Industry Profile
Hotel franchising industry is a common practice that is changing and growing. Nowadays, the largest hotel and restaurant chains largely use a franchising system at both domestic and international level. Franchising facilitates the physical growth besides increasing the accommodation capacity that underpins the territorial expansion of the selected hotel markets.
The dominant hotel franchise companies include Wyndham Hotel Group, Choice Hotels, Hilton Worldwide and Marriott International, and InterContinental Hotel Group. Choice Hotels International is the second largest franchising hotel in the world.
It currently franchises over 6,300 hotels offering limited and economy class services, mid-scale and upscale segments, and choice branded properties among others (Stover, Dolman, & Vital, 2013). It also offers both the American global business and leisure travelers numerous premium-lodging options.
Structure of Hotel Franchise Industry
The potential hotel franchise is assessed depending on the structure and height of the franchise compensations. The fee is meant to compensate the owner of the hotel for aspects such as the brand name, goodwill, marketing, and reservation systems (Jell-Ojobor & Windsperger, 2014). The franchisee pays both an initial fee with the franchise application and additional fees occasionally paid during the agreed period.
Initial Fee
The initial fee entails paying a minimum dollar determined by the number of rooms in the hotel. The franchisee places the initial fee after surrendering the franchise application. The initial fee meets costs of the application processing, review of the site, and property inspection during the development. It also caters for the services offered in the pre-launch stages (Jell-Ojobor & Windsperger, 2014). The initial fee is returnable if the franchise application approval is declined. However, in some cases portion is deducted by the franchisor of approximately 5% to 20% to cover for the review of the franchise application (Moon & Sharma, 2014).
Continuing Fees
The franchisee begins paying the continuing franchise fees upon the assumption of the hotel’s franchise affiliation. The continuing fee is payable monthly during the contract period. This fee is in the form of a royalty fee, promotion, and marketing contribution fee as well as reservation fees (Stover et al., 2013). The enduring fee also involves a frequent traveler programs amongst other additional costs.
Dominant Companies, Current Players, Their Products, Strengths and Weaknesses
Dominant companies in the hotel franchise industry in the US include Marriot, Starwood, Hyatt, Hilton, Intercontinental Hotels Group (IHG), Wyndham, Choice Hotels International, and Carlson Rezidor Hotel Group (Moon & Sharma, 2014). The following chart shows the current dominant companies in the United States, giving franchise name, country, and the industry under which it operates (Jell-Ojobor & Windsperger, 2014).
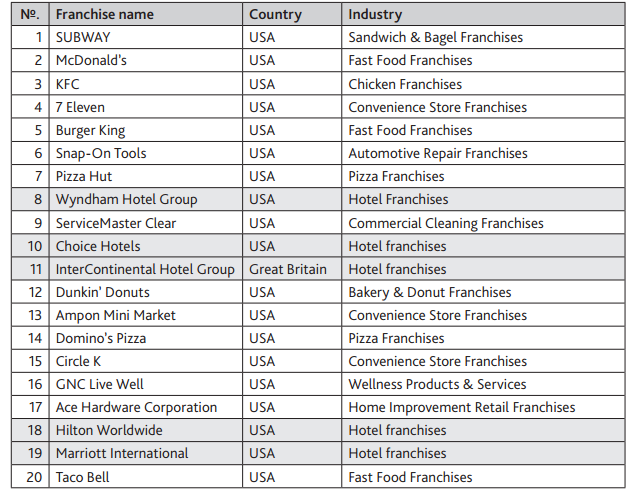
The Three Current Largest Players in Hotel Franchise Industry
Wyndham Hotel Group is the largest pure franchise hotel chain in the world owning zero hotels. Its entire business portfolio operates under the franchise system. The group has numerous brands including Baymont, Days Inn, Hawthorn Suites, and Wyndham Grand Collection among many others.
The franchise hotel group operates more than 7,000 hotels in 65 countries worldwide (Moon & Sharma, 2014).The hotels offer customers with an opportunity to accumulate points/rewards for every service purchased, which are redeemable at any of their destinations worldwide.
