Introduction
Longenecker (2005, p.3) pointed out that the modern aroused public consciousness regarding the corporate scandals with ethical failures has concerned the business leaders as well as governments to keep spotlight on the morals of the corporate world. Such awareness has concentrated strapping social pressure on the legislators to reform the existing law and to set up more control on the corporate bodies to endure ethical behavior and to bring into trail for any ethical failure and it resulted different new legislation in different territories for instance USA has introduced SOX (Sarbannes Oxley Act) to protect corporate fraud.
Most of the times, corporate managers’ pact with the management and drive to involve with unethical issues to ensure profit maximization while the medias are proactive to bring such evidences into pubic view thus it is essential for the business leaders to understanding the nature and scope of ethical issues. This research paper has aimed to investigating with the topic: The ethical failure in the modern corporate worlds – A case Study of Milk Powder producers.
Rationales of the Research
The recent scandals with milk powder has evidenced some unethical practices due to developing diseases and deaths of children consuming milk powder with melamine contamination and the skimmed milk powder market is going to serious threats to boycotting milk powder by the consumers worldwide and raised question to the compliance of ethical issues by the milk powder producers. With such background problem, this research paper has aimed to investigate the standard of ethical compliance of the milk powder producers, their moral dilemmas, negative utilitarianism practice, emergence of modern virtue, and to draw recommendation for their business ethics.
Literature Review
Theoretical Framework of Ethics
Hypothetically, business ethics is a discipline of business management where analysis of the business standard or principles has illustrated to draw harmless business operations. Framework of the business ethics has strappingly consistent with the economics, efficiency of the business performance and stakeholder’s usual decision making policies.
Key limitation of business ethics is that typically, phases of the ethics has worked to define the modes of current market structures as well as business operations. However, the key issues of ethics have assigned to draw correlation among stakeholder’s crucial preferences and norms reflect from these outcomes.
Several business holders have argued that standard of business ethics have hampered typical business flow. Alternatively, ethics is a significant constriction of business behavior towards few business people to executing illegitimate business goals and vision or commercial business movements (Barry, 1998).
Theory of Justice
Rawls (1970, p.87) presented the theory of justice in context equality of social virtues distribution and addressed that inequality of opportunity enhance the chance to amplifying the unity of opportunity unprivileged and excessive rate of such unblessed individuals would bring the burden of hardship in the society.
Rawls (1970, p.89) also identified four norms of the entire social primary goods, these are the liberty of individual and available opportunity for him, scope of income, and wealth in position, fundamental self-respect, and equally distribution of such social (goods) virtues are the prime statement of the theory of justices.
The principal views of justice has scrutinized within this case emphasize that the modern just society would demonstrates itself as an excellent society where the social goods would be distributed equally to the individuals of the prolonging society.
Under this theory, the social choices may not organize in isolated form but the decisions have taken by the disturbed populace of any part of the world and keeps impact all over the globe to carry out least individual goodness.
Theory of Utilitarianism
Blackorby, Bossert & Donaldson (2001) mentioned that the utilitarianism introduced by Bentham in the eighteen centuries from his welfare thinking that offers to ranking social alternatives to ensure integrity and wellbeing where utility is the parameter to measuring the status of happiness in the individual life span.
Utilitarianism compares among the possible alternatives in context of their total utility and identifies the best one keeping deep concern on income inequalities and social stipulation for exceptional needs.
The moral attitude of unilateralism has based on two suppositions while the first one is goodness otherwise evilness of an incident that is assessable and the second one is gained experiences could be distributable among the populace.
An individual assesses his pain and pleasure with the depth of his feelings whether it was strong or light and at the same time, he will take into account the intensity of the occurrence, duration of the action, certainty, or uncertainty of the incidence and closeness or isolation.
While any massive social change distresses the utilities level of any exacting cluster of populaces, the utility levels of that cluster would be reshaped in subsequent level that will ultimately effect on the size and consumption of the cluster.
