Abstract
Investment decisions are the most common decisions that are normally made by organizations. Getting funds approved is the second most important activity for a company wishing to raise credit facilities to assist them make investment. Investments may be international expansion or acquisition of assets for diversification purposes which will assist the company in growth. This involves setting of strategies and always choosing or setting a strategy of investment that is acceptable to the loan provider. Investments are made under conditions of uncertainty where the future is not known and is uncertain but companies follow those uncertain routes. This calls for proper decision making in the provision of credit facilities.
In this dissertation, is it going to carry out a study on risk associated with the customer’s information provided, the cost of capital adopted, the country of investment and the purpose for the money? These factors are involved in assisting the banks determine the amount of loan they will provide to the client. This research will provide first hand information to both individuals and companies who are seeking credit facilities from credit institutions.
The study was set in a commonwealth bank of Australia and bank of America ; An American bank one a multinational bank while the earlier is an Australian bank that has successfully entered the international market with her presence felt in Australia. Both offer business loans for expansion in various countries. In my study have to identify and strategies implemented by each bank, their risk analysis process and how the risk is calculated before a loan is given and the effect of the strategy to its market competitiveness.
Every Bank executive and managers wants to move forward should take this study serious. The main purpose of businesses is the maximization of goals. In order for banks to achieve these goals in this era of corporate sustainability, fraudsters and corrupt loan there is need to move towards best methods of assessing the credit facility and come up with criteria to use issue of loans. Banks need to develop strategies that will lead them to grater heights in the world stage market.
Therefore, to accommodate the rapid changes occurring in the business and banking world, quick decisions about loan approving strategies are made and well communicated.. This study is paramount to the banks understudy because the research will assist in decision-making.
Introduction
The speedy processing of credit facilities in banks are very vital especially when banks need to keep customers satisfied to bank with them and increase market share but reduce risk of losing funds. In the recent past banks have embarked on quick credit facility processing so as to get and maintain more customers into their banks. This is because they want to win market share (to have a large market share). The key to improving on profits is to get more clients, win the market share, keep the existing customers by making them to be loyal and then benefits will definitely increase by day. However, customer’s loyalty and large market shares do not bring in profits to the banks always and this need to be checked thoroughly.
For example, we have prestigious customers who are on their segments. Banks have divided customers into segments, which have customers who have similar needs and are worth broadly in the same economic value. Under these propositions, we have the prestige proposition. Non prestige customers have large amounts of money invested in banks but they do not always bring in profits because they have large costs which are associated with them because they need personalized banking, they also need special attention and on the other hand they might demand special services which are additional costs to the bank. So for the past years, companies have decided to embark on quick loan credit facility processing because they have realized that this service and value are intrinsically linked and the way you handle a customer means a lot and this is how the bank will get more and more clients.
Banks have tried to differentiate themselves for competitors through providing better customer service. Consistent delivery of superior loan service requires the careful design and execution of a whole system of activities that include people, technology and good processes. This will lead to more revenue from customers who will be impressed with services provided. To do this, banks embarked on creating loans and financial strength of their customers can be sought through monthly statements. After this, they enhanced the customer’s profitability before advancing any credit facilities. This is the analysis of the value bought in by the customer against the cost of loans facility issued to the customer owns.
So each customers cost and revenue is known to measure whether the customer is a loyal customer who has no profits to the bank or whether he is a long-term profitable customer who needs nurturing so that the bank can give the customer the nurturing he deserves that issue quick loan facility. They should also need to know about short-term customers who need to be exploited before they pull out. This will all lead to the quick credit facility issuance that will keep the customer in the business.
Background of study
Banks have also embarked on segmentation of their customers into different value propositions according to the profitability of customers, which influences credit facilities. This is when the 80-20% profit generation against customers arises from. Banks customer segments have people with similar needs and worth broadly in the same economic value, earn almost similar income etc. They are given a combination of services, products, prices and branding which fit them. This is called managing customers according to segments. Banks also compute the lifetime value or profitability of customers through forecasting and use of strategies like introducing new products that will fit the customers in future. Banks can also modify existing products to fit customers in a particular way hence making them satisfied and this will lead to increased revenue.
Banks should also try to come up with strategies that are directly related to how they know the credit worthiness to increase the rate at which credit is processed so as to solve their needs. Customer understanding is vital because a good strategy is that which is related to the improvement of bank products, whether asset products like loans or liability products where bank entrust their money to the customer. This means banks should come up with strategies aimed at particular target customers to understand their investment strategies. This type of strategy is persuasive in that it explains to customers why they should take credit facilities. it also shows that the credit facilitates depends on other factors not only the investment strategy
Banks can also pick on the behavior based segmentation strategy and this involves looking at past and present relationship of the customer and the bank before giving loans or any other credit facilitates. Banks should look at how long a client has been in the bank.
Has the client been on and off-has he ever left the bank for another bank and back? They should also look at the value of customers in terms of how much money the customer has in the bank or how much he has borrowed or he is willing to borrow. Segmentation of clients is important in banks because customers are given a bundle of benefits that have been used. Geographic- should be also be used and is where the banks take into account the geographical boundaries and this majorly assists the bank in staffing and opening of new branches and also to assess market potential. They have also been using psychographic segmentation that deals with customer lifestyle, tastes and preferences, why customer want a particular product instead of the other.
The demographic segmentation deals with dividing customers according to age, stage in life cycle etc. and it helps banks to design production for all types of people depending on their age, income, etc. this also is another factor that is considered in according credit facilitates.
Apart from the behavior based segments, the bank can also adopt segmentation, depending on what the bank wants and not what customers want, banks have different value propositions that it wishes to give customers hence it will segment its products according to its value propositions and as customers take them they automatically fall to segments. The banks have three major objectives and these are get deposits and minimize the cost of funds producing quality credit balances at maximum spread income and to generate free income and reduce services expenses. This leads to the following four segments. There are those people who want to invest others want to borrow, others want convenience and on others are fast limited customers. These segments can be used as a basis for the bank to develop long-term strategies, to attract customers to the different segments.
