Introduction
British Petroleum [BP] is a private limited company that operates in the UK oil and gas industry. The firm was established in 1909 and has been in operation for over 100 years. BP has attained substantial growth since its inception.
Its growth has arisen from integration of effective growth strategies such as internationalisation and formation of mergers and acquisition. For example, on 21st March 2013, BP acquired 5.66% of Rosneft which is the leading oil producer in Russia (BP, 2013). The firm’s success has also arisen from integration of effective marketing strategies.
The UK oil and gas industry has become very challenging over the past few decades. This has arisen from changes in the internal and the external business environment. Despite the prevailing environmental changes, firms within the industry are committed towards maximising their profitability. As a result, firms are considering expanding their marketing activities by venturing into the international market.
The objective of this paper is to provide a comprehensive definition of the marketing and to illustrate how environmental factors affect international marketing process. The analysis is achieved by comparing the macro environments of China and the US which are some of the countries that BP has ventured.
Definition of marketing
Traditionally, organisation did not pay much emphasis on the element of marketing. Their main concern was on how they would sell the products that they produced. However, the concept has undergone significant transformations over the past few decades and has gained prominence. Various experts have tried to define the term ‘marketing’. According to Phillip Kotler, marketing refers to a societal process through which consumers achieve their needs by creating and exchanging products and services that are of value.
On the other hand, Peter Drucker defines marketing as the process through which organisations try to understand consumer needs and produce products that result in delivering customer value. William J. Stanton defines marketing as the sum total of various business activities such as pricing, promotion and distribution that are aimed at satisfying consumer needs. The concept of marketing is essentially aimed at enabling organisations generate their desired level of profit.
Organisations can market their products locally or in the foreign market. The process through which organisations market their products overseas is referred to as international marketing. There are various reasons that motivate organisations to incorporate international marketing.
Some of these reasons include the need to maximise the level of profit, existence of a saturated domestic market, intense competition in the domestic market and high demand in the international market. Moreover, international marketing is also motivated by existence of product life cycle differences between the local and the foreign market.
To be effective in the international market, it is important for the parties involved to select the most appropriate market entry method. Some of the methods that an organisation can select include licensing, franchising, formation of mergers and acquisition and joint ventures.
In addition to market entry, an organisation must also incorporate the most effective international marketing mix. International marketing mix is more complex compared to domestic marketing mix. Firms entering the international market must evaluate the political, cultural and economic environments in the foreign market. To survive in international marketing, organisations are required to either standardise or adapt its domestic marketing mix to the international market.
Comparison of environmental factors between China and the US
Political and legal factors
International marketing is affected by changes within the political environment. As a result, it is paramount for multinational companies to analyse the political and legal environments in the host country. Examples of issues that should be evaluated relate to the policies adopted, the system of governance and level of political stability.
Both China and the US have experienced a relatively higher rate of political stability over the past decades. The stability in the two countries has arisen from adoption of effective system of governance. The US has adopted a democratic system of governance which has led to attainment of a high level of political stability. On the other hand, China has adopted a monarchy system of government.
Collins (2013) asserts that the political risk in China is reasonably low compared to other emerging countries. However, the degree of transparency in the country’s legal and regulatory systems is relatively low compared to the US. Corina Monaghan, a renowned political analyst opines that the low level of transparency makes it challenging for multinational companies to operate in the country.
Despite the low level of transparency, China is characterised by a predictable business environment. The countries’ level of political stability has also arisen from minimal incidences of strikes, business interruptions, political violence and riots.
China and the US have experienced significant increment in demand for oil and gas. The daily oil consumption in China amounts to 8.2 million barrels compared to that of the US which amounts to 18.69 million barrels. In an effort to satisfy the growing oil and gas demand, the Chinese government announced a plan to adopt new oil and gas exploration policies. The policies are aimed at stimulating more oil and gas exploration companies to venture the industry (US Energy Information Administration, 2013).
Similarly, the US government passed 10 bills in 2011 that were aimed at accelerating investment in oil and gas. The US government also announced plans to commence oil drilling in Alaska and offshore oil and gas exploration at the Atlantic coast (Broder, 2011). These investments are aimed at minimising the country’s overdependence on oil and gas imports (US Energy Information Administration, 2013).
Prior to joining the WTO, marketing in China was very difficult due to existence of strict government regulations. The Chinese government required firms intending to venture the market to partner with local firms in their respective industry. Such legislations limited firms’ ability to undertake international marketing in China due to loss of control. On the other hand, the US economy is liberalised which makes it easy for multinational companies to venture the market.
