Introduction
Industrial Galvanizers started way back in 1965 as a family galvanizing manufacturing business in the Hunter Valley, Hexham. Recognized as one of the largest galvanizing baths in Australia, Industrial Galvanizers slowly extended its operations of the structural galvanizing plant to Brisbane, Qld, and Sydney as well as the NSW. Established as a structural galvanizing plant, the company dominated the markets gaining a wider wide customer base as well as the communities in which it operated.
While striving to improve its plant operations, Industrial Galvanizers has actively participated in technological innovation and best business practices as a strategy to meet and exceed our customers’ expectations. The company also promises to adhere to environmental safety policies to ensure employees and customers are effectively protected.
In ensuring environmental safety awareness, Industrial Galvanizers delegate their responsibilities to the environmental manager who ensures the planning and implementation of environmental policy in different departments. His functions include performing a checklist to ensure companies continue to practice customer’s safety expectations in delivering quality and service while achieving shareholders’ expectations of financial performance. Programs that ensure commitment, planning, implementation, monitoring, and reporting of environmentally hazardous conditions along with their reference materials are provided.
Industrial Galvanizers Environmental Management System (EMS) Manual outlines the primary responsibilities of the Environmental Management System and proposes ways to ensure regular updates are performed.
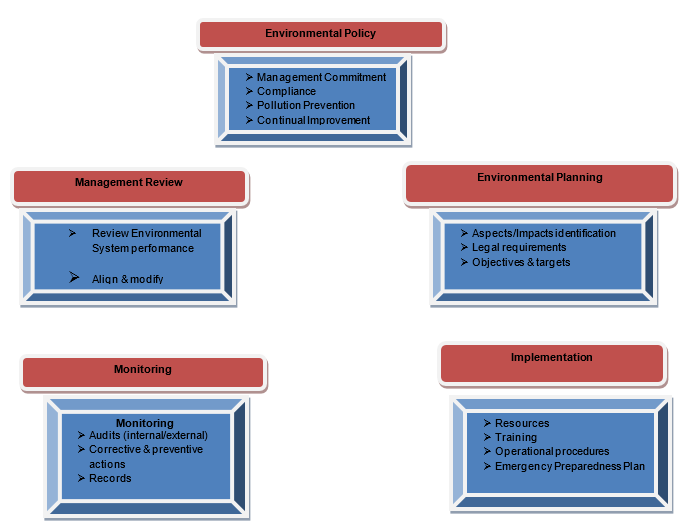
EMS manual is structured about AS/NZS ISO 14001:2004 “Environmental Management Systems – Requirements with Guidance for Use” and provides provision for;
- Environmental policy,
- Planning,
- Implementation & operation,
- Monitoring and checking,
- Management review
The manual illustrates and registers Industrial Galvanizers Standard Management Procedures (SMPs) and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
EMS manual includes Industrial Galvanizers plant environmental processes and performing operations in Melbourne, Australia Plant
The table below presents a summary of the procedures and responsibilities required by different applications.
* The procedures’ description included in this manual is for illustrative purposes only*
Industrial Galvanizers Environmental Policy
Environmental policy is a fundamental part of Industrial Galvanizer’s corporate business strategy and focuses as it helps establish environmental management programs as a means for achieving objectives and targets. This policy helps a company understand and minimize environmental impacts it is metal coating operation may have on its employees, customers, and the environment as a whole. Listed under the Environmental Policy (EMS-REC-4.2A), the outline below illustrates the prevailing policies and objectives governing the plant’s performance and operations.
The philosophy of policy function operates as a checklist to ensure companies continue to customer’s safety expectations in delivering quality and service while achieving shareholders’ expectations of financial performance.
Industrial Galvanizers Environmental Policy is mentioned as follows:
- Structure, implement, maintain and review the environmental policy periodically
- Inclusion of environmental policy in the Environmental Management System
- Implement proactive actions that deal with environmental protection and improvement
- Implement, resource, review, and regularly update the environmental management system that objectifies the company’s performance and environmental improvements.
