Introduction
Motorola lost its No.1 position as mobile handset marketer in 2008 . The financial figures for Motorola have not been grim for the company since 2008. The performance of the company has been continually deteriorating. According to analysts, the company faced a loss of 11 cents per share, and its sales figures fell by 28 percent in 2009 .
Its sales were far behind the sales of closest competitors like Nokia, Samsung, and LG. The grim financial and sales figures indicate the ailing situation of the company and the with a highly fragmented handset worldwide market, Motorola faces dire challenge to regain its lost status.
Given the current bleak situation of Motorola, it is necessary to find ways to alter the current situation of the company. This paper is a case study on Motorola. The aim of the paper is to understand the present problems Motorola faces and the strategy it has taken to cater to its global market. The case will categorically try to identify areas where Motorola falls short to achieve growth. The paper will try to ascertain the reason why Motorola has been facing continual losses and will try bringing out ways it could recover from it.
The paper is divided into three parts. First, the paper will deal with the current situation of Motorola. The second section will analyse the current situation of Motorola. Based on this analysis strategic and tactical recommendations will be drawn for the company in the third section of the paper.
Current Situation
This section will demonstrate the current situation of Motorola. This section will begin with a brief background of Motorola Inc. and then describe the current situation. This will discuss the company’s financial situation and the steps the company has taken to revamp its present situation.
Business Background
Motorola provides mobile solution for a large range of technology based product and services. Their business divisions are divided into three segments – “mobile devices”, “home and network mobility”, and enterprise mobility solutions” . The mobile devices segment manufactures and sells wireless mobile handsets and smartphones.
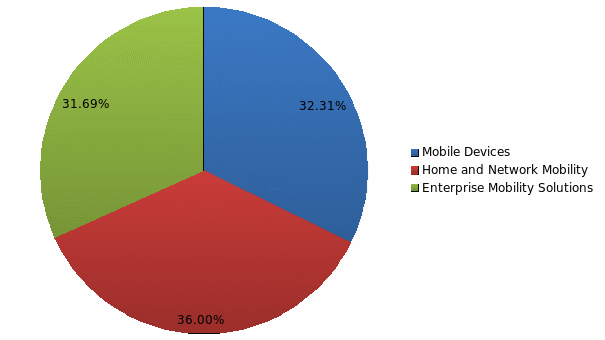
The mobile business segment is the second largest segment of the company comprising of 32 percent of the total revenue in 2009 (see figure 1). The largest segment is enterprise mobility and third is home and network mobility with 36 percent of net sales. This segment “designs, manufactures, sells, installs and services digital media products and wireless access systems” .
The network business takes care of end-to-end cellular network, radio bases stations, and allied software and services. The target customers for this segment are mobile phone operators, television operators, etc.
Financial Situation
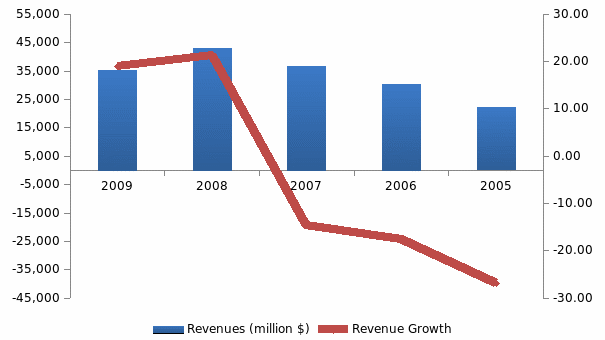
The financial condition of Motorola has been in doldrums since 2007. The company faced growth until 2006 but started to fall since 2007. The negative growth has become larger and larger every year as the revenue growth rate continued to fall further down.
Financial Analysis of Business Segments
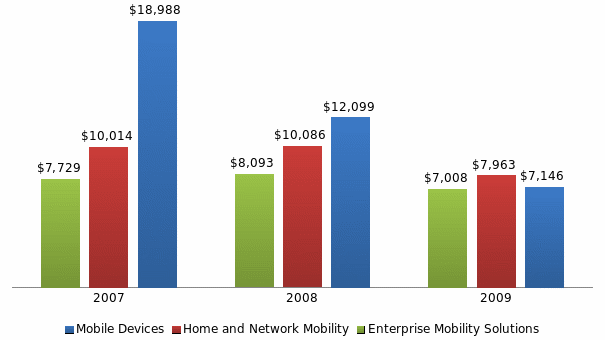
Figure 3 shows the segment wise revenue earned by Motorola from 2007 through 2009. The mobile device segment posted revenue of $18988 million in 2007, which comprised of 52 percent of the total revenue earned by the company. However, in 2008 it fell to $12099 million, and a share of 40 percent.
