Milton Friedman and his contributions to political and Economic Philosophy
Milton Friedman is a renowned American economist. In that case, he has contributed greatly to various fields such as statistics, microeconomics, macroeconomics and economic history. Furthermore, he advocated for the laissez-faire capitalism (Kasper 2002).
In his effort to create social and political freedom, Milton Friedman advocated for freedom and capitalism with an aim of limiting the government role in a free market economy. Additionally, in 1976, he was awarded with the Nobel Prize in economics.
This was in appreciation for his achievements in monetary, history and consumption analysis fields. Apart from his expertise in the above mentioned fields, he was also awarded for his portrayal of the stabilization policy complexity.
The American conservatives’ outlooks were greatly shaped by his political philosophy. This philosophy stressed on the market place advantages and challenges that accompanied government intervention.
Furthermore, his political philosophy impacted significantly on numerous countries and also Ronald Reagan economic policy during his reign as the administrator of the United States after 1980.
In his arguments, he pointed out that the great depression that was experienced in the United States was as a result of money supply mismanagement by the government. This was in reference to the United States Monetary History.
Between the years 1941-1943, Friedman had a chance to work for the centralized government. During this time, he advocated for Keynesian taxation policy (Keynes 1936). This policy helped greatly in developing the income tax payments payroll with-holding system.
In summary, Friedman was indeed the principal advocate of the monetarist economic thought. He based his argument on the claim that there exist a stable and close correlation between money supply and inflation.
Of importance is that the inflation phenomena needs to be regulated by taking charge of the amount supplied by the Federal Reserve Bank to the national economy. Friedman rejected the utilization of fiscal policy as a demand management tool.
In his view, he held that the role of the government in economy guidance should be extremely restricted (Bowman 2009).
Milton Friedman – Lesson of the Pencil
Milton Friedman outlines the concept of free to choose by use of a pencil as an example and the price system examination. The video utilizes various concepts in economics.
Adam Smith is perceived as the modern economics founder. As illustrated by Friedman in “Free to choose”, the principal insight by Smith in his treatise” The wealth of nations” was based on voluntary exchange where both parties can gain.
As individuals are in pursuit of their own benefits, they do contribute to the benefits of the society, as is lead by a hand that is invisible. This is most experienced in an environment characterized by political and environmental freedom.
In these environments, decisions are influenced by the price system. Price functions effectively in three main ways. These are some of the examples.
Price helps in transmitting of information: in case of supply disruption, consumers are often charged more by the producers. In situations where product prices increases co0nsumers seek for substitute products thereby restoring demand and supply equilibrium.
Production incentives: Limited supply of a product in the market increases its price thus allowing higher wages for the industry in question. Higher wages corresponds to increased need for labor to meet the demand in the market.
Income distribution: As a result of choices, income, wages and salary arise. Occupation characterized with low supply, to be precise those that are in need high levels of skills and training attracts more workers as result of their bid for higher incomes. Unnecessary or Oversupplied occupations have low value as less people get attracted to then due to low incomes.
Productivity is the driver of any economy. As argued by Smith, productivity can only be increased through specialization or division of labor.
The lesson of the pencil video illustrates that no single individual has the knowledge of making a pencil because no one exhibit the capacity to comprehend all that is needed to make a pencil in order to achieve that goal. The price system enables individuals to specialize in their area of their expertise.
As a result of specialization, there is manufacturing of products that are complex. The price system can be manipulated by coercion, which corrupts it. As a result of human ingenuity, wealth is not a game that one part has to gain while other looses as a result of competition.
On the contrary, new and more wealth can be generated. This is only if there is intersection between economic, political and personal freedom.
Government plays a significant role in proving for those services and goods that people cannot afford to pay for such as the national security. Most of these goods are known as public goods and are paid for through taxes (Anonymous 2012).
How Economic theory provides to government intervention
The extent of government intervention when it comes to maters regarding the economy is highly debated and divides the economists (Ng, 2000, p.10).
This has been experiences in various manifestations such as the public expenditure size as a gross domestic product (GDP) percentage, the financial regulations of the markets and the level of labor, the degree and structure of both indirect and direct taxation.
The government size and its role are among the enduring and fundamental debates in the politics of the Americans. Government intervention benefits can be analyzed in various specific areas of the economy.