Theory of Care
The ethic of care theory has developed by Carol Gilligan in the context of feminist theory but now it is a subject of corporate social responsibility and according to the concept of Velasquez (2001, p.8), the ethic of care is an ethic, which concentrates on the caring for existing well-being of those near to us. This hypothesis has some key chrematistics, such as –
- As per this theory, moral reflection cannot be based upon every person’s rights, but rather, they involve acknowledgment of the specificity of particular requirements which correspond to particular circumstances;
- In addition, it concentrates on the intimate relationship between individuals and suggests to nurture those close relationship;
- Velasquez (2001, p.15) pointed out that we ought to exercise special care for those with whom we are concretely connected by attending to their specific needs, values, desires, as well as concrete security as observed from their own personal viewpoint.
Corporate Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR has prescribed as the most powerful dynamics that has enormous promising impact on organization’s marketing strategies, consumer behavior, and major areas of corporate culture as well as society.
As a result, market researchers have rather concern on practicing CSR while studying and formulating marketing strategies. Conversely, CSR can be defined as a construct to discover through several dynamics (economic, legal, ethical, and discretionary) expected by the society from a business organization during a certain period.
Key assistance of the CSR has generate skilled workforce, high profile corporate image over and above both company and product appraisal. Hence, CSR has strategically kept durable brand image of an organization by ensuing legitimate liabilities on its consumer behavior as well as on societal norms (Enginkaya, et al., 2009).
Public Health and Ethics
In simpler form, public health ethics has stand for explaining normative ethics areas rather than empirical issues. On the contrary, public health can be formed as the parameter of right, good, and unsafe in practice. Conceptual outline of the public health ethics has justified clinically approved good and right products for human being.
Convenient perception on this sector has grounded on six major aspects like key goal of the public health, efficiency of the stated approach, major constrains, potentiality of new obstacles, effective solutions to remove the obstacles and justification of the solutions.
Normative ethics study has articulated twelve principles to ensure safer public health atmosphere, which have applicable to all type of food industry as well as in the clinical industry (Petrini, 2010).
Business Dimensions of Ethics and Food Production
MNCs (Multi National Companies) and Ethics in Food Production
MNCs has cultivated and nursing diverse mass culture where food is one of the most considerable dynamics. Under this treatment, entire issues (industrial revolution, advance technology, relationship between money and work, new relation between countries, producers and consumers, scientists, political leaders, politics and laws, economists, science and progress, nature, good and evil, and ethical way) of ethics have taken into account in order to generate best way of food production. Usually, vision of a MNC has to maximize profit internationally and yet has great participation on both domestic and host countries economy.
Currently, manipulation of food has vastly modernized globally and where function of advance technology has dominated each section of a business organization. In addition, in case of ethics of the MNCs has to be aware of host countries atmosphere (different ethical traditions, legal and political systems, forms of economic organization and different levels of economic development).
Additionally, two common code of conduct have indispensable for all type of MNCs where firstly, individual organizational policies have required defining its own ethical principles and secondly, MNCs’ code of conduct have to be command about the external atmosphere of the firm. (Kristina, et al., 2009)

Food Crimes
Disobey of the two major ethical codes of conduct of the MNCs have treated as food crime in the food industries. Brief illustration of these crimes has plotted below (McLean, 2000).
- Blackmail: globally, marketing strategies most of the MNCs have involved to attracting their consumers to take unhealthy food items those have gravely insidious human organs;
- Contamination: utilization of avoidable chemicals on land, livestock’s food item as well as on human food preservation;
- Grievous bodily harm: in order to reduce production costs ignore both human and animal rights through promote professed luxuries concept;
- Vandalism: mass transformation of natural food production organs natural fertility of land has harshly damaged.
