Introduction
The Great Britain is legitimately known as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The state is governed under a constitutional monarchy system and forms the largest island in United Kingdom. In principle, Great Britain comprises of three nations namely England, Scotland and Wales, it is simply referred to as Britain (Budd 234). A peek in the past reveals the root of the profuse growth of this economic kingdom which forms one of the strongest world’s economies.
In the primordial days of the British Empire, the UK was the leading economic giant of the world. Great Britain created an economical platform through which industrial revolution was birthed. The mammoth economy was however destabilized by the innumerable costs accrued to the first and the second world wars and the great depression in the ninety’s. The disbandment of the union between the empire and the republic of Ireland further threw the economy into tumult reducing the empires economic acumen (Dennis 44).
The UK is still very vibrant in the global economic dominion rated as the sixth largest economy in the world (Budd 93). Since the economic down turn in the early ninety’s there has been two periods of strong economic feat. Under the leadership of Margaret Thatcher, the empire was able to disband outdated economic policies paving a way for new multipart strategies which enhanced economic growth.
Thatcher fought battles to break the influence of the trade union to usher in free markets, augment competitiveness, cost control and quality improvement. Her economic restructuring enhanced the shedding off the Sick Man of Europe (This is an epithet used in the mid 1800’s to describe the relentless economical obscurity in the European countries. The Ottoman Empire was the first to be described as a sick man of Europe.) pall in 1990’s. In 1997, the ‘New Labour’ government under the headship of the economically proficient Gordon Brown, the government inherited and enlarged the earlier policies and sustained economic growth (Charlwood 83).
The History of Great Britain
In the year 1901, when Queen Victoria died, the Great Britain came into terms with the fact that their economical adeptness had diminished owing to the immerging competition menace posed by Germany and the US (Dennis 67). These countries had stealthily risen through industrial developments to offer a taut economical antagonism to the Great Britain.
The increasing economic rivalry, the First World War trouncing, and the great depression of 1930’s relatively slowed the economic growth of the Great Britain. Thus, the kingdom’s unsurpassed global position as the economic leader was thwarted. The nation’s economy was callously daunted by the Great Depression; a recent research by Ambrose suggests that the nation has not fully recovered the blow of the staggering experience (61).
After the chilling experience of the world war one and the great depression, the kingdom treaded parsimoniously to deter loss and garner economical edge in the international economic market. However, World War two emerged emitting all the detrimental economic repercussions possible. The British communication and governing structure was utterly destroyed leading to the loss of all the colonies as the Britain empire was disbanded (Bryson 211).
Labour Party came into play in the 1945’s general elections and with it came myriad reforms in the Britain’s economy which sought to augment and amend the already dilapidated economy (Bill 214). Labour Party introduced new economic policies such as tax increment and industry nationalization. Other economic facets were created to reinforce growth and economic recovery and these included health pensions and social securities (Charlwood 47).
For the period spanning 1945 to 1951, the labour government put into action a political system which was deeply rooted in collectivism. Through the collectivism governance, the government nationalized its industries and the economy was directed by the state (Dennis 73). The first and the second world Wars had confirmed the benefits accrued to state participation in running of political and leadership matters. There was thus an emphatic reinforcement of state oriented government orientation severely backed by the conservatives.
For duration lasting six years 1964-1970, the Labour Party under the leadership of Harold Wilson was incapable of providing a viable economic solution a factor which led to devaluation of the pound in 1967 (Charlwood 112). During this period there was a relatively low economic growth which was attributed to competition deficiency in some economic quarters such as the state owned industries, there was poor industrial communication and the vocational training offered was compromised.
The political parties came into a coherent conclusion, that Britain needed to join the European Economic Community EEC in order to perk up its economy and in 1973 the Prime Minister Edward Heath (Heath was the first elected leader of the Conservative Party in 1965, in 1970 he managed to succeed as the prime minister In 1971 the leader signed the Treaty of Accession, joining the European Community. Was later succeeded by Margaret Thatcher.) led Britain into EEC (Ambrose 37).
In the early years of 1970, the British economy went on a downward spiral due to the strike actions by the trade unions; in the year 1973 there was oil calamity which sapped the economic potential of the nation. A massive period of time was guzzled in strike and acrimony between the state and the trade unions.
The acute industrial contention along with mounting price rises and joblessness perked up the state with tension and there was no viable concurrence forthcoming. Eventually, in 1978 the unity between the state and the trade unions collapsed and the rule of the Labour party under Jim Callaghan came to an end.
Margaret Thatcher was elected in 1979 and she wrought forth exceedingly dissimilar approach to governance garnering diverse changes in economical approach and labor relations. Some of the policies she implemented included industrial privatization for effective management, reformed industrial relations and a reform in the taxation policy. Under her leadership competition was accentuated creating room for product improvement and quality augmentation.
All the monetary policies embraced under Thatcher’s leadership helped to cut down on public spending, and hiked prices which led to inflation of the currency. Margaret Thatcher’s more liberated policies paved room for growth, competition and quality production, this in essence bolstered economic boom in the early 1980’s by the year 1990 even the strong opponents of Thatcher’s policies dropped their antagonism. Owing to the highly charged political gale in the year 1990 Margaret Thatcher stepped down from the office.