To improve the country’s competitiveness to foreign investors, the Chinese government has over the past three decades undertaken numerous reforms in its foreign investment policies. This is likely to promote BP’s operation in the international market. In summary, the two countries political and legal environments indicate the high market potential in the US and the Chinese oil and gas industries.
Economic factors
Firms in different sectors are affected by various economic changes such as fluctuation in the level of demand and supply. There are various factors that impact demand for a product or service such as the level of the consumers’ disposable income. Prior to entering the international market, firm’s management teams should evaluate the level of consumer disposable income. It is also important for marketers to evaluate the host country’s rate of inflation and the level of employment.
China and the US have undergone significant economic growth over the past decades. Despite the 2007/ 2008 economic recession, China managed to sustain its positive rate of economic growth. However, the US economy was adversely affected. Currently, China’s Gross Domestic Product [GDP] is estimated to be $ 5.745 trillion while that of the US is estimated to be $14.6 trillion. This shows that the two economies are relatively large (US Energy Information Administration, 2013).
Chinas economic growth has emanated from various factors such as adoption of the open-door policy in the late 1970s. Additionally, the country relaxed its policies with regard to international business which is evidenced by its entry into the World Trade Organisation. This has significantly increased the number of foreign investors in China.
China and the US have relatively low rates of unemployment which average 4.3% and 9.7% respectively (Trading Economics, 2013). The two countries have also managed to maintain low rates of inflation as illustrated by figure 1 and 2 respectively. The low rate of inflation and unemployment in the two countries has significantly enhanced the consumers’ purchasing power. Consequently, there is a high probability of BP maximising its sales revenue by adopting effective international marketing strategies. 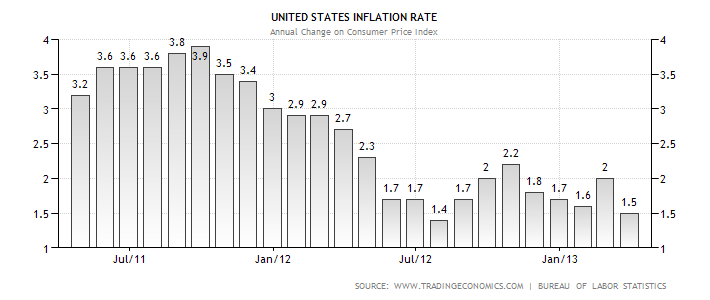
Figure 1: Web.
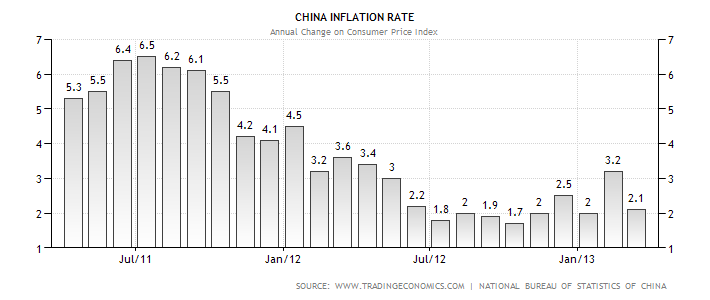
Figure 2: Web.
As a result of increment in the consumers’ disposable income, the citizens’ living standards in the two countries have improved significantly. For example, a large number of citizens in China and the US own vehicles (CNPC Economic & Technology Research Institute, 2012). It is projected that China will become the largest global economy by 2030. This presents an opportunity for BP in its international marketing efforts.
Social-cultural and environmental factors
Social trends can influence the demand of a particular product or service positively or negatively. China and the US have experienced a considerable growth in the size of their population. According to the US Energy Information Administration (2011), emerging economies such as China and India are projected to experience a robust population expansion over the next two decades.
Moreover, it is also projected that China will experience increment in energy consumption as a result of the high rate of economic growth. The demand for energy in China is projected to be higher than that of the US with a 68% by 2035 (US Energy Information Administration, 2011). Figure 3 illustrates the growth in energy consumption between China, US and India from 1990 and the projected growth in demand by 2035.
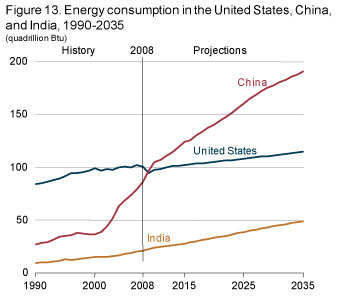
Source: (US Energy Information Administration, 2013).
Findings of a study conducted by KPMG (2012) revealed that the US is likely to experience a decline in demand for oil and gas over the next 3 years. KPMG cited the slow rate of economic recovery from the 2008 economic recession and the increase in demand for alternative sources of energy as the major factors that will lead to a decline in demand for energy in the US.