It slipped further in 2009 with a share of just 32 percent and overall revenue of $7146 million. The home and network mobility segment saw marginal growth in 2008 when it grew from $10014 million to $10086 million. However, it too fell to $7963 million in 2009. Similar trend has been observed by the enterprise mobility solution that increased its revenue in 2008, however fell by 4.5 percent. Therefore, Motorola’s segment wise revenue earnings have fallen for all segments in 2009.
However, the largest fall has been faced in the mobile devices segment. Figure 4 shows the segment wise operating profit (loss) from 2007 through 2009. The data demonstrates that the mobile devices segment of Motorola has constantly posted operating losses from 2007 through 2009, and the magnitude of the loss has been increasing constantly.
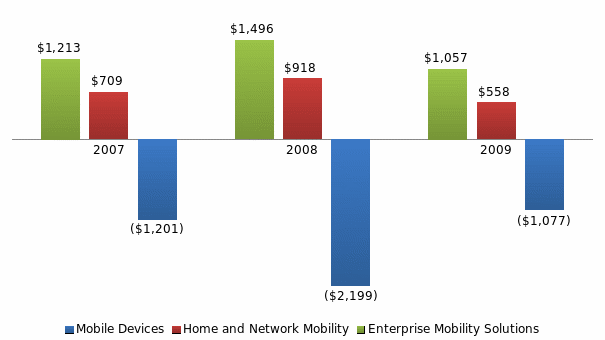
Financial Analysis of Geographic Segments
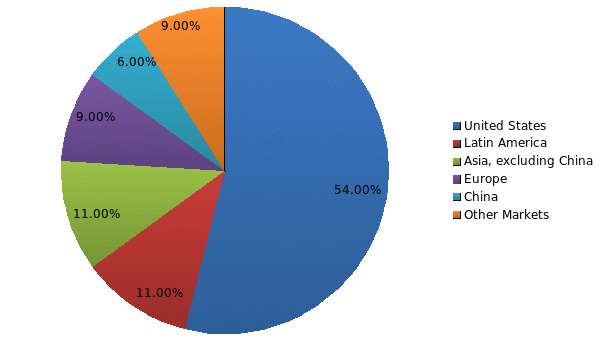
Motorola has its operations in various countries like the US, UK, China, Brazil, Israel, and others. According to the geographical division of the business of Motorola, it has the largest market in the US (54 percent) as in 2009. The net sales growth in all the geographic regions has been negative in 2008 and 2009 (see table 1). The largest fall in sales revenue has been in Brazil, China, UK, and in other nations. The sales figures have marginally improved in the US with decline in sales becoming less from 20.7 percent to 19.54 percent.
Table 1: Geographic division and financial analysis.
The asset turnover ratio of the geographic division for 2009 and 2008 shows that the highest asset turnover ratio is for the other nations in 2009 with the ratio being 60.4, which increased from 9.1 in 2008. The lowest turnover ratio has been reported for the US, China, the UK, Israel, and Singapore. Low asset turnover in the regions mentioned may indicate that there is obsolescence and inefficiency in the regions. Thus, overall, a low asset turnover ratio indicates lower efficiency.
The share regional sales to net sales according to geographic areas of operation are presented in the following figure. The figure shows that the largest market for Motorola is the US. Europe, Asia, and Latin America form the second largest market for the company. This shows that the operations of Motorola are concentrated in one region i.e. the US.
The second largest market for the US becomes Asia (including China) forming 17 percent of the total sales. Therefore, the company may try to concentrate more on this region as Asian countries are developing very fast.
Performance Analysis
Figure 6 presents the performance ratio analysis of Motorola for the year 2005 through 2009. The analysis shows there has been a constant fall in the growth of revenue, and ultimately in 2007, the revenue started falling, as revenue growth became negative. This shows that the revenue performance of the company has been declining.