- Cannibalism: producing animal feed utilizing similar group or other animal’s organs like blood. On the other hand, either permit to feed own class/variety or utilize products to conceive herbivores with animals and so on;
- Fraud: consciously assault food adornment of human in taste as well as appearance;
- Pillage: to advertise global economy/market structures MNCs have frequently exploit diverse nation’s culture, creeds, and societal norms.
Research Methodology
Research Design
The author of this research paper has organized the paper considering case study approach of Robert Yin as this approach is perfect when in-depth examination is essential about a particular issue. Tellis (1997) stated that Yin did not follow any specific formula; as a result, the author would be able to adopt discretion in order to formulate the paper.
However, this paper would be organized with qualitative data, and the researcher intended to avoid quantitative method for this report as the duration of to complete the paper was too short and the word limit was not sufficient for field survey.
Justification for Case Study Approach
- Case study approach would help to combine knowledge and ethical theories as the literature review provides theoretical framework of ethics;
- In addition, this method meet all the conditions to corroborate and widen the theory to discuss how Business Ethics reflected in milk powder production,
- Case study Sanlu scandal would assist to progress future investigations in a whole field;
- Moreover, the analysis about ethics of Nestle, Fonterra of New Zealand and other dairy companies would support the whole issues about ethical dilemmas.
Secondary Data
Yin (2003, p.57) pointed out that secondary data sources are more constructive tools since these are processed data and Malhotra (2009) stated that these data are more authentic data. They further added that secondary data assists to identify the problem easily, and to reach specific aims the topic as these data are easy to collect with minimal costs.
However, this research paper only focus on secondary data to avoid field survey or primary research as huge reliable secondary sources are available regarding how business ethics reflected in milk powder production.
However, the researcher has organized the paper by using few published book of famous writers, research papers of scholars, marketing journals, ethics and CRS case studies from about the selected companies, reports on Sanlu scandal and so on.
Findings And Results
Use of Cloning for Milk Power Production & Ethical Dilemmas
Brizekct (2007, p.17) pointed out that the milk powder producers are increasingly using the cloned cows to producing skimmed milk powder while at the beginning FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved that there is no need to mark this milk as ‘man-made. Due to growing public awareness and some scientific research has evidenced that there are huge gaps with the FDA approval and the milk produced from cloned cow has serious risk for public health.
CVM (Center for Veterinary Medicine) has conducted some investigation and urged that though the GM (Genetically Modified) Milk powders are profitable for business concerns but Genetic contamination can create major health dilemmas for the consumers while there is also ethical gaps for not to providing proper information by study, leveling by the producers and their attitudes, reactions, and responses on ethical practice out of care.
Biotechnology in the Milk Power Production & Ethical Dilemmas
Thompson (2010, p.3) that the biotechnology as well as genetic engineering adoption in the Milk production has approved by EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and FDA but public perceptions against the commercialization of biotechnology adoption is quickly increasing connecting the ethical issues.
There are further public sentiments connecting the moral status of biotech adoption and the border among the ‘natural’ and ‘artificial’ outcomes of GM implication and its long run term shocks on the public health as well as environment (Thompson, 2010, p.7).
The wide-ranging ethical concerns with the Milk powder production though using biotechnology are the impact of GM on the cows, influence on the agricultural foods research by the milk powder producers, and the relation among the human being and animal as well as religion believes while the ethical care to the animal would abolish.
Soya Bean Use by the Milk Produces and Ethical Issues
Akpan, Mohammed & Aminu (2007, p.10) explored that the Milk powder producers recently using Soya bean to produce Yoghurt which is traditionally produced from skimmed milk powder but now they formulating it through boiling, evaporating and concentrating Soya Bean and adding culture bacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria.
Different studies demonstrated that the Milk powder produced from Soya bean is lactose free and it has the protein supplement for both adult and children but the excess level of using preservatives created threats for health.
At the same time, the milk powder producers are consuming excessive Soya bean without taking into account of environmental degradation hamper of ecological balance, and they never compensating the agricultural hazards evidenced the lack of ethical care.
