Abstract
The case study of the Pernod Ricard supported by four strategic priorities- how they would get competitive advantages and what advantages they have keep enjoyed through the practice of these four strategies. In wine and spirit market, the Pernod Ricard is global co-leader in the spirit industry; on the other hand, in wine industry they are keeping the fourth position. Since creation of this Group by an acquisition during 1975, they have tried sincerely to continue an uninterrupted growth.
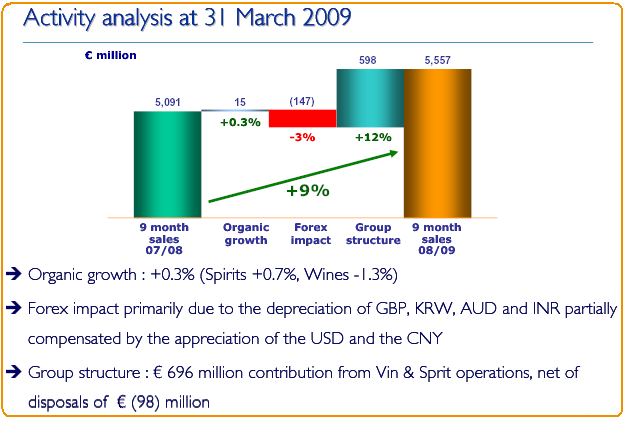
This dissertation ‘Is four strategic priorities a real source of competitive advantage? A case study of Pernod Ricard’ has been demonstrated through some of their financial indicators transacted in 2007/2008 fiscal year where the sales is about € 6,589 million, 9 % sales organic growth, group net profit € 840 million with 23 % operating margin.
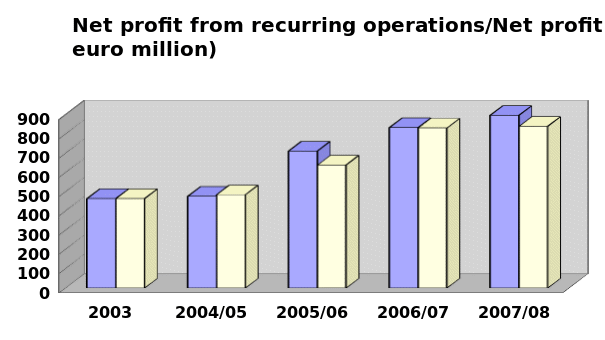
In addition, 13 % organic growth in profit was grasping from the recurring operations that amounted in € 1,522 million. Making their position on top by utilising major four competitive strategies is the optimal point of this paper. Passes through a six sequential layer- introduction, theoretical discussion, recent response conducting these four strategies, current competitive advantages evaluation, practice of these strategies gathered success in an efficient way and finally, recommendation with a conclusion proposed how would they overcome the upcoming dilemmas as well as be a global market leader in both spirit and wine industry.
Problem Statement
Background of the project
Modern and conventional strategic planning model directly emphasis on the strategic priorities whether it should ensure to achieving competitive advantages for company. The strategic analysis argue to adopt long term care and supportive method to analyse the information, setting priorities, build up strategies as well as create the plan keeping full attention to the needs and preferences to gaining competitive advantages. This dissertation would go to investigate is strategic priorities a real source of competitive advantage and look for empirical evidence from the four strategic priorities of Pernod Ricard.
Overview of the business environment of the industry
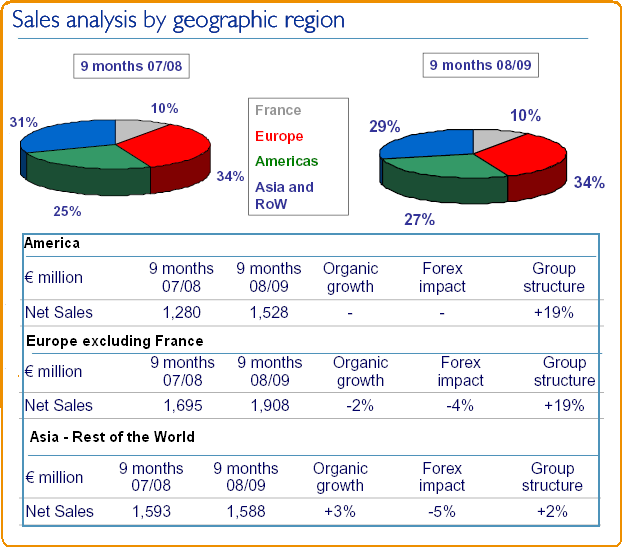
The Entreprendre, (2008) pointed out that the key factor of their success is the network that they carried out for long since starting from 1975 with operation in four countries. Pernod Ricard kept its continuous effort on the acquisition and getting hold of Seagram, Vin & Sprit and Allied Domecq and now in around in seventy countries it has owned subsidiaries with extremely well situated in the key markets. In the United States market, Pernod Ricard has positioned second with 30% of sales as well as over 50% of growth. However, in consideration of the Asian, Central Europe and Latin American market Pernod Ricard has positioned numbered one.
Another key success factor is the broad product line of Pernod Ricard that has the most far-reaching in the industry with strong portfolio of global and home brands build up with the acquisition of different brands like Ballantine’s, Vodka, Chivas Regal, Absolut and Martell that has enabled the company to gain portfolio for every market types. Apprehending the assessment of these product lines has shaped the turning point on its exceptional marketing as well as commercial proficiency that driven the company in the way to create iconic brands. The sustainable expansion charter of Pernod Ricard has been seriously emphasised on its quality control for all brands and this has facilitated unique heritage and expertise to gain brand awareness.
The Annual Report (2009) for the third quarter of 2008-09, it has reported that a decline on trade sales, materials decaling in duty free shops and most alarming decrease in East European market and rather than this it has gained most of the global market. The particular gains are as in US -4% (lose), Spain +6%, in UK Off-trade has noted +20%, in Australian market +8%, in Brazilian market +16%, in France market +10%, in Germany market +41%, in Italian market +6%, in Mexico +15% with a 60% price gained in China as a significance of Asian growing economy.
Pernod Ricard is well positioned in the global wine and sprit market they continue their journey hardly to imitate the advantages since back to the competitiveness by rethought of their current strategies was not to bring competitive revitalisation. Following are the major focusing point those are prior in strategic analysis of the Pernod Ricard:
- Pay attention on the current rivals;
- Pay attention on the resources of their current rivals resources;
- Rank the potential new competitors in a low position.
Formulations of the Pernod Ricard strategies are origin from two foundation models but they are not necessarily mutually exclusive. These models are composed of two different views described as follow:
- The Western model: works for make balance between current resources and potential opportunities.
- The Asian model: works for utilize available leverage resources so that they could enable to achieve unattainable goals near to them. (figure-1)
Behind corporate strategy, success of the today’s business environment depends on a broader understanding of principle concept of strategic analysis. With the aim of beat competition at an optimal point, the Western approach priors on the resource management hence to make improve in a sequential order. Thus it is significant to investigate do the four strategic priorities of Pernod Ricard is a real source of competitive advantage for the company with pragmatic evidences.
Research Question and Objectives
This dissertation has been designed to answer the following research question. What factors most influence the strategic priorities to implementation and productivity among the organisation to achieving competitive advantages? The answer to this question would enable the managers to organise the strategic priorities toward a greater motivation and increased productive output. Four research questions have been listed below:
- How does Theoretical Framework of four strategic priorities works on competitive advantage?