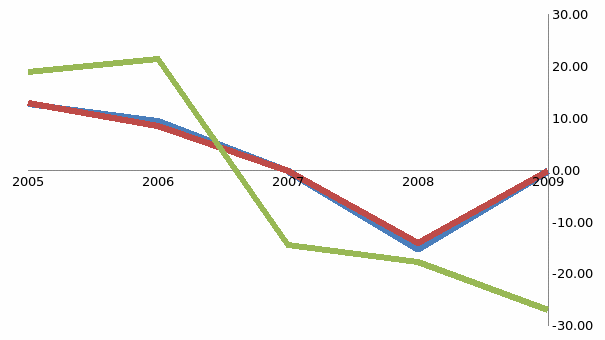
The return on sales ratio measures the amount of profit generated per unit of revenue. This shows that the company’s profit to revenue return has been declining since 2005. The return on sales was 12.97 percent in 2005 that decreased to -0.13 percent in 2007 that declined to -0.23 percent in 2009.
Actually, the situation improved in 2009 as the ratio fell to -14.08 percent in 2008. This indicates that the company had been facing adverse environmental conditions and had failed to withstand it. The financial crisis of 2008 had created a crunch in overall market and increased costs all over the world. This condition led to a decline in the profit to revenue ratio of the company.
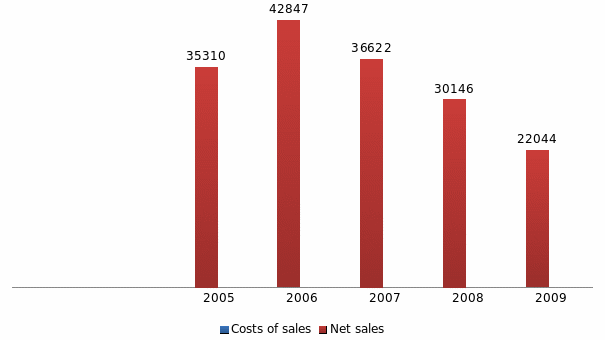
The cost of sales and net sales of the company has declined. This actually indicates that overall production has declined, which may have been due to the adverse market conditions. The overall performance of the company has declined over the period. This is evident from the lowering of the performance ratios – return on sales and return on asset ratios.
Therefore, there are evident that internally Motorola was not strong enough to handle the flux in the market conditions that led to a rapid decline in the performance of the company. In the next section, the reason for the bad performance of Motorola is dealt with elaborately. The overall performance of the company has been bad and some reasons for it has been discussed in the next section.
Related marketing problems
Internal Problems
The main problem faced by the company is due to a weak product portfolio, especially for mobile devices. There was a slump in demand for Motorola phones in 2007 and 2008 due to inadequate model or product offering in emerging mobile segments like 3G and Smartphone segment.
With the new Android software platform introduced by Motorola, it has just 8 phones that have web browsing facility and 7 of them have been recently launched on Android platform . Further, a lack of focus on smartphones had led to lower demand of Motorola phones. Though the Smartphone market is expected to grow from 1.2 billion units in 2009 to 1.5 billion units in 2012 . However, Motorola stresses more on featured phones than on Smartphones.
External Problems
Uncertain economic and political conditions globally have increased the problems for Motorola. The financial crisis that crippled the western world and shrunk the US unemployment level had adverse effect on product demand for Motorola. Further the uncertain political condition in the Middle East. The manufacturing and engineering setup that the company has in Israel may be disrupted due to the political extremism in the region.
The global financial crisis led to a credit crunch resulting in reduced business from 2008 through 2009. Due to unavailability of credit, the Motorola customers could not obtain finance to run their business, and therefore, there was a lowering of the product demand. Therefore, global economic conditions had an adverse effect on the company performance. Telecommunication industry has faced a slowdown in 2009, which had an adverse effect on the financial performance of Motorola.
Another external problem observable is due to the convergence of the telecom, data, and broadband industry that was driven to advancement of new IP-based technology . This led to changes in the market, and Motorola, unable to understand the market developments, had negative impact on their business.
