Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that contributes significantly to mortality, morbidity, and disability rates across the world. The increasing prevalence of diabetes among developed and developing countries has reversed the gains made in the eradication of non-communicable diseases. The increasing trends of diabetes in the United Arab Emirates are quite shocking because it does not only threaten the lives of people, but it also threatens economic growth because the medical costs incurred in its management are enormous. According to Boutayeb, Lamlili, Boutayeb, Maamri, Ziyyat, and Ramdani, statistics indicate that the healthcare expenditure of diabetes constitutes approximately 11% of the total healthcare costs in the Middle East, which is very significant given that it is a single chronic condition (57). Since the prevalence of diabetes varies from one country to another, depending on the lifestyles and healthcare services, the economic impacts of diabetes differ considerably. Hence, this essay examines the prevalence of diabetes in the United Arab Emirates with a view of analyzing its economic impacts, and consequently establishes if the use of erythritol is effective and cost-effective in the management of diabetes.
Prevalence of Diabetes in the UAE
The prevalence of diabetes in the UAE has increased exponentially in the recent decades. In 2011, International Diabetes Federation released alarming statistics when it reported that countries in the Middle East have an average prevalence of 11% and the UAE having the prevalence of 19.2%, which make it ranks sixth among Arab countries (Boutayeb et al. 56). The prevalence of 19.2%, which is very high when compared to prevalence rates across the world, shocked the UAE government because diabetes has a significant impact of the budgetary of healthcare and subsequently economic development. As the UAE aims to reduce or reverse the trends of both communicable and non-communicable diseases, the increasing trends of diabetes negate the achievements that the health care system has made for decades.
As the prevalence of diabetes varies from one country to another, depending on the economic development, the occurrence of diabetes in the UAE has unique epidemiology. International Federation of Diabetes indicates that the affected individuals are the ones with ages between 20 and 79 years (Boutayeb et al. 57). Since diabetes cause disability, morbidity, and mortality, it implies that it affects the working force in the UAE, and consequently decreases economic development owing to the deprived human resources in the labor sector. The diabetes in the UAE has an enormous economic impact because “nearly three quarters (73.4%) of diabetics are under 60 years of age and in the peak of their productive years, which makes the burden in terms of disability due to diabetes heavier” (Boutayeb et al. 57). Hence, the economic impact of diabetes in the UAE is significant when compared to the developed countries, where most diabetics have the ages beyond 60 years.
Economic Impacts
Diabetes has enormous economic impacts because its treatment and management requires extensive and intensive medical services. According to the epidemiological data, 745, 940 cases exist, while 303,600 cases remain undiagnosed (International Diabetes Federation par. 2). These data imply that about 1 million people in the UAE suffer from diabetes, and therefore, it is an appropriate figure that could provide an estimated economic impact of diabetes on the economy of the UAE. Diabetes has direct and indirect economic burden in terms of medical costs and disability costs respectively (Al-Maskari, El-Sadig, and Nagelkerke 1). Hence, the assessment of the direct costs and indirect costs illustrates the impact of diabetes on the economy of the UAE.
Diabetes has direct costs such as the costs incurred in the treatment and management of diabetes. According to Al-Maskari, El-Sadig, and Nagelkerke, the average costs of treating a diabetic patient without complication is $1,605±$1,473 annually, while the average costs of treating a diabetic patient with complications is $5,645±$5,966 per year in the UAE (5). The complications increase medical costs as treatment and management of diabetic complications such as diabetic foot, stroke, angina pectoris, and cardiovascular disorders. For the 1 million patients with diabetes, are prone to complications, it means that the health care system should increase its budget to cater for the diverse complications.
Table 1.
Table 1 shows the approximate medical costs that the health care system can incur depending on the complications of diabetes. Without complications the health care system of the UAE can incur about $1.605 billion, while with complications such as microvascular and macrovascular, the medical cost would increase to about $1.345 billion and $10.3 billion respectively. Moreover, if all diabetic patients experience both complications, microvascular and macrovascular, it means that the health care system requires about 15.104 billion for the provision of medical services. According to Al-Maskari, El-Sadig, and Nagelkerke, per capita expenditure on healthcare in the UAE is $497, which adds up to $3.976 billion for the population of 8 million. Comparative analysis shows medical costs of treating diabetes without complications constitute a third of health expenditure, while the medical costs of treating diabetes with microvascular complications is about 90% of health expenditure. The medical costs of treating diabetes with complications of macrovascular are about three times that of health expenditure. Furthermore, the medical costs of the combination of complications, microvascular and macrovascular, is four times that of health expenditure. On average, diabetes has potential of doubling or tripling medical costs, and thus, it overstretches the budget of the health care system and strain the economy of the UEA.
