Introduction
Like any other modern multinational, Google is facing several issues. These problems are associated with certain difficulties in the world economy, the high degree of competitiveness, diversity and so on. Google also faces issues that are quite typical for a rapidly growing company as the organization risks losing its culture. Thus, Google has been famous for its entrepreneurial culture but employees feel that their autonomy is decreasing and top management of the organization also admits that there are issues associated with leadership (Bershidsky 2013). Torrington et al. (2014) state that such issues associated with motivation and performance management can worsen the performance of the entire company and its development.
These challenges have to be addressed immediately. This paper contains some recommendations as to solving the existing issues. First, it is important to note that these recommendations are developed in terms of the consequentialist approach, as the outcomes of the changes are central. The major message concerning participation in the plan will be based on the idea of benefits for the company as well as each employee. Employees will not be assigned but they will be encouraged to participate. This approach will make them more willing to take part in the plan and create actual changes. This will ensure the effectiveness of the measures that will be consistent with Google’s entrepreneurial culture.
The vast majority of organizational changes and improvements require certain resources (human, financial and so on). Therefore, the first stage of the change will be addressing Google’s top management. It is important to inform the top management about the issues existing and provide them with a plan to address the challenges. The plan should be presented to top management during a meeting devoted to the need for change. The top management will have to be ready to invest time and money to implement the plan on improving performance at Google. The employees will have to complete certain surveys (which will be developed by HR professionals of the company) and will participate in many meetings and trainings. Hence, employees should have enough time to invest.
It is important to add that the changes will start with the notes to employees concerning the need for change. HR professionals will develop several notes to inform employees about upcoming changes. This will make employees prepared and eager to participate effectively. They will see that the changes are needed and they will try to contribute to effective transformations within the organization (Snell, Morris & Bohlander 2015). The employees should know the agenda and they will be informed about the major challenges that will be addressed in the first place. They will also be encouraged to share their ideas on the matter. HR professionals will analyze the ideas provided and they can use some of these ideas if they are consistent with the overall plan.
The process of active changes will take up to six months. After that period, the methods used to implement the change will become a part of the standard procedures of the organization. Of course, these procedures will be evaluated and adjusted to the changing environment (when necessary).
Recommendation 1: addressing challenges associated with autonomy and leadership.
The theory of self-determination and core self-evaluation
The self-determination theory (SDT) can be applied to address the issues concerning inefficient leadership. Bershidsky (2013) notes that Googlers complain about the lack of autonomy and the use of autocratic types of leadership. Such types of leadership are inconsistent with the entrepreneurial nature of the company. It is also a fact that many people choose Google for its culture and these people need significant autonomy. At the same time, Deci and Ryan (2008) stress that all people need different degrees of autonomy. The researchers claim that some people feel frustrated when they are left alone with tasks and without any supervision. Importantly, many people may be mistaken when evaluating their own needs of autonomy. Joo, Jeung and Yoon (2010) stress that core self-evaluation theory can help identify the level of autonomy needed for each employee.
It is important to add that this strategy will help to address both issues. Thus, it will provide leaders with specific knowledge and skills that will enable them to give the necessary amount of autonomy to their employees. It will also lead to an increase in autonomy in the organization. Google will be able to retain its entrepreneurial culture and the turnover will decrease as employees’ satisfaction will grow.
People Responsible for Implementation of the Plan
Human resources professionals will be responsible for the implementation of the plan. The plan will consist of several stages. These stages are as follows: a survey, analysis, development of profiles and recommendations. The recommendations developed will be forwarded to top managers and leaders as well as employees (when necessary). These recommendations will enable leaders to choose the right leadership styles when dealing with employees. This can also help teams to choose the most effective leader to work effectively on particular projects.
A brief description of the plan
Survey and analysis
The survey in Google will be based on the survey developed by Hackman and Oldham (1974). The survey will evaluate the following job characteristics: skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback. Ali et al. (2014) note that this survey enables to effectively evaluate employees’ satisfaction. However, it also reveals the level of autonomy needed (Joo, Jeung and Yoon 2010).
