Frito is a highly productive enterprise involving the use of modern technological developments and methodologies for evaluating the effectiveness of its working plan. According to Heizer et al., certain product specifications allow the organisation to stick to a particular regime and make every possible effort to impart business stability (25). Priority market preferences help company owners to focus on a single industry and finance those areas of production that are designed to strengthen existing quality standards and prevent falling consumer interest.
The performance of Frito may be assessed by comparing the performance indicators with those of other large enterprises specialising in food products. Heizer et al. cite a specific example and note that the time for picking potatoes, processing, and delivering them to the company’s production lines is less than twelve hours (25). In addition, Frito’s production facilities operate without interruption and days off, which allows for continuous work and, therefore, consistently high market supply (Heizer et al. 25). Accordingly, this order of the supply chain indicates the well-thought-out strategy of interaction between the manufacturer and its partner.
Certain sources of pressure exerted on FEEDO to ensure environmentally friendly and harmless production largely determine the mode of the operation of the enterprise and its current operating principles. One of the initiatives supported as mandatory is the policy of reducing energy consumption. Modern and high-tech elements are designed specifically for these purposes. Heizer et al. argue that “these elements include scorecards and customized action plans that empower employees and recognise their achievements” (25).
The status of a “green manufacturer” encourages the organisation to make all possible efforts in order to ensure the sustainable development of its technical base and create optimal conditions for environmentally safe work. Any violations during sanitary and epidemiological inspections may affect the company’s reputation negatively and lead to a decrease in consumer demand. In order to prevent this outcome, control over the processing of raw materials is the prerequisite that determines the effectiveness of measures in terms of maintaining FEEDO’s product quality.
The production principles applied in FEEDO meet the modern standards of the work of large enterprises and are characterised by high-efficiency indicators. However, by introducing development and growth strategies, current performance may be improved, and even more significant success and consumer acceptance can be achieved. For instance, in order to enhance the quality of products, the organisation can allocate additional funds for the assessment of market technological developments to incorporate them into its own mode of operation.
The reliability of equipment and its safety are valuable factors influencing the quality of production positively. Work flexibility is the feature that allows enterprises to maintain a consistently high level of sales and implement new growth strategies in parallel. To improve this quality, new partnership agreements can be developed with other large market participants in order to borrow current working methods and optimise individual production processes.
Such a factor as low costs does not always indicate sufficiently high product quality. Taking into account the fact that in FEEDO, “expensive special-purpose equipment” is utilised, it is essential to pay attention to other areas where it is possible to reduce costs, for instance, expensive marketing campaigns (25).
Quality is more important than promotion; therefore, it is meaningless to save on consumer trust. Accordingly, manufacturing practices improved by savings in marketing can be an effective engine for the subsequent success of FEEDO and its superiority over competitors. Updating the technology base is a natural development process, and adhering to a quality growth strategy is the evidence of a careful approach to the target audience.