- How Pernod Ricard Corporate has Response to four strategic priorities in different markets?
- What extent do the Pernod Ricard Corporate assessed on competitive advantage?
- To what degree the implementations of effect and effectiveness of four strategic priorities would support competitive advantage for Pernod Ricard Corporate.
Scope and Limitations of the Study
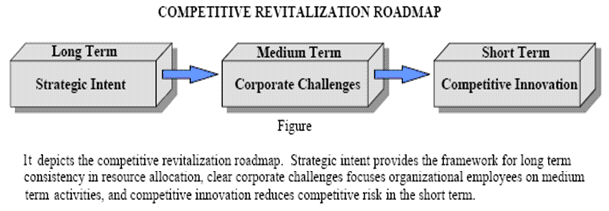
Misleading notion of strategic intent and overlapping of it among the strategic planning make barriers to enjoy competitive advantages. Strategic planning of companies like Pernod Ricard has always been emphasised on following forces like evaluation of available resources, assessment of alternative strategies and their feasibilities. The judgment of the tools and approaches where would the strategies either rejected or accepted and appropriateness of the organisational vision It also take consideration of current dilemmas are focused more than the potential opportunities with modes of the strategic intent towards to be flexible at the ultimate. Moreover, the strategic intent provide scopes for innovation and new opportunities with restriction free modes and make the corporate challenges successful at all level of employees recognising their responsibilities of the overall organisation’s competitiveness. Both penalties and grasp advantages from deep of the company has reaped by the employees and argues market key strategy of competitive advantages faced to the future.
Keeping it on mind that competitive advantages are not a long lasting process. It could be stable and flexible if the Pernod Ricard continuously develop their on going skills and adopt new opportunities. In addition, low cost leadership advantages, delivery costs, and production are the factors to beat the competition.
The Interview
Interview is conversion process with different manner, where two parties are talking about something, which they are interested in opinion. One party is interviewee and another is interviewer with careful asking of follow up questions. In this study, the employees and staffs of Pernod Ricard are interviewed for further help of the study.
There are two types of interview methods can be used, which are discussed below:
Unstructured Interview Methods: This method is a conversion way without any prepared questions for investigations, but the interview should be focused on the purpose of study and particular focus on interview with interests of parties. As, there is no developed questions, the interviewer must develop a question strategy with taking notes on answers from interviewee. The interview is controlled with area of consideration, exploration, related, and revisited to each other very frequently.
In this method, effective listening is required to concentrate by interviewer to process own thoughts in neutral way.
Structured Interview Methods: This is a formal of interviewing with sequences of activities in performances and a questionnaire is must for this method. To develop this method, specialists care, and analysis is needed to know the participants activities, and expected results from the interviewee. Records and notes are needed in the time of interview carried out by manager or other top-level people of any organisation.
For Pernod Ricard, the study is developed by interviewing with the employees and staffs to generate appropriate and logical information about the study. As this study is related with research, so the interview is taken by using structured interview method to generate accurate results with appropriate way of questionnaire and having records of questions to employees for analysis of the results in proper manner.
As the employees and staffs of Pernod Ricard is integrated in new company, after merging with Vin&Sprit and Pernod Ricard, many new employees are employed, whom are not aware about the company’s situation properly.
The consultation with employees and staffs are depending on transparency and trust of employees on the research approach and interview. The common values of employees and Pernod Ricard Company is important for interviewing.
Relevant Literature Review
Overview of the Topic
This literature review includes writings, research, and scholarly opinion concerning the description, measurement, and evaluation of Corporate Managers, “Is four strategic priorities a real source of competitive advantage? A case study of Pernod Ricard” It provides the background needed for evaluation of what strategic priorities factors most significantly influence competitive advantage for organisational success.
The views and opinions of contemporary managerial writers concerning strategic planning, strategic priorities, motivation, organisational strategies, productivity, and competitive advantage have been discussed. Collectively with the chronological theories and modern approaches form a concrete basis upon which to design a research study for further refine the causal relationships of strategic priorities with competitive advantage of affecting workplace productivity?
Scope and Limitations of this Review
The selected works included in this review reflects the authors and researchers paying attention in the description, measurement, and evaluation of strategic planning and its resultant effects in the organisation as competitive advantage. The report focuses on studies of the dimensions of strategic analysis, strategic priorities, how the organisations have measured and attributed by others, and the effect of competitive advantage upon organisational effectiveness and productivity. Special emphasis has been placed upon the effect of managerial behaviors on productivity and quality initiatives within the organisation with the view of both historic and contemporary writings are reviewed.
With massive quantities of literature concerning strategic planning available, this review is limited to the most substantiated theories and accepted principles. It is but a sampling of the mass of strategic analysis literature. Likewise, the wide range of popular writings connected to organisational success, management and productivity necessitated limiting this review to mostly mainstream writings of accepted authors.
Organisation of the Literature
The discussion portion of this review is organised into four sections. The first section describes the historical and contemporary context studies of how the theoretical framework of strategic planning works according four strategic priorities.
The second section reviews the thoughts of more contemporary writers on effective four strategic priorities and their impact within Pernod Ricard Corporate in different markets.
The Third section reviews how competitive advantage actions have been evaluated and assessed in the past and how those factors are related to Pernod Ricard’s performance.
The Fourth section summarises and ties together the philosophies, concepts, evidence, theories and practices discussed in this review to what degree the implementations of effect and effectiveness of four strategic priorities would support competitive advantage for Pernod Ricard Corporate. This section identifies how the existing theories account for causal relationships between traditional strategic analysis, overall productivity, and organisational success.
Discussion: Section-1
Decentralisation
The Entreprendre, (2008) has presented an with interview of Pierre Pringuet the CEO of Pernod Ricard where he strongly addressed that the decentralisation is the foundation of the company’s business structure that promotes the strength of venture as well as openness. Decentralisation has contributed the company to a triumphant route that intends to uphold the company’s objective in a clear and straightforward roadmap that would provide more success in the future.
Food & Drink Business, (2007), pointed out that Pernod Ricard has raised its spirit with a decentralised and collaborative supply chain that positioned the company at the top three of players of the global in wine and spirits market and enjoys sales revenue of $3.4 billion per annum. The decentralisation strategy of Pernod Ricard has enabled it to bring exceptional growth through acquisition and has turn out to be a global conglomeration of almost 60 global Wine and Spirit Company. Pernod Ricard leads its all subsidiaries just like a profit making center, but facilitated self-rule for strategic marketing as well as field decisions locally by the unites nevertheless eventually all the unites have to report to the headquarter of Pernod Ricard in Paris. The decentralisation strategies also make it possible for each brand owners and subsidiaries to administer and manage the profit centres with support its profoundly knowledge as well as market study. Food & Drink Business, (2007) added that decentralisation is the ready for action strength for the company through somewhat generates multifaceted supply chain.
Decentralisation implementation of Pernod Ricard and its operational structure has contributed the group to distributing its produced wine and spirits to the each member companies under the group as well as products of the other companies among the conglomerate. It also allows cross selling within group and generates global demand for every one brands devoid of demands for expensive external distribution channels avoiding supply chain complications.
Merge and acquisition approach of Pernod Ricard
Hitt. A. M. Ireland, D. R., & Hoskisson. E. R, (2001) stated that Merger and Acquisition approach has recognised as a service to combine two businesses in together with the profitability of high quality, comprehensive, and strategic focus on the business combination. There are three common approaches in Merger and acquisition, which are:
- Horizontal Approach: When any business has merged or acquisitioned with same line of business;
- Vertical Approach: When two businesses with different production level are merged or acquisitioned;
- Conglomerate Approach: When two unrelated businesses have merged and acquisitioned to make necessary strategies of being together.
