Introduction
Walmart is a large retail platform operating within and beyond the American borders. Walmart is active in over 20 countries and actively participates in providing social commodities and services. The company also provides a wide variety of goods and services for its customers and encourages them to purchase from it since they are reliable. In the recent past, the business has increased its sales due to its exploitation of e-commerce services provision (Weinstein, Anti and Ochoa, 2021, p. 30). This report assesses the impacts of Walmart’s activities on its customers as their main stakeholders and provides the strategies the company uses to mitigate the identified risks.
Customers As Stakeholders
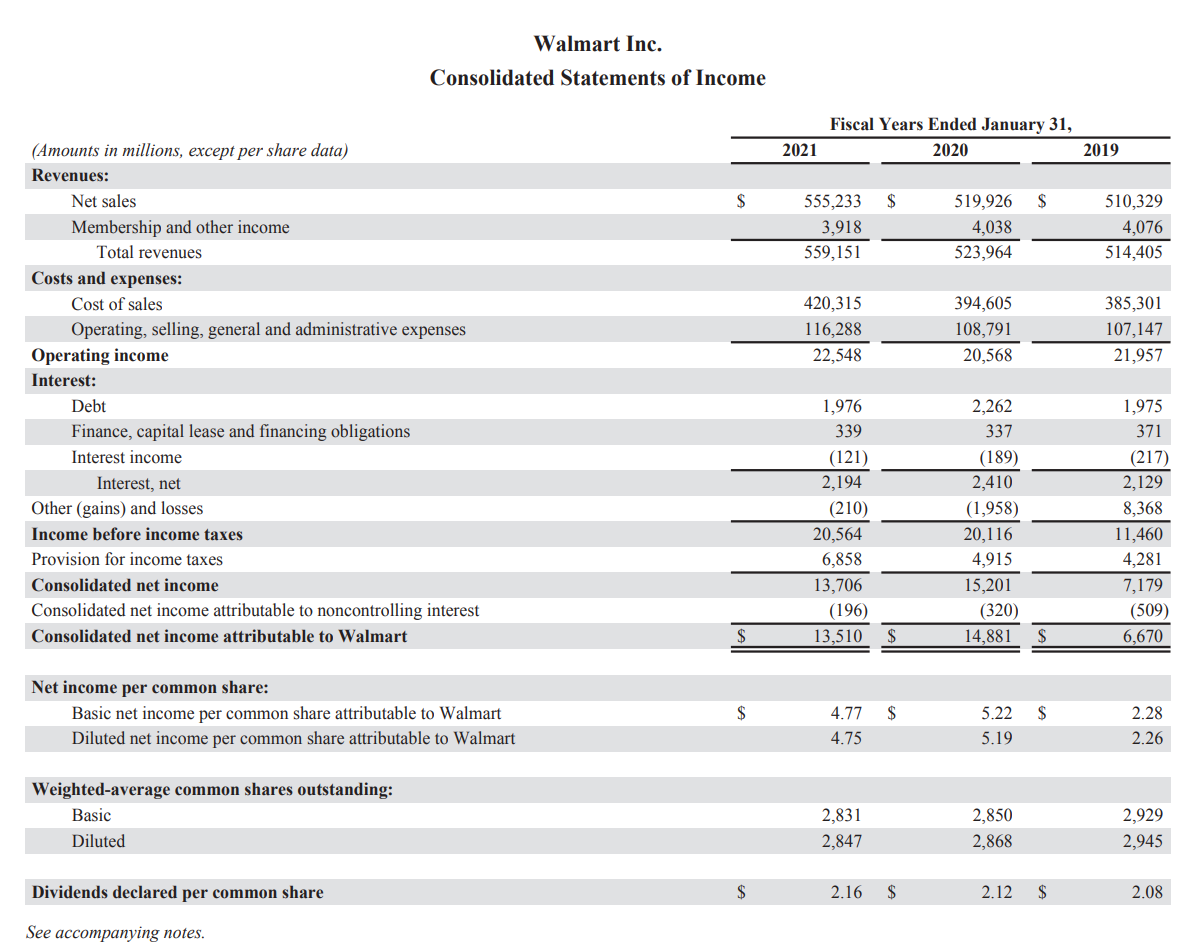
Customers are crucial for every business because they provide platforms for their expansions and increase the company’s profitability. They provide revenue that the firm uses to pay other stakeholders like employees, suppliers, and investors (Phillips and Rozworski, 2019, p. 5). In 2021, Walmart U.S. and Walmart international segments generated $370 billion and $121.4 billion in sales (Loutzenhiser and Mann, 2021, p. 658). The high volume of sales indicates how the business affects the consumers’ purchasing and consumption behaviour. Walmart helps meet the customers’ demand for products and services by helping them attain them without strain. Therefore, obtaining goods and services is one of the many ways Walmart’s activities influence the customers as stakeholders.