As much as strategies are good, bank should avoid using one strategy for all products or marketing applications effective segments or marketing applications effective segments. A strategy will vary according to what are the marketing objectives. In the case of attracting new customers who have no history with the bank. The bank will come up with a wedge product strategy where they give customers of other banks a chance to sample some of its products or services for the time being and this will enable them to cross-sell more profitable products to them and create a long lasting relationship with them. This is done by direct marketing for example they can send letters to customers requesting them to try products or phone calls.
In making existing customers to be more profitable, the bank should study their behavior carefully and give them the most appropriate product or service that can turn a marginally customers, their lifestyle and the amounts of cash they handle and the needs comes from good data management. When the bank can use the data it has to identify best ways in available banks, database can enable them to know which customers are profitable, marginally profitable and unprofitable.
Apart from keeping existing customers, banks also need get more and more customers by prospecting well and turning these prospects to potential customers. The methods we have seen that are employed here is the direct mail methods and telephone calls. Geographical prospects can also be employed by use of strategic positioning of new branches at areas where trade is high and directing advertisements to such areas to lure more customers into the banks customer base, whichever the method, banks have realized that CRM is very important because it concerns more on customer satisfaction rather than products.
Most banks then have realized that in order to understand customers well and this information is in the banks database. There should be therefore good management of data that gives information about the customers and whether they are profitable or not. For good data management, banks should ensure that:
- They have relevant and accurate data(information) about the customers,
- Develop daily, weekly, yearly etc analysis of customers’ profitability and
- Develop tactics on these segments that modify behaviors of both customers and employees to increase sales and revenue while lowering costs.
Banks should ensure good data management by careful collection of customer data, turning this data into knowledge and then using this knowledge to develop strategies and tactics to modify behavior of both employees and customers and prospects to improve long-term profits.
Banks should realize that just aiming at having a large market share is not enough to generate profits. They should also ensure that they do good customer relations management in order to achieve good results. This is by understanding their customer needs well and then the bank will match the customers with available products to ensure maximum customer satisfaction. They should also manage customers well by segmenting them into useful segments based on profitability so as to give them beneficial value prepositions that will make them have good long-term relationship with the bank and hence increase the profitability.
Using the information kept will determine the approve of the loan facilities although there are other factors which are related with the strategies of the loan seeker but they are less influential as compared to banks own information
Statement of the Problem
Making a decision, how to give loans to customers and how it should be done with the support of the management is difficult and had to believe. The conventional analysis of customers investment strategy has looked simply at efficiency of customer awarding of a loan as compared to the efficiency of banks to detect the losses that will be incurred using risk analysis : if the cost of risk analysis is greater than the cost of administering within the bank, then banks needs to change the method of assessing the customer credit worthiness.
Transaction cost analysis does not, however, provide the complete answer. In the first place, customer credit facilities strategies are not simply accept or reject choices—there are wide varieties of ways in which a bank can structure credit facilities to attract customers to product. Secondly, the most critical long-run consideration is the development of banks capability to award credit quickly. If a bank is to sustain competitive advantage, it must restrict itself to those activities where it possesses the capabilities that are superior to those of the other banks that perform those activities. The most difficult issues arise where there are linkages between customers’ investment strategy and banks risk analysis strategies.
Ultimately, investment decisions revolve around two key questions. First, which activities will we undertake for profitability and attract sponsorship? Second, how do convince the bank to attract their credit facilities and increase our profitability?
Purpose of the Study
The objectives of this study is
- To identify the strategies implemented by banks to attract credit facilities and how they are developed.
- How customer investment strategy and banks risks assessment affects the rate of loan issuance.
- Assess the relative merits of the strategies and loan transactions in organizing customer loan processing and related activities and understand the circumstances that influence their comparative advantages.
- Identify a range of possible factors that influence among banks and related firms loan processing.
- Identify scenarios of various strategies affecting loan issuance.
- Explain why some types of strategies and related activities are integrated within a single bank, whereas others are performed by separate banks.
- Identify the critical considerations pertinent to make-or-buy decisions and the extent to which a bank should adopt.
To achieve the objectives I will go through case studies of two banks whereby the concept of customer relationship and product development strategies are in use.
The scope of the study
To understand investment strategies and strategies that relate loan issuing of to their customers, services and diversification for banks, a comprehensive analysis is carried out to ascertain the various needs of customers in the banking sector in relation loans approval. This research project is on two banks. In carrying out this project, certain constraints will inhibit effective study, firstly due to short deadline period to finish this write, time factor will render certain aspects not to be examined in details. Secondly, the study assumes that effective and efficient management and application of loan approval strategies are the determinant of performance and greater market position of banks.
This due to the fact that if customers don not have money the banks will be doing badly.On the other hand, in economic reality, there are features that affect performance and market position of banks and companies such as Capital deployment, employee’s motivation, organizational structure, organization capacity, supply chain management and technology. However, this study does not consider these factors. This study also assumes that all strategies applied by two banks are geared towards increasing speed of loans approval in terms of increasing the market share. It also assumes that they are ready to implement are customer friendly strategies that increase the market share. Nevertheless, this is not the case in the real strategic management situation in as these strategies are often separated and could be use for survival.
Significance/Importance of the Study
My research study will be of great value to future researchers, management of banks, investors, educators and others because:
- To highlight the important role that investment strategies play on the bank’s market share and customers satisfaction.
- It highlights how customer investment strategies are made and how they strategies affect the bank market share.
- It helps the management in making strategic decision-making.
- Determine the risk preference function for the centre of the bank
- Determine which risk measure(s) are compatible with this risk preference function
- Assess the relevance of coherency for the internal risk measure(s)
- Assess the impact of the structure of the compensation payment function on portfolio selection and incentive-compatibility
- Identify how agency problems impact on the performance measurement framework
- Design a solution to deal with agency problems
- Evaluate how bank-wide factors impact on the decisions of managers and the assessment of their performance.
Research Questions
The key questions for the research were set as follows:
- how does the target credit rating of the bank influence portfolio selection and pricing?
- When might a higher solvency standard beneficial to a banking firm?
- should hurdle rates adjust in line with changes in the target credit rating of a bank?
- Which credit rating implemented by the two banks and they how have they developed them?
- What are the advantages of each form of form strategies?
- What are possible relationships among vertically related banks and, including spot market transactions and strategic alliances?
- What is the relationship between the investment strategies?