- Promote strong environmental ethics throughout its work policy
- Inclusion of environmental risks in the Industrial Galvanizers’ operations and place great emphasis on environmental management principles as a strategy to reduce the impacts of pollution
- Encourage waste management systems such as recycles to reduce waste production
- Mandatory environmental awareness training classes for employees
- Avail company’s policies about environmental awareness to internal and external parties
Organization chart
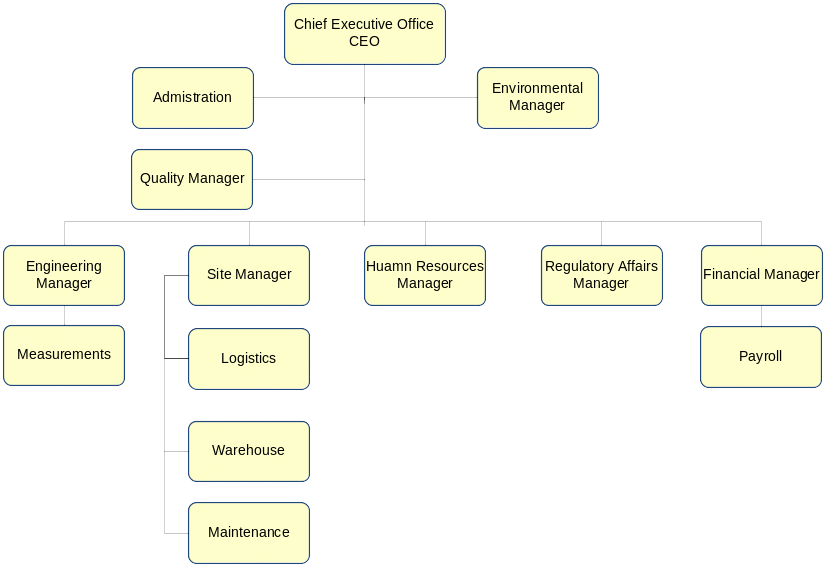
Summary of Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer
- General Environmental Direction.
- Endorse Environmental Policy.
- Certify sufficient resource availability.
- Endorse environmental Objectives & goals.
- Commend environmental management programs.
- Management reassess.
Environment Manager
- General management of the Environmental Management System.
- Management delegate.
- Internal Environmental inspection.
- Perform Environmental training and alertness.
- Environmental internal/external communications.
- Environmental system records.
- Contact with external parties connected to environmental issues.
- Following Environmental Management Program execution.
- Following corrective-preventive action execution.
- Arrange management review gatherings.
Regulatory Affairs Manager
- Notify all legislative needs.
- Combine and retain legislation record.
- Training and consciousness in co-ordination with Environmental Manager.
Engineering Manager
- Site engineering systems:
- Fire fighting system.
- Power support system.
- Piping systems.
- Stormwater management system.
- Devastated water management.
- Measurements and observes of air-emissions (Combustors, etc…).
- Site engineering systems:
Site Manager
- Managing actions inside the premises.
- Site logistics:
- Equipment adjustment.
- Stores.
- Site scenery.
- Employment management.
- Maintenance plans.
Quality Manager
- Quality Management System needs.
Human Resources Manager
- Staff employment.
- Contact in training issues.
- Worker records.
Financial Manager
- Staff Payroll.
- General finances.
Planning
Environmental Facets
Environmental facets identify environmental Industrial Galvanizers effects it has had on the environment and identifies the company’s objectives and targets. Objectives and targets significant to environmental pollution such as soil, water, and air are covered and views of interested parties mentioned.
In identifying environmental facets as a means for achieving objectives and targets, human health, safety, and environmental coordination is our primary concern. In this regard, the research begins by identifying and assessing Industrial Galvanizers environmental impacts based on the consequence and precedence through the Facets /Impacts Identification Procedure (EMS-SMP-4.3.1). This procedural analysis uses the assessment risk model as a test measure to quantify the probability of the Industrial Galvanizers effect may have to individuals or the community at large and the likelihood of their actions.
Environmental managers should be fully committed to ensuring environmental excellence and sustainment development through continuous improvement activities.
Applicable Procedure
- Industrial Galvanizers activities: Ashes, metals and rocks, wire and trapping, drums
- Identify environmental aspects (corrective and preventive actions
- Identify environmental impacts ( identification and evaluation of hazards)
- Assess & rank (Risk Assessment Model)
- Set objectives, targets, Environmental Management Program (plan for emergencies, response plan [evacuation], accident and reporting procedure)
- Management review (audit and review environmental policies)
Reference Material – EMS – SMP – 4.3.1 – Impact identification method.
