Critical analysis of the current business performance and strategies
Google has been performing very well since it was started. It recent years, it has become more entrenched leading to increased profitability. In 2009, it reported total revenue of $ 23.6 billion. In 2010, total revenue realized was $29.3 billion. At the end of last year, total revenue stood at 37.9 billion (GOOG Income Statement | Google Inc. Stock – Yahoo! Finance, 2012). As the figures suggests, the company has been growing very fast in terms of revenue.
The company capitalization stands at $198.06 billion against $18.83 billion for Yahoo, its chief competitor (GOOG Income Statement | Google Inc. Stock – Yahoo! Finance, 2012). Its stock has been rising in tandem with its good financial performance.
EPS is $33 compared to 0.88 for Yahoo. Gross margin is 64.88% while revenue growth for the last quarter was at 24.10%.
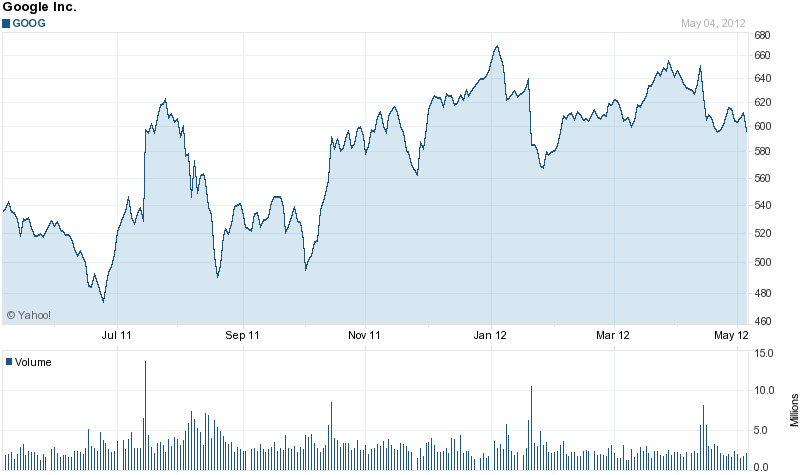
(GOOG Basic Chart | Google Inc. Stock – Yahoo! Finance, 2012)
As the above graph shows, the price of its stock has grown from around $ 540 mid last year to the current $ 600. This shows investor confidence in the company’s ability to maintain current good performance.
Google get the bulk of its revenues from advertisements placed on pages on its search engine results. It recently introduced a new revenue stream through what it called Google Cloud-a remote storage space for companies.
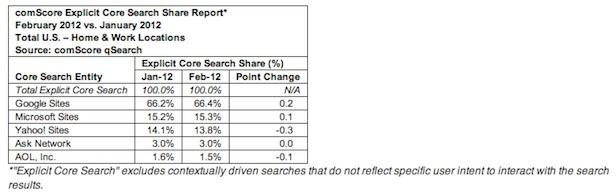
Source: Comscore
Google leads the park as the search engine of choice in America. This explains its huge advertising revenue.
To achieve its current dominant position, Google has employed a number of strategies. The most notable is acquisitions. Between 2001 and 2004, the company focused primarily on search. From 2005 and 2007, it spent much time developing software, such as Google docs and android, which is productivity software (Girard, 2009).
It focused on advertisement on mobile devices, which included making YouTube profitable, in 2008 and 2009. From 2010 to the present, the company has been working on entering the phones market through purchase of Motorola, social networking with Google plus, and e-commerce through Google Cloud.
The company followed an acquisition strategy. It has bought out companies but avoided joint ventures. Most of its signature products were initiated from the firm, but where need arose, they hired targeted key people and acquired rights to technologies.
Google has always wanted to join the lucrative Smartphone market. The recent acquisition of Motorola was interpreted as an attempt to acquire patents by Motorola so that it can produce a Smartphone that can compete with Apple’s Iphone.
Proposed strategic plan
Google is now a global company with its international operations accounting for a sizeable percentage of its revenue. Operating globally is challenging as it is exciting. Global landscape keep changing constantly and companies are coming up with strategies that will promote cultural alignment. To address the problem of working in a complex global cultural environment, a good cultural model should be adopted. For Google, the following strategic plan is proposed:
- Adopt Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of Culture as a guide in entering new markets
- Develop corporate cultural model based on the following factors identified by Terpstra and Kenneth (Tjosvold & Leung, 2003):
- Cultural variability: this factor is in reference to the conditions of stability extant in the organization. Unstable organization will requires stronger structures and the support of local experts.
- Cultural complexity with reference to consideration as to whether the culture is high or low context
- Cultural hostility: reflects the divergence between the local culture and organization values
- Cultural heterogeneity: refers to convergence between organizational culture and local culture.
- Cultural interdependence: refers to the extent the organization depends of local culture for resources.
