George Walker Bush was born on July 6, 1946 as a first-born child of President George H.W. Bush and Barbara Bush. He was born in New Haven, Connecticut. The American politician became the 43rd president of America.
His family had a heritage of success in the public service and business arena. For instance, his great grandfather Samuel P. Bush was a successful businessperson in the steel and railroad industries upon which he built the family empire. Moreover, he served as a significant advisor to President Herbert Hoover and thus his family had connections with political figures in high positions.
His grandfather Prescott Bush was a successful businessperson too. He served in the Army during World War 1 and together with his wife, raised their children and expected them to excel in everything they did hence they grew up to become competitive and achieved success in their lives as shown by their son George H.W. Bush the 41st American president (Boyd, 2007). George W. Bush did not disappoint the family legacy of greatness, as he became the American from 2001 to 2009.
He attended a public school called San Jacinto Junior High in Midland, Texas and was elected as class president. During his time in San Jacinto, he played in the football team. After a year, he transferred to a private school called Kincaid in Houston, Texas after his family moved there because of his father’s business in 1959.
The following year he moved to Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts an elite preparatory school because his parents believed in giving their children the best education. He was an average student and worked very hard because he feared to fail (Rumsch, 2009). He did not become a star in academic or in sports like his father, but he was very social and made many friends who nicknamed him ‘Lip’ as he always had an opinion on anything (Cohen, 2000).
He joined the basketball and baseball teams and become the head cheerleader for the football team during his senior year. He joined Yale University and studied history. During his stay at Yale, he joined the rugby and baseball teams. He was a social person, and he joined the Delta Kappa fraternity and Skull and Bones a secret Yale society and graduated in 1968 (Keira & Pritchard, 2009).
George W. Bush went on to join the Harvard Business School and earned a Master of Business Administration (MBA) degree (George W. Bush, 2011). He became the first president of America with a Harvard MBA (George Bush’s Legacy, 2009).
He was a businessperson in the oil industry prior to entering politics. He opposed government regulation. For a long time, he lived under the shadow of his father and wanted to build his own identity. Therefore, he thrust himself into the world of politics in 1978. He ran for a house seat in Texas, but his bid was unsuccessful.
He returned into business and started small companies in the oil industry. He formed the Arbusto Energy that later became Bush Exploration and merged with Spectrum 7. He became the chair, but his company did not escape the decline in the oil prices and it folded up becoming Harken Energy.
He became a board member at Harken. He is rumored to have had a problem with alcohol but he quite the habit in 1986 and defected to his wife’s church the Methodist (Keira & Pritchard, 2009). His evangelical faith is said to have influenced some of his decisions later in his presidency. He moved to Washington DC to help his father in his presidential campaign in 1988.
He brought in the support and vote for the Christian Conservatives, and his father was elected as the 41st president of America (Keira & Pritchard, 2009). Later George W. Bush bought shares in Texas Rangers baseball franchise and was actively involved in its team projects.
Time passed by and in 1992, his father called him to help in running his reelection campaign. He served as a campaign advisor. On the other hand, George W. Bush did not lose hope in running for an elected seat again and in 1994, he threw himself back at politics and ran for Governor of Texas. His campaign promises were the improvement of education, crime reduction and improvement of the welfare program.
He ran against Ann Richards, an incumbent Democrat on a Republican ticket. Moreover, he pledged that Texans would carry concealed weapons once they chose him. He went on to win the election and became the governor (Cohen, 2000). During his tenure, he pushed for tax cuts and give government funding to organizations so that they could educate the public on the dangers of drug and alcohol abuse and domestic violence.
Although Texas ranked poorly in environmental evaluations, the electorate looked at his efforts in improving education and ensuring better pay for teachers. His political career continued to rise because he was reelected as governor for another consecutive term becoming the first Texan governor to do so in a four-year term (Burgan, 2003).
Faith was important in his life. He encouraged faith-based organizations to take the step of helping the needy, and his support for the organizations saw his approval rating soar. He also opposed abortion due to his faith. During his first term as governor people started to speculate that he could run for the presidency in the future, his reelection made the speculation stronger, and eventually he made a decision to vie for Republican presidential nomination (Cohen, 2000).
Eventually, he announced his interest in the candidacy for the presidency in June 1999. He ran for his party’s nomination and managed to beat the other presidential hopefuls to clinch the running ticket.
After winning the Texas governor seat, George W. Bush began to get ready to run for the presidency in 2000. Many political experts and reporters dismissed him as a serious presidential candidate because he often made blunders in his speeches. However, such opinion did not deter him.
When the presidential elections came, he threw himself into the race. He was the son of a former president it was advantageous to him because he could count on the support of wealthy Republicans during his campaign. He managed to raise $93 million a very high figure at that time. Using the money he raised, he put together a talented group of people in his campaign team and numerous advertisements on television (Burgan, 2003).