Legal and Other Requirements
Legal entities commit their services to manage companies in an environmentally responsible manner.
Embedded in the company’s environmental awareness policies, Industrial Galvanizers highlights the importance of complying with all applicable laws, regulations, and standards in their daily operations. Committed to complying with current legislation, prevention of pollution, and seeking continuous improvement in its environmental performance, the Official Requirements Identification method (EMS-SMP-4.3.2) identifies and provides obligatory requirements Industrial Galvanizers are required to adhere by.
To achieve these objectives, the required policies are made available to all employees, and appropriate training provided in the induction program in accessing and understanding the legal requirements of environmental sustainability.
Applicable Procedure
- Develop, implement, resource, and maintain legal requirements about the environmental management system
- Set legal requirement objectives, targets and measure progress to ensure companies abide by them
- Develop legal register for activities likely to be hazardous to the environment
- Conduct monthly update
- Continuously update the register to ensure improved environmental performance
- Ensure adequate training for employees and suppliers and raise awareness on their environmental responsibilities
- Management review (periodically assess each company to benchmark performance against the best practice)
Reference Material – EMS – SMP – 4.3.2 – Legal Requirements Identification Procedure.
Environmental Objectives and Targets
Regarding Industrial Galvanizers’ environmental policy, companies should define environmental objectives and goals suitable for their operations. Below is a summary of the environmental objectives and targets necessary for realizing environmental policies.
These objectives and goals are aimed at:
- Suggesting reclamation methods that are technically effective, cost-efficient, and environmentally friendly.
- Monitoring performance in and after reclamation to ensure environmental sustainment objectives are achieved.
- Remove all contamination facilities to the surrounding environment such as soil.
- Safe disposal of industrial waste products.
- Measurements, audits, and monitoring to make sure the nearby water is safe.
- Proactive emergency plans and continuously updated policies.
Applicable Procedure
- Analyze aspects/impacts to ensure achieved environmental performance.
- Analyze legal requirements to ensure compliance with all applicable laws, regulations, and standards.
- Set objectives by enabling open and effective communication between the company and employees.
- Set targets.
- Discuss & approve (providing greater opportunities for external stakeholders input).
- Management review on the current standards to ensure the overall effectiveness of the EMS is reviewed periodically to assess progress toward ongoing improvements.
Reference Material – EMS-SMP-4.3.3 – Objectives & Targets Identification Procedure.
Environmental Management Programme
Environmental Management Plan (EMP) presents one of the likely issues industrial Galvanizers should consider when preparing each site-specific EMP in planning and implementation. In this regard, Industrial Galvanizers establish a program that involves the allocated responsibilities, establishments, schedules, working processes, and resources. An EMP is developed in stages that include; commitment, planning, implementation, monitoring, and reporting.
Applicable Summary:
The environmental manager is solely responsible for program setting & proceedings in all operations. The question such as what are the most likely environmental issues? Likely effects they can cause to the environment and how to manage these issues to minimize harm to the environment are often asked. In this regard, environmental manager duties and responsibilities below as;
- Commitment: make statements of commitment about environmental Policy.
- Planning: analyze objectives & targets related to site activities and their likely impact on the surrounding environment.
- Ensure full compliance of legal requirements applicable to environmental protection legislation.
- Set actions: Prepare emergence Response Plan.
- Implementation: Assign responsibilities for implementing work instructions.
- Set time-line: provide adequate training for personnel responsible for EMP implementation.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Approve the plan.
- Follow up implementation: Provide monitoring report card in EMP and provide in-house audit process.
- Management review to ensure full compliance.
Reference Material– EMS – SMP – 4.3.4 – Environmental Management Program Procedure.
Implementation and Operations
Structure and Responsibilities
Environmental manager responsibilities entail promoting the adoption of environmental policies to meaningful results. Their primary objective is to ensure adherence to safety provisions and produce significant improvements in environmental outcomes. He imposes real requirements, monitor, and enforce environmental policies to ensure Industrial Galvanizers apply to Environmental Management System efficiently. The provided Industrial Galvanizers organization diagram (EMS-REC-4.4.1A) objectifies employees’ positions within the organization. The main environmental responsibilities are specified in the Summary Tasks (EMS-REC-4.4.1B).
In summary, the Environmental Manager can implement the environmental legislation and reassess the organization diagram and responsibilities and present them at the management review gathering.
