- Heineken portfolio in US market
- Why Heineken introduced every brand in the US market
- Statistic of beer drinkers in US
- The target market of Heineken beer in US and its strategies in this market
- Why Heineken in US market chooses this segment to target them
- Does this strategy work? With evidence
- Reference List
Heineken portfolio in US market
The major brewers within the US market include; Anheuser-Busch, Inc., SAB-Miller, and Molson Coors Company. The major supplier amongst the three is Anheuser-Busch followed by SAB-miller (Finnegan, 1997). The beers sold within the US market are of desired taste to consumers. The drinking trend in the US is largely dependent on location and social status.
One of the most sold beer brand in the US are Bud Light, Budweiser, Coors Light, Miller Lite, Natural light, Busch Light, Miller Genuine Draft, Miller High Life, and Michelob Light. USA has one of the largest beer import market with a total value of about $2.7 billion.
The overall high demand for beer in the USA is because of the growing demand for larger that has low amount of calorie. Heineken was attracted to the US market because the company anticipated that high margin could be obtained from its special brands (Barsby, 1999; Reid, 1997).
Heineken is one of the world’s leading brewing companies within the US market. This became possible because of the networking that the Company introduced between breweries and its distributors. The company introduced Heineken Premium light to the satisfaction of most consumers who preffered light drinks.
This led to one of the greatest excitement around the Heineken brand in the USA market since it served so well the diversified population. Later Amstel Light was upgraded and became one of the most interesting drinks to consumers. These strategies of offering quality products guaranteed the Company a big success within the US market.
The US market consumers became so much attracted to imported beer since they considered the European brands to be of more quality. The consumers within the US market were willing to pay the costs of obtaining Heineken because of its good image. Statistics in 1992 showed that the world beer consumption had increased and US was one of the leading regions in terms of beer consumption followed closely by Asia. This indeed offered a very lucrative market for Heineken hence its interest in the US market (Elzinga, 2005).
Why Heineken introduced every brand in the US market
Heineken Company in the US is located in New York and produces some of the best beer brands which include; Heineken Lager, Heineken Light, Newcastle Brown Ale, Tecate, Amstel Light, Dos Equis, and Tecate Light. The Company has become one of the leaders in importing high quality beer products in the US market The company introduced most of its products in the US because consumers were in so much attentive to special beer brands.
Many consumers preferred drinking beer they considered of more quality and this gave Heineken the advantage of supplying the US market with the desired beer brands from the European market. This made the drink to be one of the leading beer imported in the United States market, making Heineken portfolio in the USA to rise by 1994 (Heineken USA, 2010).
Heineken USA is primed for a continued growth since the demand for Light and import beers is high within the market. Due to its large powerful portfolio and wide consumer base, the Company changed the sales tactics by increasing the prices for purposes of maintaining value within every market segment.
In its portfolio Heineken USA promoted the Mexican brands by making efforts to raise their profile. The company entered into agreement with FEMSA to sale its products within US market and this gave Heineken USA a good base for developing its brand (Katz, 1991).
Table1: Heineken Brand Portfolio in USA.
Statistic of beer drinkers in US
According to statistics from Gallop poll, majority of Americans prefer drinking beer as their choice beverage. According to recent surveys, the percentage of Americans who drink beer stand at 64%, the frequency by which Americans drink beer has risen tremendously over the past decade.
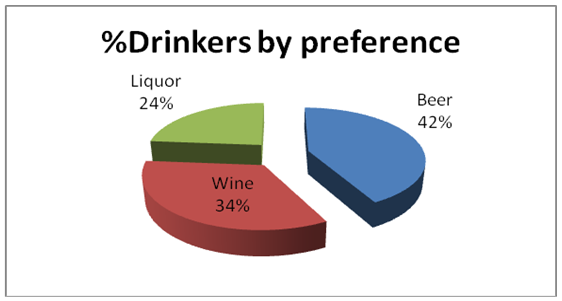
The statistics showed that there is an average of 4.5 drinks per week on those who use beer; this may be attributed to the fact that drinking beer may boost health of an individual. Early 2010 statistics showed that almost 41% of Americans declared beer as their drink of choice with 33% preferring wine and 23% liquor (Tremblay and Carol, 2005; Harney, 1995).
Drinking by preference in US
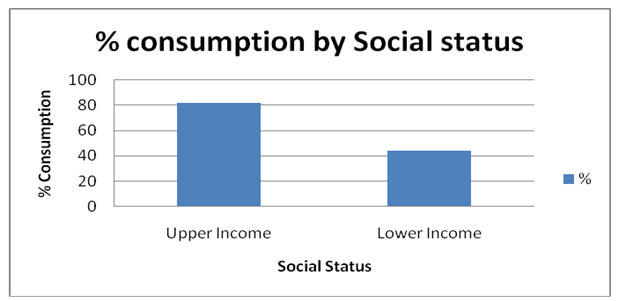
In terms of social status, drinking habit has been revealed to be low among the low-income earners. The survey revealed that 82% of the upper-income earners drink beer compared to 44% of those earning low income.