George W. Bush is conservative, and he ran his campaign by saying that he was a compassionate person. He promised to cut taxes, as it was the right thing to do to help save and build America. He argued that people could use the tax cuts to open businesses. He also urged churches and other private organizations to get involved in helping the community instead of waiting around for the government to be directly involved.
Moreover, he called for the increase of money spent in the military to develop a missile-defense system. The defense system would enable the U.S. destroy large missiles that would target the country. He believed in a safe country that could defend itself against attacks. He promised to improve education as well as aid the minorities (Burgan, 2003).
Furthermore, George W. Bush painted himself as a uniting factor and many people listened to him as he promised to unite the nation in a bid to overcome their problems and make America a prosperous country that could make them proud. He also came across as a person who could connect with the population as he relied on his Texan roots to portray an image that many would approve thus elect him president (Carney & Dickerson, 2000).
The Republican nomination was a close battle, but George W. Bush edged out John McCain, his closest rival, and he chose Dick Cheney as his running mate. Cheney had experience, as he was a veteran politician. George W. Bush hoped Cheney’s experience would make people feel comfortable thus overlook his own inexperience (Keira & Pritchard, 2009).
He ran a fierce campaign against the Democratic candidate Al Gore. During the campaign, he faced many criticisms from his lack of experience. He was also criticized for the way he handled complex issues by ignoring them off or treating them casually. The Democratic Party highlighted his strong opposition against abortion and the opposition to the hate-crime legislation.
Others such as the liberals criticized him for supporting the death penalty, and they talked about the high numbers of death penalties that were given in Texas during his tenure as governor (Keira & Pritchard, 2009).
The 2000 presidential campaign was hotly contested and ended up to be one of the closely contested races in the American history. Different media houses called the election in favor of both candidates, and eventually a court battle followed as Al Gore sought for a recount of the Florida votes.
The state’s votes were important, as the winner would be the president. The Florida state would determine the winner of the Electoral College votes and after a month-long court battle, the Supreme Court ruled to end the vote recounts in Florida, and George W. Bush was declared the winner according to the initial Florida results that showed he had won. H e became president despite losing the popular vote that left a deep division between the Democrats and the Republicans.
President George W. Bush promised to heal the rift that had emerged during the elections between the Republicans and the Democrats as many people still harbored doubts about his legitimacy as he was inaugurated into office on January 20, 2001. The shadow of doubt did not go away, and it followed George W. Bush until the terrorist attack on American soil in 2001.
Meanwhile, George W. Bush worked toward getting tax cut proposal passage as he had promised during the campaigns. Moreover, he supported the exploration of oil in Alaska, and many criticized him for allowing the exploration to take place in the protected natural reserves (Graham, 2010).
His greatest test in office was yet to come until on that fateful day dubbed 9/11. Terrorists hijacked two planes and rammed them into the world trade center in New York, bringing it down.
Another plane hit the Pentagon building, the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense killing nearly three thousand people and injuring more than six thousand. The country was shaken by the attack thrown into grief. The division seen before quickly took a back seat as people rallied behind the President, when he declared war on terror.
They were more concerned about their safety than politics many people were satisfied with the action taken by the president, and his approval ratings went high. He declared war on global terror, and he aimed to destroy the terrorists of the group A Qaeda led by Osama Bin Laden. The group consisted of Islamic fundamentalists.
The U.S. military attacked Afghanistan using air strikes, as it was believed to be the grounds in which the terrorist trained for their terrorist acts (Lind & Tamas, 2007).
The United States military toppled the central governing regime of the Taliban and although the operation did not capture the exiled Al Qaeda leader, many countries supported the United States action. Consequently, the federal office of Homeland Security was established.
The war continued and the country entered an economic recession, and the Bush administration received critic from the people who were opposed to the war from the onset. The administration was accused of violating human rights of the detainees and the civil rights of the Americans (Lind & Tamas, 2007). For instance, the civil liberties of Americans were violated as some citizens were detained in secret locations and denied access to an attorney.
Hence, people began becoming uncomfortable with the ongoing war, which was very costly for a country going through an economic downturn, and when the Bush administration extended the war to Iraq based on intelligence of the presence of weapons of mass destruction in Iraq (Draper, 2007).
Thus, it became necessary to wage a second war in Iraq. The invasion went well, and the Sadam regime was brought down but the aftermath of the war left the country in a bad situation due to a power vacuum that was left behind (Keira & Pritchard, 2009).
Moreover, many people were killed in Iraq in the violence that followed from various militia groups. The war was very costly, and the president’s ratings began to decline sharply. It turned many nations against the United States as n weapons of mass destruction was found in Iraq (Lind &Tamas, 2007).