Coconut Milk Use by the Milk Produces and Ethical Issues
Sanful (2009, p.1) added that the milk powder producers are increasingly using coconut milk to reducing the production cost of Yoghurt and within the process they are mixing coconut milk directly with cow milk.
Such implication has facilitated the milk with the opportunity of maximizing profit for the powder producers but there is not enough study to make sense whether it complies with the original natural products on not. Meanwhile the ethical issues concerning the environmental and ecological balance has not yet addressed b the milk powder producers.
Table 1: Milk Powder Scandal. Source: Self-generated.
Discussion
Case Study of the Sanlu Scandal
Sanlu Group was one of the foremost participants of the milk powder producing companies in China; however, the company itself is liable for the ruin that occurred not only in the company, but also to some extent to the entire milk producing industry in the country and consequently in the world as a whole.
Today, this company symbolizes those thousands of businesses, which could go below the minimum moral standards and devastate the general human values devoid of any hesitation to destroy thousands of life for the moneymaking objective by staying under the veil of “Corporate Social Responsibility Policies”.
The Sanlu milk incident has reminded the world that undertaking a few number of charitable programs, participating in communal works, sponsoring local events, or forming some environmental schemes simply contributes to a mere show-off in order to increase corporation’s public reputation; these so-called CSR practices hardly have something to do with “social welfare” in a true sense (Song, 2009).
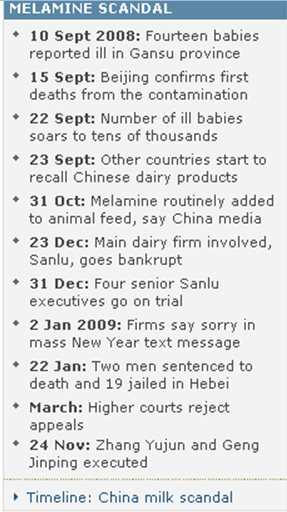
Sanlu was one of China’s most trusted brands – its packs contained an official seal of approval; despite of this, about 3 lac kids fell ill, and minimum 6 died out of kidney-disorders and complexities resulting from a deadly poisonous compound called melamine- as the scale of the problem became apparent, anger began to spread (Somerville, 2009).
The profit maximizing aim induced the company to lessen the quantity of pure milk powder and add a larger proportion of melamine into the product.
The offence performed by Sanlu milk company have induced billions of milk buyers throughout the world to move back and stop their milk purchases from any kind of well-known Chinese-brands; several renowned dairy brands and dairy farmers intended to dispose of their milk and even kill their cows since there was no firm buying milk because of lack of buyers.
The Sanlu milk incidence has nearly destroyed the entire dairy and even the entire food industry of China; with intention of solving this occurrence in an apposite method within a very small period, the Party Central Committee, undertook an approach of the ultimate liability of the public, and it took numerous directorial and lawful actions to strengthen the dairy industry.
Xinhua News Agency (2009) reported that Chinese Court upheld the death penalty and an 8 years imprisonment of the culprits, who were directly involved with this scandal; in the appeal trial, the Court supported the original verdict by showing no mercy for producing and selling poisoned food.
Geng Jinping got the death penalty, he lost his of political rights, and all his private properties has seized; on the other hand, Geng Jinzhu got an 8 years imprisonment according to the judgment.
Huei (2009) suggested that the ex-chairperson of this controversial organization who was also one of the main actors of the alarming adulterated milk powder panic, has received a mere life imprisonment whereas most people expected her to be in a death penalty; however, this 66-year-old woman has already enraged the Chinese communities and fueled severe outrages in streets.
The company became insolvent as a repercussion of this upsetting calamity and the court penalized about fifty million Yuan to the company.