These approaches have been taken as an investment decision, which is most important for acquiring company and targeted company. For taking this approach by Pernod Ricard, it has to take crucial decision by analysing with financial managers and corporate managers. They would take decision of merge and acquisition for having goodwill in business environment.
Pernod Ricard has merged and acquisitioned with different companies and it always taken “Horizontal Approach” as an acquisition approach to continue its business in spirits and wines market profitability. By taking horizontal approach, Pernod Ricard has acquisitioned its business from 2005, with Allied Domecq, which became very successful and bring the Pernod Ricard in number 2 position in world market. (Accenture, 2006)
Some other success factors related with Pernod Ricard after merger and acquisition are discussed below:
To achieve goals as leader in worldwide: Pernod Ricard has already achieved their goals of leadership in the international market of Vodka brand. It has increased its Vodka market more than 8% by last 10 years. In the fiscal year 2006/07, this rate was amplified about 12.6%. It also holds the second largest category in market of spirits by selling of 18% international spirits and 33% whisky worldwide. Therefore, they are merging for gaining market share with their premium products, which is one of the best strategies of Pernod Ricard. They have also concerning on clients and customers’ cultures for providing friendly products and independent acquisition.
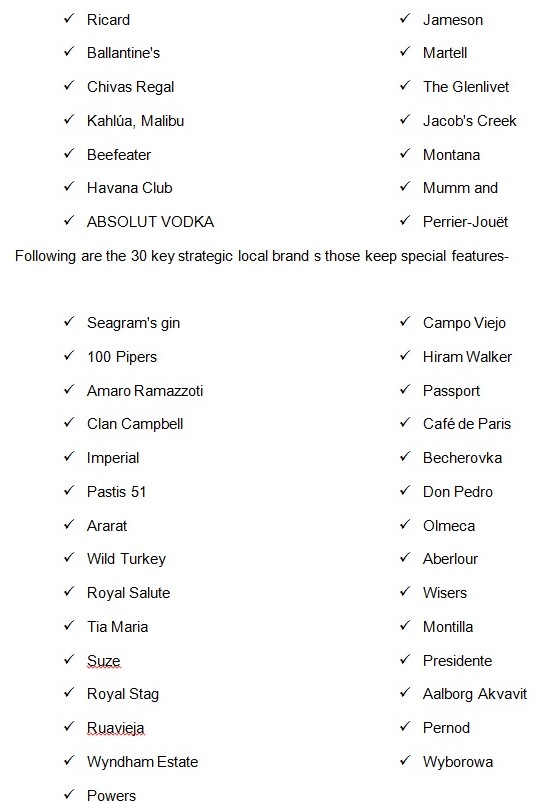
To merge with leading international brands: Pernod Ricard has merged with leading international brands like Richard, Ballantine’s, Chivas Regal, Kahlúa, Malibu, Beefeater, Jameson, Glenlivet, Jacob’s Creek, Montana, Mumm and Perrier-Jouët. By these merging, the distribution network has enhanced not only France, but also all over the global market. The sales have increased up to $7.4 billion in 2005-2006 annual year of Pernod Ricard. (Entreprendre, 2008)
To capture maximum countries by acquisition: Recently Pernod Ricard has acquisitioned with Seagram, Allied Domecq and VIN&Sprit, which opened the chance to business in 70 countries with well-positioned market. They have become regional power with clear leadership and local brands and captured the international market in same positioning. Having 37% shares in market after acquisitioned with V&S in Denmark, it has generated €150 million of sales after merged with V&S.
To make portfolio of strong brand: Pernod Ricard has become successful in creation of strong international and local brand by merged after Absolut, for the brand vodka, which accrued the strength in marketing presence of portfolio. It is also created dynamic growth, large geographic coverage, great reputation and much more profitability of it after merged with Absolut. The debt amount of the company has reduced after merged with Absolut, with the priority and support of financial community and shareholders. (Entreprendre, 2007)
To decentralise Pernod Ricard: After acquisition with successful brands, the brand of Pernod Ricard is decentralised in organisation.
Framework of Competitive Advantage & Strategic Priorities
Porter & Kramer (2006) mentioned that the perception of competitive advantage analysis attains the ways of achieve a greater appreciation and strapping position of a firm take up against its rivals. Now a day, it is a crucial task for international firms that produce a larger product line. Through this system examining of industry boundary, structure, competitive factors, as well as key success factors (KSFs) are easily recognised by the organisation’s executives. Key forces that need to defined and analysed in the creation of competitive advantage include:
Identify and evaluate the company’s current and potential competitors:
- Draw the firm’s vision, mission, goals, objectives, aspirations, and capabilities.
- Define the concept of company’s strategic intent along with description of strategies.
- Identify the areas of the firm’s competition. In another words, how and where the firm will compete.
Griffin (2006) explained another form of the competitive analysis as driven force to complemented the industry analysis where the managers’ of an organisation are easily focus the key rivals, strengths and weaknesses of the firm. The subsequent terms through which competitive analysis could be defined are also distinctive competence as well as ready for action analysis. A distinctive competence is the task that makes a comparison among the rivals of the firm in order to identify the rank where it could be placed in superior.
This comparison delivers spirit to launch new products or services in market. At the same time competitive advantage compare to the rivals the firm is placed in superior is the inspiration for the firm to enlarge its profitability. At first formulation and execution of distinctive competence of the firm would easily drive to the new competitive way, and consequently boosts its profitability.
McGahan (1994) argued that the objectives of the competitive advantage analysis to carry out a gather sensation and understanding of the action plan of industry and dynamic market prophecy of its competitor. Nowadays, competitive advantage analysis has been considered as a supportive tool for managers in order to gather data or information module, deduce and analyse the collected records to gaining the objectives of the organisation.
- Competitive arena of the company would well define and defined the concept of the served markets.
- Seek and define prospective business opportunities.
- Adopt benchmarking properly supervise a slam competition.
- Through a precise time frame or through an effective utilisation of response time, competitor’s movement of a firm would be traced.
- Competitor’s movement would be restricted or preempting by this analysis.
- For an effective organisational motivation, develop the communication system.
- Enjoys superior competitive advantages rather than rivals this analysis provides necessary information to the executives of the firm.
- Promote, expose, and continue competitive learning in order to counter the ideas and actions of the rivals.
Kotler and Keller (2006) explained the competitive advantage analysis procedure and added that competitive advantage and industry analysis is a complex procedure. A precise form of this is as below:
Thompson, et al, (2007) has defined industry boundary, select served market, and in first step of the competitive advantage, analysis is to sketch the boundaries of the industry. At the end of this, market segmentation based on customers’ need and desired products and services should be planned. Plan of the market segmentation have to pay attention on the following three significant variables. For more clarification, a graphical presented is also given in below after mention of the variables. (Figure-2)
- Segmentation of the customers should be served.
- Needs, wants, demand and the purchasing patterns of the customer have to consider significantly.
- In order to meet customers needs and expectations try to make best effort to adopt new and upgraded technologies.
Skinner and Ivancevich (2003) explained that the industry life-cycle in existence of the external factors like- socio cultural forces, economic factors, political legal items, technological developments turn an industry into an existing form and this form is continuously changed with change of time. Managers have to understand these changes throughout the sequential phase or stages of the industry life cycle as described in below in order to observe fairly the predictable stages of the industry.