- Deploy systems theory to organizational contexts
- Cross-cultural communication
A diversified workforce may not deliver desired results without proper management. The plan will guide the organization in shattering stereotypes about cultures, how to approach different cultures, how to meld employees extracted from difference cultures to fit in, and communication skills to initiate dialogue and understanding.
Key issues and challenges to implement the plan
Employer’s perspective
The problem of culture change: implementing the plan requires basic change of organization’s culture to remodel it along a new cultural model that will create cultural synergy to increase workforce effectiveness and efficiency. People are naturally fearful of change. Overcoming this fear of change will be the first obstacle the management will face first.
Difficulty in determining the extent of cultural variability: According to Terpstra and Kenneth, unstable organization requires open communication channels and decentralization of decision making (Tjosvold & Leung, 2003). Determining the extent of cultural variability is however not easy.
Lack of cultural awareness: essentially, the purpose of the plan is to enhance cultural awareness. Ignorance of differences among people is the first obstacle to overcome.
Poor understanding of culture and cross- cultural communication: many people in North America are, to a great extent, ignorant of how complex the world is culturally. Due to this ignorance, implementing the plan may be challenging.
The money allocated for the program may not be enough. Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of Culture, systems theory, and theories of cross cultural communication are a wide topic that requires time and resources to train employees. In an organizational setting, it’s common to underestimate the resources that may be required.
Others issues that managers may face include methods of delivery, place, and the extent of coverage of the key contents.
Developing a synergetic cultural model requires good understanding of the values of the organization in the context of the local culture. This is not always easy.
The challenge of setting up and maintaining a synergetic system: The key requirements required to set up and maintain a system are not easy.
Employee’s perspective
Complexity: understanding other cultures may be difficult because people often lack reference point to understand foreign concepts. It may be hard to understand why people from high context cultures communicate the way they do, as opposed to doing it the American way. Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of Culture requires looking at the culture from a holistic perspective (French, 2010).
Lack of motivation to learn: some employee may feel that training on cultural issues does not have any relevance to them or the nature of their work. A technical person, for instance, may feel that their work does not expose them to customers. This can make him/her lose interest in the program altogether.
Recommendations to address the challenges
Introduce a program to enhancing cultural awareness after recruiting: this will orient the employee from the beginning on the fact that the customers and fellow employees may be from a different cultural background apart from the mainstream.
Cross-cultural communication training: ability to communicate across cultures is an invaluable skill. It helps avoid conflict and people understand each other and live harmoniously. Training can be conducted by introducing workplace meetings where participants are drawn from various cultures.
Introduction of activities that shows the importance of language and communication, training employees on tips and techniques that can help communicate effectively in a cross-cultural environment, and coaching them on how to solve conflicts emanating from cultural misunderstanding (Aaker, 2001).
Better planning and budgeting: the training can be scheduled as part of the wider program of the company for training and development.
Seeking expert advice: handling cultural differences hold the key to succeeding in the international market. The extent to which a company is able to understand the local culture and adapt to it will determine how it will perform in that market. In that case, training employees on cultural competence cannot be left to chance; hence, the importance to engaging experts.
Simplifying concepts: it’s possible to train employees on other people’s cultures in an easy and fun way by developing a simple training manual. Use of graphics, videos, and other such learning tools can be very useful.
Linking goal of the program to the wider financial objectives of the firm: when the link is clearly delineated, employees will be motivated. They should not feel that the program is unimportant.
Resources needed
Human resources: training need to be planned, coordinated, and executed by people hired to do that. These people form part of the human resources required for the program.
Training materials: at the very basic, training materials need to be provided. Items such as books, pens, computers, projectors, and other materials should be provided.
Financial resources: deployment of all the resources required for training depends on availability of financial resources. Availability of both human resource and training materials depend of the availability of financial resources. If training is to be conducted by a consultant, they must be paid their dues.
Evaluation of the implementation
Implementation should be gradual and guided by human resource department. Periodic evaluation to gauge the effectiveness of the program is recommended. The best way to gauge how well the program has been implemented is through soliciting for customer’s feedback on their treatment where cultural competence was required.
Time frame
One year.
References
Aaker, D. (2001). Strategic market management. New York: John Wily & sons, Inc.
French, R. (2010). Cross-cultural management in work organisations (2nd ed.). London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.
Girard, B. (2009). The Google way: how one company is revolutionizing management as we know it. San Francisco: No Starch Press.
GOOG Basic Chart | Google Inc. Stock – Yahoo! Finance. (2012). Yahoo! Finance – Business Finance, Stock Market, Quotes, News. Web.
GOOG Income Statement | Google Inc. Stock – Yahoo! Finance. (2012). Yahoo! Finance – Business Finance, Stock Market, Quotes, News. Retrieved from https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/GOOG/financials?ltr=1
Tjosvold, D., & Leung, K. (2003). Cross-cultural management: foundations and future. Aldershot, Hants, England: Ashgate.