Training Awareness and Competence
The environmental manager’s primary objective is to proving training and awareness to employees with the aim of disaster risk reduction in the area of industrial disaster. He provides the required knowledge to help in implementing the Environmental management system.
The Training Package Prime Objectives is to provide knowledge and awareness in the following;
- Environmental Management System Requirements.
- Industrial Galvanizers Environmental Policy.
- Environmental facet and impacts.
- Environmental goals and objectives.
- General environmental attentiveness training.
- Environmental Management Program.
- Orientation training.
Applicable Procedure
- Improve awareness in the area of industrial disaster management.
- Identify training requirements on on-site and off-site energy planning development.
- Assess current knowledge by sharing experiences to get a common understanding and get ideas on increasing emergency preparedness.
- Bridge gap – environmental training plan.
- Conduct training.
- Document training records.
- Management review (review documents and assess processes and provide direct access to safety knowledge.
Reference Material – EMS – SMP – 4.4.2 – Environmental Training & Awareness Procedure.
Communication
Communication is considered one of the important core elements in the Environmental Management System. It’s evidenced that convenient implementation of the Environmental Management System requires proper communication between different levels of management. In essence, effective communication ensures environmental risks are well-identified in internal and external environments.
Applicable Procedure;
- Gather information.
- Determine the target audience.
- Determine the type of information to be gathered.
- Implement.
- Management review.
Reference Material – EMS – SMP – 4.4.3 – Environmental Communication Procedure.
Environmental Management System Documentation
Environmental Management System Documentation identifies the process and responsibilities of their environmental requirements and makes it accessible to each employee in Industrial Galvanizers.
Document Control
Industrial Galvanizers EMS document controls are performed by an environmental manager who ensures regular updates are performed. Below is a summary of Document Control Procedure and description techniques used in the plant in controlling and issuing of the EMS documents.
Applicable Procedure;
- Need to issue/amend/delete document.
- Fill form EMS-REC-4.4.4D.
- Environmental Manager Assessment.
- Draft EMS Document.
- Approve & issue.
- Update register.
- Management review.
Summary – EMS – SMP – 4.4.4 – Environmental System Documentation Procedure.
Operational Control
The environmental manager in the operation control department oversees the implementation of operations plans by identifying the roles and responsibilities of each employee in EMS about environmental policy, goals, and objectives. The primary responsibility of operational control is to set up, apply, and sustain documented procedures. Operational Control procedures are classified as:
- Standard Management Procedures: ensures communication of management operations that influence the environmental performance of the company is regulated in operation processes
- Standard Operating Procedure: Standards operating procedure influence environmental performance activities such as truck unloading and disposal phase.
Outlined in the “Environmental System Documentation Method (EMS-SMP-4.4.4)”, operation control procedures are regularly updated and include aspects such as the date and version number, which are then integrated into the “Internal/External Document Control Record (EMS-REC-4.4.4A)”.
Environmental Records related to operation control are outlined in the “Records Registering (EMS-REC-4.4.4C)”.
The environmental manager ensures throughout training employees are adequately notified on the Standard Procedures to ensure safe operations. Environmental Manager conducts regular updates on EMS and avails it to the management review conference.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Facets; clearly defines safety procedures outlined in the Identification Method (EMS-SMP-4.3.1) and classifies accident-prone situations stated in the Environmental Facets/Impacts Record (EMS-REC-4.3.1A).
Once disaster-prone areas are identified, the Environmental manager outlines safety procedures in the Emergency Preparedness and Response Plan which are then passed on to the Environmental Management Programme.
For an effective application, Emergency Preparedness & Response Plan is updated yearly under the Environmental Manager view.
Checking and Corrective Actions
Monitoring and Measurement
As outlined in the Measurement Process (EMS-SMP-4.5.1), monitoring and measurement primary responsibility is checking and formulating a corrective action plan as provided by the environmental policy.
The checking procedure correlates with actions of environmental policy, goals, aims, and the legal requirement.
Applicable Procedure
- Monitoring and Measurement of objectives & targets.
- Corrective and preventive action.
- Records.
- Environmental management audit.
- Check legal requirements.
- Identify monitored areas.
- Develop a plan.
- Calibrate equipment.
- Perform measurements.
- Management review.
Reference Material – EMS-SMP-4.5.1 – Environmental Monitoring & Measuring Procedure.
