Executive summary
After carrying out a ratio analysis for the company, it can be concluded that the company is performing poorly as compared to the competitor. The company’s profitability, liquidity, efficiency and solvency ratios are on the decline and are far beyond the competitor. The performance trend if the company is declining. However, the company’s financial stability is stable based on the current ratio but unstable using the quickest asset to generate revenue to offset current financial obligations. The firm is not as well utilizing the company’s assets well as trade receivables and inventory periods are too high as compared to the competitor.
The company ought to improve profitability through a cost reduction mechanism as well as invest in a project that reduces costs. They should also investigate the company’s expenses.
Introduction
Babushka plc limited is a company that is involved in the manufacture and distribution of Jewellery and fashion accessories since 1975. What follows is a financial statement analysis of the company. This report on financial ratio analysis is aimed at measuring the general performance of the company. And this report can be used by shareholders, potential investors, the government, customers, employees and environmentalists. The ratios would help them get an in-depth understanding of the company’s profitability, liquidity, long–term solvency, financial stability and efficiency with which it is utilizing its assets to generate sales revenue. For the management, their objective would be on how to improve on poor areas and maintain good performance. Its intended users are the management of the company, customers, employees and the government, who would use it for taxation purposes. The sources of the data used have been the published financial statements, i.e. the Profit and loss accounts and the balance sheets of the years 2007 and 2008 that has been provided for this assignment.
Users of financial statement
There are many users of financial statements, and they include creditors, suppliers, customers, investors, government and the local community. Investors are interested in the firms’ ability to generate cash flow operations, make profits, and how the company is valued, they are also interested in the way the company pays dividends and the long-term sustainability of the company. They are interested in the firms’ liquidity and ability to finance its growth from internally generated funds. Their main interest is the dividends paid, the dividend declared, liquidity position, investing activities, and the performance of the share in the market. Creditors, customers and employees are interested in ratios such as activity ratio, liquidity ratios, profitability ratio, and long-term debt and solvency of the company. Activity ratios measure the ability of the firm to generate revenue; it also measures the ability of the management to raise revenue. Liquidity ratios measure the ability of the firm to raise cash resources to meet obligations and pay salaries. Profitability ratios measure the ability of the firm to use resources to generate profit.
They also need long-term and solvency ratios to understand the capital structure of the company and be able to analyze the essential risk for their money. They are also interested in the way the firm will be able to pay them.
Ratio analysis
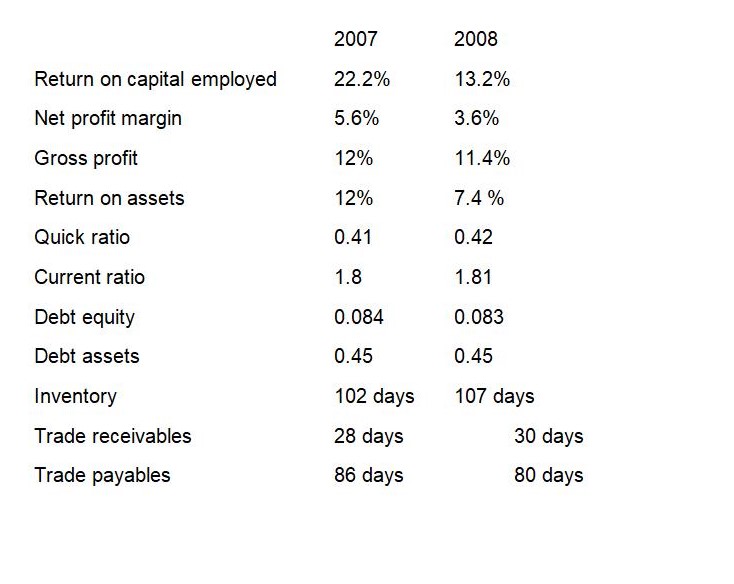
On profitability, it can be noted that the company’s profits are coming down, and it cannot be explained through the ratios as to what may be the reason. However, carrying out common-sense analysis, the main reason why profitability is coming down will be known. But from observation, it is seen that selling and distribution costs and administrative expenses grew even though revenue decreased. Going to the ratios shown above, return on capital employed decreased from 22.2 % to 13.2% in the year 2007 to 2008. This means that the return on assets decreased, and this can be attributed to an increase in expenses as well as the cost of sales. Inflation cannot be blamed here since revenue was not affected. Net profit margin has also decreased from 5.6% to 3.6% in the year 2007 to 2008. The gross profit margin decreased but at a minimal rate. It decreased from 12% to 11.4% in the year 2007 to 2008. Return on assets decreased on a greater margin from 12% to 7.4% in the year 2007 to 2008. looking at the competitors’ results for the same period, one can conclude that the company is performing below the competitor in terms of profitability. This is because the competitor had a return on capital of 8% and 7% for the years 2008 and 2007. Net profit margin the competitor has 5.7 and 6% for the years 2007 and 2008 while the gross profit margin is 25% and 26% in years 2007 and 2008. The profitability of the competitor is also on the decline but not at a higher rate as compared to this company.