Financial Risks that Customers Face
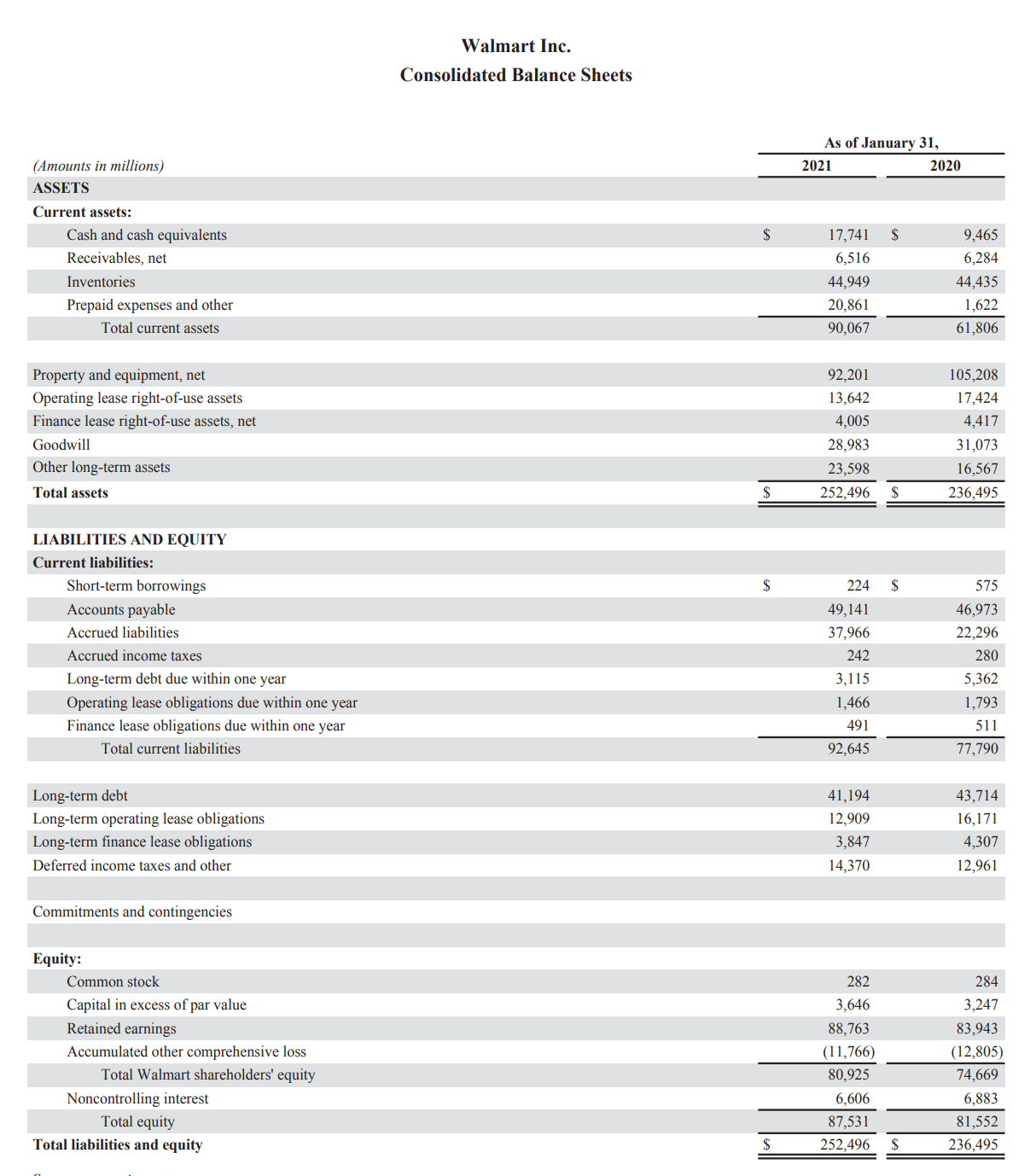
One of the financial risks that the firm faces is the liquidity risk that amounts to difficulty converting most of its assets into liquid cash (Svetlova and Thielmann, 2020, p. 142). The business made most of its earnings in 2021 in form of electronic money since the customers barely visited the stores physically. The firm may mitigate the financial liquidity risk by undertaking cautious financial planning and analysis by forecasting future cash flows (Seaman and Bowman, 2021, p. 6). Therefore, the business should use comprehend appropriate structures to deal with the issue of financial liquidity risks that may contribute to significant losses.