Importantly, HR professionals will use the survey developed by Hackman and Oldham (1974) but they will also adjust it to the peculiarities of the company. The question can contain some degree of humor or can be less formal. All employees should complete the survey. This can become a part of the recruitment process. The survey contains around 40 questions. Sample questions, as well as the key to the survey, are provided in the report by Hackman and Oldham (1974).
Profiles and recommendations
After analysis of the surveys, the HR professionals will develop profiles for all employees. These profiles will focus on needs and especially on the degree of autonomy needed. The profiles can be developed in a form of a fact sheet about each employee, which will include information on qualifications, experience, achievements (including performance scores) and the degree of autonomy of a person. The latter section (concerning autonomy) will be filled in by the HR professionals while the rest of the information will be provided by each employee.
These profiles may be helpful when rewarding staff when distributing projects and identifying employees who need training. Notably, the surveys may be implemented regularly within particular periods (each 2 or 5 years). Thus, employees will self-develop and will be able to change (improve) their profiles. The profiles will be available to all employees of the company.
Recommendations
HR professionals will also develop recommendations based on the results of the survey. These recommendations will also focus on the autonomy needed by this or that employee. The recommendations will be available to top managers and supervisors.
HR professionals will develop the recommendations using ideas suggested by Hocine and Zhang (2014) and Deci and Ryan (2008). Leaders will take into account the degree of autonomy needed and will choose the necessary leadership style and methods. Employees can be put into three groups where specific methods will be applied. These methods will include close supervision, autonomy support, and significant freedom.
Close supervision will be suggested for working with employees who do not need a significant amount of autonomy. This approach will involve setting clear goals and timelines, discussing ways to complete tasks, guidance, control of performance. Autonomy support implies a greater deal of autonomy for employees. The leader also sets goals and timelines. However, there are no (or almost no) discussions concerning the ways to complete tasks. It is noteworthy that these discussions can take place if the employee does not meet the necessary deadlines or is stuck with some parts of the project. The third group of employees will have a significant amount of freedom. These employees will get tasks and timelines. Their work will not be supervised, as only the result of the project will be assessed.
Importantly, to avoid various issues, excellent work on projects should be included in employees’ profiles. Likewise, failures to meet deadlines, as well as other issues, will also be included in the profile. This will enable leaders to monitor the progress of employees. It will be clear whether an employee is ready to have a lot of autonomy or he/she still needs certain supervision.
To make sure that the plan is effective, it is important to have certain information on the work of leaders. They as well as their subordinates will be asked to complete brief reports on particular projects. Leaders and employees will evaluate the leadership styles used. The leaders’ effectiveness will be analyzed in terms of the following aspects: the success of the project, leadership style applied (whether it corresponds to the one suggested in the recommendations), employees’ satisfaction with the leader and the project. The form of the report will be developed by HR professionals. The questions will be quite straightforward. Of course, there will be the necessary degree of anonymity to ensure the reliability of the data obtained. They will be mainly multiple-choice and scale questions.
Timing
As has been mentioned above, the implementation of the plan will require six months (see table 1). The first stage will take up one month. This stage will include the development of the survey and report forms. During this month, employees will be informed about the coming survey and will be asked to share their ideas on the matter. The next stage is carrying out the survey and analysis of the data obtained. The survey will be held for two weeks. Since it will be held online (questionnaires will be sent via the corporate email), it will not take too much time to carry out.
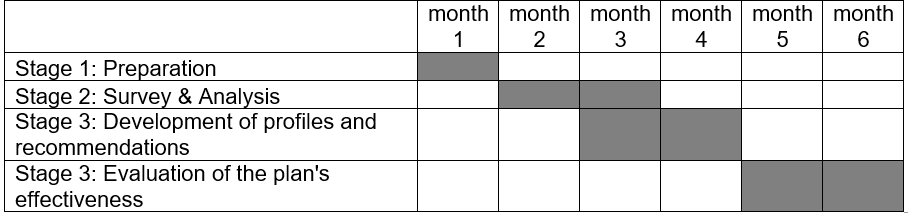
Profiles and recommendations can also be developed with the help of applications. Luckily, this cannot be a problem for Googlers. Recommendations may need specific attention and, hence, apart from being developed by certain applications, they will be assessed by HR professionals when forwarded to leaders and supervisors as per their request.A month and a half is necessary to analyze the data. The data can be analyzed with the help of an application that can be developed during the first stage. Of course, HR professionals will have to collaborate with IT specialists to develop proper analysis engines. The company employs many people, so there will be considerable workload for HR professionals if the survey is analyzed by people.