Skinner and Ivancevich (2003 also added that the first stage of the industry life cycle is emergence or introduction. At the beginning of an industry, technological development for the offering products are not well developed but try to serve in a large market. When growth is the second stage of an industry life cycle is most exciting phase for the industry. Companies start to go forward through following modes-
- For survive of the company get start their fight or struggle.
- Magnify profitability.
- Start to acquire market shares.
- Strengthen of brand name of the company.
Pringuet (2009) addressed that a wide modification has occurred in this shakeout stage. Factors involved in the modification are as below:
- Industry saturation or dispersion.
- Evaluate a little decline of the industry’s growth rate.
- Area of the competition radically modified.
Pringuet (2009) also argued that at maturity approach the firm has to consider new forces to foster their competition. Following are the tools of maturity approach:
- Fairly standardize products and services by adopting recent technologies
- Continuously develop and invent new products to extent their existing product line
- Efficient and effective marketing in all phase- either advertising or maturity
Schuler, Jackson, S. E., & Storey, (2000) mentioned that decline is the new phase evaluated in an industry due to the demand of the product and services have been declined. It is a challenging phase for an industry and the executives are under pressure to evaluate causes behind the decline of the industry growth. Consequence of this executive are required to modify the mission of the company and determine how long the company would exists. (Figure-3)
Industry structure analysis
McGahan (1994) conceptualised the competitive profile of the industry is termed by industry structure analysis. Four major factors make easier to understand lion of the industry. Brief presentation of this four factors are given below:
- Barriers to entry and exit: At first, all new entries in an existing market are a great challenge and on the other side, for the new firms entrance is a great barrier for that company. Barriers might be in two forms- either tangible or intangible. Tangible barriers are involved in- requirement of capital, access to technological formation, distribution channel adoption, enlarge the public policies that control an industry’s operations. On the other hand, intangible barriers involve in- existing companies and brands good will, loyalty of the customers on the existing products and services, evaluate the cost to switch a customer from the existing industry. Task of mangers is to examine and make decision whether exit from a market from viewpoint of market demand.
- Product differentiation level: Enjoy competitive advantage products and a service of a company is diverse from other by their advance technology utilisation, varieties of marketing approaches- promotional activities, advertising through different modes, provide a wide service after sales occur.
- Level of concentration: Level of concentration is the concept that evaluates the ratio of the dominating sales of a leading company.
- Scope of economics of scale: Economics of scale is significant factors that involves in- competition understanding, utilises continuous innovative production system, enlarge the product line, patronizes large scale of production at a lower cost and keep continue the economic achievement.
Identifying the dynamics of the competition
Porter (2004) has presented the phase of competition dynamics is evaluated through five factors define by Michael Porter, 1980. Five factors of competition dynamics are:
- Potential entry: Potential entry is controlled through a number of variables those act as threat of entry into industry and reduce potential entry. Such variables are distribution channel, capital requirement, rules, and regulation.
- Buyers bargaining power: Bargaining power capable a buyer influence the production capability of the industry.
- Suppliers bargaining power: Suppliers influence an industry when they are few at numbers, lacking of substitute product, product price system.
- Threat of substitute product: Products that has the ability to fulfill same purpose is termed as substitute product. Exist of substitute product affects competitive dynamics and rivalry intensity.
- Existing Competitors’ Rivalry: Several equal balanced company, competition diversity, and slow growth rate, high fixed costs etc. are the forces that control Existing competitors’ rivalry. (Figure-4)
David (2008) explained the key success factors (CSFs) of the industry, which could be understood by customer analysis and competition analysis. These analyses include market segment, consumers want, and strategy formulating way. Analysis of strategic group performance is a set of key success factors (KSFs)-most significantly, competition dynamics and industry structure has executed the strategic group analysis. Strategic group performance analysis brought a graphical presentation of the various companies’ market position, objectives, drawbacks, and ways to overcome limitation. A short description of these factors is as follow:
Dess, Lumpkin, & Eisner (2008) pointed out the market position of the same group of companies: In following figure, market position of the same group of companies is drawn. Assumptions from this sketch are as follow. Considering four groups- professional, skill, mass market, and private level group in a common industry four categories of hypothesis are plotted here. (Figure-5)
- Target market segmentation and viewpoint of the customers’ demand and test brand quality is determined. This segmentation has diverse each group from another.
- Among the four groups, most populated group in the industry is the professional group that serves most high quality branded image products and services.
- Third, assumptions from the figure focused that between professional group and mass-market group collaboration continued through skill. In other word, skill performs as an intermediate between two groups.
- However, the mass-market group has delivered a medium level of quality brand but it has covered a larger portion than the private and professional group.
Dess, Lumpkin, & Eisner (2008) also mentioned that the objectives of the strategic group performance analysis: Following are the crafted objectives from strategic group analysis:
- Present the key strategies in a summarized form those are regularly used by the industry.
- Identify the company’s direct rivals
- Identify the company’s potential rivals
- Support to evaluate alternative strategies
- Support to evaluate the current market performance and position of the company
Auburn University (2009) has demonstrated the drawbacks of the strategic group performance analysis: Strategic group performance analysis has evaluated a number of drawbacks as below:
- Most of the companies continue their analysis on the existing rival companies recent data
- In order to classify the rival companies poor criteria used in analysis would evaluate wrong critical success factors (KSFs) relate to different strategic groups in the industry
- Most of the industries relies on the tangible factors when it identifying the groups
Ways to overcome the limitation of the strategic group performance analysis: Limitations of the strategic group analysis would be overcome by the executives in following ways:
- Make an right classification its useful to deals with versatile criteria during group performance analysis
- Evaluate the amendment of the industry form diverse time frame affecting factors behind this changes could be easily identified
- Travel around the diverse scenarios an effective approach is to ask “what if” questions
Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., & Gilbert, D. R. (2006) argued that the competitive intelligence (CI) is an effective industry gathers formation about its rivals and analyses that by their competitive intelligence group so that they invent counter plan and strategy against their rivals. Rivals of an industry would be ranked by the CI’s gathered information analysis. Competitive signal interpreting involves in- cost reducing, analysis of the competitor’s hypothesis and war the rivals. Environment scanning would be effective if there have proper definition of the threats and opportunities with this competition would make hostile.
Section-2
SWOT Analysis of Pernod Ricard
For Pernod Ricard, SWOT analysis is an essential source of company’s information that has provided company’s structural, operational, productions, and strategically analysis of strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats of the Pernod Ricard.

Strengths of Pernod Ricard: (Entreprendre, 2007), (Entreprendre, 2009):
- Access in Duty free consumption of continent: Pernod Ricard has facilitated with duty consumption in Latin America, China, India, and the Middle East-Africa zone, which is very strong positioning of the company. This is also increasing the strengths of portfolio of brands by quality products. This also helped the company to earning a billion Euros in profit from their operations in other continent.
- Advantages of being decentralised organisation: Economic future has always been uncertain and risky. However, having decentralised organisation, Pernod Ricard can take advantages with broad autonomy of subsidiaries, which can change the consumption pattern of customers very easily. This will help in encouragement of resources of brand portfolio.
- Boosting Brand’s Growth: The owners of Pernod Ricard have the power to boost brand’s growth, which is an important asset of the company. For an example, after merged with Pernod Ricard, ABSOLUT became a tremendous range of premium brand drinks in the customers’ mind.
