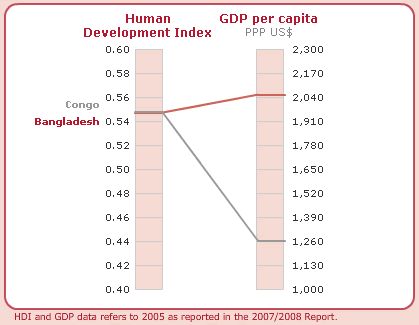
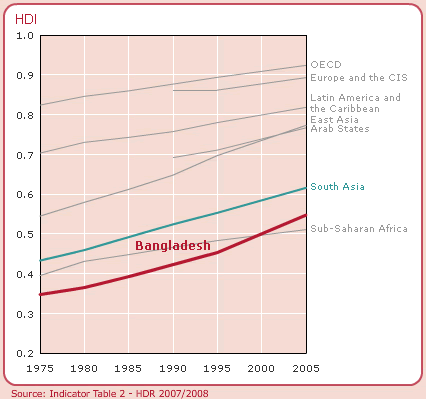
HDI does not make any sense of wide-ranging measures of human advancement. It also not include gender discriminates, income discrimination, and human rights situation and political environment. HDI affords a broader aspect of human development and the multifaceted relationship among income and happiness. For Bangladesh, the HDI indicates 0.547 and out of among 177 countries, it has graded the country 140th (Appendix- Table 1).
Environmental sustainability of Bangladesh
Bangladesh has signed MDG (Millennium Development Goals) of United Nation and has obliged to accomplish the dedication as participant of MDGs. So the country has to confirm Environmental Sustainability mentioned in MDGs. As per MDG the country has to comply with irradiate the hard core hunger poverty, trim down child mortality rate, support maternal health and make sure sustainable environment development as an obligation of global partnership.
Thus, Environmental sustainability is a vital issue for Bangladesh to face the challenge of Millennium Development. The UN report (2007) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) stated that in 2100, the earth surface temperature would be increased 1.1 degree to 2.9 degree, which may cause to rise of sea water level up to 23 inch. The major threat of Bangladesh is that for an increase of 1 meter of sea level, 15-17% land surface of Bangladesh go underwater. The southern part of the country has been identified as most threaten region.
Other environmental strains for Bangladesh are as vicious circle of poverty, flood, scares of rainfall, river erosion, use of insecticides & chemical fertilizer, poisoned gases from Ships breaking yards and deforestation. The Shomokal (2007) reported that 120 kilometers of Bangladeshi land go under sea within 2030. For crop growing, Bangladesh uses almost 1800 tons insecticides in every year. Ships breaking are a rising industry in Bangladesh where thousands of workers are affected by dangerous gasses and life in threat.
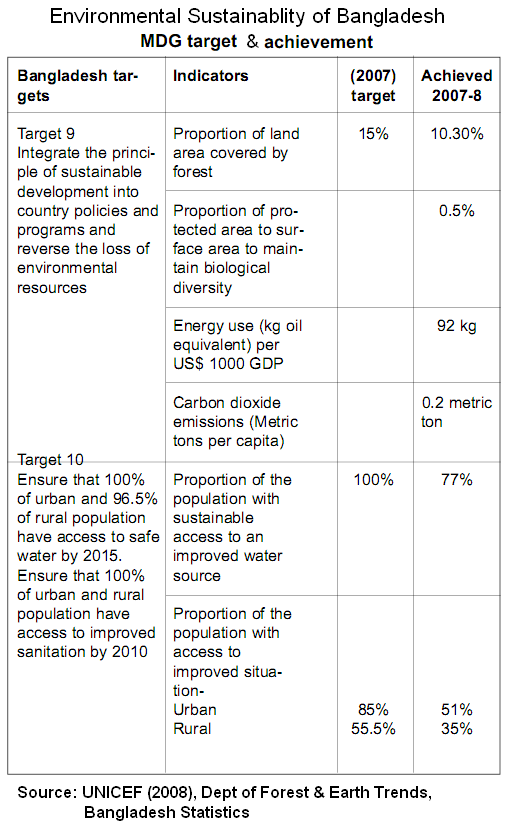
UNICEF (2007) reported that Bangladesh is straggling to achieve MDG target and it is now 4.7% at the back from the target. The official argued that they have achieved 15% land area has been covered by forest, when UNICEF mentioned it as 10.3% at the same time The daily Sangbad (2007) mentioned it has owned only 8% forest region which is just half of the target. It is also pure water 23%, urban sanitation 34%, and rural sanitation 19.5% is far from the MDG target.