Concepts of Corporate Ethics
Sanlu Group has shown no significant features in its behavior that can stand as an ethical base of the company; however, there are a few basic concepts of corporate ethics that every corporation has a responsibility to follow with the purpose to comply with a minimal stance of ethics:
- Communication of Corporate Morals and Corporate Effectiveness
- Quality of Goods and Safety Morals;
- Cooperative values between Companies and Stakeholders
- Ethical Evaluation Hypothesis- Teleology and Deontology are the two concepts that exist in the ethical hypothesis; therefore, moral evaluation also involves the two aspects which can entail on moral evaluation from five phases including Utilitarianism, theories of right, justice, caring and virtues;
- Corporation’s Duties for Customers- There are three distinctive thoughts about this matter, namely, Contract Theory, Theory of Reasonable Care and Theory of Social Cost; as per Contract Theory, it is a contract relationship between companies and customers, and this decides corporations’ proper duties for customers;
- Concept of Disagreement between Ethics and Interest- Some companies suggest that if other companies ignore ethics whilst they follow it, they will experience some losses (Song, 2009).
Case Study of Fonterra, New Zealand Scandal
Fairfax (2010) reported that the gigantic milk power exporter Fonterra of New Zealand has been associated with tremendous scandal of mixing harmful hormones which already clamed to turn little girls with grown big breasts in 2008.
There was serious effect of the Fonterra’s milk powder among the female children that out of four girls three were shaped with premature grow breasts and faced different social and mental hazard while the medical investigation has proved that the formula that Fonterra applied in its milk powder was contamination of esteem hormone that cause illness of the babies.
The facts come into view when Chinese company Sanlu imported milk powder from Fonterra of New Zealand and marketed in the local market and the reality of such scandal has spread out serious threats with the dairy product export of New Zealand.
The scandal concerned with Fonterra, has also raised the question of ethical issues in the milk producers and both the Fonterra and Ministry of trade may not by pass their concern with lack of ethics.
Fairfax (2008) also reported that the management of Fonterra was well informed with esteem hormone contamination that may cause serious illness for the infants but due to lack of business ethics the company has connected with such massive scandal and Fonterra needed to be charged with criminal contamination.
Ethical Issues – A Case Study of Nestle
Nestle boycott movement: since 1977 Nestle boycott movement has started due to disobedience of the WHO (World Health Organization) code of conduct (Cracking the Code). During this disobedience, Nestle has earned huge profit by utilization of predatory marketing strategy to sell their baby foods in the third world countries. After 1988, more than eighteen countries (Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Mauritius, Mexico, Norway, Philippines, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, UK and USA) have joined in this movement to defend harmful baby milk selling (Breastfeeding, 2010).
Violate major ethical issues: as reported by the WHO globally one and half million children were died who was not breastfed but during 2009, Nestle have gained profit around $9.58 billion by selling baby milk. Moreover, baby milk produce by Nestle has cause of several chronic diseases (diarrhea, bacterial meningitis, gastroenteritis, ear infection, and respiratory infection).
Marketing strategy of Nestlé has misguided mothers of the third world countries not to breastfeeding but clinically advised that within first six months of a child it have healthy to breastfeed. Alternatively, international marketing code for breastfeeding has prohibited interface, protection, as well as advertising of anti- breastfeeding movements.
Additionally, it has also prohibited to gift child accessories to a pregnant woman as well as mother of a newborn baby without any charge. On the other hand, baby milk and other baby foods have to contain proper nutrition proportion, which should not be unsafe for babies. All of these international marketing code issues have contravened by the Nestlé; as a result, lot of infants has died by taking their baby milk (Heather, 2010).
Conclusion
Recommendations
Conducting the investigation with the case study of Sanlu, Fonterra, Nestle, and other scandal of the whole industry, this research paper would deliver following recommendations:
It has observed from the case study of Sanlu that the Chinese Court upheld the decision of death sentence of the Chairwomen but in the case of other firm like Nestle, it can be found that there was absence of strong securities litigation by which they can secure themselves from strong punishment and recovery of wealth and reputation.