In the year 2001 after the New Labor Party had taken over the office, new policies and government regulatory policies were embraced such as tax increment, industrial specialization and increased competition in the manufacturing industries.
Great Britain’s Major Exports
Research carried out by United Nations established that the Great Britain garners only 1% of the world’s populace (Bill 89). The UK is rated as the fourth prime trading nation in the world (Student Encyclopedia 29). The major export products manufactured by the Great Britain include heavy machinery and transport products, these products are mainly sent abroad to growing economies like China, Malaysia and Singapore.
The UK has also established its predominant place as the exporter of chemical products such as pharmaceutical drugs and Biotech products produced by specialized companies like Glaxo Smith Kleine, the Astra medical drug company and Zeneca. US is a major importer of chemical products from the UK to cater for its cosmic market demands.
The Great Britain contributes immensely in the global arena to export defense and aviation products such as firearms and armory which is manufactured by specialized companies such as Rolls Royce Engines and BAe .The Great Britain exports a ten percentage of the global service exports (Krassimir 14).
Owing to the literacy level and economic stability, the country is able to export banking service, computer related services such as programming and computer network troubleshooting, broking of sticks in the shares markets and the insurance service.
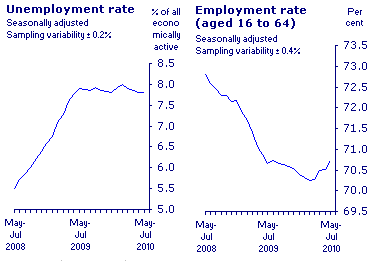
Unemployment Figures in Great Britain
Owing to the increased literacy level and industrial growth, unemployment and inactivity in the Great Britain has been reduced to minimum levels. This trend has however been hampered by the current economic crisis which has both ravaged and dented the global economic function.
Since the year 2008 there has been a rising drift in the rate of unemployment due to the recession and the fall in the UK’S GDP (Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs 12). As a result of this, the number of individuals enrolled for receiving workless benefits has increased.
In 1996 labor market laws were implemented to ensure that the employment rate has increased, the current economic hurdle however poses a major challenge to those policies and their dexterity during harsh economic down turns is yet to be hard-edged (Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs 7). The current indicators point out there is a decreased inactivity rate for the people aged between sixteen to sixty four as the economy thrash in an endeavor to pick up (labor market 3).
Goods and Services Supplied by Great Britain
Great Britain exerts its place in the international trade market as the major supplier of plastic goods, aerospace products for transportation and US is a key importer of these products (Ambrose 57). The UK also exports electrical products and hi-tech electronic equipment allover the globe. Some specialized companies like Uniliver export foodstuff and drinks allover the globe, uniliver has stretched its tentacles to reach out and tame the African markets.
Communication devices which have garnered massive use in the contemporary computer savvy society form a major export basis for the Great Britain. It thus supplies communication accessories and satellite dishes to the booming economic nations like china. BP, Shell and Centrica are three major specialized industries which export finished petroleum and energy products to the US and the other active economies of the world.
Use of American Resources to Market Products Globally
The Great Britain and the US form a compact trade union through which they exchange goods and services. The UK has been able to gain mileage in the global trade by utilizing technology, the US currency and the personnel to enhance its trade activities.
The British foreign policy exerts a strong emphasis on a close harmonization of its trade activities with the US (Student Encyclopedia 37). The bilateral coordination of the two economic giant is reflected in commonality in ideas, language and economic practices which keep both nation in accord in their trade activities.
After the end of the Second World War the two economies merged their potential after realizing they needed each other to stay afloat in the global economic arena. The US and the UK have established a working rapport and share similar foreign policies and foreign security policies (Paul 33).
American Production Technology
Some non-profit organizations in the US such as GT2 embrace the globe to enhance ease in exportation of goods and services. Through this organization the UK has established latitude through which it can export products to the American market faster and economically (Bill 13). The organization creates a link through which the American labor can be exported to the UK hence providing jobs for Americans and labor for the UK.
Through computer-aided technologies the organization is able to create and expand enterprises on a global scope. The computers aid to lower the cost of production and improve the quality of the finished goods. The labor obtained from America comprise of thoroughly trained and mentored employees. The organization has integrated and simplified the export process and helps the UK to sell its export products to the US with a lot of ease.
American Currency
Trade has a massive latent for raising income and bolster growth and development. Economic growth can be attained when the trading filed and currency is unified. The US dollar acts as the globally standardized currency for trade in all countries. Through the standardization of the currency, the UK has been able to cut down costs since its currency is very powerful and commands the market demand.
In the year 1944 a specialized agency for enhancing international buying and selling of the foreign currency was enacted to at the Bretton Woods Conference, there are over 180 country members who are members of the IMF which is mandated to oversee foreign currency trade (Labor Market 34).