- What loans approval strategy is favorable to bank board members?
- What is in house policy and what is it used for?
- Are the policies of the two banks different from those of competitors?
Assumptions regarding the hurdle rate, and in particular, whether it should adjust to reflect changes in leverage, are critical to determining the optimal credit rating for a bank. This in turn impacts on pricing decisions and the market value of credit portfolios, and consequently, the risk-adjusted performance measures of portfolios under the control of managers. A loan pricing model was constructed to test the impact of changes in the target credit rating of a bank on the pricing of its loans.
The decision of a bank to increase its solvency standard increases the minimum interest rate on its loans in order to achieve the required hurdle rate on capital assigned to the loans. Offsetting this upward pressure is the impact of the reduced funding costs arising from the higher credit rating. If retail deposit rates are insensitive to an upgrade in the credit rating of bank debt securities, we find that the benefits to a bank from increasing its target credit rating rest with the extent to which the cost of wholesale funds falls relative to the increase in the price of bank loans.
Research Hypothesis
The following hypothesis will guide the research:
- H1. On average, behavior segmentation in loan approval will be similar all the banks and the sample will be a true representative.
- H2. The investment strategy of the loan seekers will be positive or negative depending on the motive and the customer management embraced.
- H3. On average, risk of the investment of the bank customers will be more powerful predictors of customer relationship management.
- H4. All banks makes choices of the credit facility management without the banking sector regulator interfering.
- H5. Bank customers of banks are aware of the loan application rules and willing to served by them.
- H6. Risk assessment depends on the policies of the banks.
- H7 The ideas underlying the problem-solving task to be solved is understood by key players in the industry.
Loan approval is very powerful in shaping the banks profitability and the investor’s success. The result obtained can not be ignored it should be used to make some few changes in the banking sector and investors strategies. Banks are an important sector in the circular flow of money in any economy and thus the beginning of economic development of a country. Therefore it is an important sector that should be managed with care.
Limitation of the Study
This research project is on a session of the project. In carrying out this project, certain constraints will inhibit effective study:
- Time factor will render certain aspects not to be investigated in details because of the deadline period to finish this thesis,
- The study assumes that effective and efficient management and application of investment strategies are the sole determinant of loan approval. However, in economic reality, there are features that affect loan approval such as Capital deployment, employee’s motivation, organizational structure, organization capacity, supply chain management and technology.
- My study also assumes that the all loan approval strategies will be applied by banks and they are geared towards increasing market share banks.
Delimitation of the Study
The researcher is a student, he will be carrying out the research with the trust that managements will co-operate.
The research will be carried out by a full time student thus having enough time for coverage of the topic.
The researcher will access the banks with easy because of he is an insider that is he works in the baking sector.
Definition of Terms
The terms that are in use in this thesis are defined in the context in which they are being used in this research and they are as follows:
- Strategy: Strategy is the direction and scope of an organization over the long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through the configuration of resources and competencies with the aim of fulfilling stakeholders’ expectations.
- Market share: This refers to the total sales of a bank divided by the total sales of other firms for a specified product –market. It may be calculated on the basis of actual sales or forecast sales.
- Intended strategy: This is an expression of desired strategic direction deliberately formulated or planned by managers.
Overview Summary
This section gives a general outline of the main parts of this Thesis. It will have an abstract and five chapters written and each chapter will contain the following.
Abstract
The final report will begin with an abstract that will summarize the topic, the findings and the importance.
Executive Summaries
This will summarize all the chapters and the conclusion reached.
Chapter I
The chapter will have introduction, which will explain issues surrounding the topic and the importance of the study. Then there will be background information that will cover topic and the banks under study , it will also provide with an overview of the study, purpose of the study, research question, research hypothesis, limitation and delimitation, Significant of the study and definition of the terms used.
Chapters 2
This chapter covers literature relating to the topic under study and in my case this will cover an introduction, literature review, Collection of theories and secondary sources and Criticism of secondary sources
Chapter Three
In this chapter the researcher will explain the methodology used that is the Research Approach, the Research Design and discussion of its quality, validity and reliability, , The Target company, Procedure, Instruments for data and continuous prose collection and data analysis technique.
Chapter 4
This chapter contains empirical data presentation, which is made up of the strategies implemented by banks and their market situation.
Chapter 5
This will be the last chapter. It will contain summary of the findings recommendations and conclusion.
Literature Review
Introduction
This is a literature review of investment strategy, risks associated with investments and standards set out for loan issuance. The literature consolidates information from various literatures written by various groups, scholars and central bank. The thesis will differentiate between the capital budgeting decisions of companies, cost of capital, risks associated with loans and other related issues. Analysis on credit facilities will be carried out and this will be in form of scholarly written documents,.
Collection of theories and secondary sources
The researcher will use books available in the University for the Collection of literature. The computer laboratory in the university and personal computer in the house has contributed greatly in the success of my project through the access of scholarly written documents available in the internet. Therefore, the process of gathering data from articles, journals and books is done primarily by the use of university material. The research on internet was done through funnel manner by using key worse such as cost of capital, credit worthiness and issuance of loans. The World Bank and reserve bank facilities that have been used will also be acknowledged.
In addition, the government and other state documents have been used intensively as supplementary sources during the search of information for this project.
Factors influencing capital decision
In any manufacturing organization, the largest dollar investment maintained is in fixed assets. Fixed assets are necessary for production and without them their will be no production. Each firm maintains fixed assets depending on their nature of production processes. Because of change in techno lodge and competition, organization make capital expenditure specifically to acquire, replace, or modernize fixed assets or gain a less tangible benefit over along period of time.
Capital Budgeting
This is the overall process of generating, evaluating, selecting and following up on capital expenditure alternatives. In most cases, firms are affected by the amounts available for this process and the type of the proposal they are undertaking into consideration. Because of this constraint, firms opt to undertake those projects which maximize their benefits in the long run. They can also rank the proposals according to the predetermined criterion and choose the best depending on their returns to the company. Further a company can limit its funds such that only those proposals that yield high return in the long run will be accepted whereas it can accept all the projects considered if its funds are unlimited.
