A business-oriented information system can be characterized as a set of interconnected system elements that function in combination to input, process, store, control, and analyze the data obtained by the company (Rao & Klein 2013). The organization can use this data to take proactive measures and make the best use of decision-making activities. Five essential elements make up a business-oriented information system – human resources, software, hardware, data, and communications (Qiu 2013). Human resources contain the system developers, technical support, and the final users of the product.
Computers and other peripheral devices represent the majority of the hardware resources. The software is commonly perceived as the employees’ program to accomplish the organizational objectives (Plattfaut 2014). The data resources are represented by the company’s electronic database and all other files stored by the company. Communications resources are merely network resources (including intranet) used to connect the employees and maintain that connection (Linger, Fisher & Barnden 2016). Business-oriented information systems are essential because they provide their users with numerous advantages such as accuracy and agility. What is even more important, these systems are relatively flexible and can be programmed to perform an extensive array of complex tasks (Korunka 2014).
To analyze a business, several different models can be used. For instance, Porter’s 5 Forces Model, Porter’s Diamond Model, and McKinsey’s 7S Model (Isaias 2016). This report will analyze one of the work systems of Etihad Airways.
Business Overview
Etihad Airways is one of the most respectable UAE companies. They are aimed at providing high-quality services at competitive prices (Fleisher & Bensoussan, 2013). Etihad Airways represents Abu Dhabi, and their approach to business is based on Arabian hospitality and generous services. The company’s key focus is the collaborative growth and implementation of the latest technologies in their work systems. The company’s pricing policy complies with the middle-class requirements and can be described as reasonable (Rocha et al. 2014).
Business Strategy
Table 1. Porter’s Five Forces.
The value chain of Etihad Airways can be outlined as follows – primary activities -> logistics -> operations -> customer service -> secondary activities -> human resource management -> marketing and sales -> technology.
System Analysis
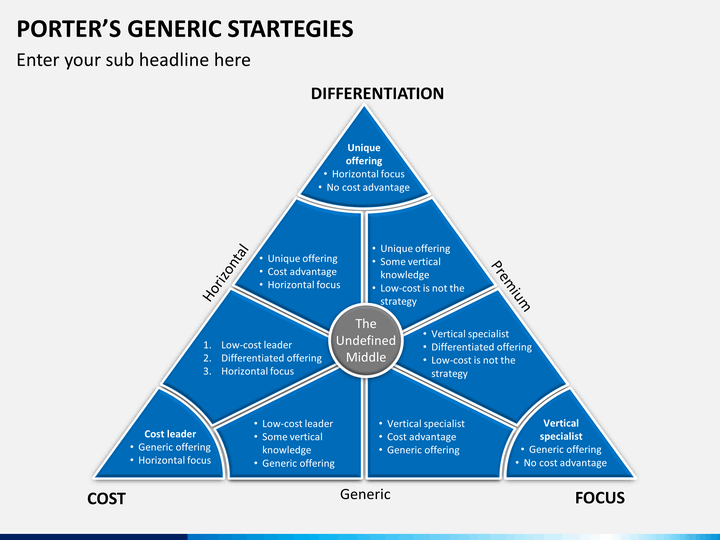
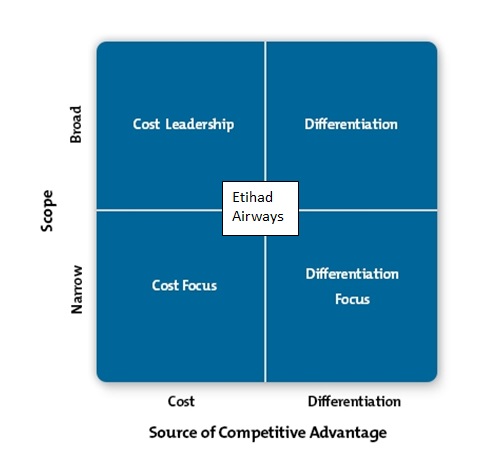
The system of ticket ordering is reviewed within the framework of this report. The fundamental notions that can be used to characterize it are unique offerings and cost leadership. This can be explained by the fact that Etihad’s strategy is developed horizontally but focuses on the customer advantages that may help them win over the market. The company moved away from the undefined middle and allowed their customers to order tickets at an advantageous price (Balgieri 2014). Therefore, this Etihad Airways system allowed the company to become one of the most widely recognized airlines who showcase their differentiated offerings. The company’s horizontal focus can explain the complexity of the process of ordering tickets. In other words, Etihad Airways is aimed at connecting to more clients than simply adjusting their price/ quality ratio to the customers’ requirements.
Therefore, the ticket ordering system accurately reflects the overall company’s strategy and follows differentiation. If we look at Etihad’s competitors, we will see that most of these companies propose only generic offerings and specialize in vertical development. In perspective, this crucial difference will become the decisive factor in terms of the ticket purchasing process but may lead to the elimination of Etihad’s competitors. The company draws attention to their special offers and does not consider its pricing strategy to be the cornerstone of Etihad’s success. The current ticket ordering system can be improved by creating a “wizard” that will guide the customers through the stages of ordering the ticket instead of presenting all the information on the screen simultaneously. This strategy is costly, but it will allow Etihad to develop horizontally even more. On a long-term scale, this should improve the system’s performance and ultimate customer satisfaction regarding the interaction with the system.
