Introduction
Despite the fact that the introduction of the Internet is not different from the way other technologies have found their entry into the society, it seems to be advancing faster than all other technologies. The reality is that the Internet is being used actively in many areas of our lives today.
With increased use of the Internet, the need for web security has taken center stage. Unlike in the early stages of the Internet, business enterprises and individuals are relying on the Internet to provide an efficient platform for business operations. This includes the need to guarantee support for reliable financial transactions. However, for this to succeed, it is imperative to ensure that web security is not compromised in any way. To encourage the growth of e-commerce operations, for example, it is imperative for designers to build stable and secure web browsers.
This paper looks at the security of web browsers and focuses on determining the most secure of them.
The Most Secure Web Browser
According to Wayner (2010), choosing the best and most secure browser is not an easy task. Despite the fact that all browsers have been designed with qualities that distinguish them from each other, some come with features that make them superior. In a study funded by Google to determine how secure web browsers are, it emerged that Google Chrome had the best security features compared to the rest (Henry, 2011). According to the study, Chrome exhibited superiority in features such as sandboxing, just-in-time hardening, and plug-in security. As pointed out by Ledford and Davis (2009), Google’s intention of coming up with Chrome was to provide the market with the fastest, stable and most secure web browser. Based on the findings of this study, Chrome is one of the most preferred web browsers available in the market today.
By and large, Google Chrome is designed with a powerful defense mechanism to ensure the security of users on the web. It has inbuilt features to deal with malware and other related attacks. Furthermore, the browser includes automatic updates to ensure that the browser is always up to date with the most current security updates. Arguably, the popularity of Chrome as the most secure browser has been rising since its inception. Chrome is also very stable and can run on different platforms. In addition, it can easily be customized by existing extensions that can be obtained and installed. Among other things, the extensions offer great support for parental controls that help to monitor the content accessed and viewed by children.
Drawing from a study by Wayner (2010), Mozilla Firefox is the only browser that comes next to Chrome in terms of features, performance, configurability, and extensibility. This is clearly illustrated by figure 1. As depicted by the figure, the other browsers are equally good, but they do not match Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
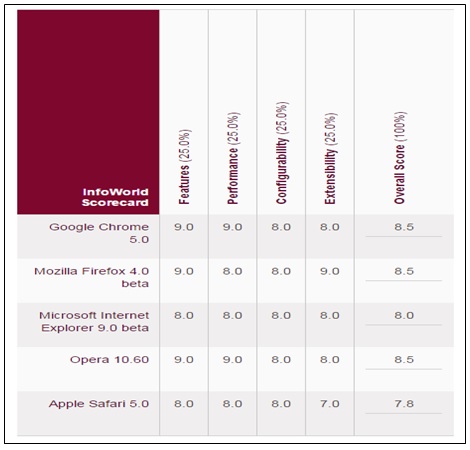
This is a fact emphasized by Jahankhani et al. (2015). Through various experiments they were able to demonstrate that Mozilla Firefox is the second most secure browser after Google Chrome. Unlike Chrome, Mozilla Firefox cannot be considered secure and private given the possibility of intruders accessing content illegally during a user’s browsing session (Jahankhani et al., 2015). According to Ledford and Davis (2009), improved stability makes it possible for users to do more with their web applications without fear of the browser crashing. As an additional security feature, Chrome will automatically send warnings to users whenever they are accessing any website that is known to contain malware. Google chrome is also regarded as the most appropriate browser for any user who has to rely on remote web applications.
While Chrome comes with nice features to support security, it has a few drawbacks. One of its disadvantages is that it consumes so much in terms of the needed system resources. For this reason, it performs poorly on machines with limited resources available. However, these weaknesses are neutralized by the many powerful features that are integrated within the browser.
Conclusion
As pointed out in this paper, increased use of the Internet has created a new set of problems that must be addressed very carefully. Key among these problems is security. Designers of web browsers are thus with a challenge to ensure that they are able to provide users with the most secure are reliable web browsers.
While there are many browsers available in the market, the need for security is forcing users to look out for key features that guarantee better performance, stability, and security. This presents designers with a tough task of making sure that web browsers are developed with features that enhance performance without compromising security in any manner.
As discussed in this paper, Google Chrome stands out as the most secure and reliable web browser followed by Mozilla Firefox. Although Google Chrome has a few weaknesses as earlier mentioned, its advantages far outweigh the disadvantages. Besides being stable, for example, Google Chrome has the ability to run on multiple platforms.
References
Henry, A. (2011). What’s the most secure web browser? Web.
Jahankhani, H., Carlile, A., Akhgar, B., Taal, A., Hessami, A. and Hosseinian-Far A. (2015). Global Security, Safety and Sustainability: Tomorrow’s Challenges of Cyber Security. London, UK: Springer.
Ledford, J. & Davis, Y. (2009). Web Geek’s Guide to Google Chrome. United States of America: Que Publishing.
Wayner, P. (2010). The best Web browser: Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, or Safari? Web.