Strategic marketing solution
Industry Analysis
The marketing for Motorola and its business segments are divided into three business areas, facing different industry structure. However, the mobile market can be analysed using porter’s five forces model (see figure 8). The industry analysis shows that mobile industry has a high degree of competition within the industry, as there are a number of mobile device makers.
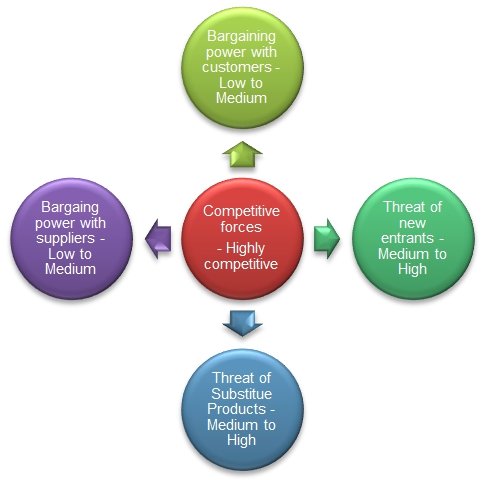
The bargaining power of the customers is high, as there are a large number of mobile brands, and customers get a large number of options to choose from. As there are few suppliers supplying key technology and raw material, the bargaining power of suppliers is high . For instance, Google supplies Android software platform to Motorola.
Google being the sole supplier of the software has a high bargaining power. This increases the bargaining power of the suppliers. Further, the threat of new entrants is high as there are new players who are entering the mobile market like Apple, Microsoft, HP, etc. the attractiveness of the mobile market is in its expected growth and the possibilities of mobile commerce.
The industry faces a high threat from substitutes, as there are many substitute products for mobile phones such as traditional telephones, or the internet that provides possibilities of Internet telephones, etc. therefore, the mobile industry is highly competitive, and operation in the industry would involve constant up gradation of technology and new product development.
SWOT Analysis
Figure 9 presents the SWOT analysis for Motorola. They are discussed in detail in the next paragraph.
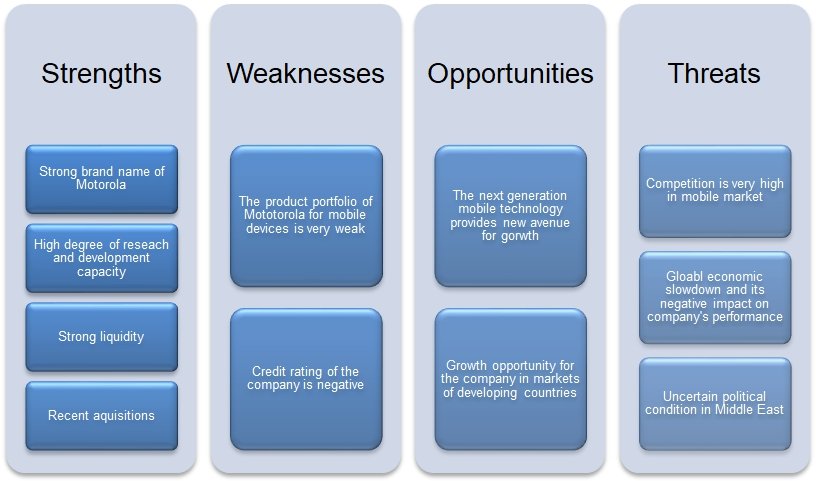
Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) is a strong point for Motorola. It has significant capability in developing R&D and transforming them into new product, nurturing product innovation. There is constant interaction and exchange of innovation and ideas between its business segments that helps in constant development .
The R&D expenditure of the company was 14.4 percent of net sales in 2009, which increased from 13.6 percent of net sales in 2008 . However, due to cost reduction strategy the absolute R&D expenditure was reduced. Further, the company owns almost 9907 patents in the US, which are used in its operations.
The high stress on R&D has helped Motorola to develop new products and achieve excellence in developing new products. For instance, the company has developed WiMAX that helps users to transfer at fraction of the cost of transferring multimedia file in 3G . Further with Motorola’s new contract with Google to use its Android-OS platform for its Smartphones .
This is expected to change Motorola’s position in the Smartphone segment of the mobile device market. Further, Motorola also developed the new TETRA portfolio for its enterprise segment, in order to provide greater safety, security, and efficiency to its users. New features that have been included in this are “over-the-air programming”, voice, and TEDs .
