Overview
Problem Definition
Entrepreneurship is originates from the word entrepreneur which according to the Oxford dictionary is “a person who sets up a business or businesses, taking on financial risks in the hope of making profit.”
A recent research conducted by the Forbes with Odesk (the leading online employment agency) shows that the definition of an entrepreneur has gradually shifted from “someone who starts a company” to a more modern definition that is found on the basis of the innate mindset of an individual who explores change, responds towards an opportunity and acts on it.
The idea of entrepreneurship was initially invented in the 16th century, and the meaning has been changing over and over. According to Howard Stevenson (professor of economics at the Harvard Business School) entrepreneurship is the pursuit of opportunity beyond resources controlled. Entrepreneurship is influenced by the following factors:
- Economic factors: availability and size of capital, availability and quality of the labor force, availability of raw materials, market size and level of development of the infrastructure.
- Social factors: case factors, family background, education, attitude of society and cultural values.
- Psychological factors: need achievement, Withdrawal of Status Respect, motives and willingness to take risks.
Entrepreneurship in developed countries
The USA
The United States has the highest level of Entrepreneurial activities among advanced economies with about 12 in every 100 people engaging in entrepreneurial venture. The success of entrepreneurialism in the US is due to a number of Factors;
Access to capital, research and quality infrastructure; the relationship between American universities and Industries is very close and the education system focuses on promoting entrepreneurship.
The US has a culture that promotes experimentation and risk taking with an open immigration policy and good regulation structures that allow firms venture into new markets while allowing less productive firms to survive.
Finland
Entrepreneurship is considered as solution Finland’s challenges of job creation, economic growth and competitiveness.
Success in entrepreneurship is highly attributed to the support from the government which has created entrepreneurship policies that support industrial development focusing mainly on SMEs and that remove obstacles for entrepreneurial startups and growth. Numerous entrepreneurship promotion programs are implemented regionally and nationally.
Entrepreneurship is embedded in the education system; from the elementary school curriculum up to higher education institutions. Universities conduct researches related to entrepreneurial development.
Sweden
Sweden relies on entrepreneurial development for its competitive growth. The Swedish government has set up policies that favor a culture of entrepreneurship development. Success of entrepreneurial development in Sweden is also attributed to its education system that promotes entrepreneurial studies in universities.
UAE
Entrepreneurs in the UAE encounter difficulties of investing their resources in new business ideas due to stiff competition. These challenges include;
- Insufficient knowledge on getting support from the government.
- Inadequate knowledge on the benefits of venturing into small businesses.
- Insufficient awareness of business and poor skills.
- Negative attitudes about self employment and risk taking.
Entrepreneurship is a new business field in the UAE and enterprising entrepreneurs needs adequate training on ways of coming up with business ideas by studying the market trends and identifying niches. Good business ideas require acquisition of entrepreneurial skills and application of business knowledge from an individual’s education.
The UAE government offers funds for business development; entrepreneurs need to be informed on how these funds can be accessed and how to use them in implementing their ideas in the competitive business environment of the UAE.
Motivation and relevance to Masdar/UAE
The UAE has a potential capacity for entrepreneurship development; this proposal is motivated by the entrepreneurial capacity of Masdar City and its significance to the UAE.
This is a project of the Mubadala; a development company of the Abu Dhabi Government, it is a project purposed to fast track economic development of the United Arab Emirates. It is
The 5 Integrated units of Masdar
Masdar City
Built on the model of a modern smart city; It is a walled city with a six million square meter area and employs traditional Arab building technology. It’s based on the principles of zero tolerance on carbon emission, zero waste production and innovation of new energy production technologies. Technological inventions of Masdar City include:
- Harnessing of solar powered energy through installation of solar cells.
- Pollution free underground light rail transport system.
- Construction of wind turbines to harness wind energy.
- Minimal water wastage as over 80% of used water is to be recycled and gray water used for irrigation of agricultural land.
Due to its dedication and promotion of the use of clean power and renewable sources of energy, Masdar City hosts the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA); an intergovernmental organization that promotes the implementation and use of renewable energy on a global scale.
Masdar Institute
The Masdar Institute of Science and Technology is located in Abu Dhabi was created in collaboration with Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), is dedicated to c bring up a culture of innovation and entrepreneurial studies. The institute aims to nurture high skilled personalities and work with industry leaders to build a strong economy and foster Abu Dhabi’s economic diversity.