Drinking by Income status
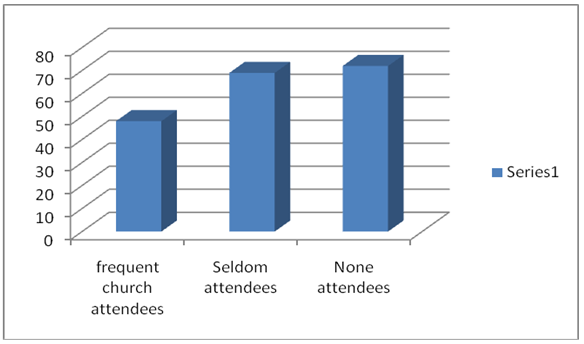
Even those who profess their commitment to their faith still drink beer. The statistics revealed that out of those who frequently attend churches 48% drink beer, out of those who seldom attend churches 69% drink while those who are never committed to any faith 72% drink beer (Warner, 2006). Men accounts for higher percentage of beer consumers compared to women, with light beer being the highest consumed brand amongst women (Sadler, 2005).
Christian Level of consumption
Statistic have revealed that most of the US drinkers have the tendency of shifting preferences from beer to wine as they approach old age. Mixed drinks are however liked by young ladies and women.
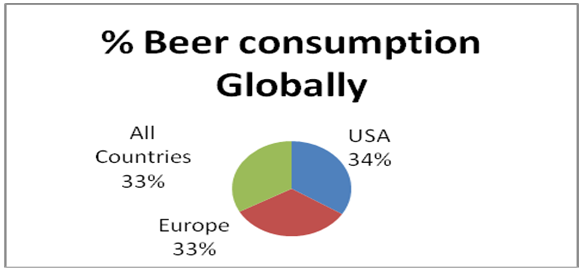
Table1: Percentage of Global Alcohol Consumption (Source: GfK “Alcohol consumption” survey 2008, GfK Custom Research/).WSJE
The target market of Heineken beer in US and its strategies in this market
Heineken’s target market are the young drinkers, this provides grounds for expansion within U.S. market (Weinberg, 1999). Heineken strategizes on how to appeal to young drinkers through various entertainment sources. The company strategizes on how to rebrand Heineken so as not to be viewed as beer only meant for special occasions, but can also be consumed off-premise. Therefore the need for Heineken brand to appear more ordinary and appealing to the young people (Elzinga, 2005).
Heineken has embarked on global music initiative known as thirst, which brings together famous deejays and organizes for dance concerts in major cities and towns. Also as part of its strategy sponsors live music acts in green room sessions and inaugural Heineken Jazz Festivals.
The green nights organized and the Deejay tours acts as promotion strategies for the brand amongst the younger audience. The brand has also been promoted through world of movies like James Bond blockbuster. Heineken is also a major sponsor to sports like tennis, golf and rugby (Elzinga, 2005).
Why Heineken in US market chooses this segment to target them
Heineken specifically focuses on urban dwelling youths because they consider them to be upgraded beer drinkers. They consume lots of beer without any fear of loss i.e. they are considered risk takers. Heineken chooses entertainment as a way to reach the young because young people like entertainment concerts.
Does this strategy work? With evidence
This strategy seems to work since most of the drinkers according to recent statistics are young people between age 21 and 35. According to the beverage industry the statistics shows that a young man in its mid-twenties consumes an average of 65 gallons of beer per year, while old men of over 50 years averagely 15 gallons per year (Warner, 2006).
Reference List
Barsby, S. L. 1999, Beer Wholesalers: Their Role and Economic Performance. National Beer Wholesalers Association; Alexandria, Virginia.
Elzinga, K., 2005, Beer: The Structure of American Industry, edited by Walter Adams and James Brock. Upper Saddle Rive r, New Jersey: Pearson Hall.
Finnegan, T., 1997, Modern Brewery Age Blue Book. Modern Brewery Age Publishing: Stamford, Connecticut.
Harney, A. K., 1995, Malt Beverages. Washington, D.C.: Office of Industries, United States International Trade Commission, USITC Publication.
Heineken USA, 2010, The Company history products brands. Web.
Katz, P., 1991, Brewing Industry in the United States; Brewers Almanac. The Beer Institute, Washington, D.C.
Reid, V.K., 1997. Year in Review: 1996. Modern Brewery Age , 48 (11).
Sadler, J., 2005, Gender Marketing Strategies in Food and Drinks, Business Insights Ltd. Washington.
Tremblay, V. & Carol H., 2005. The U.S. Beer Industry: Data and Economic Analysis. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press.
Warner, J.,2006, Gallup Organization, consumption Habits Poll, News release: Gallup Poll News Service. Web.
Weinberg, R., 1999, Watching the Market. Modern Brewery Age , 48 (11), pp 4-30.