Motorola is expected to launch tablet TV that would increase its offering in the home mobility segment . Therefore, Motorola’s strong position in developing new products through research in new technology and innovation will help it to enhance its competitive position in the market.
Strong Brand
The brand image of Motorola is very strong . Motorola has launched many marketing campaigns to enhance its brand equity. Motorola has recently launched its advertising campaign for Motorola DEXT with MOTOBLUR campaign . Therefore, in order to remain competitive at all price points and maintain brand awareness to all customer segments, Motorola develops mobile devices available at all price points.
In order to create greater degree of brand equity, Motorola does direct to consumer promotion in order to emphasize on Motorola brand. The advertising expenditure of the company amounted to $412 million, $790 million, and $1.1 billion in 2009, 2008, and 2007 respectively . Further customer targeted advertising helps the company to achieve greater brand recall and creates a more positive and strong brand image.
Strong Liquidity
The company has a strong liquidity and balance sheet. As stated in it Annual Report, 2009: “We remain very focused on the strength of our balance sheet and our overall liquidity position. We believe we have more than sufficient liquidity to operate our business.” In 2009 cash and cash equivalent, that the company held was $2.9 billion.
Recent Acquisitions
The home and network mobility segment acquired assets of “Zhejiang Dahua Digital Technology Co, Ltd. And Hangzhou Image Silicon” . this acquisition would help the company to develop and strengthen its position in the cable market, especially in China. Further, in 2008, Motorola acquired interests in vertex Standards Co. Ltd. and AirDefense Inc. for their radio and security solutions.
Motorola acquired Symbol Technologies, Good Technology, Netopia, and Terayon Communication Systems in 2007. These acquisitions are expected to help and enhance marketing and product development in their particular segments.
Weaknesses
Weak Product Portfolio
Even though Motorola is one of the largest players in the mobile device market, it has a very weak portfolio of mobile devices. In 2007 and 2008, there was a significant decline in the demand for Motorola phones due to weak portfolio. Until 2009, there was no mention of smartphones in the product portfolio of Motorola, despite the growing demand for Motorola phones.
Motorola has stressed more on feature phones, while the market trend was moving towards smart phones. Further, Motorola was late to anticipate the shift in the demand from voice centric devices to data centric devices due to the increased demand for 3G and smartphones. However, in 2008, Motorola tried to revive its product portfolio with increased devices like CDMA and iDEN handsets.
There was a slump in demand for Motorola phones in 2007 and 2008 due to inadequate model or product offering in emerging mobile segments like 3G and Smartphone segment. With the new Android software platform introduced by Motorola, it has just 8 phones that have web browsing facility and 7 of them have been recently launched on Android platform . Further, a lack of focus on smartphones had led to lower demand of Motorola phones.
Further, Motorola phones were heavy on features, whereas lower on longevity. The mobile devices faced this problem. Further, there was a brand diminution as Motorola’s brand depleted.
They also made smartphones on Android and Microsoft platform . However, they failed to prevent revenue fall due to increased market presence and acceptance of non-traditional competitors like Apple, HC, Palm, etc. in higher end Smartphone market and South Korean players like LG and Samsung in lower-end market. This resulted in weak financial performance of the mobile device segment.
Negative Credit Rating
The credit rating of Motorola, both in short-term and long-term has been downgraded in 2009. Therefore, the company has faced problems in getting finance from third party due to low credit rating. The credit rating has been very low. This has created problems for the company.
Standard and Poor (S&P) has rated Motorola in non-investment grade for long-term debt . Rating given by Fitch and Moody’s Investor Research rated the long-term debt gave the lowest rating for investment and F-3 for short-term debt. This limited the access of Motorola to generate long-term debt. Further, this also limited the ability to generate performance bonds, bids, surety bonds, etc.
Opportunities
Next generation technology solutions
Technology convergence has provides greater ability to increase the ease of innovation. The company has entered into the next generation technology, with telecom providers stepping into the data services with increased broadband. Therefore, there is a convergence of the mobile devices from voice based to data based features. Therefore, growth in next generation mobile technology will ensure steady revenue.