Availability of funds
This affects capital budgeting because if a firm has to incur any capital expenditure it must have some funds to use. Therefore it affects the decision process making environment of the management as to how much to spend. Some firms have unlimited funds for investment hence making the process even cheaper but others have limited funds meaning that the amounts for capital expenditure is fixed normally specified in the company annual budget. Where there are unlimited funds the company accepts all projects that yield gains higher than the predetermined level. If it is limited, the organization ranks the proposals and chooses the best. Firms use cash flows to measure their ability to acquire the proposed assets or pay bills
Type of the Project
The firm has to establish the best project from a number of different proposals available. This is difficult because any project undertaken must be capable of bringing high returns to the organization in the long run. Some projects are independent such that acceptance of one project does not eliminate the consideration of the others. Whereas others are mutually exclusive meaning that in allocating funds to these projects, the firm has to rank them according to the long term gains.
The cost of the new projects
This is the outlay of the intended fixed asset and normally the purchase price is definite. The firm must consider its available funds for purchasing this new asset. This is done by measuring its net cash flows which is called net investment. If the company is not replacing an existing asset and does not incur any installation cost, then the purchase price is equal to the net investment.
Installation costs
These are extra costs incurred to make the machine into operation and all this must be recognized by the firm and capitalized. This is because they are part of the initial cost and they should be capitalized.this will enhance accuracy of determining depreciation.
Loans
A loan is an arrangement whereby the lender, which may be a commercial bank or commercial finance company, receives control of the pledged collateral. This arrangement provides the lender with the ultimate degree of security.
Lending procedures
In the case of a loan, the lender selects the collateral that is acceptable as collateral for the loan. Once the collateral has been selected, the lender takes or hires to physically take possession of the collateral.
Terminal warehouses (inventory loan)
A terminal warehouse is one located in the geographical vicinity of the borrower. It is a central warehouse that is used to store the merchandise of various customers. A terminal warehouse is normally used by the lender when the inventory used as security is easily transported and can be delivered to the warehouse relatively inexpensively. When the goods arrive at the warehouse designated by the lender the warehousemen checks the merchandise in. he lists each item received on a warehouse receipt, noting the quantity, serial or lot numbers, and the estimated value. Once the warehouseman has checked in all the merchandise, he forwards the warehouse receipt to the lender, who then files a lien on all the items listed on the receipt.
Field warehouses
Under a field warehouse arrangement, the lender hires a field warehousing company to actually set up a warehouse on the borrower’s premises or lease part of the borrower’s warehouse. There are a number of companies in the united states that specialize in establishing field warehouses for a fee. The procedures followed by the field warehousemen are quite similar to those followed by the terminal warehousemen. Once they have isolated the inventory to be used as collateral, they check it in, listing the items and their characteristics on the warehouse receipt, files a lien on the pledged collateral. A field warehouse may take the form of a fence around a stock of raw materials located outdoors, it may consist of a rope-off section of the lender’s warehouse, or it may actually be a warehouse constructed by the warehousing company on the lender’s premises, which have been leased by the warehousing company.
Regardless of whether a terminal or field warehouse is established, the ware housing company places a guard over the inventory. Public warehouses always have a guard; under a field warehousing arrangement, a guard is stationed by the warehoused collateral. The guard or warehouseman is not permitted to release the collateral without authorization from the lender. In other words, the lender has complete control over the inventory used to collateralize the loan. Only upon written approval of the lender can any portion of the secured inventory be released.
The loan agreement
The actual lending agreement will specifically state the requirements for the release of inventory. As in the case of other secured loans, the lender accepts only collateral believed to be readily marketable and advances only a portion of the collateral’s book value. The types of collateral normally found most acceptable for warehouse receipt loans are canned foods, lumber, refined products, and basic metal stocks. The loan agreement typically provides for the release of certain pledged items upon receipt of partial repayments of the loan. The lien on the released merchandise is, of course, removed.
Although most warehouse receipts are nonnegotiable, some are negotiable, which means that they may be transferred by the lender to other parties. If the lender wants to remove a warehouse receipt loan from his books, he can sell a negotiable warehouse receipt to another party, who then replaces the original lender in the agreement. In some instances the ability to transfer a warehouse receipt to another party may be desirable.
The cost of warehouse receipt loans
The specific costs of warehouse receipt loans are generally higher than those of nay other secured lending arrangements due to the need to hire and pay a third party (the warehousing company) to guard and attend to the collateral. The basic interest charged on warehouse receipt loans is higher than that charged on unsecured loans. It generally ranges from 3 to 5 percent above the prime rate. In addition to the interest charge, the borrower must absorb the costs of warehousing by paying the warehouse fee, which is generally between 1 and 3 percent of the amount of the loan. These charges vary depending upon the size of the loan and other factors. In some instances the firm’s marginal warehousing costs are small since they have to warehouse the inventory anyway. The borrower is normally required to pay the insurance costs on warehoused merchandise.
Whenever warehouse receipt loans are arranged, it is important for the lender to select a reputable warehousing company. The warehousing company as his agent is responsible for seeing that the collateral pledged is actually in the warehouse. There have been instances in the past where receipts against nonexistent collateral. If this happens, and the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender is in the same position as an unsecured creditor.
The main features and complexities of capital budgeting
Capital budgeting involves the decision making for long-term projects or investments for company. It involves the for following decision making model:
- identification of objectives;
- search for investment opportunities;
- identify states of nature;
- list possible outcomes;
- Measure payoffs;
- select investment projects;
- obtain authorization and implement projects;
- review capital investment decisions.
The effects of inflation on future cash flows and the required rate of return
Always the discount rate of return has required rate of return on a risk less investment plus the risk premium that is associated with the project risk. Inflation affects both the risk free rate and the risk premium. In order for one to incorporate inflation in the future, cash flows, the interest rate has to be adjusted for inflation. Fisher proposed the following formula for adjusting the required rate of return.
(1+nominal rate of return)= (1 + real rate of interest) x (1 +expected rate of inflation)
Using the above rate of return as an example and the inflation rate of is 8%. then applying the fisher equation it would be
(1+0.0925)(1+0.08)= 1.1799
The nominal rate of return then it would be 17.99%. This means the shareholders who were earning at 9.25 for every 100 before inflation for the time value of money will now earn 17.99 for every 100. if the return is less than that then they will be loosing.