The IMF stabilizes exchange rates of currency, provides financial advice and assists the borrowing countries. The US dollar is the standard currency which gauges the worth of a foreign currency. The UK uses the currency to standardize the sterling pound in order to trade in the global arena. Since the sterling pound is a well managed currency with minimal inflation rates, once exchanged into dollars the country obtains more fiscal value and it is empowered to trade more easily in the global markets.
American Labor Force
America is a densely populated continent; it offers a glut of labor force to the global market. Owing to the improved computer technology and the high literacy rate, some of the Americans migrate to the UK to pursue professional careers in the manufacturing industries and this helps the UK to cut down on costs and improve productivity.
Topical trends garnered by the wave of globalization like the massive growth in China and India has spurred a wave of job outsourcing. Thus the American labor force has been immensely outsourced to the UK. This trend helps to bolster productivity and improve growth and industrial profitability.
The Great Britain Economic Indicators
The British economy is highly global and it enmeshes with the American economy to create a pool through which international trade is enhance and bolstered to reap maximum benefits to the global village.
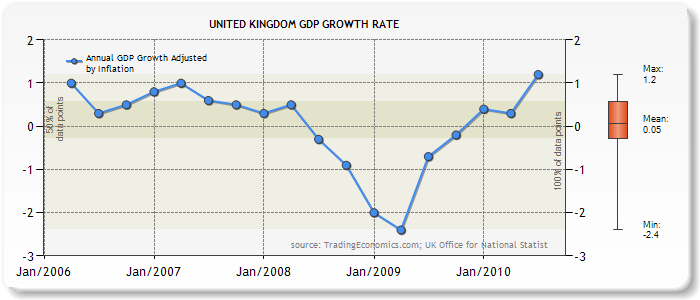
Great Britain’s Gross Domestic Product
The United kingdom is rated number two largest economy in Europe with a Gross Domestic Product of $2.27 trillion. In the year 2008, the GDP growth was rated at 1.1 % but in 2009 it reduced to -3.2% with the raising economic indicators, the GDP is expected to increase by -1.1% in 2010 fiscal year. The UK current population is sixty one million people and the GDP percerpita is US$37.4k. Consequently, UK is rated as the thirtieth richest country in the world (Student Encyclopedia, 56).
Great Britain Literacy Rate
A report carried out by the national literacy trust recently revealed that one out of every five UK citizens is illiterate, the report further elaborated that one out of every six adults in the UK has lower literacy rate than an 11-year-old child (National Literacy Trust 45).
Great Britain Current Economy Conditions
The Great Britain is ascending from economic trough and its gradually recovering from the economic despoil and ascending to the recovery phase. Innumerable economical miscalculations are associated with the economical furor which ravaged different sectors of the national economy(Bill 34).
Since the year 1990 there was accumulation of Asset bubbles in the stock market which created a vacuum in the economy thus in return thinned the currency value of the pound, devaluation of the currency led to inflation which pushed the economy in a downward trend.
There was a poorly calculated subterfuge implemented in the economic realm to unwind leverage in the global markets, the deleveraging process was done acutely. The presence of fraudulent financial gatekeepers created a leeway through which corrupt business deals were conducted.
This in essence left the financial institutions open to treachery and financial malfunction. Rating agencies made the best out of the situation and made profits while no one made watch of their activities. Some financial machinations engineered the crisis, for instance financial institutions evaded all the regulations and restrictions and there was increased financial leverage (Krassimir 56).
Conclusion
There are myriad sectors of the UK economy coming in to grip with the global economic tumult which affected the economic stability adversely. The sectors are now struggling to instill consumer confidence. The housing market has been ripped by consumer paranoia and the employment sector is still exerting efforts to absorb the available labor force.
The manufacturing markets are picking from their lowest point and gradually gaining mileage as the recovery move unhurriedly, owing to the many factors affected by sour economic factors. It is anticipated that by the end of the year 2010, the UK economy will have recovered at a surmountable degree albeit the rising public debt.
Works Cited
Ambrose, Edwards. America slides deeper into depression. Wall street journal. Vol 26. pp 56-61.
Bill, James. United Nations (UN) Human Development Report. (HDR). 2010. Web.
Bryson, Aniston. Managerial receptiveness to Unionize and Nonuninized Worker Voice in Britain, Industrial Relations. Vol 43, No 1, pp. 213-241. 2004.
Budd, Jake. Trade unions and employee friendly regulations in Britain. Industrial and Labor Relations Review. Vol 27, No 4, pp. 125-134. 2006.
Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs. Diplomacy in action. 2010. Web.
Charlwood, Usher. Influences on Trade Union Organizing Effectiveness in Britain British Journal of Industrial Relations. Vol 22, No 1, pp. 67-83. 2003.
Dennis, Kleiman Michael. The UK Politics. Pearson Education Ltd. London. 2004.
Labor Market. Employment rate rises by 70.7 percent. 2010. Web.
Krassimir, Petrov. Current Economic Crisis Worse than the Great Depression. 2008. Web.
National Literacy Trust. Transforming lives. 2010. Web.
Paul, Graham. Unemployment and inactivity in the 2008–2009 recession. Labor Market Review, Vol 21, no 12, pp 32-34.
Student Encyclopedia. Britannica Online. The Ottoman Empire. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2010. Web.