The President failed in some of his domestic policies such as in the Sarbanes-Oxley legislation that involved ethanol mandate. George W. Bush included the bill in his agenda even though it was not among his campaign promises, and it proved to be a wrong choice. Critics say the Bush administration should have acted to veto the legislation, but it did not and the legislation achieved its short-term goal that restored investor confidence in the American securities.
On the contrary, its long-term effects are being felt now, as companies are discouraged from going public. Foreign investors have started to look elsewhere to invest because the legislation has increased the cost of doing business in America. The legislation has also imposed rigidities and added extra coast in running public companies (Graham, 2010).
Conversely, President Bush achieved some success during his reign such as revamping the economy due to his open policy on free trade that ensured that America enjoyed a good relationship with countries in South and Central America. One of the ways through which President George W. Bush tried to improve the economy was by signing the Andean Trade Preference Act that helped to improve the relationship between entrants into the global market (Lind &Tamas, 2007).
The President used a cross partisan technique to reach out to moderate Democrats and have them support his policies. Using the cross partisan approach he brought about legislative packages that saw bills on tax cuts sail through the Congress successful. Other legislative bills that passed were the Medicare and nuclear energy (Graham, 2010).
In addition, the two bailouts that were passed during the Bush administration prevented the collapse of the largest financial institutions in America as their collapse would have destroyed the United States economy and resulted in unspeakable repercussions to other countries in the world. Even Bush was criticized for deregulating of the financial industry that eventually led to the problem the action taken saved American and the world (Keira &Pritchard, 2009).
His first term in the White House was relatively successful in implementing important domestic policies such as on education and tax cuts, and he proved that he was a capable leader.
He also managed to overcome the polarization that had occurred during the controversial 2000 election and managed to pass key campaign policies. His second term in office was different from the first as he achieved less success in his agenda.
He became more assertive and tried to pass legislation that the political climate did not favor. The President’s power was limited, and he seemed to take Republicans in Congress for granted by failing to deliberate on what would have been his priority agenda during his second term. However, he still managed to win some bills such as the energy bill and housing sectors bill.
The failure that George W. Bush experienced during his second term was his inability to select bills that could earn support of some Democrats instead they did not appeal to the Democrats, and it was very easy for them to oppose the bill thus hurting his presidency by weakening it as he failed to unify them.
The Immigration reform appealed to the Democrats, but it did not go well with some Conservative Republicans, who opposed it and he responded by attacking his base. Therefore, the Democrats gained an upper hand against the divided Republicans (Graham, 2010).
The natural disaster the Katrina Hurricane saw the Bush administration come under fire as many cried against the White House response to the disaster. The race issue arose and image of the President together with the Republican Party was hurt as many criticized the slow response and lack of preparedness in the disaster (Maranto & Lansford, 2009).
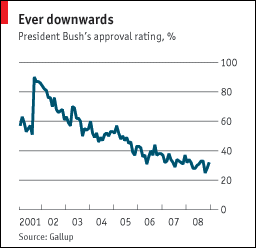
Finally, President George W. Bush will go down in history as one of the most interesting American presidents. He managed to elicit hate and anger in an equal measure both at home and abroad. He left the office with the lowest ratings than any former president as shown in appendix 1.
However, the decisions he made in 9/11 attack, Iraq war and the 2008 global downturn will remain as the most significant marks of his presidential legacy.
Some reporters may have dismissed George W. Bush as not smart enough to run for president, but he proved them wrong as he showed he was a capable leader in his own right, and he could make major decisions in spite of the unfavorable political mood.
His failure in some foreign policies eclipsed the success he achieved in domestic policy. Nonetheless, the decision made by the President influenced not only America, but also the whole world.
Appendix 1
Reference List
Boyd, V.J. (2007). George W. Bush. New York: InfoBase Publishing.
Burgan, M. (2003). George W. Bush. Minneapolis, MN: Compass Point Book.
Carney, J. & Dickerson, J.F. (2000). The selling of George Bush. Time, 156(4), p30.
Cohen, D. (2000). George W. Bush: the family business. Brookfield, CT: Millbrook Press Inc.
Draper, R. (2007). Dead certain: the presidency of George W. Bush. New York: Simon & Schuster.
George Bush’s legacy (2009). Web.
George W. Bush. (2011). Web.
Graham, J.D. (2010). Bush on the home front: domestic policy triumphs and failures. Indiana: Indiana University Press.
Keira, S. & Pritchard, J. (2009). George W. Bush. Retrieved from EBSCHOST Database.
Lind, N. & Tamas, B. (2007). Controversies of George W. Bush presidency: pro and con documents. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press.
Maranto, R. & Lansford, T. (2009). Judging Bush. California: Stanford University Press.
Rumsch, B. (2009). George W. Bush. New York: ABDO Publishing Company.