How Business Activities Affect Customers
After purchasing the items on Walmart, the customers receive delivery services to locations they can easily choose. The delivery unit saves consumers’ time and controls their spending on the item’s transportation to their doorsteps. Walmart has many deliveries and picking outlets within their hosting countries to meet their customers’ delivery needs. For example, from Walmart’s 2021 financial report, Walmart international has 3000 delivery and 3750 pickup joints. The delivery affects the consumer’s accessibility to their products and affects their time schedules since they have to plan to pick their belongings from the specific locations. Thus, Walmart serves a wide audience due to their delivery unit that supplies the purchased items to the consumer.
Another Walmart’s use of legal protection rights such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and domain names affect the consumers. Other ownership rights are trade dress, trade secrets, and proprietary technology to secure the items and services they provide for the consumers (Germain and Sitler, 2021, p. 90). They influence the customers purchasing since they can rely on the products and services. Such securities guarantee customers of the quality and correct measurements that Walmart offers. Walmart has registered all these rights with the relevant authorities, thus assuring customers that their products are appropriate for their consumption. The registration influences the consumer’s purchasing since more customers can rely on the quality and quantity that the firm provides.
Strategies Walmart Uses to Solve their Activities’ Effects on Customers
Nevertheless, Walmart uses different promotional techniques to maximize its consumer base. It employs technological development to attract more customers since the high technology guarantees high response speed and the right quality items. Therefore, customers depend on technological upgrades to ensure appropriate goods and services. Great technological improvement encourages a proactive customer care desk that quickly responds to the customer’s complaints, thus effective product delivery that attracts more customers (Sharma and Kumar, 2021, p. 217). Moreover, the business has adapted advanced e-commerce knowledge to increase its outreach to consumers (Cao, 2021. p. 60). Embracing important technological approaches encourages a good relationship between the company and customers and attracts more customers through effective service delivery.
After the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in late 2019 that persisted beyond 2021, Walmart made some losses in its one-on-one business engagements with customers. However, the company made overwhelming profits through its e-commerce platform that attracted high volumes of customers due to the restrictions from movements outside households to contain the disease (Reardon et al., 2021. p. 464). The company rescheduled the visiting hours to its premises and often conducted cleaning and sanitizing activities to contain the spread of the COVID-19 viruses (Chopra and Stamatopoulos, 2021, p. 1). Shipping strategies also played a vital role in expanding its profits since many customers demanded delivery services to their households. Walmart enjoys a high customer ratio due to its involvement in more customer maintenance activities and generates high revenue from the positive relations.
Conclusion
Walmart’s activities influence consumer behavior and control important consumer responses such as decision-making. The shipping activity and ownership of credits and other ownership rights significantly boost consumer reliability on the business and guarantee them safety. The firm uses advanced technology systems to attract more customers by having a well-functioning customer care system. The company also encourages e-commerce as a method of purchase due to the COVID-19 virus that requires them to protect consumers from catching the pandemic.
Reference List
Cao, P. (2021) ‘December. Big data in customer acquisition and retention for e-commerce–taking walmart as an example, In 2021 3rd International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2021) (pp. 259-262). Atlantis Press.
Chopra, S. and Stamatopoulos, I.Y. (2021) The impacts of Covid-19 on U.S. retail: An empirical investigation [Project]. Web.
Germain, K.B. and Sitler, L.H. (2021) ‘The constitution commandeth: Thou shalt not protect the same subject matter under design patent and trade dress laws’, Chicago-Kent Journal of Intellectual Property, 21(1), p.90. Web.
Loutzenhiser, G. and Mann, E. (2021) ‘Liquidity issues: Solutions for the asset rich, cash poor’ Fiscal Studies, 42(3-4), pp.651-675. Web.
Phillips, L. and Rozworski, M. (2019) The people’s republic of Walmart: how the world’s biggest corporations are laying the foundation for socialism. Verso Books. Web.
Reardon, T., Heiman, A., Lu, L., Nuthalapati, C.S., Vos, R. and Zilberman, D. (2021) ‘“Pivoting” by food industry firms to cope with COVID‐19 in developing regions: E‐commerce and “copivoting” delivery intermediaries’, Agricultural Economics, 52(3), pp.459-475. Web.
Seaman, B. and Bowman, J. (2021) ‘Applicability of the M5 to Forecasting at Walmart’, International Journal of Forecasting. Web.
Sharma, M. and Kumar, P. (2021) ‘Adoption of blockchain technology: a case study of Walmart’, In Blockchain Technology and Applications for Digital Marketing (pp. 210-225). Web.
Svetlova, E. and Thielmann, K. (2020) ‘Financial risks and management’, International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 5 pp.139-145. Web.
Weinstein, A.T., Anti, K. and Ochoa, E. (2021) ‘World’s biggest retailer launches Walmart Plus and customers have their say, Journal of Business Strategy. Web.
Appendix
Walmart Integrated Report