Inflation also affects the future cash flows. Take for instance; assume that you expect a cash flow of 1000 in one year’s time the rate of inflation remains at 8% as used above. The expected cash flow will be 1080 instead of the expected. However, the investors will not better off than when receiving 1000 without inflation
Capital budgeting under uncertainty of cash flows
Uncertainty exists where there are several possible outcomes, but there is little previous information or statistical evidence to enable the possible outcomes to be predicted. There many methods of handling uncertainty this includes (1) probabilities; this is the likelihood that an event is will occur for example using the above data given and assuming that the probabilities of having 440,000 per year is 70% and probability of having 500,000 is 30%.
Then the cash flows will be as follows

The cash flows that will be subjected to measure NPV analysis will be 452,000.
From the probabilities that some cash is likely to be earned then standard deviations is used to measure dispersion of the probabilities.
Investment risk
Assessing the risk attitude of bank owners is more contentious. When limited liability and the regulatory safety net are taken into consideration, bank shareholders may be risk-seeking and have a convex risk preference function. If a bank carries significant franchise value, however, owners may prefer that the bank acts in a risk-averse manner in order to preserve the associated benefits. In this case the objective function for the bank would be concave. This also assumes that the owners are concerned with total bank risk, and not just systemic risk.245 On the assumption that the value of the franchise to bank owners exceeds the value of the option associated with limited liability, we make the assumption that bank owners will also be risk-averse.
Consequently it was concluded that the bank risk preference function should possess the characteristics of non-satiety, risk-aversion and a preference for positive skewness in the distribution of returns. Stochastic dominance is used as the methodology to rank portfolios in accordance with the risk preferences of the centre. The key to using stochastic dominance criteria is that the methodology allows portfolios to be ranked without having to specify the exact form of the investor utility function – different orders of stochastic dominance correspond to different classes of utility function. Third-order stochastic dominance (TSD) criteria embody non-satiety, risk aversion and a preference for positive skewness in the distribution of returns. This makes it the most applicable criteria for risk-ordering portfolios given our conclusions regarding the characteristics of the risk preference function of the centre.
It was found that the lower partial moment of order n = 2 (LPM2) provides a measure of risk that is consistent with the risk preference function of the centre. More specifically, portfolios that dominate by TSD criteria are decreasing in risk according to the LPM2 risk measure. The quadratic power function in this measure means large deviations from the loss threshold receive a greater penalty than smaller deviations in the risk measure – consistent with a risk-averse attitude to losses and a preference for positive skewness in the distribution of returns.
Methodology
Introduction
The intention of research is to identify factors that influence issuance of loans to individuals and how individuals get past against them. The research looks at strategies that are implemented by banks. The research is based on two companies, the bank of America and the common wealth bank of Australia.
Research Methodology
The main objective of this dissertation is to identify how the chosen research methodology will match the main objective of the dissertation question and how it will be achieved. Essentially, there are two types of research methodology; they are qualitative and quantitative research. While the quantitative research is carried out through obtaining primary data such as questionnaire, qualitative research is a research that is conducted through interviews and observations. Therefore, the method enables a researcher to explore the details of individual perceptions over phenomena.
Research Approach
The research approach that develops the methodology explained below is based on descriptive research theory and inductive reasoning. This is important to develop the foundation by which the research will be designed, conducted and consequently analyzed.
Firstly, it is important to establish the research approach in order to create a significant qualitative methodology. The research approach undertakes a specific design that is “the overall strategy chosen to obtain the information required answering the research question” (Ghauri and Gronhaug p 47, 2002). The research approach will review the types of research design and data collection methods. The research approach is built on logical relations and not just beliefs.
Descriptive research is used when the research question is understood (Ghauri and Gronhaug 2002). In the research approach, the data measurements are dependent on the obtainment of required information and the quality of the information. The outcome of the research, therefore, is dependent on the measurement procedures used in the collection of the data, and this in turn is dependent on the types of data collection (Ghauri and Gronhaug p 47 2002).
This is an important concept of qualitative research, where the description is either inductive or deductive. Inductive research begins with a question and seeks to describe it, and deductive research begins with the problem by working backwards to the answers. Therefore, this research uses the inductive approach to build the theory from the data gathered to explore possible conclusions towards credit facilities factors.
Collection of Theories and Secondary Sources
The researcher has collected information from various literature reviews, which are available at internet scholarly books, journals and newspapers. Theses materials used are not sufficient to add something new to the subject, which has been extensively researched.
Research Method
There are many approaches to this research being a case study. Case studies are always investigated using two-research method, Qualitative and Quantitative. Quantitative approach involves the collection of figures and facts in a form of tables and graphs. Qualitative involves measuring people’s attitude, behaviors and opinions. One can note that a person’s perceptions opinions and attitudes cannot be measured using quantitative technique. I.e. you cannot assign a figure to somebody’s attitude of something. Researchers have written that qualitative method of collecting data or information is through observation, interviews and analysis in a narrative manner. In this case, quantitative analysis will not benefit us much as compared to qualitative analysis.
The researcher is going to use qualitative method of research in analyzing the strategies or factors adopted by group common wealth bank of Australia and bank of America. We shall also look using the same method affect the issuance of loans. Therefore, in my final report, I am producing an analysis for the two.
Data Collection
Data collection was carried out through internet search engines and interviews. The researcher is a student with authority in the university to target the two banks to get insight of credit facilities given out by banks, although the interview will be very difficult. Other considerations have been made for this quantitative method but the result is to interpret the information as it was seen visible through interviews. I shall use questioners I carrying out this important research.
For, me to carry out the test interviews possible and bring an employee of one of the company; I have selected the best option possible for my colleagues. I have also use conventional interviews, which are interview through internet for common wealth bank of Australia and Australian bank. Although I gathered information sufficient for me to make decisions, I realized that face-to-face interview is more appropriate as compared to telephone and internet. This is because face-to-face interviews are easier since the questions can be rephrased if the respondent does not understand the question. However, in the internet and telephone the respondent can choose to ignore the questions.
Quality Criteria
I shall explore whether there is a quality criteria for the qualitative method used. This will be possible if we give in depth analysis to give the findings a degree of truth and validate them.
