System Objectives and Goal
Human resource management implies to combine decisions concerning people with decisions on the objectives and goals that the organization aims to achieve. The most successful organizations are those that are able to integrate human resource management (HRM) into the organization’s planning strategies by laying emphasis on human resource processes that augment mission goals and create an effective bond between human resource and management.
Apart from playing a key role in the achievement of the organization’s goal and objectives, the HRM alignment also contributes to accountability in the organization. Although the human resource management accountability starts with elementary legal compliance (see Figure 1), it eventually includes all levels of the pyramid, as well as an illustration of how HRM sustains the success of the agency’s goals (US Office of Personnel Management 1).
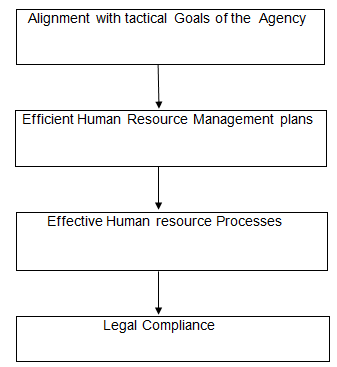
Once the HRM alignment is established, it is vital to ascertain where the organization’s current position vis-à-vis its HRM alignment with strategic goal and objectives.
In order to determine its position, an organization must explore several objectives: first, evaluate the effectiveness of the relationship between HR and the organization’s goal achievement; second, assess the function of human resource team vis-à-vis the organization’s strategic plan; third, find out how the HR staff relate with line supervisors to accomplish organization’s strategic goals; fourth, establish effective strategies that will align human resource management with the organization’s strategic goals (US Office of Personnel Management 3).
The next section will discuss the HRM strategic processes with reference to strategic plan, strategic implementation and the strategic bond in an organization.
To a number of firms, a strategic plan is vital to their business. It enables firms to find out their current status, create goals and plan how to achieve them. Strategic plans differ from one firm to another. On one hand, some firms have adopted an all-inclusive processes that involve senior managers, line managers and HR staff in the planning processes.
On the other hand, a number of firms have developed a plan that is only carried out by senior managers with a minimal role from the line managers and HR staff (see Figure 2). Each office tenders in its individual goal and objectives without liaising with other offices (US Office of Personnel Management 6). The way HR staff is managed play a vital role in ascertaining how a firm will carry out its goals.
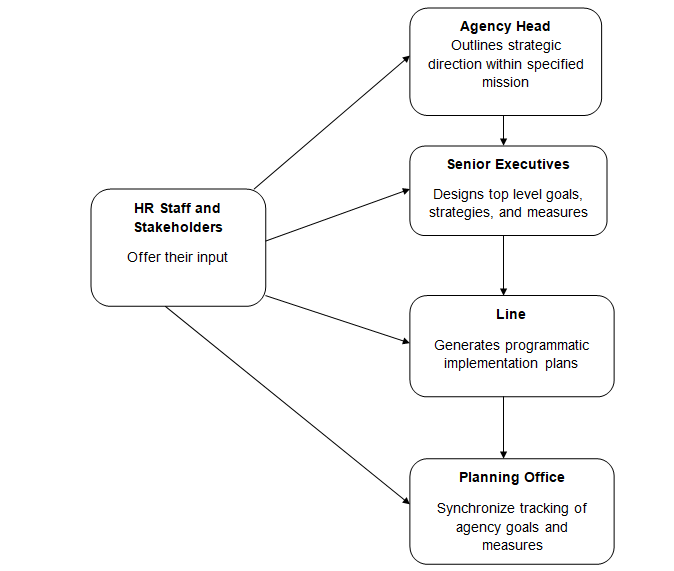
Without the staff, work cannot be done. Thus, the input of HR staff in the strategic plan of the firm must be the considered if the firm intends to achieve its goals. Therefore, by including the HR in the strategic plan, the firm is able to know vital aspects of the human resource management that are most relevant to the process. When assessing the plan, staffing, retention, HR development and quality of the labour force are crucial elements to consider.
Even though these aspects of HR could be seen as output programs, when they are planned and employed efficiently, they give credence to the ultimate outcome: the right HR staff, with apt skills, and in the right place to implement the mission of the firm (US Office of Personnel Management 8).
A number of agencies have integrated HRM with their business planning processes by including HR objectives, goals and strategies into the organization’s strategic plans. However, most agencies have not been successful in this respect. It is vital that senior managers identify the significance of human resource on priorities, activities and goals of the agency.
