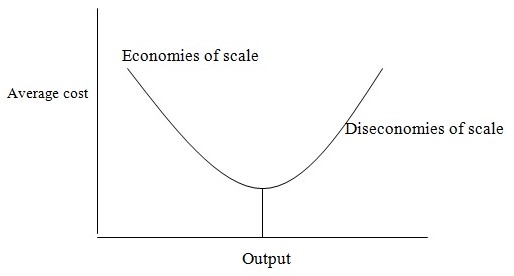
The concept of economies of scales is not an old one but developed through careful analysis of various firms regarding their purchases and expenses. In simple words, the concept explains the cost reductions in the long run when businesses make different attempts to buy or manage the inventory and as a result the production increases while the inputs decrease. There could be numerous explanations to that for instance; a firm may start developing good relations with the supplier and starts buying bulk purchases which could save costs (transportation costs incurred time after time to bring the raw material to the warehouse). To make it easier, the following figure will explain the economies of scale and diseconomies of scale. The figure explains the fact that higher the average costs lower the output and vice versa. It is also useful to consider few of the top US firms and analyse how they are reaching economies of scales.
The top US firm named Wal-Mart (Fortune: Global 500) has achieved economies of scales by purchasing fresh stock on daily basis from the suppliers on credit and yet in bulk, and as the edibles (fruits, vegetables) usually get sold within a day or two, Wal-Mart successfully pays the credit back while making profit from it. The other top firm named Exxon mobil, reached economies of scales by forming ventures with Saudi Aramco while undertaking billion dollar projects; synergy helped the two reaching economies of scales.
In case of General Motors, the economies of scale were reached with the help of outsourcing as the manufacturing plant in China helped it reduce costs (particularly labor). ConocoPhillips seems to be struggling in reaching economies of scale as it took a huge debt and diverted most of its efforts in clearing it, however it did make an attempt to recover through acquisitions, it will take a bit longer to recover completely. Ford Motor is although a successful conglomerate but has faced ups and downs throughout its history, the economies of scale is meaningless to it when it has just been able to recover from a huge loss, it is occasionally hit by changing patterns which do not allow it to be successful, an example could be the increase in gas prices when it started manufacturing such cars requiring gas.
The key to success for CitiGroup is its ability to offer wide range of services while keeping the same input which is money; however it has taken certain unethical measures such as eliminating the employees. Bank of America has also managed to reach economies of the scale with the help of extended brand portfolio while having the same input that is money. One of the supporting points in the cases of financial institutions is the availability of money to the markets, the more the loans are given to the market the higher the interests generated.
The companies like Hewlett-Packard have reached the economies of scale by managing its assets tactfully, it has used the same assets to modernize its products and hence the use of the same assets to produce an increasing number of goods has given it the advantage. The same case applies to IBM, which was once under pressure but using the technology wisely to produce modern goods in large quantities benefited it. The fact that such technological equipment should usually remain updated (from customers view point) helped the growth of companies dealing with technology.
References
Fortune 500 Global. 2008. Web.
Heakal, R. Investopedia: What are economies of scale. Web.
Anonymous. Investopedia: Diseconomies of scale.