The environmental issues have been disregarded in the national budget in context of percentage allocation condensed incessantly. Nevertheless, there is a lot of excellent way out such as environmental friendly integration policies, incensement of land fertility, dropping land erosion, decreasing deforestation, biodiversity protection, air and water pollution eradication, development of lives of life has been placed top of sustainable development.
Main development indicators
The major development indicators of Bangladesh are as –
- Poverty Reduction
- Literacy & Higher Education
- Gender Equity
- Health
- Child Health
- Maternal Health
- HIV/AIDS & other Diseases
- Environment
- Global Partnership
The Cross Cutting Development indicators Bangladesh are as –
- Human Rights
- Good Governance
- Indigenous People
- Disability & Development
- Youth Development
- Information Technology & Communication
Poverty Reduction
Bangladesh has been fighting to removal of poverty for long. Predetermined foreign Aids and loans are invested in the unproductive sectors due to World Bank and IMF prescription, which is the main obstacle of Bangladesh. Dinners are not interested for funding in productive sectors. More over the foreign funded projects collapsed the nation with burden of high interest, corruption and spoiled the political prospects.
For example, when the country has serious scarcity of power production, so-called development partners of Bangladesh i.e. European Union and USA are interested to funding for town beatification rather then electrification. Moreover, the World Bank and IMF are continuously presser the government to increase oil price, decrease subsidy for fertilizer. So it is real problem of reducing the poverty of Bangladesh.
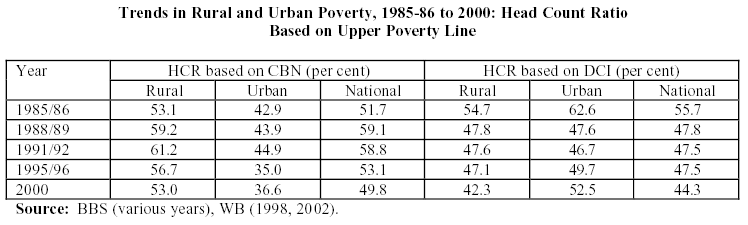
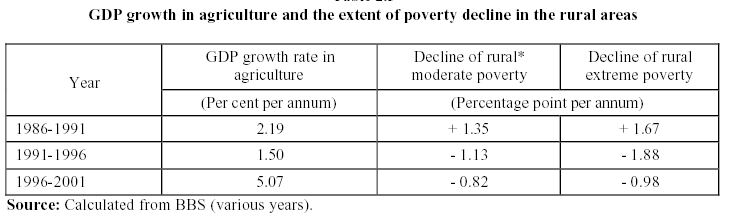
The Rural poverty turned down by 3.7 % whilst the urban poverty circumstances enlarged by 1.6 % for the duration of 1985-86 to 1999-2000. The diversity of rate of poverty diminution is so outsized within the periods that can recognize the observation such as frequency of poverty decline in a more rapidly rate in comparison with the first epoch than the second. Some local researchers have articulated the identical observation. The critical data has been placed in the appendix for better understanding.
Literacy & Higher Education
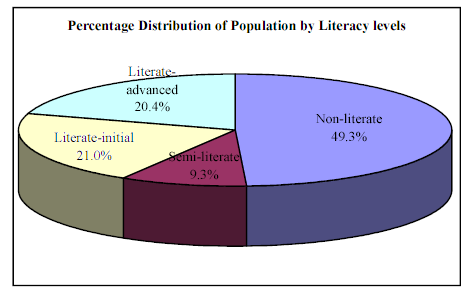
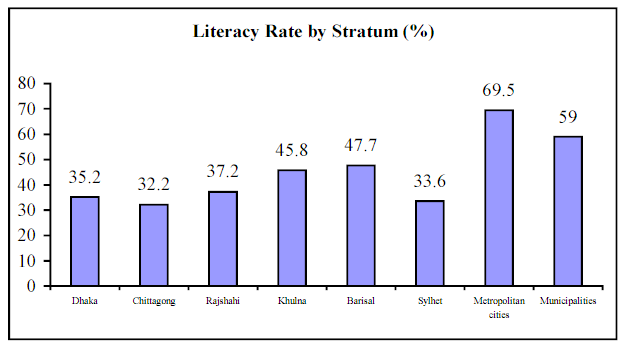
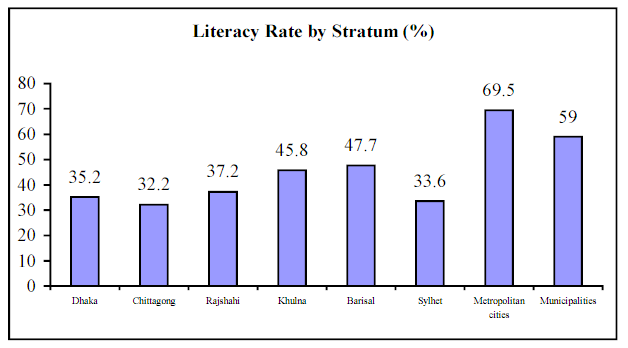
The official statistics concerning literacy rate is 63.3%, but is practical it is much lower. Most recent researches like Education Watch-2001 implied that such outcomes that over half of the population is illiterate. It also demonstrated that 10% are semi literate who placed between 25 and 50 of the literacy rate.