Validity
The validity of this investigation is achieved if it measures what was intended for. The valuables should be able to measure what the research intended to do. Validity can be characterized by internal and external validities. In this case, we are not going to use laboratory measures.
Quality criteria
The purpose of this section is to establish the stance used in the qualitative approach to this Study. In doing so, the reader will better comprehend the degree of truth that this dissertation has In addition, validate the findings.
Validity
The validity of a study is achieved if it measures what it was intended for, that is variables measure what the research was intended to measure with little or no error. This is characterized by internal and external validity, which varies between types of research; field experiments (research done in natural environment) and lab experiment (done in contrived or artificial environment). In lab experiments, the researcher controls the setting, in which the research is been conducted, may influence the variables, while observing the changes or no changes in variables. Due to the ability to control and eliminate certain variables or conditions that may have a profound effect on the outcomes of the research, would likely improve the validity of the research. On the other hand, in field experiments, the researcher retains control over the independent variables but conducts the research in a natural setting, without control over environmental influences.
Internal validity describes or accounts for all factors, including those that are not directly specified in the theory being tested, but might affect the outcome of the study. That is, it usually concerns the soundness of the research being carried out. External validity on the other hand refers to the generalization of the research, which is the ability of the conclusions
To be validly extended from the specific environment in which the research study is conducted to similar real world situations.
The research for this thesis could be considered as a field research (survey) as it is carried out in a particular company in the real world. The literature on this survey was got from an interview on human beings of the company thus; we cannot influence their responses in any significant way. To ensure for both internal and external validity, we believe to have used the most accurate and up-to-date literature, the right and relevant questions asked during the interview (face-to-face interview), the most feasible data collection method utilized and the tools used to analyze the data are also considered to be the most appropriate in this situation. Therefore, this thesis is considered accurate and hence produces valid results. Thus, we assume that the overall validity of the results is considered high. However, we would argue that the internal validity of this thesis is relatively high but the same cannot e said for its external validity. The reason for this position is discussed under the degree of generalization.
Reliability
The aim of any researcher we believe is to use a given procedure and reach a conclusion that will be applicable in any given environment. The primary objective should be that if a later investigation followed exactly the same procedure as described by an earlier investigator and conducted the same study all over again; this later investigator should be able to arrive at the same findings and conclusions.
Thus, the study could be considered highly reliable. However, due to the very nature of human beings, a 100% reliability (especially regarding External validity) cannot be guaranteed for this thesis, as errors might occur in the course of writing down answers during the interview or in coding answers due to human nature. In this study, the errors were minimized as one interviewer poses the questions and the other concentrates in writing down responses. Immediately after each interview, the two interviewers sat together to discuss and document the final responses. With all these measures put in place to minimize error, we believe that the results of this study could be regard as reliable.
Degree of generalization
Generalization is the applicability of results of a research study to other settings. Probability sample is only what justifies that inference can be made about the population but this is not a guarantee as the results from the sample cant be generalized because of the risk of random and
Systematic errors in the sample. In case studies, it is not important to make generalization of the study but to explain what is the situation of that company in that particular situation and there is no problem if the results cannot be generalized. This is so because no two companies can be the same, thereby case studies in general do not return appropriate information for generalization but in optimal case, can produce a rough guideline/understanding of how theories are practically applicable. Thus, our findings from the study can be considered as Guidelines for companies implementing certain strategies to gain growth in their market
Choice of Case Study
The research problem is that the investment strategies adopted by bank of America influence decisions to receive credit facilities as compared to strategies required by common wealth bank of Australia. I shall have to explore the complex and different perspectives on how investment strategies are developed and implemented by common wealth bank of Australia. Therefore, I have used scientific study methods to understand how these strategies have been implemented and how to assist the bank. It is because of this perspective that I decided to choose bank of America and common wealth bank of Australia with different approaches to expansion from different parts of the world i.e. developed and developing.
Background of bank of America
Bank of America is the largest bank in the world which resulted from the merger of two major banks in the US. They have expanded into various economies of the world and have created themselves a name in the banking sector with few issues remaining unsolved. Being one of the largest banks in the world, it was incorporated in the United States of America for the purpose of providing banking services to the American society. The company has expanded to almost all countries of the world through strategic alliances, takeovers, and mergers as methods of diversification.
Bank is a public traded company and for years, this company has moved to many countries geographically and they have had products and services improved to the level of online banking for the world. The owners and their families run the management of the bank and its activities influence decisions of many economies of the world. They provide highly valuable services to the world. At the present the company issues credit facilities after assessing the riskiness of the client’s information. This has strengthened their market share through providing loan facilities to companies or individuals who have stable financial records..
Background of Commonwealth bank of Australia
The common wealth bank of Australia was incorporated in Australia as moved to various parts of the world and they represent interests of Australia to many places. The bank has a good credit facility policy which ought to be emulated by many banking institutions while issuing credit facilities.
Results
Assume the is approached by a customer to finance a project it risk will be analyzed as followed
COST OF CAPITAL : Cost of capital for retaining
Ke = D1 /PO + g
Po = 35 D1 = 3.25 g = 5%
Ke = 3.25/ 35 +5% = 14.3%
= 14.3%
Cost of capital for common stock
Ke = D1 /PO – f + g
Po = 35 D1 = 3.25 g = 5% f= 2
Ke = 3.25 +5% = 14.8%
35-2 = 14.8%
Cost of capital for preferred stock
Kp = D1/ PO – f
Po = 102 D1 = 6% of 100 f= 4
Kp = 6 = 6.1%
102-4 = 6.1%
Cost of capital for debt
Pd =CF+ interest/(1- Kd)n
Pd – CF = interest Pd – 1000
(1- Kd)n CF —( 1000-20- 20)= 960
1000 – 960 = 6.5% X1000
(1- Kd)10
40 (1- KD) 10 = 65
(1- KD) 10 = 65/40
10 log (1- KD) =log 1.625
log (1- KD) =log 1.625/10
log (1- KD) =0.21085/10
log (1- KD) = log 1.0497
1- KD = 1.0497
Kd =5%
WACC = wdrd(1-T) + wprp + wkerke WACC= 0X 5%( 1-0.4) + 0 X 6.1% + 599,300/699,300 X 14.8% + 100,000/ 699,300 X 14.3%= 14.7%
The project Initial Investment
- Cost of purchase of a new machine = 14 million
- Cost of installation = 1 million
- Increase in account receivable = 1.5 million
- Inventory increase = 2 million
- Account payable = (1 million )
- Disposable value of old machine = (3.5 million)
- Initial Investment 14 million
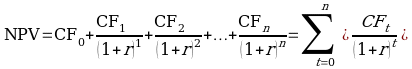
Therefore NPV = (1,000,000)+ 440,000 + 440,000 +440,000 +440,000 + 440,000
(1.0925)1 (1.0925) 2 (1.0925)3 (1.0925)4 (1.0925)5
(1,000,000) + 402,746 + 368,646+ 337,433+ 308,863+ 282,712
= 700,400
Analysis
Assumptions regarding the hurdle rate, and in particular, whether it should adjust to reflect changes in leverage, are critical to determining the optimal credit rating for a bank. This in turn impacts on pricing decisions and the market value of credit portfolios, and consequently, the risk-adjusted performance measures of portfolios under the control of managers. A loan pricing model was constructed to test the impact of changes in the target credit rating of a bank on the pricing of its loans.