Masdar Carbon
Masdar Carbon is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) project aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emission in the City. The stored carbon will be pumped to oil fields and used for maintenance of underground pressure to boost oil recovery.
Masdar Power
Masdar power is mandated to put up a range of large scale renewable energy power systems using renewable energy technologies of Photovoltaic cells, harnessing solar power and wind power.
Masdar Capital
Masdar Capital has invested in commercialization via clean-tech funds to support the development of new technology projects to promote and commercialize renewable technologies in UAE 11.
The major companies that are in collaboration with Masdar City include; Cosmo Oil Company of Japan, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yazak, 3M Targetti Siemens and Schneider Electric 9. Others include The Abu Dhabi Company for Onshore Oil Operations (ADCO), Petroleum Institute (PI) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Center for Innovation Systems and Entrepreneurship (CISE)
This is a new project developed at the Masdar Institute of Science and technology. Its goals are;
- Developing and promoting entrepreneurial motivation among youths in the UAE.
- Formulation of new and creative systems that encourage entrepreneurs to come up with new businesses in order to promote local empowerement and the financial system.
- Creation of new instructive programs in creativity and invention management and adoption the world class methods in the local environment.
- Plan for new areas of funds and guidelines while offering new assets and supporting the current ones.
Objectives
The MIT Desphande Centre is a department that helps in commercialization of innovative technologies and inventions through transformation of potential ideas into inventive products and revolutionary business enterprises.
Innovations and ideas are evaluated for funds and grants based on their ability to be practically applied in competitive business environments, their ability to be commercialized, their likelihood of success, the level of their fundamental implications and ability to yield high rewards.
MIT’s Desphande Centre supports outside cross-disciplinary collaborative proposals for evaluation and funding of innovations and splendid business ideas from students and entrepreneurs that are non MIT members.
Collaboration among professional photographers, Arabic and English literature writers between MIT and UAE would be a success since it involves an innovative ideas venturing into strong market and whose success is likely.
This project aims to foster entrepreneurial activities in the UAE by;
Empowering UAE’s young entrepreneurs to seek collaborations with educational and research institutes that promote development of novel innovative and practical business ideas.
Educating enterprising entrepreneurs on development and creation of creative innovations that have high chances of legalization, with potentially big impacts on the economy where ready market is available.
Empowering entrepreneurs with knowledge of identifying the processes and procedures those innovative ideas must pass through in order to be socially accepted as viable and worth investing in.
Empowering young entrepreneurs with the knowledge and skills for identifying potential collaboration partners; most entrepreneurs with potential investment ideas hardly have information on how to find potential like minded partners.
Educating entrepreneurs on ways of getting government funding and reaching out to non-governmental organizations to fund their innovations and noble ideas; entrepreneurs fail to venture into markets due to inadequacy or complete lack of funds and under-informed on available sources of funds.
Encouraging entrepreneurs to come with strong innovation ideas that have clear paths to success, this is in order to impact in the UAE business environment that is characterized by stiff competition.
Most potential innovations have failed to achieve commercial success due to the inability of their inventors to choose viable markets and venturing into wrong markets. This project aims at educating entrepreneurs to identify feasible markets and adapt their ideas to fit the market requirements.
The project also purposes to advise potential entrepreneurs to put their ideas into practice. Having a business idea does not guarantee business success; it requires the owner to put it into practice by venturing into a variety of markets before finally settling on the best market environment for their idea.
Literature Review
Scholars in the field of economics have approached entrepreneurship from different perspectives with numerous views regarding entrepreneurships and innovation, Peter Drucker suggests that entrepreneurship goes in hand with innovation, changes and opportunities for innovation while Steve Blank, a business school professor says that entrepreneurship is about getting out into the world and doing and not basically researching and writing.
These scholars do agree that entrepreneurs face difficulties of finding the right opportunities and the needed innovation, creating competitive brands using strong products and finding the right markets.
Rob McSherry and Marry Douglas postulate that innovation involves doing things differently or doing different thing in order to arrive at large gains in performance, they further recognize that lack of capital and funding is the main obstacle for innovation. Others however contrast with Rob McSherry and Marry Douglas by associating innovations with the rise of technical inventions such as the computers and steam engines.
Entrepreneurs in the developed countries (USA, Sweden and Finland)
Although government policies, infrastructure and large markets provide vast investment opportunities in developed countries, young entrepreneurs continue to face challenges. Point out that the decline in economic growth has resulted in decline in entrepreneurship opportunities and constant increase in business’ start-up costs.