- Having Balanced Brand Portfolio: The brand portfolio of Pernod Ricard has balanced with numerous product category and geographical segments. The benefit of Pre-immunisation is potential for marginal growth in productivity gains and expansion of sales.
- Available Resources: Pernod Ricard has much confidence to have access to resources under the situation of present economic crisis of American market and customers.
Weakness: (Entreprendre, 2008):
- Enhancing Status of brand: The main weakness of Pernod Ricard is to enhance the status of the brand portfolio as a premium brand in customers’ mind and to take the first choice of customers’ in their drinking sections.
- To tackle the economic crisis in emerging market: Pernod Ricard has lacked behind because of having economic crisis in America. However, in long-term plan, they have positive forecast to capture the wines and spirits sectors worldwide.
Opportunities:
- Tremendous Growth Opportunities: To being second largest market of vodka in United States, Pernod Ricard is having 14% of market share. After merging with Absolut, the growth opportunities are expected to raise more in tremendous way. (Entreprendre, 2007)
- Increased Demand of international Brands: The customers demand has increased more on international brands, rather than regional. After merging with Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, demand is obviously increased.
- Benefited importers by trading products in retail market: Pernod Ricard has launched the system for importers to position the company’s products in retail market too, with public outfits of regular tenders.
- Significance in Travel Retail channel in regional market: Pernod Ricard is following a tendency of population to travel in lot of countries. For this reason, they are generating significance opportunities in Travel Retail channel in their regional market. (Entreprendre, 2009)
Trade Opportunities: The trade segments of Pernod Ricard are representing low proportion comparing with overall consumption of Nordic region. It helps on promotion of brands, like advertising restriction in Norway, where the products are contained less than 22% of alcohol.
- Affordable product ranges for customers: According with challenging market conditions, Pernod Ricard believes on potentiality of customers to consume luxurious products of the company with affordable prices. They also motivated the potential customers to do in such manner.
- Off trade channel: In the off- trade channels, like Baltic States, which has potential customers, having 7 million people in the region, has emerged with Pernod Ricard. In this region, consumers are conscious and attracted by premium products of Pernod Ricard.
- Brand Potentiality: The brand of Pernod Ricard has potentiality in the market with +9% growths in various countries, like, Brazil, France, Poland, and Greece. The brand of this company has also popularity in premium products category of Asian, Central and Eastern European, and Latin American markets.
- Strong relation with brand and portfolio: In European and French market, the relationship between brand name of Pernod Ricard and portfolio is emphasised on distribution network in global business with tremendous growth opportunities in every continent worldwide.
- Brand Awareness to middle class people: Pernod Ricard is growing the sector of beverages by 30% in India, where 300 millions people are living. On those, most of them are middle class, but now concerning on brand awareness of beverages.
Threats:
- Distribution in Monopoly: Sweden is one of three countries between Finland and Norway, which is restrictive in distribution of alcoholic beverages as a state monopoly.
- To hold growth in US market: As the exposures of economic cycles has been increasing in United States because of growth in market, (improvement of Seagram brands), Pernod Ricard is facing problems in marketing goods. For this reason, they are being dependences on Asia and Pacific market to generate more profits.
Strategic Analysis of Pernod Ricard
Pernod Ricard, (2008) mentioned that during 1975, in order to both acquisition and organic growth Pernod Ricard was born by the merger of Pernod and Ricard. This group has make their identity as the world’s co-leader of selling wines and spirits amounted € 6,589 million in the fiscal year 2007/08 and through as following:
- Purchase a part of Seagram in 2001.
- During 2005 make an acquisition with the Allied Domecq.
- Another acquisition make with the wine and Sprit in 2008.
Success behind Pernod Ricard grounds through a set of prestigious brands and strongly invests on it to achieve its Premiumisation strategy.
Premiumisation of Pernod Ricard
The development of brand portfolio by Pernod Ricard with its 15 key brands is a strategic decision of the organisation and known as Premiumisation. In the developed countries, consumers always look for quality and luxury, for which they can pay a maximum price. Although in India, China, which is recently developed, and developing their living standards, they are also seeking quality in their local brands. To meeting customers demand, Pernod Ricard has ranked numbers of premium and high quality spirits, scotch and vodka as a market leader, which has recognised as good quality. This is Premiumisation that has taken by Pernod Ricard as strategic growth of business.
To gather Premiumisation, the strategic growth must have to develop positioning as high profit margin organisation. They are generating Premiumisation by meeting customers’ standards, reducing group exposure in world economic fluctuations. This strategy has developed sales with high margins and can have moderate pricing in time of inflations. Some actions should be taken to have the benefits from Premiumisation, which has discussed in below: (Entreprendre, 2007)
Quality Improvement with continual basis
The improvement of quality of branded products are required accessible luxurious, which contributes to become a legend of Pernod Ricard in the market. They are focusing on strategy of premium brands with high range products, rather than mid range products, which ended up sustainable trend of wines and spirits in 2008. The company also noticed that, consumers are not concerning on showing the brands of their drinks, but they are emotionally attached and attracted with the luxurious brands to be consumed.
Strong Communications with Focus group and Customers: Pernod Ricard has focused on the group on flagship and prestige brand in accordance with global image and culture of market player of vodka and spirits. They are building up relation with their customers group to present their Premiumisation more easily. They are also developed their sales and marketing programme with training from Pernod Ricard Professional Training Centre.
They are also developed Premiumisation with great publicity, taking recognised and award winning chefs and having strong relationship with luxurious brands. The trend of this strategy is extending customers to move from lower priced to premium priced as a status symbol of their living standards. (Entreprendre, 2008)
Emphasise on Innovation: Pernod Ricard has concentrated its major investments in the development of top brands, like Martell XO, Or de Martell, Chivas Regal 18 Year Old, Chivas 25 Year Old, Ballantine’s 21 Year Old, Glenlivet 25 Year Old, Cuvée R Lalou, and ‘By & For’ by Perrier-Jouët. By Premiumisation, Pernod Ricard is become successful in 15 strategic brands of international spirits and wines.
Pernod Ricard (2008) adopted a decentralised management hierarchy in their entire organisation. In addition, they owned “7 Brands” and these are distributed through about 70 distribution companies, which were grounds on their own key market. Number of employees is more than 19,300. Surround by a strong dedication as follow this corporation walking toward its vision.
- Business policy and strategies are born from a sustainable development thought.
- Consumption of their products is encouraged hold responsibility.
Pernod Ricard (2008) affiliated with a forward-looking statement escape from a press release. Moreover, Pernod Ricard’s future performance does not influence through this. A clear portrait of the nature of risks and uncertainties is brought by these statements. Following are the terms those do not carry out by the press release and the entire information of the statement:
- A selling offer.
- Offer to subscribe.
- Offer to a socialisation any order.
- Offer to buy any order.
- In any country offer to subscribe securities.
According to the applicable laws and regulations distribution of their both press statements and products are restricted in several countries. Consequence of this restriction, if there is any existence of any of these- published statement or circulation or any kind of distribution people of the listed counties should comply with the corporation. The existing local legislation and securities has a serious influence on Pernod Ricard’s US operation in following points:
The United States Securities Act of 1933 that amended as the Securities Act:
- Any type of registration is prohibited either to offer or to sold any product in United States if there is absent of any registration laws.
- As per requirement of the Securities Act the registration was prohibited by an applicable exemption.