The decision of a bank to increase its solvency standard increases the minimum interest rate on its loans in order to achieve the required hurdle rate on capital assigned to the loans. Offsetting this upward pressure is the impact of the reduced funding costs arising from the higher credit rating. If retail deposit rates are insensitive to an upgrade in the credit rating of bank debt securities, we find that the benefits to a bank from increasing its target credit rating rest with the extent to which the cost of wholesale funds falls relative to the increase in the price of bank loans.
A number of scenarios are employed to measure the impact of bank-wide decisions on target credit rating and funding mix on the pricing of bank loans. As the bank increases its target credit rating, there is a significant divergence between the change required in the cost of wholesale funds to maintain unchanged loan rates and empirical data on bank credit spreads. This divergence narrows, however, as the credit quality of the bank loan book increases and the proportion of retail deposits falls. The divergence also narrows considerably when the hurdle rate on capital is allowed to adjust to reflect changes in bank leverage.
Further, our model shows that a bank can gain from increasing its solvency standard, in the sense that the cost of funds falls more than the increase in loan prices, when the regulatory capital requirement for the loan exceeds the economic capital requirement.
This occurs when banks make loans to high credit-quality borrowers, because capital ‘capacity’ enables the bank to realize a reduction in funding costs without an offsetting increase in economic capital, and hence an increase in loan interest rates. Our analysis shows that the benefits of changes in credit rating are contingent upon assumptions regarding changes in the hurdle rate in response to changes in leverage.
This is also relevant at the level of managers, where performance on portfolios is measured by the RORAC against the bank hurdle rate. In chapter four we found that a fixed hurdle rate for pricing bank assets is not consistent with a constant probability of default when bank returns are less than perfectly correlated with the return on the market portfolio. We argued that the internal hurdle rate should capture the additional costs to investors associated with bank-specific risks. If the contributors of economic capital to the bank perceive that bank leverage is governed by minimum regulatory requirements, then a case might be established for a constant hurdle rate. However as banks target higher solvency standards, and the gap between economic capital and regulatory capital widens, the contributors of capital should be willing to accept a lower required return in response to lower bank leverage.
Recommendations and Conclusion
Most organizations and individuals seek loan facilities for investment. However, all these organizations that seek loan facilities face risks of various magnitudes. From the perspective of a bank, each individual or entity seeking a loan has a risk and it differs from one entity to another because of differences in fundamentals. For a bank to give an individual the loan, they must be ready to transform the risk, price it and monitor the risk to ensure that their money is given to the right person. Investment policy or investment strategy of an organization will assist them get loan facilities depending on the loan facility they intend to give.
Therefore before the bank advances credit facilities, they have a responsibility of managing their credit facility, market the company’s products and manage the operational risk associated with the loan. The company is charged with the responsibility of ensuring that the risk associated with giving loans is properly managed. It may be simple but accompanying risk must be captured in order to ensure that loans are issued to people who have provided all information needed to estimate the amount of risk involved in issue of loans.
The information about investment strategy is important as it will assist the bank or the credit facility provider to estimate the risk associated with the loan. You cannot dismiss the investment strategy as a way of assisting an organization or individual in receiving a loan facility or facilitating the quick process of the loan facility. Then much in the same way as the business operates, the bank will have a reduced risk. Businesses operated by individual owners have high risks compared to business operated by a group of partners.
The information provided by each person will be the reasons for the money and of course the bank or a lending institution cannot issue money to a business with a poor investment strategy. For example, a company wanting to investment in a factory to produce new products in the market will stand a better chance of getting credit facilities as compared to a company with a strategy to invest in a company which is producing products saturated in the market.
The bank will have to calculate the expected risk of the investment opportunity available and estimate the profit of the investment proposed by the loan seeker. The risk will be allocated the available capital and other resources within the organization. This will provide the bank with the required rate for lending money. If the rate is lower than the proposed, then the project will not be risky and the bank will not provide the loan. First, the loan interest rate must be higher. Therefore, provides best opportunities of the investment. If the investment strategy is not sound and bearing in mind the supply of capital is limited, the task is reduced, that is investing in those opportunities that have high returns.
There are many factors that determine the getting of a loan from a banking facility. As identified, these factors are crucial and necessary for the loan facilities. Unfortunately, most banks do not use these facilities in issuing of loans. The center of the bank charged with responsibilities of issuing loans at item find themselves looking at other issues which are irrelevant in issuance of loans. However, almost all apart from the few cases, bank loans are issued based on the facts. There is no universally accepted means of measuring risks of the loan seeker from the perspective of the bank. The literature reviewed show that the amount of information provided by the clients influences issuance of loans. The literature further shows ha banks view risk based on the information provided.