Young entrepreneurs sale their ideas to capital ventures and find themselves exploited as capital ventures benefit and leave them with nothing. Other scholars argue that the content of entrepreneurship in the local education especially in Finland is so wide; the methods of teaching entrepreneurship in schools are poor and the goals of the entrepreneurial education conflict with the local business environment.
According to Monia Lougui, entrepreneurs in Sweden face regulation barriers; there are over 1200 laws, 2200 regulations and 8100 governmental rules that Swedish entrepreneurs must comply to. She goes on to say state that Swedish entrepreneurs are also faced with regulation burdens; these are the financial, economic and non-economic costs that are encountered when one is complying with the regulations 20.
She further states that young entrepreneurs in developed countries face entry barriers; these are obstacles that promote existing firms to make constructive economic proceeds while making it difficult for new firms to make impacts in the market. They also face financial barriers and cultural and value barriers.
Entrepreneurs in the gulf region
The Gulf region has attracted a lot of attention in the recent past due to its rapidly growing economy, especially Abu Dhabi and Dubai.
Researchers suggest that the main obstacles facing young entrepreneurs in the Arab world is having access to capital, Saifur Rahman further says that despite Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) contributing greater percentages in national GDP, they are highly neglected and Lending for SMEs in the Gulf Coast Countries is very low and access to finance is the Greatest Challenge.
Khalid Al Ameri argues that that the Middle East education system has not shifted to meet the needs of the current technology and young entrepreneurs may not have enough knowledge about the business environment.
Hanifa Itani, Yusuf M. Sidani and Imad Baalbaki support Khalid Al Ameri saying that insufficient managerial and financial information and lack of government support are major obstacles to UAE SMEs and entrepreneurs.
They argue that societal traditions of the Arab are a major setback to aspiring women entrepreneurs in UAE, further more personal reasons such as attitude of risk taking and fear of failure are also factors inhibiting Entrepreneurship development in the UAE.
Some previous literature has portrayed the gulf region as having inhibitive policies; markets are not unified making it difficult for mobility of entrepreneurs and free trade.
A common stereotype in Kuwait impedes the success of young entrepreneurs; the economy of this GCC country is dominated by few merchant families and starting businesses is usually viewed as an act keeping the family’s legacy alive rather than as innovations. Bruhn et al point out that lacks of managerial capital is the key restriction for young entrepreneurs in most developing countries.
Entrepreneurs in other parts of the world
Young entrepreneurs in the developing countries have also had their share of the cake in terms of the challenges they face. Studies show a continuing trend of the lack of sufficient government support for young and female entrepreneurs.
Some scholars have argued that poor policies on entrepreneurship in developing countries result I entry of non-potential entrepreneurs in the field leading to failures and constant negative attitudes toward entrepreneurship.
Following the above literature review, it surfaces that capital, insufficient government support and unfavorable government policies are the most common and most pressing issues that suppress young entrepreneurs worldwide and specific entrepreneurs in the UAE for which this research focuses on.
Research Plan
Methodology
This chapter discusses the following, the design and data collection.
Research Design
The research design of this study will encompass both qualitative and quantitative methods with greater emphasis being relayed on the qualitative research approach due to its effectiveness when descriptions are required.
Methods of data collection
Survey
This study will conduct surveys in the UAE by identifying the most innovative and successful entrepreneurs, looking at the new business ventures established in the near past. Conduct a survey of the number of new businesses that have thrived and compare with those that failed to survive.
Focused Group Discussions
The study will conduct focused group discussions with aspiring entrepreneurial students pursuing various degree programs and diploma courses across the United Arab Emirates institutions.
Included in the group discussions will be renowned business personnel and entrepreneurs from various sectors of the UAE and small and medium enterprises (SMEs) owners with discussions being centered on the barriers faced by young entrepreneurs in the UAE. Top of the discussion will also be the measures to be taken to motivate young entrepreneurs to venture into the market.
Questionnaires
For the purpose this research two types of questionnaires were prepared:
- Structured questionnaire; this is closed ended questionnaire prepared for the purpose of quantitative data collection and analysis.
- Unstructured questionnaire; this questionnaire was prepared for purposes of interviews to guide the interviews during the interviews.
