Executive Summary
Project scheduling, estimating, and costing controls are the main factors of a project management system. For companies engaged in future construction, the right forecast of the future project cost is quite significant. The construction project is the basis of project scheduling and cost control. The paper looks at various scenarios in the construction project. They include using normal time, crashing, and using the PERT technique. In all of them, the project remains within budget. However, the duration keeps changing.
Introduction
This project seeks to construct a new house for a family in Dubai. The company will incorporate the use of experts in the development of the house design and will use internally developed architects. The whole project will last for approximately 73 weeks. It will have various stages including planning, construction, interiors design, and painting. The project manager estimates that the project (constructing one customized home) will cost about $2.5. The project will increase the product portfolio of the company. Hence, it will increase the company’s competitive advantage. The company plans to construct eleven such houses annually.
Project Objectives
The company commissioned this project to develop and launch high quality customized homes in the entire Dubai market. The homes, meant to give customers aesthetic options and to expand the product portfolio of Ahmed and Mohamed Construction Company, was to roll out in cities in the United Arab Emirates before spreading in other countries. Other objectives were to expand the company’s bottom line by at least 50% and improve the customers’ satisfaction by an acceptable level of at least 50%.
Project Stakeholders
The stakeholders in this project were happy with the outcome. Customers appreciated the introduction of customized products that would increase their options in the market place when purchasing homes. The design, aesthetics, and durability of the homes elated the management of Ahmed and Mohamed Ltd Company. The company staffs involved in the process of the construction, advertising, launching and promoting the homes, prior and after the launch, we’re happy with the experience.
Normal Project Scheduling
Project scheduling, estimating, and cost controls are the main factors of a project management system. For companies engaged in future construction, the right forecast of the future project cost is very significant. The AHMED Project Plan, mentioned above, is the basis of the project scheduling and costing control. Once the prospective subcontractors have been informed of the deadline for completion of their subcontracts, they submit their bids. Those, which fit within the AHMED project plan parameters of time cost and quality, are selected and permitted to proceed. This is carried out at the specification phase. However, this is an ongoing process, as a subcontractor may go over budget. This is the responsibility of the particular subcontractor involved, who will cover all extra costs.
Scheduling often begins tentatively; detailed schedules are developed as along the process. This requires consistent communication between the project manager and project stakeholders, as they will need to be informed of scheduling changes or delays in implementation. It is due to the tentative nature of scheduling that cost control is also a dynamic process. The initial schedule and cost estimates need to be revised in the light of new information acquired during the project lifespan. This means that scheduling and cost control will fluctuate during the project, as the project manager adjusts to changing circumstances.
Scheduling
The project manager at AHMED controls and coordinates the project through the managerial actions of planning, organizing, and leading, among others. Project managers’ actions are constantly aimed at change, while other managers’ jobs involve maintaining a stable working environment (Chase & Jacobs 56).
Thus, the AHMED project manager has to be a team manager, by interacting with project members, from the General Manager, Construction Managers, and Engineers to the builders, drillers, and technicians at the site. As the AHMED project involves international expertise, the project manager has to build team ethos in a multicultural and multilingual group of project staff. Earning the respect of the team is crucial for the project manager; therefore, he/she must be a person of utmost honesty, integrity, and vision (Barrat 76). The project manager shall control the project constraints to ensure that everything goes as planned. The constraints are time constraints, quality constraints, cost constraints, and scope constraints. The manager will do this by checking project specifications, schedule, and budget allocations. The project manager will use the tools outlined below for that purpose (Gray & Larson 136).
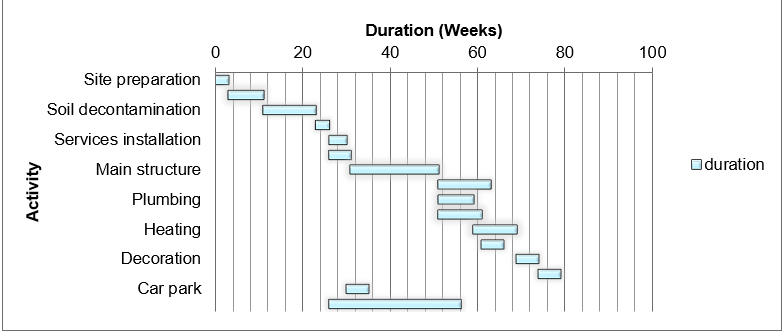
Interpretation of findings
In normal time, the project will complete at 79 weeks, which is behind schedule by 6 weeks. However, it will be within budget using around $2.02M. The budget is $2.5M.