- In the United States there has no intention of the Pernod Ricard to deliver any part of their offers.
- Moreover, in the United States the Pernod Ricard has no intention to conduct a public offering of securities.
Reinforced positioning in emerging markets of Pernod Ricard
For positioning, it is important for Pernod Ricard to position in the market, in which they are emerging recently and having less control in market of wine, vodka, scotch etc. The mission of company emphasised of building and positioning brand in every communications, events, partnerships, packaging, and display of luxurious markets. Some positioning of brand has discussed according to some specific markets emerged with company, is given:
Asia with Booming Economy
Asia has a booming economy with an annual growth rate of over 8% in the emerging markets. For this reason, it has already become more populous continent in all over world for growth opportunities of business. It has also turned out to be largest consumption of alcoholic beverages, so Pernod Ricard has large opportunity to extend its business of wines and spirits in Asia. Some important countries of Asia are emerging markets with 30% of sales and more than 50% growth in China & India. However, the dynamic growth is less expected in Thailand with high foreign exchange and interest rates in 2008-2009. Japan has given importance too on prestige wines, for such as Perrier-Jouët Belle Époque. However, comparing with Japan, China is showing more strength in growth of market share.
If it is concentrating on vodka, China is a good market to emerge positioning of it with strong presence and various categories, which can motivated the potential customers’ of China. The positioning of Pernod Ricard is poor in Asian countries because of lack of knowledge of customers’ expectations and under investment in human and financial terms of brand positioning. So, these emerged markets must be positioned with effective sales network, advertisements, and promotional investments of brand. (Entreprendre, 2007)
Strong Market of United States
In emerging market, the strong presences of United States must be needed for positioning in geographic context. The US is the largest market of spirits with +2%-3% in market share. Pernod Ricard has some brands such as Jameson and The Glenlivet those are improving dynamic growth in the market and has benefited the entire portfolio of brand. There are some possibilities for the company to suffer from crisis and may not grow up with emerging market. By selling Vodka, Pernod Ricard is generating 60% sales of 75% growing consumption. The market of US has high potential in Absolut brand, as premium vodka. Not only vodka, the business of rum and whisky market is also growing very rapidly. In addition, market has a crisis, but in long-term positioning plan, company is assuring the product sales in a good shape. To overcome short-term conditions, company could reduce structural costs, being innovative and efficient in distribution and marketing in trade in United States. (Entreprendre, 2008)
Regional Market of Europe
As a France company, Pernod Ricard’s has observed major events of Europe, which celebrated with Champagne. That is why; the demands are not as beverages, but also an important item for celebration of any occasion in Europe. The celebration is not major events, but the strong distribution channel with quality products would ensure the market positioning and customers’ demand. They are also showing the simplicity, authenticity, and experience with their customers. For an example, for Genuine Scotch, they are stating their positioning statement as “Genuine Scotch for Genuine Friends”, which is very effective in market.
Focus on other countries
Some important countries could be emerged and reinforced by Pernod Ricard’s brand, which are Mexico, Canada, Brazil, Poland, and Russia. These countries have already captured by the brand of vodka, ABSOLUT. The positioning can be made more strongly by focusing on super premium sector of ABSOLUT 100. They are developing other brands by carrying out common platform for brand with traditional brand associations.
Section-3
Focusing on external growth in Merge and acquisition
In the external growth of merge and acquisition, Pernod Ricard has focused on cost savings of €270 million, which proves a tremendous growth in net profit for the organisation. In European and France market, the benefits of merge and acquisition are generated so easily because of having strong brand positing in market. This has also helped by the growth of network in US market of strong beverages. The global business opportunity is growing not only in US, but also everywhere with booming growth.
Considering the Chinese economy, the sales of Pernod Ricard’s products are growing with a sharp upward trend after merging. The growth of local brands also helped to build suitable gross margin performances with very promising brand. The company is not focusing on costs savings, they are focusing on growth synergy to move forward of their business. (Entreprendre, 2007)
The worldwide network of Pernod Ricard shown that, it has generating € 507 million sales (+7.3%) growth by providing high quality products to potential customers. The net profit of the company has gained € 529 million (Growth of +18%) after merged with branded company of beverages.
The continuous sales growth of Pernod Ricard has generated with profitability for both company and for brand. After merging with Allied Domecq, the sales have increased to €270 million in 2007, because of being world’s second largest company in producing wines and spirits. (Entreprendre, 2008)
As it has been demonstrated before that, Asian market having with fastest growing economy, so after merging, the power of Pernod Ricard has increased with increased sales volume of 50% in 2005-2006. Nevertheless, in South Korea, the growth has increased from 4% to 35%, as because of duty free economy in Asia. The growth in Asian market is becoming large, because of greater purchasing power of potential customers and providing high quality products comparing with Asian wines and spirits market. The growth opportunities are also extending in India within 300 million middle class people with more opportunities.
The cultural development of corporate sponsorship has supported Pernod Ricard to bring growth opportunities in business. The company has also built up group for super premium segment of beverages in South Korea since 1995 to 2006, and become famous for aged whiskies. The wine and champagne market is growing with 1.7 million cases sold in the year of 2005.
After merging with successful international spirits market, like, Beefeater, Malibu-Kahlùa, Stolichnaya, Perrier-Jouët and Mumm, has helped to grow annually by 2% every year for last five years. The growths become possible for these brands, because customers are desired for these products rather than their needs for these products. The image of Pernod Ricard is growing more effectively after merging and acquisitioned.
Strategic Involvement & Concentrated investment 15 key brands
Pernod Ricard has merged and acquisitioned with most prestigious brands of wines and spirits to make an impressive brand portfolio of both alcoholic and non-alcoholic customers. Several acquisition of the company is given below: (Pernod Ricard)
Acquisitions
- Irish Distillers (Jameson): 1988.
- Orlando Wyndham (Jacob’s Creek) 1989.
- Havana Club International 1993.
- Share with Seagram’s wines and spirits business (Chivas Regal, Martell, The Glenlivet) 2001.
- Allied Domecq (Ballantine’s, Malibu, Kahlúa, Beefeater, Stolichnaya, Mumm, Perrier-Jouët, Montana) 2005.
- V&S (ABSOLUT VODKA) 2008.
Pernod Ricard has merged with top 15 brands of global market by which the business is generating 70% of profits and almost reducing advertising expenditures of the company. It also helped the company with growth potential strongly as profitable brands. Some other strategic involvements are presented by company to focus on the investment on key brands, which are:
- To deliver the effect of Premiumisation, as a major opportunity by Chivas, Martell XO, Ballantine’s having more preferences.
- To become a market leader for imported wines and spirits in China with the help of Chivas Regal, Martell and Royal Salute having strong growth in market,
- To being reliable on stable and sustainable growth of merged brands of Pernod Ricard,
- To support sustainable development in drinking quality of products,
- To commit with corporate and social culture of market,
- To maintain the political instability of market (difficult economic situation in Thailand in 2006),
- To maintain a leadership position in Thailand with 50% of market share.
- To bring the company as prominent brand by the help of Absolut, V&S,
- To hold the local traditions and holidays by Aalborg and OP Anderson aquavits, the Gammel Dansk bitter in Denmark, and Blossa glögg (mulled wine) in Sweden.
Section-4
Competitive advantage Assessment of the Pernod Ricard
Strategy
Organic and External Growth of Pernod Ricard: for wine and sprit market, the Pernod Ricard has dominated the market as market leader. Following are the tonic act behind this leadership position at their birth:
- Organic growth is enough strong.