However, government intervention cannot provide answers to various questions asked such as if there is “too little” or “too much” of overall government activity. Some governments programs have been found to be ineffective and insufficient by economists.
Some of them are counterproductive and cannot met targets sets by specific policies. Limiting government spending that is inefficient would benefit a country’s economy. Besides, reducing effective spending by the government will destroy it.
Furthermore, reducing government size could include either efficient or inefficient government spending. Government intervention can help in increasing the efficiency of an economy. This is applicable where there is markets and externalities failure.
In the light of the above, government intervention was supported by Keynes during the economic turmoil crisis. The theories presented by Keynes were such as the “General theory”.
The theory points out that, most economies are unstable and full employment can only occur if there is a boost from the public investments and government policies. It is the work of the government to close the gap that exists between the potential of an economy and its actual output at times of financial crisis.
As a matter of fact, during economic depression, the governments have the capability of boosting demand by spending a lot of cash. In support of the statement, during economic depression, a lot of resources lie idle for instance individual who are in need of a job and surplus capacities in the factory in the period of the economy.
Given this context, government is allowed to spend more money. According to Keynes point of view, when the principal economy pillar (including next exports, investment and consumer spending) falls, the only pillar that can offer support to the economy is the government.
Explanation of Increases in GDP in the United States and Other Developed Nations
The increase in the GDP in most developed countries is as a result of gradual increase of government outlays. The emergence of democracy in the 20th century and the provision of social welfare gains including major wars, have significantly contributed to government spending increases in the economy.
In addition to that, the government extreme intervention forms also referred to as ‘command economies’ have failed in matching the economic rate of growth and development in mixed economies.
Inexistence of private properties and free enterprises has subdued innovations and incentives in various developed countries such as Cuba and North Korea.
This was also evident in the downfall of the USSR. Government intervention impacts detrimentally on the growth of the economy as well as people’s standards of living.
In comparison to developing countries where the principal form of government spending is the defense, in developed countries, the government s[pending largest share is channeled to social welfare benefits such as family allowances, pensions, unemployment and sickness benefits, housing, education and health.
The attention to equity considerations by developed countries needs to be adequately financed through taxation. Taxation is viewed by free marketers as resulting to inefficiency (Lombard, 2010, p.313).
The Demand and Supply Curve(No intervention from the government)
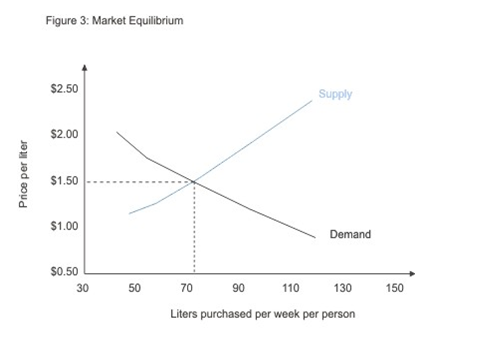
The point at which the demand and supply curve meets is what is known as Equilibrium. As a result, the consumers in the market do not experience goods shortage or surplus. A shortage can only be experienced when the quantity demanded is higher than the quantity supplied.
This occurs when the prices for products or services are too low in the market. However, there exists surplus in the market when prices are high and consumers are unwilling to purchase the products. In free market economy, quantities and prices of goods supplied tend to move towards the equilibrium thereby stabilizing the market.
From the above demand and supply curve, the equilibrium price in the market is $ 1.50. With this price, consumers are supplied with seventy five liters of petrol per week.
Market equilibrium helps in explaining the movement of goods along the supply or demand curve. Market equilibrium does not give illustrations on the changes on demand and (Mind tools, 2012, p.1).
The graph below illustrates the impacts of a price cap that is below the market equilibrium price.
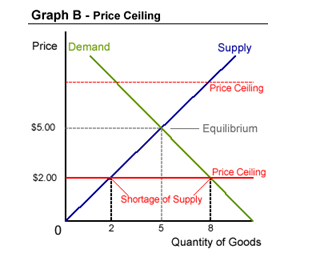
The graph dashed line indicates the maximum price (ceiling price) imposed by the government above the equilibrium price determined by the market. In that case, it has no significant impact on the price of the product.