Consumers in the developed and the emerging economies such as the US and China are increasingly shifting to consumption of clean forms of energy such as electricity, biogas, bio fuel and nuclear energy. Other forms of energy that consumers are integrating include wind energy and solar energy (US Energy Information Administration, 2013). This transformation has arisen from increased knowledge and level of awareness on the importance of integrating alternative forms of energy.
For example, consumers have realised that using hydrocarbons such as petroleum based fuels as a source of energy increases the rate of global warming. This arises from the fact that petroleum based fuels increase the amount of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases increase the rate of global warming and hence the rate of climate changes.
In their consumption process, most consumers are committed towards minimising the amount of greenhouse gases they emit into the atmosphere in order to counter the high rate of climate change (Wang, n.d) Additionally, numerous environmental conscious organisations are advocating for consumption of alternative forms of energy in order to lower the rate of environmental pollution.
These social transformations are likely to affect BP’s operation in the US and Chinese markets. Consequently, the firm will be required to review its operational strategies. To survive in the long term, BP will be required to integrate the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility.
Adopting CSR will enable BP to develop a high level of customer loyalty. This arises from the fact that consumers will develop a perception that the firm is conscious of the prevailing environmental issues. This will increase the probability of BP gaining a high rate of market acceptability in the two countries.
Technological environment
The global oil and gas industry has undergone considerable growth. One of the factors that have stimulated the industry’s growth relate to the high rate of technological innovation. Firms in the industry are investing in research and development in order to design technologies that can improve their competitiveness. Development computer technology is one of the aspects that have promoted the industry’s growth.
China and the US have invested heavily in oil and gas exploration and refining. As a result, there is a high probability of BP experiencing intense competition in the process of marketing its products in the two countries. In addition to oil and gas exploration and refining, the two countries have managed to develop an elaborate pipeline network.
This has significantly increased the two governments’ competitiveness in distributing oil and gas within their boundaries. However, BP does not have an elaborate pipeline network in the two countries. Consequently, the firm is likely to experience a challenge in its marketing process.
The high rate of technological innovation in the industry has also increased the intensity of competition due to emergence of alternative forms of energy. Industry players are investing in development of renewable forms of energy such as geothermal, wind, nuclear energy and biomass amongst others.
China and the US are amongst the leading countries with regard to investment in renewable forms of energy. Consequently, the likelihood of BP experiencing intense competition in its international marketing processes in China and the US is high. To cope with the intense competition, BP should ensure that it evaluate the technological environment in order to make the necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Marketing is one of the most important concepts that firms’ management teams should consider in their strategic management processes. This arises from the fact that the effectiveness with which a firm markets its products determines its success. Changes in the domestic market make most firms to consider venturing the international market.
However, international marketing is a complex task. This arises from the fact that the firm has deal with a wide range of factors that are different from the domestic market. In the course of its operation, BP has managed to attain global strategy. The firm has achieved this by incorporating the concept of internationalisation. Some of the countries that the firm has entered include China and the US.
The essay entails a comparative study of the US and the Chinese oil and gas industry. The report entails a comprehensive evaluation of the political, legal, social, economic, environmental and technological factors that are likely to affect BP’s international marketing activities in the two countries.
To effectively market its products in the Chinese and the US markets, BP’s management team should develop a comprehensive understanding of the two countries’ business environments. Additionally, the firm should ensure that it undertakes continuous review of changes within the host country. This will enable the firm to make the necessary adjustments.
One of the ways through which the firm can achieve this is by conducting continuous market research. The research should mainly focus on macro environmental factors such as the politics, economic changes, social and technological trends, legal and environmental changes.
By developing a comprehensive understanding of the macro environment in the US and China, BP will be able to achieve its internationalisation objective. This arises from the fact that the firm will formulate and implement effective international marketing strategies. As a result, the probability of the firm succeeding will be increased.
Reference List
BP: Company information. (2013). Web.
Broder, J. (2011). Obama shifts to speed oil and gas drilling in US. Web.
Collins, S. (2013). Political stability in China comes with little transparency. Web.
CNPC Economic and Technology Research Institute: Current status of Chinas oil industry. (2012). Web.
KPMG: US oil and gas outlook. (2012). Web.
Trading Economics: United States inflation rates. (2013). Web
Trading Economics: China inflation rates. (2013). Web.
US Energy Information Administration: International energy outlook. (2013). Web.
Wang, H. (n.d). Characteristics and trends of China’s oil demand. Web.