Choice Hotels International comes after Wyndham, as the second largest franchiser in the globe. The company embraced franchising after ending real-estate business. It franchises more than 6,000 hotels having over 480,000 rooms. Some of the brands for the Choice Hotels International comprise the Comfort Inn, Comfort Suites, Quality, Sleep Inn, Clarion, Cambria Suites, Mainstay Suites, Econo Lodge, and Suburban (Jell-Ojobor & Windsperger, 2014).
The group offers a variety of products and services ranging from golf, romance, dining, and attractive travel packages that can be booked online regardless of the geographical a $50 gift card for shopping, dining, and other services to customers who stay twice at any of their hotels worldwide (Moon & Sharma, 2014).
Intercontinental Hotels Group is franchising hotels with over 3,800 hotels worldwide. The group operates various brands including the InterContinental Hotels and Resorts, Crowne Plaza, Holiday Inn Resorts, Holiday Inn Express, Stay Bridge Suites, and Hotel Indigo among others. It operates more than 200 hotels in Great Britain, over 100 in France, Germany, and over 50 hotels in Belgium, Italy, and Spain.
It has hotels in other countries including Holland, Russia, Portugal, Ireland, and Austria among others (Moon & Sharma, 2014). These hotels have common strengths including command on their home markets, high profitability and revenue, and barriers to entry in new emerging markets. The major weaknesses for these large franchise hotels include stiff competition and future profitability.
Overview of Hotel Franchise Industry (Recent Performance and Future Prospects)
As at 2012, the franchise performance indicator reveals that the sector suffered a great deal from the 2008 financial crisis that caused a major dramatic impact on world economy. However, the industry managed to record more than 10% revenue growth, which nearly hit the franchisors forecast mark for the year.
Profitability suffered the great blow, as it was way below 17%. The survey indicated that the customer booking, inquiries, a customer spending surpassed the franchisers’ expectations. In 2013, the lodging sector accounted for 5.7% of all the franchised outlets in the U.S.
The franchised outlets increased from 22,400 to 23,100 between 2010 and 2013 representing approximately 3% growth for the period of four years (Stover et al., 2013). The 2014 report featured 17 franchised hotels out of 20 largest hotels in the world. This situation accounted for more than 66% of the industry locations. The report also revealed that the hotel franchising industry is an enduring, stable, and highly successful. The following chart presents the franchised hotel (lodging sector) performance from 2010 through to 2013 (Stover et al., 2013).
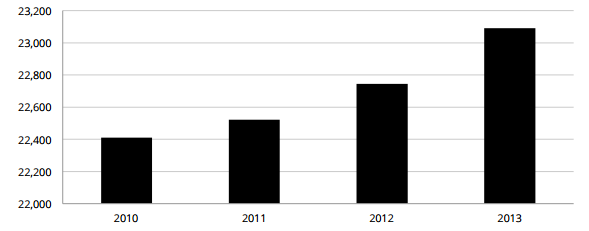
The future looks bright for the hotel franchising industry as key markets continue to stabilize and regain strength after the 2008 economic downturn. Franchisors and economist look forward to a brilliant decade ahead in the franchising hotel industry.
Government Regulation of the Hotel Franchising Industry
The federal and state laws and regulations govern the way in which the franchises are sold regulates hotel business in the US. The regulations mostly entail the imposition of substantive requirements on the franchise contracts that oblige particular materials to be registered before the franchises are sold to specific states in the US (Stover et al., 2013).
Furthermore, the government regulates the hospitality industry including inspection of property and restaurants for safety standards, health requirements, licensure, registration, disclosure statements, and compliance to specific conducts such as the sale of liquor.
Reference List
Franchise Direct. The Best Franchise Opportunities & Franchises for Sale. (n.d.). Web.
Jell-Ojobor, M., & Windsperger, J. (2014). The Choice of Governance Modes of International Franchise Firms — Development of an Integrative Model. Journal of International Management, 20(2), 153–187.
Moon, J., & Sharma, A. (2014). Franchising effects on the lodging industry: optimal franchising proportion in terms of profitability and intangible value. Tourism Economics, 20(5), 1027-1045.
Stover, J., Dolman, J., & Vital, V. (2013). Franchising (& Distribution) Currents. Franchise Law Journal, 33(2), 279.