- In 2001, successful integration of Seagram and in 2005 with Allied Domes is the reflection of their ambition acquisition strategy. An influential Group movement has occurred with the acquisition of the Swedish company VIN&Spirit (V&S) during July 2008.
In the market of wine and sprit, the Pernod Ricard has made the most prestigious brands portfolio through above ways.
Local roots, Global reach of Pernod Ricard: To touch their global ambitions and make safer the local roots the Pernod Ricard has taken over brands in different countries. Since their birth until now, special feature of the PR is that their organisational structure is decentralized. Some of them are:
- Prior the customers demand first in decision making
- Continuously motivate and empower their teams and team members
- Focus and strengthening culture of the Group’s entrepreneurial
Four strategic objectives
Efficiency of the Pernod Ricard convey on the following four key strategic objectives.
- To touch their global vision each of 15 brands are strongly invested.
- Significantly consider brand portfolio pre-immunisation
- In case of emerging markets they are committed to reinforce their position and
- Recreate their external growth
Values of Pernod Ricard
Group of the Pernod Ricard Corporate have historically featured by a set of values as below:
- Conviviality: Openness, friendship, and caring are the source of their willingness through this they reach to others. Three areas of their relationship-internal relation, the public, and clients they apply these modes.
- Entrepreneurship: At all level of their organisation, entrepreneurial spirit and decision making of the Pernod Ricard occurred only through decentralization. Inventiveness of the employees is encouraged by it. In addition, financial performance interest of this corporate are also has directed by their employees.
- Integrity: Transparency and respect to ethics are the source of encourage and train all the employees for working. The Pernod Ricard has always release reliable information for their client, consumers and shareholders. On the other hand, the company is committed to the local community to serve excellence products.
- Commitment: In order to develop and respect group brands employees of the Pernod Ricard are arrogant of their products. Moreover, the Group itself is also strongly bond with a commitment- to respect both their employees and organisational culture.
Key figures: During 1975, by a merger the Pernod Ricard was formed. In the fiscal year 2007/2008, key financial terms and amounts are plotted in following table
Table 1: By selling 95 million case of following branded spirit the Group is established them as the world’s co-leader.
Table 2: They sold in 2007/2008 26 million of n°4 in wines and champagnes as following table around the world.
Table 3: Categories of spirit volume split.
Table 4: Origin of the spirit volume split.
Table 5: All financial information as follow is available at their internet site Shares and dividends.
- Presentations and web casts.
- Financial diary.
The Organisation
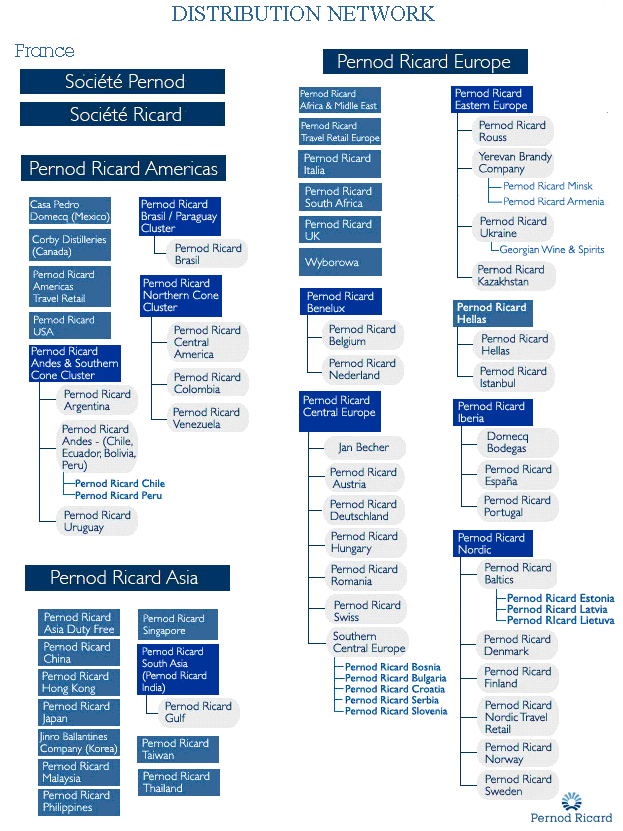
Organisational Structure of Pernod Ricard: (Annual Report, 2007-2008):
From 1975, Pernod Ricard has matured with the development of organic growth and successful merging. It is also building up strong portfolio of premium brands in every continent with decentralised organisational structure both internationally and locally.
A figure is given to specify the organisational structure with specification of brand:
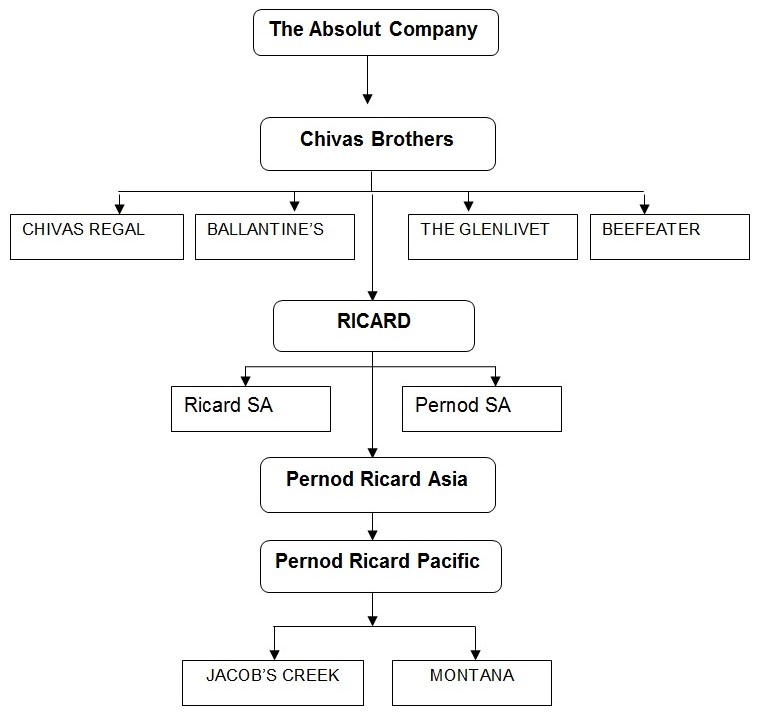
The groups of Pernod Ricard are successful in worldwide by following strategies:
- To use highly talented teams.
- To have decentralised organisational structure.
- To follow product based culture.
- To have outstanding sales and marketing strategies.
- To attach with ethical commitment.
The internal organisational structure of Pernod Ricard has followed as in decentralised way, which is shown below:
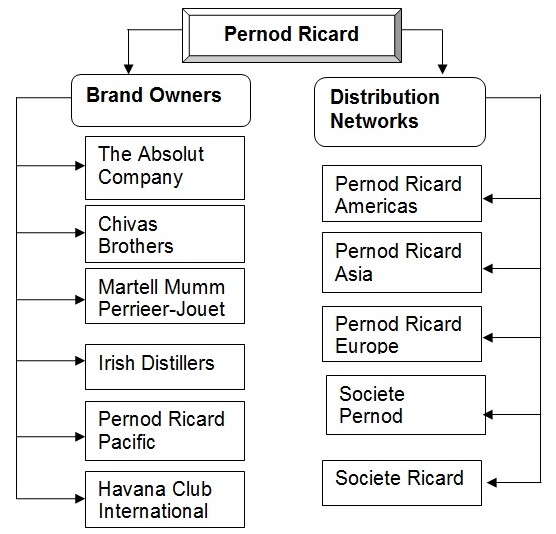
In the company of Pernod Ricard, it has two types of subsidiaries, Brand Owner and Distribution Network. The organisational structure of management has worked for:
- Holding company has involved in monitoring.