Recommendation 2: addressing challenges associated with leadership with the help of knowledge management.
Apart from issues concerning autonomy, it becomes clear that many leaders at Google are inefficient. Bershidsky (2013) claims that employees often complain about ineffective and too autocratic methods. One of the major reasons for ineffective leadership at Google is its rapid expansion. Leaders in numerous divisions and subsidiaries are unprepared to work in such an entrepreneurial environment while employees expect to work in an environment that is already seen as typical for Google. Barak (2013) states that the company’s expansion often leads to issues associated with leadership as diversity issues are not always completely addressed.
To avoid such issues, it is crucial to make sure that leaders are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to be effective when working on particular projects and in particular environments. Foss et al. (2009) argue that knowledge sharing can address this issue effectively. Leaders will share their experiences and they will be able to develop and choose effective leadership strategies.
Responsibilities
The person responsible for the implementation of this plan will be an HR professional (or rather a team of HR professionals). These employees will supervise the process and will make sure that knowledge sharing takes place. Of course, leaders will be active participants in discussions and workshops.
The plan details
Stage one
Implementation of the plan will take up to six months and will be divided into three major stages: preparation, implementation, evaluation (see table 2). The preparation part will take up to 2 months. HR professionals will develop some leadership strategies that have been effectively applied in different divisions. Meantime, leaders will be notified about the start of the project and they will be encouraged to come up with ideas on leadership strategies that can be employed. These ideas will be sent to the HR professionals responsible for the implementation of the plan. They will include the brightest and most helpful ideas in their presentations of the most efficient leadership strategies.
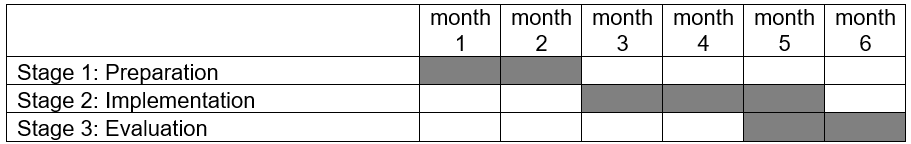
Stage twoClearly, it is essential to motivate employees to actively participate in the project. Thus, all employees will have a note (sent via email) concerning the plan and its expected outcomes. It will also be noted that the contribution of each employee will be mentioned in his/her profile, which can affect the performance score and financial awards (or other types of motivation strategies). HR professionals will send certain schedules so that leaders could be present.
The implementation of the project will include discussions, workshops, training sessions as well as temporal work in different teams or even divisions. First discussions will be developed and run by the HR professionals responsible for the project. These employees will deliver presentations on major strategies that have been successfully used at Google. These discussions can be held online or with partial use of technology. Thus, HR professionals can deliver their speech while leaders gather in meeting rooms of their divisions listen to the presentation and then a discussion starts. The second part of this section can include discussions involving leaders working at different divisions. It is also possible to hire outside trainers to run workshops and training sessions. Most effective leaders will also be sent to other divisions to see the way leadership strategies are employed there and to share their own experiences.
Stage three
It is also important to make sure that knowledge sharing is an efficient strategy. After three months of discussions, workshops and so on leaders will assess the effectiveness of the sessions. They will also evaluate their own performance identifying improvements if any. Employees will also assess the performance of leaders. This will be done through the completion of brief questionnaires sent via email. The questionnaires will include scale questions. Some questions developed by Hackman and Oldham (1974) can be used in this case as well. If there are significant improvements in leaders’ performance, the approach based on knowledge sharing will be utilized in the future. Thus, discussions, workshops and so on will be held regularly. It is noteworthy that outside trainers are unlikely to be necessary, as Googlers will be able to generate effective ideas on their own.