As diabetes cause disability and mobility, it reduces the capacity of people to work optimally. According to Boutayeb et al., 73.4% of diabetic patients are under the ages of 60 years, which implies that they are productive people (57). Out of 1 million patients with diabetes, about 700,000 experience different forms of debilitating conditions, which lessen their productivity in their workplaces. From the calculation of the per capita income of $48,158 and the working population of 700,000, the UAE losses approximately $33.705 billion annually owing to the debilitating effects of diabetes among human employees.
Financial Prediction
Projections of the diabetes in the UAE show that in the next 10 years, the prevalence rates would be about 30%. Al-Maskari, El-Sadig, and Nagelkerke argue that a change in lifestyles is responsible for the exponential increase in diabetes among the population, which is set to double or even triple every passing decade (3). As the current medical costs are about $10 billion, by 2025 medical costs would be about $15 billion. Moreover, the debilitating costs would cost the employment sector approximately $45 billion in the next 10 years.
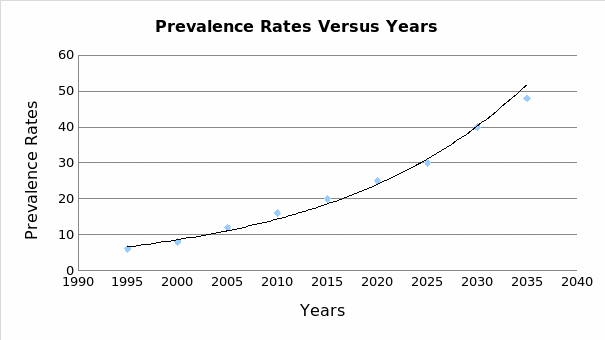
Solution
The use of erythritol is one of the effective solutions that can aid in the prevention and management of diabetes and associated complications. Fundamentally, erythritol is an alcohol sugar, which is a sweetener with reduced calorie. Reduced calorie implies that erythritol reduces energy intake, glycemia, and weight gain. As medical nutrition therapy is applicable in the prevention and management of diabetes, American Diabetes Association recommends the use of erythritol as one of the sugar alcohols that the Food and Drug Administration has approved as safe and effective in the prevention and management of diabetes with its complications (65). Therefore, the use of erythritol in the prevention and management of diabetes among diabetic patients in the UAE is cost-effective. Speight argues that intensive glycemic control prevent complications of diabetes (16). In this view, if the UAE encourages diabetic patients to use erythritol in the management of diabetes, it would save about $13 billion, which health care system uses in the treatment of complications associated with diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic disorder that is dominant across the world and its prevalence in the UAE is alarming. According to International Diabetes Federation, the UAE has a prevalence of 19% and projections shows that by the year 2025, the prevalence rates would be about 30%. Likewise, current medical costs add up to about $10 million, while debilitating costs of employees is about $30 billion. Projections show that by 2025, the debilitating costs would be $15 billion and $45 billion respectively. Since glycemic control is central to the management of diabetes, the use erythritol is effective because it reduces glucose in the blood and prevent occurrence of complications, which double or triple medical costs.
Works Cited
Al-Maskari, Fatma, Mohammed El-Sadig, and Nicholas Nagelkerke. Assessment of the direct medical costs of diabetes and its complications in the United Arab. BMC Central Public Health 10.679 (2010): 1-10. Print.
American Diabetes Association. Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes. Diabetes Care 31.1 (2008): 61-78. Print.
Boutayeb, Abdesslam, Mohamed Lamlili, Wiam Boutayeb, Abdellatif Maamri, Abderrahim Ziyyat, and Noureddine Ramdani. The rise of diabetes prevalence in the Arab region. Open Journal of Epidemiology 2.1 (2012): 55-60. Print.
International Diabetes Federations. The United Arabs Emirates. 2014. Web.
Speight, Jane. Managing diabetes and preventing complications: What makes the difference? The Medical Journal of Australia 198.1 (2012): 16-17. Print.