On the other hand, the human resource managers need to grasp the goals of the agency so that they can play a vital role in crafting innovative strategies to achieve these goals. The moment HRM is integrated in the agency’s business planning process; the human resource will no longer be set apart and confined to auxiliary functions but will turn out to be an essential factor that contributes to the agency strategic planning and achievements (US Office of Personnel Management 25).
System Functions and Requirements
Webdunia HRMS is an online-based application that entails a number of HR related functions such as HR staff management system, performance evaluation, leave management system, recruitment management system and administrative functions for maintaining master files. The online-based Leave Management System harmonizes communication between workers and staff. The Leave management makes sure all applications for leaves are efficiently documented and implemented (Webdunia 1).
The system enables workers to ascertain their vacation availability at any time and tracks the employees’ leave plans and balances. Webdunia HRMs also has an online-based Performance Assessment System that assists an organization to generate an efficient performance assessment for its staff. Some of the features of the performance appraisal system include: questionnaire for grading staff; auto initiate assessment of workers; and management appraisal lock days.
The Attendance Tracking System enables an organization to track time and attendance of staff in an efficient way. Some features of this software are: closely integrated with Access Control system; and display of several report using LMS and Access Control data (Webdunia 2).
The Recruitment and Management System (RMS) offers an automated hiring process as it tracks details to be analyzed later. The system enables an organization to improve its recruitment process. Some features of RMS include: interviewer management; candidate management; resource requisition; applicant tracking; employee referral; and schedule interview (Webdunia 2).
Webdunia is thus able to assist managers to cut on the manual workload of their administrative work since its simple and offers automated data that is used in decision-making process.
System Integration and Features
The HRIS system has three main features. These are: Input; Data Maintenance; and Output. The input feature captures the information of workers into the HRIS system. The data maintenance component adds and brings up to date new data to the database after information has been entered in the system.
The output component processes data captured in the system and then arrange the output data in a manner that the HR managers can understand easily. However, for the system to be effective the input data must be valid and reliable before it can be processed (Boateng 25). In addition, the HRIS integrates a number of functions such as data input, tracking data, payroll management, and accounting roles of an organization.
An efficient HRIS can provide several services such as: managing information of all workers; managing a number of documents such as staff booklets, and safety guidelines; benefits management by offering data on changes in enrollment status and updating staff information; it integrate payroll with other accounting systems and financial software used by the organization. In addition, HRIS tracks pay upgrades, staff attendance, training programs, and disciplinary measures to be adopted (Heathfield 2).
By using an efficient HRIS, the HRM can delegate some duties to its workers such as updating their benefits and changes in contact address. The HRM is thus able to concentrate on implementing critical strategic goals of the company. In addition, the system facilitates information needed for managing workers, training and career development.
Finally, the management is able to access data needed to facilitate the success of their staff ethically, legally and efficiently. This will enable the organization to align its strategic goals with the role of its workers (Heathfield 3).
Business Models used in this System
The Ulrich’s HR Roles model is an example of business model that is used in human resource management. This model facilitates business partnering by bringing about substantial changes in the HR organization. The Ulrich’s model has facilitated the restructuring of HR resources in a flexible way and allowed HRM to prioritize the implementation of the organization’s strategic goals. Ulrich’s model four main components: strategic partner; staff champion; change agent; and administrative expert (Ulrich 1).
Strategic partner concerns aligning human resource programs and activities with the international business strategy. This function is carried out by the HR Partners and HR Management. The change Agent component of Ulrich’s model is vital because it deals with sustaining the transition and change of the organization with respect to the organization’s human resource pool (Ulrich 2).
The function of HR is to support changes in the HR area and to ensure that the transition is smooth. The Administrative Expert component of the model takes time to change. It lays emphasis on the ability of an organization to offer efficient services at optimally reduced cost (Ulrich 3). The Staff Champion component is also vital in management of human resources.
It enables the management to ascertain need of workers. The Staff Champion is thus able to cater for the needs of workers and to offer them protection when the change process is activated within the organization (Ulrich 4). Thus the four components of Ulrich’s model are to the success of the HRM activities.
Works Cited
Boateng, Agyenim. The Role of Human Resource Information Systems in Strategic Human Resource Management. Hanken: Swedish School of Economics and Business Administration, 2007.
Heathfield, Susan. “Human Resources Information System (HRIS)”. About, 2010. Web.
Ulrich, David. “Ulrich’s HR Roles Model”. HRM Advice. 2008. Web.
US Office of Personnel Management. “Strategic Human Resources Management: Aligning with the Mission”. Office of Merit Systems Oversight and Effectiveness. 1999. Web.
Webdunia. “Human Resource Management System”. Webdunia. 2011. Web.