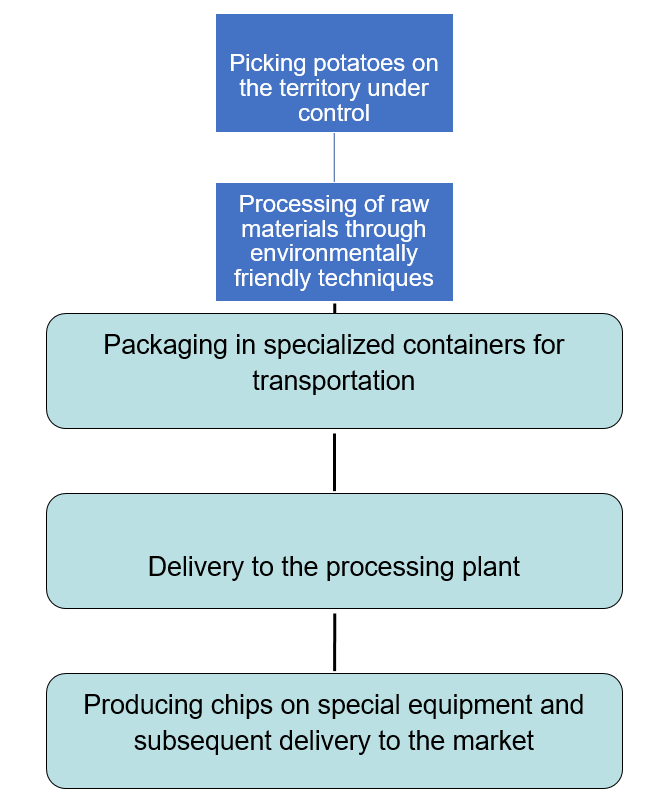
To trace one of the stages of FEEDO, it is possible to give an example of Lay’s potato chips production, which is shown in Figure 1. This method is the detailed description of all applicable processes. To analyse the effectiveness of this principle, one may estimate the time and cost required for each of the stages. Since the delivery of raw materials is fast, the production can be optimised by establishing profitable partnership agreements with suppliers. As a potentially productive interaction strategy, barter can be offered so as not to waste financial resources and use products as the means of advertising or payment.
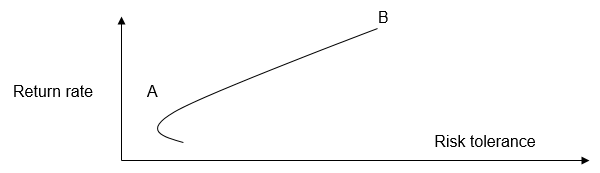
To promote an optimal investment strategy, it is customary to use appropriate schemes called efficient frontiers. Risk minimization is a key task assigned to such strategic tools, and drawing up the best ways of making a profit is also one of its features. Using the example of Figure 2, it is possible to assess the ratio of low- and high-risk investments (A and B respectively).
The dominant firms producing potato chips in the region are Cheetos, Tartitos, Lay’s, and Ruffles. Each of the representatives of the market adheres to an individual risk strategy and applies specific efficient frontiers. Cheetos aims to reduce the cost of its products, responding to customer interests. Ruffles and Lay’s, conversely, focus on their goods quality. The greatest flexibility can be traced from Tartitos that controls the production cost of chips with the greatest attention.
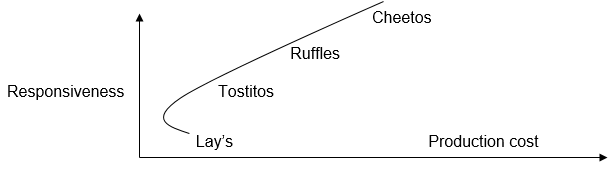
In Figure 3, Cheetos’ high responsiveness to the target audience is seen along with its low production cost.
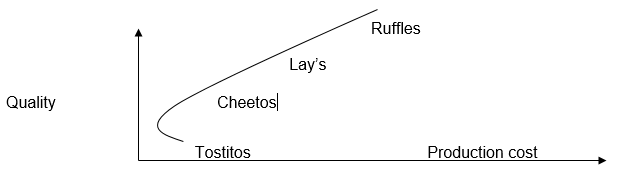
In figure 4, two firms (Ruffles and Lay’s) strive to increase their quality indicators to meet customer needs, while production cost increases.
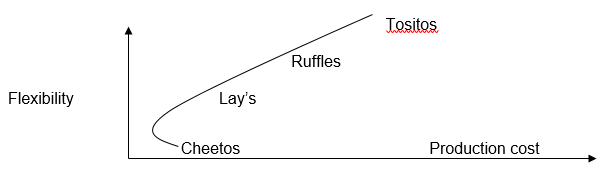
In Figure 5, Tositos’ high flexibility as its priority strategy is demonstrated.
Work Cited
Heizer, Jay H., et al. Operations Management. 12th ed., Pearson, 2017.