In Sanlu, Chinese government showed less tolerance to punish the culprits and they strictly reformed corporate laws to develop corporate social responsibility of the companies. In this context, this paper recommends that the government of the rest of the world should follow the example of the verdict of Sanlu case and governments should develop the new regulatory framework and suggests for more stick security legislation;
the attitude of Milk manufactures should change as the companies are not yet come out from their pursuit of profit though it is too unfortunate that the management does not take any corrective actions instantly;
The manufacturer of Mild powder only concentrate on maximize profit; therefore they mixed melamine, and harmful hormones. These chemicals changed the normal behavior and affected the physical growth of the consumers; so the manufacturer should develop their morality as it comes from inside of own mind as the corporate social responsibilities or ethical motivation has failed to bring any change of serial fraud in milk powder production.
Conclusion
There is no reason to take into account of milk powder production as an unethical function but the increasing trend of profit maximization in the industry has driven it to implement cost-effective production method, and to do so the milk powder producers have involved with some unethical activities those are necessarily needed to reverse.
Due to increasing awareness with ethical issues and health concerns there is a raising demand from the society to integrate ethical care by the milk powder producers.
Milk powder producers needed to introduce special care in the method of production, quality, public health, carbon emissions, and environmental degradation through its distribution channel, marketing campaign on breast milk substitutes with ethical views, and to ensure fair trade, justice, and such ethical integration will contribute the globe with a sustainable heritage.
Reference List
Akpan, U. G. Mohammed, A. D. & Aminu, I. (2007). Effect of Preservative on the Shelf Life of Yoghurt Produced from Soya Beans Milk. Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies, 7(11). Web.
Barry, N. (1998). Business Ethics. Web.
BBC (2010). Chinese dairy executives charged in tainted milk case. Web.
Blackorby, C. Bossert, W. & Donaldson, D. (2001) Utilitarianism, and the Theory of Justice. Web.
Breastfeeding (2010). The Nestle Boycott. Web.
Brizekct, M. G. (2007). Food cloning – ethical considerations for business organizations. Journal of Academic and Business Ethics, 10(494). Web.
Enginkaya, E. et al. (2009). A Theoretical Framework About How Organizations Promote Their Corporate Social Responsibility. Initiatives International Journal of Business and Management, 1(2). Web.
Fairfax (2008) Fonterra blames ‘criminal contamination. Web.
Fairfax (2010) Scandal over ‘NZ’ milk powder. Web.
Heather (2010). The Nestle Boycott – what’s that all about then? Web.
Huei, P. S. (2009). Ex-Sanlu boss jailed for life. Web.
Kristina, B. et al. (2009). Multinational Companies in Food Production- Ethical Issues. Web.
Longenecker, J. G. (2005). Ethical Attitudes in Small Businesses and Large Corporations: Theory and Empirical Findings from a Tracking Study Spanning Three Decades. Journal of Small Business Management. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009). Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. (5th ed.). London: Prentice-Hall.
McLean, W. (2000). A Consumer Perspective on The Ethics Of Modern Food Production. Web.
Petrini, C. (2010). Theoretical Models and Operational Frameworks in Public Health Ethics. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. Web.
Rawls, J. (1970) A Theory of Justice. Web.
Sanful, R. E. (2009). Promotion of coconut in the production of yoghurt. African Journal of Food Science, 3 (5).
Song, M. (2009). Business Ethics Reflected in Sanlu Milk Incident. International Journal of Business and Management, 4(9). Web.
Tellis, W. (1997) Application of a Case Study Methodology. The Qualitative Report, 3(3). Web.
Thompson, P. B. (2010). Ethical Implications of Animal Biotechnology: Considerations for Animal Welfare Decision Making. Web.
Velasquez, M. (2001). Business Ethics Concepts & Cases. Web.
Xinhua News Agency (2009). Appeal against death sentence and jail term rejected in Sanlu milk scandal. Web.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. (3rd ed.). London: Sage Publication.