The preponderance of adolescents and youth take the primary education. A large part of them takes non-formal basic education that is just comparable lower grade primary education. The adult ones could be benefit from literacy courses those are elevated quality and long-lasting education opportunities. Non-Formal education is just going as a business of Local NGOs to making money.
The figure gender disparities are also remarkable. The literacy status of Bangladesh evident a large disparity in stipulations of gender, geography, socio-economic attributes and urban rural descriptions. The most disadvantages for female are pronounced is the urban- rural gaps. As the literacy has considered as a means of triumph over socioeconomic divisions, and encouraging social mobility, the gender inequality in education must be removed.
In Bangladesh, literacy rate among the age group 11-14 years represents the consequence of current advancement in reverence of primary education. On the other hand, groups and strata among population has some improvement in reverence of gender equality has been determined. The comparable data of literacy status of Bangladesh has presented in appendix for better understanding.
Gender Equity
For Bangladesh, the employment opportunity is an imperative variable in gaining economic growth among the poverty level population. It is most significant to scrutinize the situation of employment because of growth. There is twice way out in this purpose; firstly, it would be required to scrutinize employment intensive growth female workers. This can be framed by means of the perception of employment elasticity with reverence to production growth.
The perception would be functional within the economy as major sectors. The secondary approach would be to scrutinize on the configuration of employment has take action to economic growth. For economic growth Bangladesh has achieve the target of poverty reduction. It must turn in to a renovation of the makeup of employment among the gender equality faced towards sectors of higher productivity. For Bangladesh, this would characteristically entail a move towards IT enabled services, manufacturing and other labor incentive sectors.
Child Health
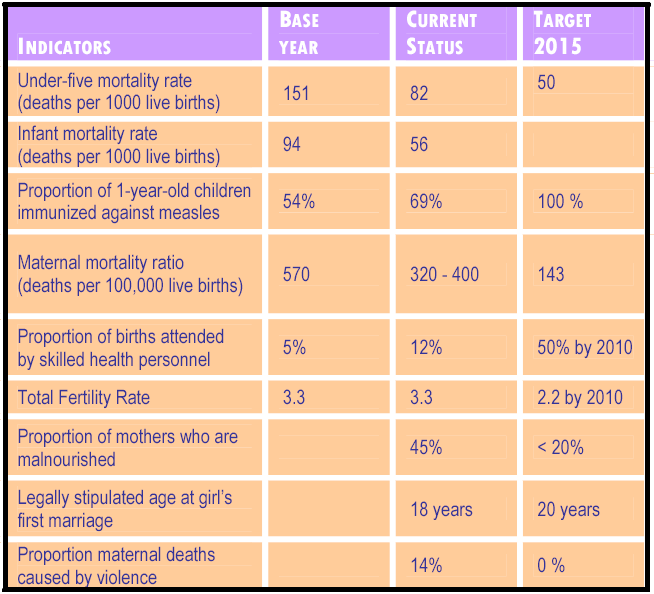
The country sets up its target to reduce under Five years Child mortality rate by two thirds between 1990 to 2015. In 1990, it was 151 per 1000 live births. Currently it has achieved 82% of its target.
Maternal Health
The maternal concerning mortality has turn down from almost 574 per 100,000 live births in the base year 1990 targeted to keep in 320 to 400 in 2013. Bangladesh possess the uppermost in the world maternal mortality ratio (MMR). The projected maternal death is 14% those are occurred by violence against children and women, even as for maternal health complications 12,000 to 15,000 women murdered per annum.