Market Growth in Developing Countries
Developing markets like china and India have started to their expand their 3G infrastructure therefore providing new avenue for the mobile device industry.
New technology and 3G enabled devices are expected to become more in demand in these regions, thus, providing opportunities for investment in these regions. Growth opportunity that is offered in developing countries of Asia and Latin America will provide the vehicle of growth for Motorola.
Threats
High competition in mobile market
Industry competition is high in the mobile device industry, as there are many non-traditional players like Apple, HTC, Palm, etc. who have entered the higher end market, while others like LG and Samsung have captured a substantial market share in the lower-end price point.
Competitors in the higher end or Smartphone segment are Nokia, Apple, HTC, Palm, RIM, and Samsung. In the lower-end segment, the competitors are Nokia, Samsung, LG, and Sony Ericsson. Further, many mobile phone operators provide mobile phones under their own brand name like Alcatel, Virgin, Huawei, etc. therefore the market is highly competitive for Motorola.
Economic Slowdown
Economic slowdown in North America and Europe has crippled many industries. Sluggish growth in most developed countries in 2009 led to a lower product demand in both 2008 and 2009. Economic slowdown is expected to continue to reduce demand for products and services in near future.
Uncertain political condition in Middle East
Middle East comprises of 6 percent of the net sales of Motorola. Further, it has a plant in Israel. However, political and terrorist problems in the region may lead to disruption of production, as well as reduce demand in the region. This is expected to reduce the demand for Motorola products largely.
Competitor Analysis
Competition in the wireless mobile handset market is very high with competition from non-traditional players increasing. Competitors in the higher end or Smartphone segment are Nokia, Apple, HTC, Palm, RIM, and Samsung. In the lower-end segment, the competitors are Nokia, Samsung, LG, and Sony Ericsson.
Further, many mobile phone operators provide mobile phones under their own brand name like Alcatel, Virgin, Huawei, etc. therefore the market is highly competitive for Motorola. In 2009, Motorola remained the fifth largest market shareholder. In 2009, the market share of Nokia was 7 percent in Smartphone segment . Motorola currently has a market share of 6 percent . The market condition in the mobile device market is highly competitive.
Recommendations
Marketing strategic recommendation
This section provides recommendations for Motorola based on the above analysis of the company. The strategic marketing recommendations that are derived are –
Motorola must develop Smartphones and invest more in R&D in order to enhance its product portfolio. Further, companies like Apple, HTC, and Palm have gained market share using touch-based smartphones. As the mobile device technology are moving to next generation technology based on data, new technology like HD programming and VoIP must be adopted by the company to remain competitive.
This technology has allowed operators to optimize their bandwidth. In mobile technology, the industry has shifted to UMTS and WiMAX technology. Therefore, Motorola must be ahead of them in order to gain a greater market share.
Motorola must concentrate on developing countries for increasing its market as new technological advancement in the developing countries provides a greater market. Further, the North American market is the largest market for the company. The GDP growth of the US, which is Motorola’s largest geographic market, was just 1.1 percent in 2008 and 2.6 percent in 2009. That in Canada was just 0.4 percent in 2008 and 2.3 percent in 2009.
The Euro region grew by just 0.8 percent in 2008 and 4 percent in 2009. Slow growth rate led to weak consumer demand in the developed countries leading to reduced demand. Therefore, the company should concentrate on the market of the regions where the economic recession has not strongly affected consumer demand, and this is observable in developing countries like India and China.
The brand equity of Motorola has depleted considerably due to the lack of strong software base of its hit model Razr. Therefore, product development and targeted advertising must be done in order to regain brand equity. Strong brand equity will help in market penetration and product demand.
In order to remain competitive at all price points and maintain brand awareness to all customer segments, Motorola develops mobile devices available at all price points. Brand equity can be increased by increasing direct to target consumer promotion in order to emphasize on Motorola brand.
The customer targeted by Motorola should make different products for different targeted segments. For instance the young segment below 25are more interested in multimedia phones, and other data services like MMS, SMS, game, song download, etc.
Whereas, the people above 35 and below 60 may be interested in interested in smartphones, while older customer segment want voice based, basic mobile phones. Therefore, customer targeting must be done and products should be made based on the specific need of the target segment.