On liquidity, the current ratio and quick ratio shows that the company is stable and it is performing at par with the competitor except for the quick ratio. The current ratio of the company was 1.8 in the year 2007 as well as in the year 2008, 1.81 times. While the competitor’s ratio was s1.8 and declined to 1.7 times for the years 2007 to 2008. Using the current ratio, I will state that the firm is financially stable, unlike the competitors. What it means is that for every one dollar of current liability, there are 1.8 dollars of current assets. We do not have the industrial average, but normally it is assumed that a good ratio should be 2 times. The quick asset/ acid test ratio for the company is far below that of the competitor. However, the ratio improved from 0.41 to 0.42 in the year 2007 to the year 2008. The competitor’s ratio was 0.8 times for the two years. The ratio is stable. However, the ratio is far below in the company because the firm had a huge reserve of inventory, and this can be seen from the days in sales a hooping 100 days. The company should strive to reduce the amount of stock being held in-store to avoid being stolen and obsolete. The ratio indicates the ability of the firm in meeting short term financial obligations from the most liquid assets. If the firm fails to meet these obligations, it may find itself in technical default.
As per the company’s ability to pay its long term debt, it seems its assets are sufficient using the two ratios calculated. Its total debt to assets was 0.45 for the two years. This is a good ratio for a company. However, the company should increase borrowing to reduce dependence on equity and reduce the cost of capital. The company is not heavily leveraged for every dollar of assets being financed by 0.045 cents of long term debt. Long term debt is a component of the total financing of the company, stood at 8% for the two years in comparison to equity. There is no change in terms of borrowing from debt capital to finance the operations of the company.
The efficiency of the management is in doubt as the company keeps huge amounts of inventory in-store, which should be sold off. The amount of inventory in the store was held for 102 days in the year 2007 while it was held for 107 days in the year 2008. Looking at the figures of the company from the year 2004, it can be noted that there is an upward trend in inventory period and the year 2008 marks the highest inventory period of all times. Trade receivables have also been fluctuating from the year 2004 and currently stand at 30 days which is an increase from 28 days. These are conversion days in which inventory can be converted into sales as well as sales can be converted into cash. Looking at trade payable, one realizes that the company takes a whole 86 days to pay creditors in the year 2007, while in the year 2008, it was 80 days. What it means is the company took 57 days to get cash from her operations for the year 2008. That is the inventory period plus trade receivables minus trade receivables. It shows that the company performance did not improve; it was declining. The management needs to improve their operational efficiency to reduce the number of days in which they convert their business transactions into cash.
Limitations of ratio analysis
There are a number of limitations associated with ratio analysis. Ratio analysis has the following limitations. To begin with, they depend on historical data, which is outdated and therefore relying on them to make decisions in these economic times when there is a constant change may be suicidal. Secondly, the ratios, if used for comparisons over time, a wrong solution or decision may be made because they don’t consider the time value for money.
Ratio analysis, although used commonly to access and compare financial statement and performance of the company, they may give a wrong answer if the ratios used are not collected in a systematic and uniform manner. The ratios must be of the same period in companies of the same industry as well as companies using similar accounting policies. The accounting measurements used must be understood; otherwise, the users of financial statements may end up making wrong decisions.
Recommendation
I commend that the company’s performance is not sound as compared to the competitor. If an investor is willing to invest in the industry, he should invest in Benny’s Bling plc for those shareholders who have the shares; they should hold them and monitor the trend of profitability. They should participate in the appointment of the directors. The current shareholders should change the top management of the company as well as overhaul the whole directorship.
Based on the debt ratio, and if the restaurant is to finance the investment by the company should be through external borrowings (debt), and then it would be advisable to do so. This is because the company’s debt management is efficient, as shown by the declining trends of debt. However, the management of the company is not efficiently utilizing the current equity, as shown by the return to equity over time. If additional borrowings would, however, adversely affect the company’s balance sheet position, they should not come up with an investment plan. Additional borrowings can increase the gearing hence subjecting it to financial risk.
Conclusion
In order to achieve better future results, better or close to industrial average, the firm needs to cut down its operating expenses. This would considerably improve the profitability ratios. They also have to review their policy on capital management and keep optimal levels of various items of current assets. This would improve the firm’s liquidity position. In order to improve the return on owner’s equity ratio, the management should invest in viable projects that would yield positive NPV’s. This has the effect of maximizing their wealth. To improve on the financial ratios, the firm would ensure that it has more liquid assets and also resort to internal sources of finance as opposed to external ones.
Appndix
Ratio analysis
References
- Davis, H.Z,. and Y.C Peles (1993); Measuring equilibrating forces of financial ratios , the accounting review.
- Givens C. (2002); More Wealth without Risk, Mc GrawHill, 2002 USA
- Largay, James A III and Clyde P. Stickney,(1980); cash flows, ratio analysis and the W.T Grant Bankruptcy, financial analysis journal.
- Sanzo R. (2005); Ratio Analysis for small Business, Yale University Publishers, USA.
- Vandyke C. (2006); Financial ratio analysis, Wiley books, USA