Interviews
The study will interviews sampled university and college students and university dons, SMEs owners and renowned innovative people in the UAE. These innovative people include; MDs and CEOs, government officials, owners of companies and people with creative ideas.
Research plane
Objectives
The objectives of this study are as follows:
- To identify the major challenges facing young entrepreneurs in the UAE.
- To identify the available sources of funding; those young entrepreneurs in the UAE can access to fund their ideas.
- To identify the healthy partnerships and collaborations that entrepreneurs in the UAE can engage in to build their innovative ideas.
Thesis statement
Lack of capital, government support and insufficient entrepreneurial knowledge and skills continuously undermined investment for young UAE entrepreneurs.
Sample Questionnaire

Sample Interview Questions
- Mr./Dr/Proff…. you are a well known entrepreneur. How do you define entrepreneurship?
- What is your opinion about entrepreneurship in the UAE?
- What do you feel for young entrepreneurs of the UAE?
- What are the obstacles for young entrepreneurs of the UAE?
- What do you think is the biggest challenge of entrepreneurs in UAE?
- How did you overcome these challenges to be who you are?
- For how long have you been an entrepreneur?
- Could suggest the most appropriate solutions for challenges facing young entrepreneurs?
Closing remarks and thanking the respondent.
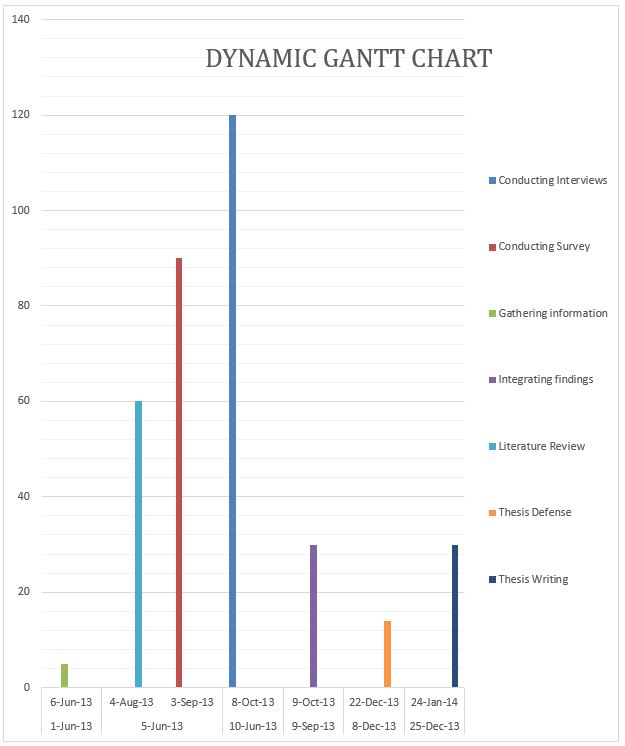
Gantt chart explanation
The Gantt chart above does not the exact timelines that would be required, the figures used are estimates durations of the research scope and are used mainly to aid in the generalization of the concept.
Gathering information
This is the very initial stage of the study; it must first be completed before other processes kick off. Information gathering generally entails the problem definition whereby the researcher identifies and defines the problem, defines the objectives and motivation for their study.
Literature review
The literature review is the second phase of implementation of the study; it involves researching on what previous scholars and writers have done in the same field. The literature review can be done in parallel with other activities.
Conducting the survey
This is the third phase of the research. It involves going to the field and identifying the potential people and resource that will be of significance to the study. The survey phase is done in parallel with the literature review as they are mutually independent.
Conducting interviews
This is the actual process of collecting data related to the study, the interview process runs in parallel with the survey process and the literature review but cannot be done before the survey phase.
Integrating findings
This process comes fifth in the study process and is done after all its preceding stages are complete because it involves analyzing the data.
Thesis defense
After integration of the findings and drawing of conclusions the study report is presented for approval. This is done after the preceding stages are completed.
Thesis writing
After the approval of the research proposal, the research finding is written down in a master’s thesis report and published. This is the final process of the study.
References
Dan Schawbel, “The Re-Definition Of Entrepreneurship And Rise Of Freedom-Seeking Freelancers,” Forbes, p. 1, 2013.
Thomas R. Eisenmann, “Entrepreneurship: A Working Definition,” Harvard Business Review, p. 1, 2013.
Justin Tadlock. (2012) Relivingmbadays. Web.