Indicator: HIV/AIDS
The country sets up its target to halted HIV/AIDS by 2015 and begun to reverse broaden of HIV/AIDS. However, the current rate of HIV/AIDS is very low and the peoples awareness has development has gained significant level. The data of HIV/AIDS achievements has been represented in the Appendix.
Major developmental challenges
The Millennium Development Goals of Bangladesh are in serious threat from different perspectives. Precautionary measures can successfully overcome the challenges. Bangladesh is striving to achieve it goals. The challenges to achieve the development goals have been pointed as bellow-
Bangladesh has to promoting robust economic growth to eradicate poverty. Identifying the most important factor contributing to poverty reduction it has to achieving and sustaining strong economic growth will require attention on many fronts such as:
- Identify to practice fiscal policies that prolong macroeconomic stability.
- Humanizing transparency, accountability, good governess
- Transparency in taxation, public procurement, law enforcement, land administration, Banking, & insurance as well as credit market.
- Independence of Judiciary
- Enhancement of government effectiveness focusing on core state functions as well as delivery of public services.
- Increasing national competence to design and put into effect laws, policies, and regulations that smooth the progress of private sector investment.
- Liberalizing the trade establishment to comply with advantages of the speedily globalization
- Retrain privatizing of profitable state-owned enterprises
- Developing business activities in proper incentive and regulatory schemes
- Reallocating public resources to the stipulation of high priority public goods
- Accelerating development of communications in key areas
- Priority provided on such as power, ports, transport, and telecommunications
- Amplification capacity for enhanced absorption of aid resources
- Attractive government effectiveness by focus on core state purpose and delivery of public services
- Rising national capacity to enforce policies that facilitate private sector investment
- Liberalizing the trade regime in context of globalizing
In Bangladesh, pointed out its second goal of millennium development as to reducing poverty. To eradicate poverty it has the challenges as –
- To structuring the income-generating capacities of the poor
- Develop policies that develop its human capital
- Improving Poor’s open access to the essential health service package (ESP)
- Addressing the dilemma of child malnutrition
- Undertaking a comprehensive program to improve the exposure quality of education
- Facilitate the poor to participate more economic activities
- Initiatives access to credit, land, and labor
- Developing cooperation and partnership among private and public sector
- Recognizing policy for public spending,
Strategies for economic development
In current situation Bangladesh strategies to drive for the designed economic development should be based on-
- Come out from the Vicious circle of poverty
- Subsidizing Agriculture
- Food production increase
- Industrial development
- Literacy and Education Development
- Reduction of Birth rate.
- Reduction of Dependency on Foreign Aid
- Emphasis on Natural resource
Conclusion
In aspect of current economic recession of USA is an integral part of global economy. Bangladesh as a developing country required to evaluate the consequence of following the donor’s adopted policies. It must require coming out form the vicious circle of IMF & World Bank’s prescribed policies. It must emphasize to its agriculture and become self dependent on food production, subsidizing the agriculture and remove a large number of unemployment and save its foreign currency for food importing which will turn the country to the designed development.
References
Ahmed, Manzoor, Nath, Samir R. & Ahmed, Kazi Saleh (2003), Literacy In Bangladesh: NEED FOR A NEW VISION, Campaign for Popular Education, Education Watch.
Biswas, Mousumi, et al (2007), How far is Bangladesh in Ensuring, Environmental Sustainability? Costal Studies: Campaign for Good Governess. Web.
Bangladesh (2008). Web.
EPB (2008), Bangladesh country Profile, Export Promotion Bureau, Bangladesh. Web.
Johannesburg Summit (2002), Introduction – Country Profiles Series. Web.
The daily Sangbad (2007), Environmental debate of Bangladesh, issue 2007, Dhaka: The Sangbad Ltd.
UNDP (2008), Bangladesh: The Human Development Index – going beyond income. Web.
Rahman, Rushidan Islam & Islam, K.M. Nabiul (2003), Employment Poverty Linkages: Bangladesh, Recovery and Reconstruction Department, International Labour Office, Geneva.
Supro Position Paper, (2007), How far is Bangladesh in Ensuring Environmental Sustainability?. Web.
UNDP (2008), Bangladesh: The Human Development Index – going beyond income. Web.
UNDAF (2006), United Nations Development Assistance Framework in Bangladesh. Web.
Appendix
The HDI for Bangladesh is 0.547, which gives the country a rank of 140th out of 177 countries with data (Table 1).