Sources of Business Start-up capital
When starting a new business, there are different sources of funding, however every source has its own advantage and disadvantage, the following are the main sources of business startup capital and their rationale:
Personal savings and borrowing from friends and relatives: this approach happens mostly with small-scale businesses whose capital is not so huge, the capital comes from saved funds and incase there are some willing friends, they can be consulted to offer some grants in the business.
This source of finance is good as the money lenders keep the start-up on its toes to ensure that the business has succeeded.
Financial institutions lending: with current rise and growth in the financial sector, there is money available from banks and micro-finances institutions that can be used by a start up.
In developing countries and some developed worlds, financial institutions are offering loans to women and youth groups to assist them start up business; the financing may come in different forms like loans, extension of house mortgage, credit card, and groups lending. The main rationale of this approach is the weight placed on the entrepreneur to pay the funding.
Government, angel investors and non-governmental institutions: to facilitate economic growth, some government has come-up with micro-business financing projects; the projects are mostly targeted at the most vulnerable among the communities like the youth, women or people from a location with a low economic growth rate.
Angel investors are people who finance a certain idea; if an entrepreneur has a viable idea, they are willing to offer the necessary capital. A number of nongovernmental organizations that support poverty eradication offer some business startup capital.
Discuss whether the venture intends to accept government grants or guarantees as part of the capital structure
Government grants are available funds in the United States, however the nature of the grants seems to support existing businesses to expand their business through the purchase of fixed assets like machinery, complicated motor vehicles like drilling machine, research and developments.
In most cases, unless when they have been specially being made to support a certain sector of the economy, they are not meant for capital for startups. The above said and done, if the funds are available, there is entirely no problem or crime using the funds for capital structure.
The repayments rates of the grants is flexible and one that can allow a business to generate the funds and repay the grants comfortably, thus they offer a cheap and reliable source of capital to the company. The government allows the funds to be spread for a long period so they will be used for funding the capital structure.
Discuss the ratio of debt to equity in the initial capital structure and the rationale for this decision
When making the decision on the capital structure, and considering the business is a start up, the structure that is recommended is one that has 30:70 ratio of dept and owners equity.
The rational for the above structure is to ensure that the business is not high indebted at the start, so that incase of any risk that the venture will not pick, then the assets of the company can cover the costs of borrowed capital.
On the other hand, when a company has a low debt structure, then it can source for funds to financing activities that prove to be promising after the start; it will not have exhausted its borrowing capacity thus it can get funds for further development.
Discuss whether the new venture intends to go public
The new venture will start as a private owned company where it will embark on using quality management structures and strategic management tools to become competitive and diversify its operations.
When a base of operation has been acquired, that can guarantee shareholders return for their investments, then the company will consider selling shares to the public.
When going public, the company will start with 12.5% public ownership then with time and as demand for additional capital arises, and then it will offload other shares to the public.
Break-even analysis for the new venture
To manage the financial performance of the business, the company will be using breakeven charts to analyze the situation; breakeven charts are strategic management tools where a company compares the cost of a project and the revenue from the project.
At break even, the cost of production and sales equals the revenue gotten from the project. From the projections made, the company is expected to breakeven after a period of one year. The following chart will be used to project the cost and revenue relationship:
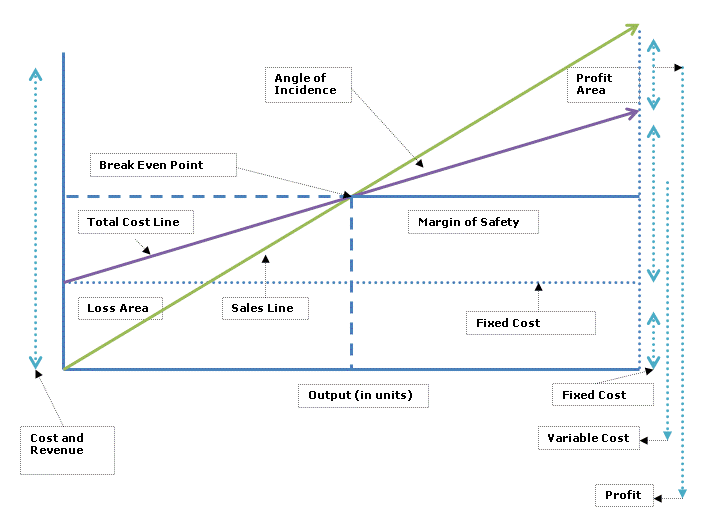
The management understands that for an effectively managed business, there should be cost management strategies as well as improving the sales of the company; the two management principles will be the main areas of concern in the company.
Occasionally, the company will be undertaking internal and external analysis to assist in establishing areas that can be improved to increase the company efficiency and competitiveness.
References
Livingston, J. (2008). Founders at work: stories of startups’ early days. New York: Berkeley.
Shane, S. (2003). A General Theory of Entrepreneurship: the Individual-Opportunity Nexus. New York: Edward Elgar