Conclusion
On balance, it is necessary to note that Google is now facing two major issues associated with performance management. The lack of autonomy and inefficient leadership have led to the rise of employees’ dissatisfaction and, as a result, to a significant degree of turnover. Implementation of the two plans suggested can help the organization solve these issues. The two plans are aimed at improving leadership and increasing the motivation of employees through the maintenance of Google’s entrepreneurial culture. The projects can be held simultaneously as they involve quite different participants and people will not be overloaded, especially when it comes to the first plan.
The first plan is two-folded and it addresses both issues (lack of autonomy and inefficient leadership). Employees’ needs and the level of autonomy required will be evaluated. This will enable leaders to choose the right leadership style. Importantly, employees will better understand their own needs and abilities. This will also contribute to employees’ satisfaction, as they will know exactly what they want, need and can. Employees’ profiles will enable management to evaluate employees’ performance more effectively. Leaders will also have some recommendations as to choosing the best leadership strategies when working with certain types of employees. Of course, this will improve leadership in Google. The use of particular applications or software will make the plan more efficient in terms of time and human resources.
The other plan focuses on leadership and it is based on sharing knowledge. Leaders will be encouraged to share their experiences and effective leadership strategies will be utilized in the most appropriate settings. Importantly, it is necessary to remember about the motivation of the participants (financial awards, promotion and so on). Of course, the two projects will be evaluated and if they turn out to be effective, they should become standard procedures within the organization. For instance, identification of the necessary amount of autonomy can be used during the recruitment process or at the beginning of the employee’s career. There are some scores in Google but more detailed profiles can improve performance management. Workshops and discussions, as well as temporal work at other divisions, will also be employed if found effective.
It is necessary to add that HR professionals will be responsible for the implementation of the two projects. They have the necessary tools to supervise the process. These professionals also have the necessary knowledge and skills to improve leadership strategies used at Google. They can cover all the employees of the company.
Of course, it is important to make sure that top managers understand the benefits of the two projects, as without their consent and investment of certain resources (human resources, time, funds and so on) the projects’ implementation is impossible. At the same time, the extensive body of the research suggests that the two projects can help to improve employees’ performance significantly. The two projects are based on approaches that have been successfully utilized. Googlers will be committed to work harder if the entrepreneurial nature of the organization is maintained. Having the necessary amount of autonomy and efficient leadership will make employees more satisfied and motivated.
Reference List
Ali, SAM, Said, NA, Yunus, NM, Kader, SFA, Latif, DSA & Munap, R 2014, ‘Hackman and Oldham’s job characteristics model to job satisfaction’, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, vol. 129, pp. 46-52.
Barak, MEM 2013, Managing diversity: toward a globally inclusive workplace, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks.
Bershidsky, L 2013, ‘Why are Google employees so disloyal’, BloombergView. Web.
Deci, EL & Ryan, RM 2008, ‘Facilitating optimal motivation and psychological well-being across life’s domains’, Canadian Psychology, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 14-23.
Foss, NJ, Minbaeva, DB, Pedersen, T & Reinholt, M 2009, ‘Encouraging knowledge sharing among employees: how job design matters’, Human Resource Management, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 871-893.
Hackman, J & Oldham, GR 1974, The job diagnostic survey: an instrument for the diagnosis of jobs and the evaluation of job redesign projects. Web.
Hocine, Z & Zhang, J 2014, ‘Autonomy support: explaining the path from leadership to employee creative performance’, Open Journal of Social Sciences, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 417-423.
Joo, BKB, Jeung, CW & Yoon, HJ 2010, ‘Investigating the influences of core self-evaluations, job autonomy, and intrinsic motivation on in-role job performance’, Human Resource Development Quarterly, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 353-371.
Snell, S, Morris, S & Bohlander, G 2015, Managing human resources, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Torrington, D, Hall, L, Taylor, S & Atkinson, C 2014, Human resource management, Pearson Education Limited, Harlow.