Website Critique
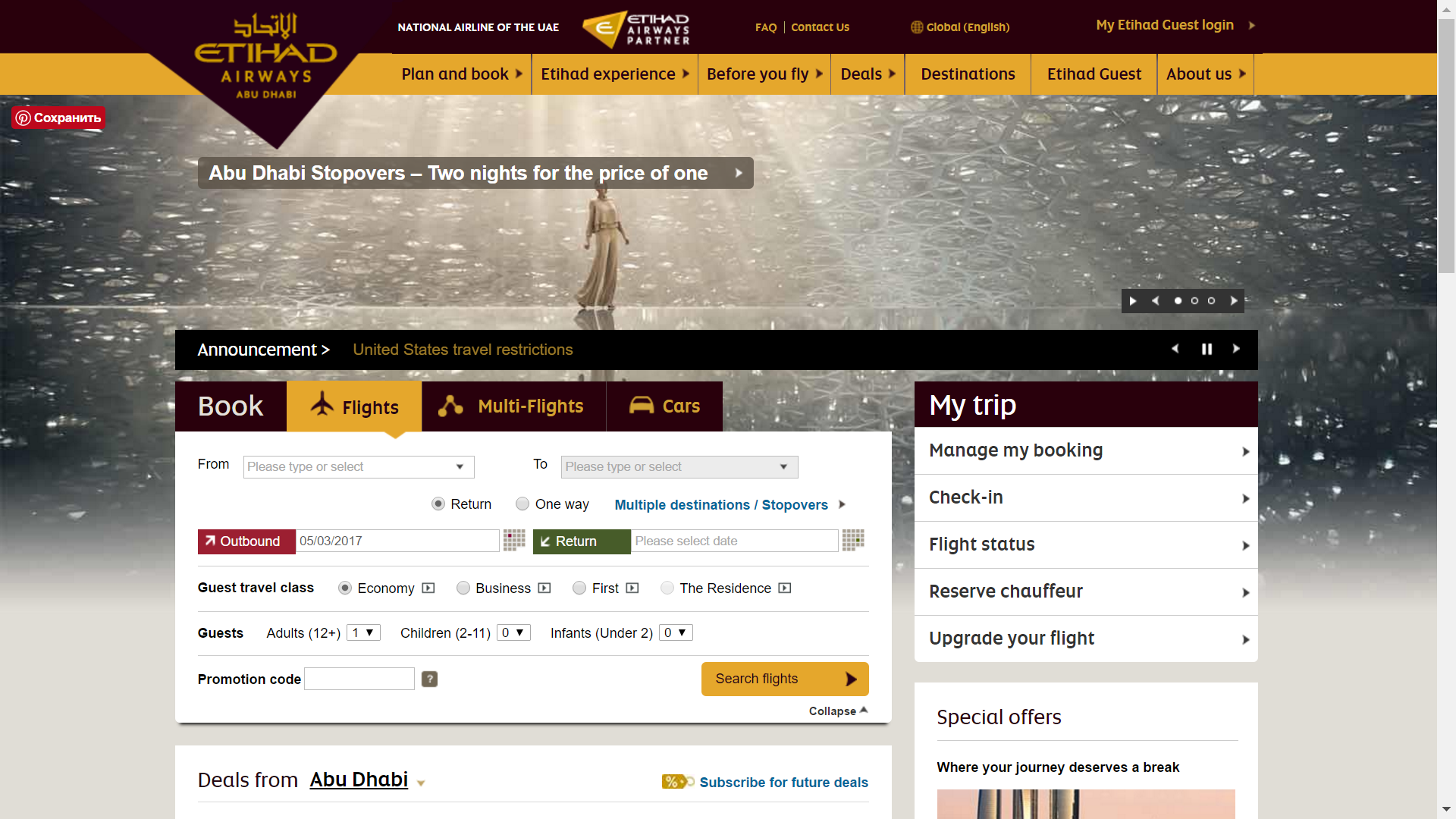
The business strategy of Etihad Airways is aimed at providing its customers with high-quality services at a reasonable price. Therefore, if we analyze the ticket order system, we will see that the company’s strategy does not correlate to the website’s design. This is reflected in the complexity of displayed information and the inability to intuitively comprehend the information (Sorokin & Pardalos 2013). There are too many items on the home page of Etihad Airways’ website that may confuse the customers and take them away from ordering the tickets (See Figure 3). Moreover, the color scheme does not appeal to middle-class customers. It may turn off a cluster of clients who consider this company luxurious and expensive regardless of their offers.
Reference List
Balgieri, D 2014, Information systems, management, organization and control, Springer, New York, NY.
Fleisher, C & Bensoussan, B 2013, Business and competitive analysis methods: Effective application of new and classic methods, Financial Times Press, Indianapolis, IN.
Isaias, P 2016, High level models and methodologies for information systems, Springer, New York, NY.
Korunka, C 2014, The impact of ICT on quality of working life, Springer, New York, NY.
Linger, H, Fisher, J & Barnden, A 2016, Building sustainable information systems, Springer, New York, NY.
Plattfaut, R 2014, Process-oriented dynamic capabilities: Framework development, empirical applications and methodological support, Springer, New York, NY.
Qiu, R 2013, Business-oriented enterprise integration for organizational agility, Business Science Reference, Hershey, PA.
Rao, P & Klein, J 2013, Strategies for high-tech firms marketing, economic, and legal issues, M.E. Sharpe, Armonk, NY.
Rocha, A, Correia, A, Tan, F & Stroetmann, K 2014, New perspectives in information systems and technologies, Springer, New York, NY.
Sorokin, A & Pardalos, P 2013, Dynamics of information systems: Algorithmic approaches, Springer, New York, NY.