Non-Conformance and Corrective and Preventive Actions
Non-Conformance and Corrective and Preventive define the responsibilities and processes required in investigating non-conformance organization’s environmental management systems. Works by taking actions to mitigate any negative impacts caused and applied for corrective and preventive actions. Identified thorough internal audit process of Industrial Galvanizers, detecting non-correct actions, and dealing with them effectively ensures appropriate planning, scheduling ad managing corrective and preventive actions comply.
As outlined in the Incident Reporting and Investigation Procedure, the environmental manager’s responsibility includes managing and investigating non-conformance, taking proactive action to mitigate impacts caused by industrial galvanizers, initiating and completing corrective and preventive action as provided in the Incident Reporting and Investigation Process.
The Incident Reporting and Investigation Procedure outlines clearly state accountability and rights for managing and examining non-conformance, actions handling to lessen impacts, and application and implementation of remedial and anticipatory action.
Applicable Procedure:
- Identify non-conformities in all areas and departments.
- Fill non-conformity report (Corrective and Preventive Action Request).
- Identify the cause & potential risks of non-conformance or non-compliance.
- Action.
- Record (modifying or creating environmental procedures and work practices.
- Plan and implement corrective and preventive actions.
- Management review (verify the close-out effectiveness of corrective and preventive actions).
Reference Material – EMS-SMP-4.5.3 – Incident Reporting & Investigation Procedure.
Records
Industrial Galvanizers uses record-keeping methodology as a self-evaluating tool to benchmark and evaluate its environmental performance. Record keeping performs controls and records management requests as provided by Environmental System Documentation Method (EMS-SMP-4.4.4).
Environmental System Documentation Method as outlined in the Industrial Galvanizers environmental measures ensures;
- Records are produced and stored properly.
- Records are identifiable and protected.
- Information in the records is clear and perceptible.
Conclusively, Environmental Manager adheres to all requirements and responsibilities provided in the “Records registering EMS-REC-4.4.4C”.
Environmental Management System Audit
Environmental Management System Audit performs yearly audits on the EMS to ensure the system’s effectiveness and compliance with the requirements AS/NZS ISO 14001:2004. He conducts periodic EMS audits to determine if all standard elements and applicable and if they have been properly implemented and maintained. Internal audits are performed every quarter while the external audits are coordinated by an EPA Environmental Auditor once a year.
Procedures required in the Internal Audit system are outlined below as;
To ensure the effectiveness and conformity of the Environmental Management System Audit, the AS/NZS ISO 14001:2004 requirement is required for yearly audits of EMS.
Applicable Procedure Summary:
- Develop Annual Audit Plan (internal/external)
- Issue & distribute
- Conduct audit; [record audit finding using corrective/preventive action report]
- Record findings; [auditors ensure signed reports are collected and filed in the EMS]
- [Audit reports availed to employees]
- [Audits assigned a record ID number]
- Discuss & approve actions with the audited person
- Follow-up implementation
- Management review; [availed every quarter at the management review board meeting]
Reference Material – EMS – SMP – 4.5.5 – Internal/external Environmental Audit Procedure.
Management Review
In management review, Industrial Galvanizers’ top management has primary responsibility for monitoring and assessing the organization’s performance of the environmental management system. They ensure the implementation of safety and environmental practices, conduct safety observation, provide emergency response plans, deliver training, and manage compliance with environmental policy.
Committed to ensuring the safety of employees, management reviews are performed annually to ensure companies comply with the provided policies of system operation to ensure environmental safety.
A summary of Management Review responsibility is outlined below as;
- The document, implement, maintain and review environmental policy as part of the EMS
- Provide employees with access to environmental awareness training
- Implement, resources, review and continually review EMS
- Plan, develop and operate all hazardous locations to achieve compliance with appropriate regulations
- Publish Audit results.
- Communications from external concerned parties as well as complaints.
- The level to which objectives and goals are achieved.
- Regular audits for Environmental performance of the plant.
- Status of remedial and anticipatory actions.
- Resume activities from preceding management review meetings.
- Suggestions for upgrading.
- Improvements in authorized or other environmental requirements.
Applicable Procedure
- Prepare meeting agenda.
- Prepare meeting documents.
- Conduct meeting.
- Issue & record minutes & actions.
- Follow-up implementation.
Reference Material – EMS-SMP-4.6 – Management Review Meeting Procedure.