Paul Davidson Reynolds, Entrepreneurship in The United States, 1010079780387456713th ed.: Springer US, 2007, vol. 15.
Chad Evans, Randall Kempner,David Attis, Samuel Leiken Debra van Opstal, “Where America Stands: Entrepreneurship Competitiveness Index,” Washington, D.C, 2007.
Ulla Hytti Jarna Heinonen, “Analysis Of Entrepreneurship And Innovation Policy in Finland,” Business Research And Development Centre, Turku School Of Economics, UDK 658.11 (480) 608, 2007.
Going Global, “Sweden Career Guide 2006: Small Business / Entrepreneurship / Start-Ups Employment Trends,” Uited States, 2006.
Srinivas Inguva Samia Kargwell, “Factors Influencing the First Generation Entrepreneurs: An Analytical Study on the Graduates of UAE Universities,” International Journal of Business and Social Science, p. 145, 2012.
Masdar City. (2011) Masdar City. Web.
Nnamdi O Madichie, “IRENA – Masdar City (UAE) – exemplars of innovation into emerging markets,” Foresight : the Journal of Futures Studies, Strategic Thinking and Policy, pp. 34-47, 2011.
Masdar Institute. (2013) Masdar Institute. Web.
MIT School of Engineering: Deshpande Center for Technological Innovation. (2013) MIT Desphande Centre For Technological Innovation. Web.
Chad Brooks, “What is Entrepreneurship?” Business News Daily, 2012. Web.
Francesca Di Meglio, “Real Entrepreneurs Don’t Write Business Plans” Bloomberg Business Week, 2013. Web.
M Hunter, “On some of the misconceptions about entrepreneurship.,” Economics, Management and Financial Markets, pp. 55-104, 2012, 7(2). Web.
Rob Mcsherry, “Innovation in Nursing Practise: A Means to Tackling the Global Challenges Facing Nurses, Midwives and Nurse Leaders and Mangers in Future,” Journal of Nursing and Management, pp. 165-169, 2011.
Erick A. Borg and Karl Gratzer, “Theories, Brands and Entrepreneurship: Conceptualising Brand Strategies,” in 3rd Annual InterNational Conference on Business Strategy and Organisational behaviour, Huddinge, Sweden, 2013, p. 58.
Gedmin Jeffrey and Gamester Nathan, “U.S. Prosperity Is in Decline; The latest data on economic well-being show the biggest slide in entrepreneurship and opportunity. Businesses’ start-up costs are rising in the land of pioneers and patents.,” Wall Street Journal, 2012. Web.
Steven M. Davidoff, “Dealbook; In Venture Capital Deals, Not Every Founder Will Be a Zuckerberg,” The New York Times, 2013.
Monia Lougui, “Identifying Obstacles Encountered by Swedish Entrepreneurs? Evidences from the Start-line,” Stockholm, Sweden, Master’s Thesis 2010.
Samia BadihStaff. (2012) Gulfnews. Web.
Saifur Rahman. (2013) Gulf News. Web.
Khalid Al Ameri, “To nurture human potential, invest in vocational training,” The National, 2013. Web.
Hanifa Itani, Yusuf M. Sidani, and and Imad Baalbaki, “United Arab Emirates female entrepreneurs: motivations and frustrations,” Equality, Diversity and Inclusion: An International Journal, 30(5), pp. 409-424, 2011.
Saadouli Nasreddine, “Mechanisms for Seeking and Developing Young Entrepreneurs in Kuwait and the GCC Region,” Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability 6(1), pp. 67-84, 2010. Web.
Miriam Bruhn, Dean Karlan, and Antoinette Schoar, “What Capital Is missinng in Developing Coutries,” The American Economic Review, no. 2, pp. 629-633, 2010. Web
Jong Ha Lee and So Young Sohn, “How Effective Is Government Support for Korean Women Entrepreneurs in Small and Medium Enterprises?,” Journal of Small Business Management49. 4 (2011): 599-616. , pp. 599-616, 2011.
Imed Drine and Mouna Grach, “Supporting Women Entrepreneurs in Tunisia,” The European Journal of Development Research24. 3:, pp. 450-464., 2012.
Victoria Burnett, “Amid Fealty to Socialism, a Nod to Capitalism,” The New York Times, 2013.
Wim Naudé, “Promoting Entrepreneurship in Developing Countries: Policy Challenges,” United Nations University, Helsinki, special report 978-92-808-3083-5, 2010.