Marketing tactical recommendation
The tactical strategy that the company must undertake as follows:
- Motorola targets both the lower and higher-end customer segment. Customer segmentation must be done such that the products are targeted t the right kind of customers. For instance, in the US, people over 65 are essentially looking for voice-based handsets, while the age group below 24 years used their phones only for voice. However, the age users within the age groups of 19-24 used mobile phones for multimedia services like MMS, music download, etc. the age group between 35 to 44 years used data services . Therefore, the products must be targeted according to the customer demand.
- The marketing mix adopted by Motorola should be as follows:
- Price – differentially placed and targeted to the right customer segment. The Smartphone pricing is vital, as the largest competitors like Apple, Palm , HTC, and Blackberry have prices their product pretty high, however, Nokia’s smartphones are moderately priced. Therefore, a more moderate approach to pricing can target a larger segment of the market, which has not yet used the more expensive iPhone of Blackberries.
- Promotion – Targeted advertising and promotional activities will help in building brand image. In order to create greater degree of brand equity, direct to consumer promotion is necessary to emphasize on Motorola brand. This would help the company to achieve greater brand recall and creates a more positive and strong brand image.
- Product – Innovation and widening of the product offering will give customers greater options to choose from and concentration on new technological solution like Android based smartphones and cloud-based MOTOBLUR. Android-based smartphones can become the prize winner for Motorola as Android has gained more market share in the US than Apple’s iPhone in the US .
- Place – Motorola must concentrate on specific regions like the developing countries of Asia and the US. Manufacturing should be dispersed and shifted to areas where cost of production is low. This would increase the possibility of increasing the profit margin of the company.
- The company must concentrate on one area rather than being widely separated. Therefore, restructuring of the business segments’ is essential in order to help in more compact business administration. This will help in development and distribution of the products by reducing unnecessary bureaucracy.
Conclusion
The case study demonstrates the problems and issues faced by Motorola due to internal and external constraints. The industry, company, and competitor level analysis demonstrates the strategically imperative that the company must undertake in order to become more successful. The paper also provides significant recommendations for the company. The case study provides greater understanding of the current situation of Motorola and provides recommendations to solve the issues.
References
CED, 2010. Game changing at Motorola. CED. p.6.
Datamonitor, 2009. Global Mobile Phones. Industry Profile. New York: Datamonitor.
Gardner, W.D., 2008. Motorola Expected To Lose No. 1 U.S. Handset Position. Web.
Gohring, N., 2005. Mobile data usage is on the rise. Web.
Heater, B., 2010. Motorola, Verizon Working on Android TV Tablet. Web.
Motorola , 2007. Annual Report. Annual Report. Motorola.
Motorola Inc., 2010. Motorola Expands Low Teledensity WiMAX Deployment Options for Small Operators. Web.
Motorola Inc., 2010. Motorola Launches Advertising Campaign for MOTOROLA DEXT™ with MOTOBLUR™ in Mexico. Web.
Motorola, Inc., 2010. Motorola Launches Next Generation of Mission Critical Terminals With the MTM5400 TETRA Radio. Web.
Motorola, 2008. Motorola Annual Report. Annual Report. Motorola.
Motorola, 2010. Mobile Device & Home. Web.
Motorola, 2010. Mobile Phones. Web.
Motorola, 2010. Motorola Inc. 10-K. Annual Report. Motorola.
New York Times, 2010. Motorola Inc. Web.
O’Brien, K.J., 2009. Nokia Tries to Undo Blunders in U.S. Web.
Palenchar, J., 2010. Motorola Debuts Android Plans. [Online] EBSCO. Web.
Paul, I., 2010. Motorola and Verizon To Launch TV Tablet, Report Says. Web.
Shankar, V., 2008. Motorola Credit Rating Is Downgraded to Junk by S&P. Web.
Svensson, P., 2009. Motorola Loss Widens; Analysts See Worrisome Signs. Web.
Voight, J., 2010. What the duel between Google and Apple’s operating system? means for brands. Adweek, Vol. 51, No. 26. pp.10-12.
Appendices
Table 2: Historical Financial highlight of Motorola, Source: Annual Report 2009.
Table 3: Segment-wise performance.
Table 4: Geographical segment wise performance of Motorola.