Crashing
Crash schedule
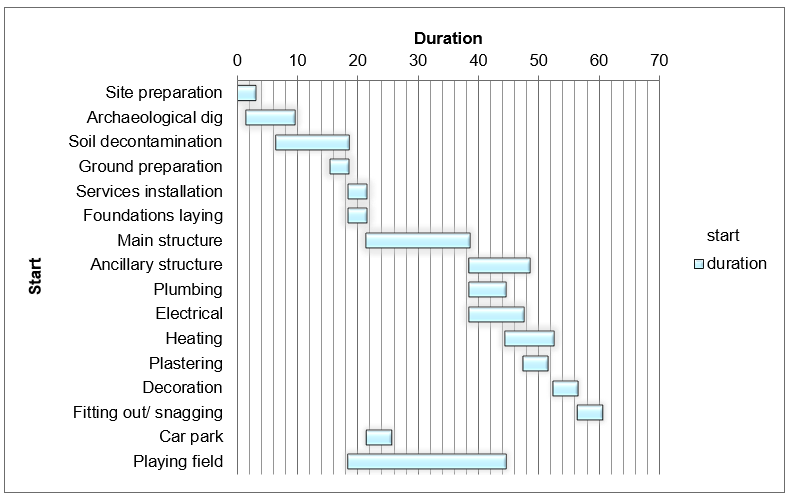
As the above figure indicates, a Gantt chart has several benefits to the project manager. First, it diagrammatically represents the whole project, which makes it easy for the project manager to identify the activities to complete first and clearly shows the relationships between tasks. Second, it shows the duration of a project. The construction project is likely to take 61 weeks as shown in the Gantt chart. However, in as much as it may show the tasks clearly, it does not indicate dependencies among tasks and the project manager may not know from the Gantt chart how the delay of one task may affect another. For this purpose, the project manager will have to use the network diagram.
Interpretation of findings
In crashed conditions, the project will complete at 61 weeks, which is on schedule. The timeline beats the projected deadline by 12 weeks. Additionally, it will be within budget using less than the budget ($2.5M) on all crashed scenarios.
PERT Project Scheduling and Cost
There are two types of network diagrams. These are very useful tools in project control. There are two types of network diagrams: Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and Critical Path Analysis (CPM). They are complex decision-making tools that enable project managers to organize work and plan workflows. They provide necessary information that is vital in scheduling and budgeting. This information includes the earliest start times of a project, the latest completion times, time floats, and the critical path. The critical path is the longest route in a network diagram that indicates the time the project will take. It is hard to construct a network diagram for a project with complex times and huge budgets but the availability of software for that purpose makes it easy. In this project, the techniques may be useful to the project manager in evaluating the progress of the project (Graham 87).
PERT schedule
Use of a Gantt chart
This project’s project manager may find it quite useful to engage the use of a Gantt chart in managing complexity in cost and time. A Gantt chart is an intricate tool used for the management of interrelated tasks with different durations. When using a Gantt chart, the project manager assumes that the tasks are linear and their durations can be determined beforehand with a high degree of precision. However, management should have duration estimates with the relevant possible contingencies.
A Gantt chart has some benefits to the project manager. First, it diagrammatically represents the whole project. This makes it easy for the project manager to identify the activities to complete first and clearly, shows the relationships between tasks. Second, it shows the duration of a project. However, in as much as it may show the tasks clearly, it does not indicate dependencies among tasks and the project manager may not know from the Gantt chart how the delay of one task may affect another. For this purpose, the project manager will have to use the network diagrams. Figure 2 below shows the Gantt chart for the AHMED project. It indicates the start times and durations for each activity. However, it does indicate the costs. The durations are indicated in weeks (Kloppenborg 89).
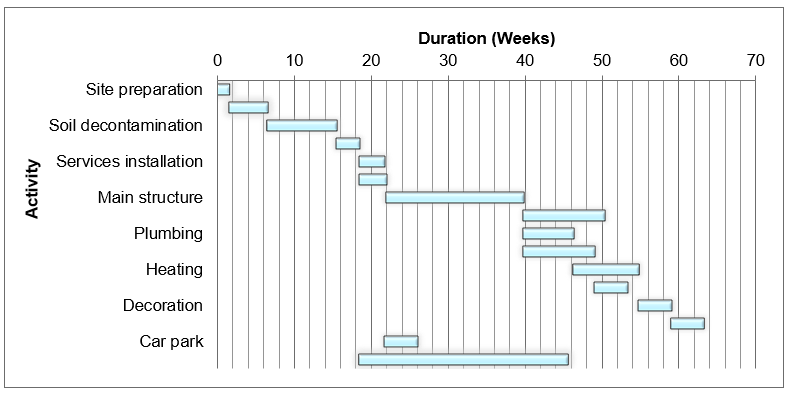
Interpretation of findings
Using PERT, the project will complete at 63 weeks, which is on schedule. The timeline beats the projected deadline by 10 weeks. Additionally, it will be within budget using less than the budget ($2.5M) on all scenarios.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Measuring performance is used to determine the success or failure of a project. The project is successful if it has been completed according to specifications and on time. However, for a long-term project such as AHMED, these criteria cannot be used to assess the entire project while it is still ongoing. However, they can be used to measure the performance of project tasks, which are an indicator of the eventual outcome of the project. As the project parameters are time, cost, and performance, the first measurement parameter for AHMED is whether the subcontracts have been completed on time and within budget. In terms of performance, some aspects of the project can only be assessed when it is complete. Nevertheless, if quality control is done for each segment of the project as and when it is completed, the likelihood of the completed project meeting and /or exceeding performance requirements will be increased.
Works Cited
Barrat, Whitehead. Buying for Business: Insight in Purchasing and Supply Management, New York: Wiley, 2004. Print.
Chase, Richard, and Jacobs Richard. Operations Management for Competitive Advantage, New York: McGraw Irwin, 2006. Print.
Graham, Smith. Competition, Regulation and New Economy, New York: Hart Publishing, 2004. Print.
Gray, Carlos, and Larson, Edwin. Project Management: The Managerial Process, Singapore: McGraw–Hill Education, 2008. Print.
Kloppenborg, Timothy. Contemporary Project Management, New York: Cengage Learning, 2011. Print.