Introduction
In August 2016, several Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Smartphones were reported to explode. The manufacturer called upon its engineers hurriedly to diagnose the source of the problem. The initial report pointed to a fault in batteries procured from one of the suppliers. This led to a recall of these smartphones and continued shipping of the same mobile device with batteries from a different supplier. However, the issue surfaced again with reports of the new replacements also exploding, prompting the company to halt the entire Samsung Galaxy Note 7 production. The failure, subsequent recall, and the complete halt of the Galaxy Note 7 production have had social and legal ramifications.
This Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure case study aims to analyze the issue, its history, and the aftermath, including the crisis management and the discovered reasons behind the battery explosion.
Background
Smartphones have very advanced computing capabilities, such as high-definition cameras, media players, sensors, GPS navigation units, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, among other features. For most Smartphones, an Android operating system is used. The features need to be supported by stable memory, batteries with the correct power output, an efficient power system, and a good shell to operate efficiently. The risk of failure of Smartphones is mainly in the memory access violation and mobile phone hardware such as the batteries and the shell. Overall, studies on the failure of Smartphones have pointed to two major types of failures, i.e., accidental or malfunction of the software or Android. For this report, the focus is on the hardware or software malfunction.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure
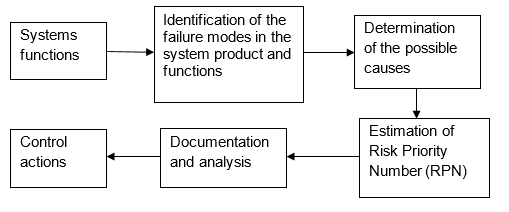
The explosion of the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 resulted in the recall of the phones. The phones that were overheating were analyzed to establish the causes of the explosion. The techniques employed for the analysis were Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA). This entails a critical analysis of the entire lifecycle of a product. It analyzes the specifications of the design, operation, and maintenance by establishing the system functions, identification of the failure modes in the system, and functions which then determine the effects and possible causes. The analysis covers both the software and hardware functionalities.
The FMEA is used by engineers in the design stages of a product or post-analysis in the case of issues arising. The initial FMEA conducted after the failure was hardware FMEA. This is a straightforward analysis guided by the understanding that mechanical, electronic, and electrical failures happen due to some issues, such as unanticipated stress, overload, and faulty wiring. The analysis by the engineers concluded that lithium-ion batteries from one of the suppliers had a fault. Part of the battery’s inside was coiled incorrectly, causing stress to the battery.
By performing critical risk analysis, the possible malfunction of software or hardware can be established before the product is launched into the market. The critical failure modes can be ascertained by calculating the Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) through brainstorming. This helps to establish the potential areas of failure and the possible degree of damage. As a result, mitigation measures are taken before the product is released to ensure that the risk is contained.
It is thus paramount that Samsung should have carried out a thorough risk analysis for all the hardware and software from the suppliers before launching the product. Also, after the recall, the analysis was hurriedly carried out; hence, the conclusion that the failure was from a battery procured from a particular manufacturer was theorized rather than being scientifically proven with quantifiable data.
Discussion on Samsung Note 7 Failure
The failure of Samsung’s Galaxy Note 7 has had enormous financial implications. It is estimated that it may lead to a revenue loss of over $ 5 billion. Even though the company could easily deal with the loss of income, the failure has great social and legal ramifications. For instance, the failure has already attracted class-action lawsuits against the company, which touch on how the recall and replacement were carried out.
Also, there is a high likelihood of lawsuits that relate to the damages and injuries caused by the explosions. These lawsuits will affect the consumer perception of Samsung’s Smartphones. For example, the Google search for ‘Samsung Explosion’ spiked in August and September despite the recall being only for Galaxy Note 7. The failure has also had social implications for Samsung phone users. Some airlines in the U.S. do not allow passengers to use any Samsung phone onboard their planes.
Conclusions
The failure of any product leads to unintended consequences for the manufacturer and the consumers. Even though investigations are still ongoing to establish the exact cause of the Samsung Note 7 explosions, Samsung’s engineers need to give more care to the materials used to develop the software and hardware of its Smartphones. Also, there should be a critical risk analysis in which an RPN for each possible failure mode is calculated before a product is released to the market. This will ensure that parameters with high-risk factors are properly investigated, and risk reduction measures are taken in advance.
References
- B. Chen and C. Sang-Hun, “Why Samsung Abandoned Its Galaxy Note 7 Flagship Phone”, The New YorK Times, 2016.
- K. Krishnakanth and P. Kavipriya, “Android application development for environment monitoring using Smartphones”, International journal of Mobile Network Communications & Telematics, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 41-45, 2013.
- S. Malek, R. Roshandel, D. Kilgore and I. Elhag, “Improving the reliability of mobile software systems through continuous analysis and proactive reconfiguration,” Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering-Companion Volume. ICSE-Companion 2009. Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp. 275-278, 2009.