Although market prices determine the loan to be issued, risk is also considered. According to Domar and Musgrave, the banks view risks as the probability of losing their money while Savage (1951) argued that risk is making wrong investment choice and Roy (1952) describes risk as the perception about the future cash inflows. There are many writers and scholars who have viewed risks from the perspective of the bank as terms of variability of the expected amount from the loan seeker. The unavailability of a standard way of understanding risk based on the information provided from the client and no proper objectives stating how risk is measured then banks will rely on the information provided. This information provided will revolve around your investment strategy. Therefore, it is necessary for the person seeking credit facilities to draw up proper information relating to risk investment strategy to assist him get credit facilities.
Companies who are faced with lack of information on how to measure risk describe it or spread it will find themselves making wrong investment decisions in not getting credit facilities. Therefore, they should be able to come up with strategies that will assist them get credit facilities and other institutions. Therefore, the credit facility provider requirements implicitly involve a notion of risks as determined by bank regulators that is the free interest arte security setters who are the government arm sets the minimum risk before issuing loan facilities. There are credit risks which are set out by bank regulators and these determine whether the loan seeker will get credit facility.
Therefore it is common knowledge that the cost of capital of the firm in question will determine the amount of loan that will be provided. If the company has a high cost of capital, the probability of getting a loan becomes low because this company will not be bale to raise money that will sustain the interest that accrue on the loan. To avoid technical defaults, banks will avoid such a client.
Banks will use the perspective which identifies risks as a probability that the client will not be bale to pay and there is a risk of this client getting out of business thus determines the economic capital requirement of that firm before raising funds. Investment strategy is affected by great rating by the bank and credit worthiness.
There is a problem with the above mentioned method since solvency follows a company after they have failed to deliver the part of the agreement. This is why the companies or an individual seeking credit facilities need to disclose the loan provider the purpose of the loan, proposed method on how it will be paid back and the thresh hold. There fore there is another standard of measure that assists the company to get credit facilities. This measure is the measure of solvency. This implies that the risk measured using the ability of the firm to pay the loan does not capture the potential losses which will be incurred upon failure by the company to honor their agreements.
Viewed from one perspective, that is from the bank’s point of view, the risk is greater if the financial statements of the company reflects poor profitability and performance. The challenge is in the hands of the bank to ensure that there is relevant measure for risk of the client’s information provided. The methods used should be recognized method for risk measurement. This requires the ability of the bank to decentralize her activities in issuance of loans. If the bank’s credit facility is not decentralized, then the loan will not be forthcoming as quick as industrialized areas.
Take for example Commercial bank of Australia discussed in this case and Bank of America who have decentralized their facilities and another bank in the third world which has failed to decentralize. The third world bank will take long to issue credit facility and it will be riskier for that bank since the credit facility offered is not properly decentralized.
The question that arises from the above two examples is whether the creditor or the person seeking the credit facility is risk averse or risk taker. This is another that well determines the issuance of loan.
References
Beidleman, C. ed. (1987) the handbook of international investing. Chicago: probus publishing.
Bierman. H (1996) “Investing in junk bonds.” Journal Portfolio Management.
Bicksler and Thorp E., “The capital growth model: An empirical investigation,‘” J. Financial and Quantitative Anal.
Black, F(1981); “The ABC’s of business cycles” financial analysts Journal.
Booth J., and D. Officer (1985). “Expectations, interest rates, and commercial bank stocks.” “journal of financial research (spring 1985), pp.51 -58.
Brick, J.R..H.K.Baker, and J. A. Haslem.(1986); Eds Financial Markets Instruments and concepts. 2d ed. Redston Publishing.
Cox, J,.J. Ingersoll, and S. Ross( 1981);. A Re –examination of Traditional Hypothesis about the Term Structure of Interest rates. “Journal of finance.
Fabozzi F.J. Bond makers (1993); Analysis and Strategies. Englewood Cliffs, N J.: prentice Hall.
Federal reserve bank of Richmond,(1990); instruments of the money market. 8th ed. Richmond: federal reserved bank of Richmond.
Krutzmer, P. (1992)“Monetary vs. Fiscal policy: new evidence on an old debate. “economic review, federal reserve bank of kansasa city.
Nyemira, M.P and G. Fredman. (1991); “An evaluation of the composite index of leading indicators for signaling turning points in business and growth cycles. “ business economics.
Sprinkel,B. (1971; Money and Markets: A Monetarists view, Homewood, III.: Richard D. Irwin. The handbook of fixed income securities, 3d ed. Homewood, II.: Business one Irwin, 1991.
First Boston Corp. handbook of securities of the United States Government and federal agencies 35th ed. New York :first boston corp., 1990.
Ibboston, R,G., and L,B. Siegel. (1991); “The. World bond market; market values yields, and returns. ‘ journal of fixed – income.
Van Horne, J.C. (1983); Financial market rates and flows. 4th ed. Englewood cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
Wilson, R.S and F.J Fabozzi (1990);. The New corporate bond market. Chicago: probus publishing.
Yago Glenn (1991);. Junk bonds. New York: oxford university press.
Latane H, “Criteria for choice among risk ventures,” J. Politic. Economy, vol. 67, pp. 144-155,1959.
Thorp E., (1969); “Optimal gambling systems for favorable games,” Rev.Internat. Statist., vol. 37, pp. 273-293, 1969.
-, “Portfolio choice and the Kelly criterion,” Business Econom.Statist. Proc. Amer. Stat. Assoc., pp. 215-224.
Williams J, (1936) “Speculation and the carryover,” Quart. J. Econom.,vol. 50, pp. 436-455, 1936.
Kelly J, (1956) “A new interpretation of information rate,” Bell Syst.Tech. J., pp. 917-926, 1956.
H. Latane,(1959) “Criteria for choice among risk ventures,” J. Politic.Economy, vol. 67, pp. 144-155,1959.
N. Hakansson and T. Liu, “Optimal growth portfolios when yields are serially correlated,” Rev. Econom. Statist., pp. 385-394, 1970.
N. Hakansson, “Capital growth and the mean-variance approach toportfolio selection,” J. Financial and Quantitative Anal., vol. VI, pp.517-557,197l.
R. Bell and T. Cover, “Competitive optimality of logarithmic investment,” Math. of O.R., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 161-166, 1980.
-, “Competitive portfolio selection,” in preparation.
K. Arrow, Essays in Theov of Risk Bearing. Amsterdam: North Holland, 1974.
S. Kullback, Information Theoql and Statistics. New York: Dover,1959.