In this condition, the market is incapable of generating a price that is high other than the ceiling price. A different impact results when the maximum price imposed by the government is below the equilibrium price set by the market.
This is illustrated by the solid line in the above graph. The price demanded by the market can no longer be charged by suppliers. As a result, they are compelled to adhere to the government’s maximum price set by the price ceiling.
Suppliers can be drawn out of the market by a low ceiling price. On the other hand, low ceiling price increases the demand of the consumers. When demand surpasses supply, shortage occurs.
As a result, products in the market are subjected to rationing. This is evidenced by long customer lines. Sometimes products are unavailable despite the consumers’ desire or need to buy the products.
In some instances, governments integrate government rationing programs with low price ceilings. The combination of these two controls how the allocation of insufficient supply of goods will be done by the market.
Short-term and Long-term effects of introducing a first home buyer grant and then phasing it out
In order to perfectly answer the above question, Australia will be taken as a case study. Housing is a necessity that is basic and plays a significant role in promoting individual health and living standards.
Therefore, housing demand services can be said to be inelastic. The demand price elasticity links the change in the demanded quantity as an outcome of a change in the housing prices (Mayo 1981).
Alternatively, the demand income elasticity for homeownership is elastic. This is because income levels that are high tend to produce more spending on home purchases in comparison to rent (Housing Industry of Australia, 2002, p.4). Households with higher incomes have the opportunity of saving a housing deposit.
In addition to that, they are highly qualified for a home loan in comparison to their counterparts. As a result, home owners exhibiting a mortgage number increases proportionately with income (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2008).
Before examining the effects of the First Home Buyers Grant (FHOG) on first home buyers’ decision to buy a home, it is vital to take into consideration of other factors affecting home ownership demand. The key determinant factors are such as population growth and size.
For example, the more the people in the market, the housing stronger demand. Household size and age, rate of divorce and marriage, the income household levels influences the location, type of dwelling and housing demand preferred by purchasers.
Interest rate changing affects home ownership affordability. The FHOG helps buyers to home ownership deposit requirements. This increases their chance of buying a house and becoming home owners.
The stump duty reduction impacted negatively on housing demand before stamp policy enactment (Costello, 2006, p.10). The negative impact was as a result of prospective purchasers stalling their purchases.
However, after the introduction of the concessions there was substantial increase in the segments market of specific first home buyers. The concession resulted to a lagged impact on the collective housing market. This is because cheap housing sellers traded up to properties that were extremely expensive.
The FHOG impacts significantly on borrowing. For instance, it relaxes constraints in borrowing for first time buyers. In addition to that, grant enhances home buyers potential saving with an aim of fulfilling the deposit needs for a loan. Even with the absence of grant, first home buyers would afford to purchase a home.
However, McDonald et al (2009, p.5) argues that first time buyers set conditions can result to financial crisis as a result of continued unemployment rates.
Bastiat main contributions to economics
The above author is portrayed as a champion of the harmony principle. However, this principle is not clearly understood. For instance, how it contradicts with views on the interaction of social phenomena.
The Magnum opus by Bastiat’s is labeled Economic Harmonies. Through the use of this book, he defends and develops the argument that the society members’ interests are harmonious just as the rights of the private property are respected amongst others (Bastiat 1964).
In addition to that, he believes that, un-tempered markets can independently operate without the intervention of the government. His central argument is easy to understand. He argues that, the free market economy cannot go against the interest of a specific population.
Furthermore,he intellectually argues that all proposals claimed that free markets antagonize some certain people or groups interests (Bastiat, 1851, p.3). Bastiat insight is confirmed by the economic history of the 20th century. His insight was based on interventionists’ schemes common denominator.
When government intervenes, it acts on situations such as unemployment, business cycles, monopoly and public goods. The major challenge with the above named cases was argued to be failure of markets. The problems cannot be solved well by the market unlike the government.
Economic policy decisions that explains the above points
Economic policy is an action taken by the government in order to influence or control the behavior of the economy. Most of these policies are government administered and implemented.
Policy decisions revolve around government taxation and spending. In addition to that, it encompasses the income redistribution from the wealthy individuals to the poor people and also the general supply of money.
In an economic system characterized by free market, scarce resources are equitably distributed via price mechanism. In this case, consumer decisions and consumer preferences and business supply decisions join effort to agree on equilibrium prices.
Government intervention may play a role in price mechanism in order to reorganize resource allocation. This is done with an aim of achieving social welfare and economic improvement. In pursuit of political endeavors, the economy is intervened by the government in order to allocate resources that are scarce among uses that are competing.
In summary, the economy is intervened by government in various ways such as producing more services and goods such as national security, infrastructure and education.
In addition to that, incomes can be transferred both horizontally and vertically in the population. Similarly, the government can alter the taxation costs without interfering with its size (Labonte, 2010, p.1).
Index of Economic Freedom
The previous years have experienced a decline in global economic freedom. Globally, there has been increased tension between free market and government control. This is more experienced in countries that are developed.
The economic freedom gains have been tempered with as a result of uncontrolled government spending. However, Economic freedom plays a significant role in driving prosperity resulting to improved level of education, health and wealth.
Economic freedom by definition is the extent to which an individual can pursue their economic interest without government interference. In pursuit of one interests, an individual should ensure that his or her action do not violate others identical rights.
The index of economic freedom measures regulatory efficiency, government intrusiveness, market openness and rule of law. The three countries that have moved up the ranking are such as Australia, Mauritius and Iceland. Generally, there was improvement on seventy five economies.
However, ninety countries lost their economic freedom whilst fourteen never showed any significant change. Out of the seventy five economies that have shown great improvement, seventy three of them are categorized as emerging or developing countries.
Most of them are found in the Sub-Saharan Africa, Caribbean/ Central and South America and the Asian Pacific. The only two countries in the developed world that have shown great improvement are Iceland and Australia as indicated by the 2012 index.
This is as a result of these countries effort to control their government spending. Mauritius also greatly improved after coming in the top ten for the first time.
The three countries that have declined in terms of ranking are such as the United States, Denmark and Ireland. Ireland was ranked 9th whilst the United States was ranked 10.
On the hand, despite Denmark rule of law that is strong and an efficient regulatory it dropped from top ten lists. This is as a result of its huge spending by the government which is similar to the approximately sixty percent of sum of domestic output and corresponding high burden of tax.
Australia is ranked number three with a score of eighty three point one (83.1). To further improve its position, the country needs to commit itself to the rule of law, reduced spending by governments, improve on its regulatory efficiency and advocate for open markets.
All these can act as an impressive flexibility in times of hard economic times (Miller et al, 2012, p.3).
References
Anonymous 2012, The price system. Web.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2008, ‘Housing assistance in Australia’, cat. no. HOU 173, Canberra.
Bastiat, F 1851, Harmonies economics, Guillaumin, Paris.
Bastiat, F 1964, Economic Harmonies. Van Nostrand, New York.
Bowman, Q 2009, Keynes economic theories re-emerge in government intervention policies. Web.
Costello, G 2006, ‘The Impact of Stamp Duty Reductions on Demand in the Perth Housing Market’, Pacific Rim Property Research Journal, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 198-212.
Kasper, S 2002, The Revival of Laissez-Faire in American Macroeconomic Theory: A Case Study of Its Pioneers, Pearson. New York.
Keynes, J.M 1936, The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, Macmillan, London.
Labonte, M 2010, The size and role of government: Economic issues. Journal of Macroeconomic policy, vol 4 (2), pp.1-27.
Lombard, M 2010, ‘Government intervention in OECD member countries: Equity at the expence of efficiency’, Journal of Economic Society of Australia, vol 36 (5), pp.310-316.
Mayo, S.K 1981, ‘Theory and Estimation in the Economics of Housing Demand’, Journal of Urban Economics, vol. 10, pp. 96-116.
McDonald, G., Mullineux, A & Sensarma, R 2009, ‘Asymmetric effects of interest rate changes: the role of the consumption-wealth channel’, Applied Economics, Vol 56 (2), pp. 1-11.
Miller, T., Holmes, K.R, & Feuler, E.J 2012, ‘Highlights of the 2012 index of economic freedom : Promoting Economic opportunity and prosperity’, The Wall Street Journal, Vol 12, pp. 1-12.
Mind tools 2012, Supply and Demand Curves: Understanding price and quantity in the market place. Web.
Ng, Y.-K. 2000, Efficiency, Equality and Public Policy: With a Case for Higher Public Spending, Palgrave Macmillan, London.