- Subsidiary companies are involved in operating decisions, which are staying very close to customers.
From the organisational structure, two broad sections are discussed in below: (Entreprendre, 2009)
- The Absolut Company: This company has been producing ABSOLUT vodka in worldwide, which becomes a major part of brand owner network of Pernod Ricard Company. It has attached with Chivas Brothers, Martell Mumm Perrier-Jouët, Irish Distillers, Malibu-Kahlúa International, Pernod Ricard Pacific, and the joint venture Havana Club International.
- Pernod Ricard Nordic: It is a local and international brand of Pernod Ricard in Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Norway, the Baltic States, and Iceland. This company has merged with V&S Wines (North-European wine producer and importer), V&S Distillers (North-European producer and distributor of regional & local spirit brands), and Pernod Ricard Nordic countries with existing Pernod Ricard distribution subsidiary in the Nordic region).
PEST analysis of Pernod Ricard
The Pernod Ricard’s PEST analysis is very significant to decide whether their strategic plan would be successful for the Pernod Ricard or not:
Political factors
The Pernod Ricard’s distribution channel, investment policy, market segment and the increase or decreases the business risk depends on political factors such as the government of different country can impose different taxes, rules and regulation, which may adversely effects on companies success. As Pernod Ricard has operation on 4 regions of the world so it has to comply different laws when Pernod import and sales its product in those countries for example depending on the volume of alcohol local legislation or narcotics department impose embargo or determine the duty structure vital issue for Pernod Ricard. For instance, Hong Kong regulations have declared to have duty free entrance for 30% volume and Pernod Ricard has driven to avail this advantage.
Economic factors
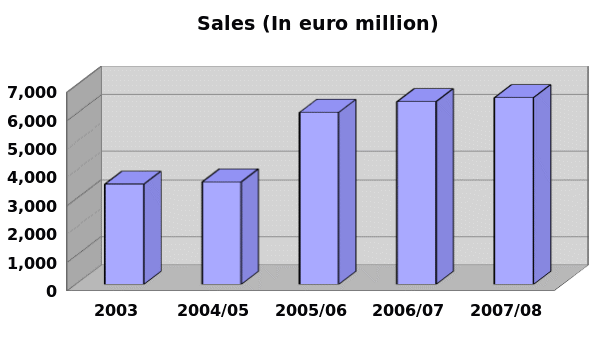
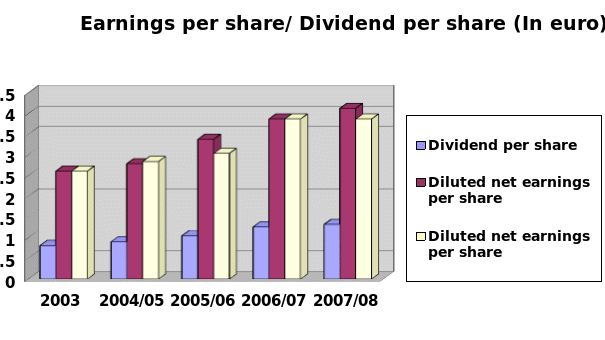
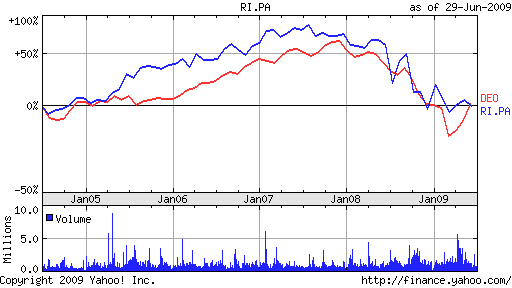
From the annual report 2007/08 of Pernod Ricard, it can be identified that its sales and net profit from operation has increased gradually for example in 2003 its sales was 3,534 million but it was increased additional 3055 million within 5 years. Its sales and profit before tax also increased in 2009 though for global financial crisis people would like to fulfill fundamental needs and avoid to purchasing luxurious products. Figure 15 shows that the earning per share has also increasing but figure 16 shows that in 2007/08 fiscal year the Pernod Ricard had enjoyed more competitive advantages than the current year for global financial crisis.
Global Financial Downturn & Pernod Ricard
The Entreprendre, (2008) has stated that under the global financial crisis started from 2008, Pernod Ricard has reported very strapping results in support of the first quarter of 2008-09. The executive teams and competitive management of Pernod Ricard has dedicated their efforts to face the impact of global financial crisis. In despite of the complex situation of 2008 Pernod Ricard has presented quarterly turnover raised 13% that amounted €1.76 billion when the internal growth rate demonstrated 7% and in some extent above for well-built performance accounted in September 2008. Pernod Ricard has break down its performance according to the region and demonstrated that there was little growth in the US and European market but the some parts of Europe, Asia and Latin Americas presented as emerging market with sustained dynamic growth [Economic Develop Commission, (2009)].
The performance of Pernod Ricard has enabled the company to uphold its objectives at a double-digit escalation of net revenue keeping interest rate and foreign exchange within the current levels.
Pernod Ricard emphasised on its strength of decentralised business model, which is the vital power of their network including brand portfolio, should provide the capability to take action quickly against the financial downturn. In the global financial crisis goes too far difficult the group is ready to implement following preventive measures:
- Pernod has devoted to amplify the level of its advertising as well as promotional budget that would be preserved at an elevated level among the previous four years, which is targeted to € 1.4 billion per annum. This promotional budget is 18% of the annual turnover and corresponds to a very significant amount, which is 3% above than its competitors.
- To face the recessionary impacts stocks Pernod has planned to reduce complying with the changed situation in the aging course of whiskey, champagne, cognac, and wine considering the alteration of predictable growth indicators.
- To overcome the more complicated stage of financial downturn Pernod has designed would be intelligent to amend their level of industrial investments though at this stage this is just hypothetical issue.
Socio-cultural factors
Pernod Ricard Ltd (2008) reported that it has more than 19,300 employees and it will incessantly develop its workers’ professionalism and competence to accomplish corporate goals by developing correlation between workers. Lowry & Dignam (2007) mentioned that the corporate governance system will be collapsed if remuneration committee of a company influenced by the executives so Pernod Ricard has own corporate governance team to control its management and it also follow the recommendation of listing rules. Moreover, in Europe, America, people come from different culture, race and religion and 40% are minorities among them the total population so culture has direct link with Pernod Ricard business.
Technological factor
Technological factors are most significant for Pernod Ricard. When Pernod Ricard is working on differentiation focus, it would be able to protect its intellectual property rights to ensure security measures for it’s invest on its core brand to prevent replication by the competitors. It has emphasised on brand recognition and invested extensive endeavor in protecting its intellectual property rights as well as trademark and domain name registration.. In 2007, Pernod Ricard has introduced some patents with process technology including bottle-marking techniques.
Porter’s five-force Analysis for Pernod Ricard
According to Porter, M. E., (2004), five forces shape the competition within the industry and in the operation of Pernod Ricard, the five forces analysis assists the company to differentiate as a ready for action environment.
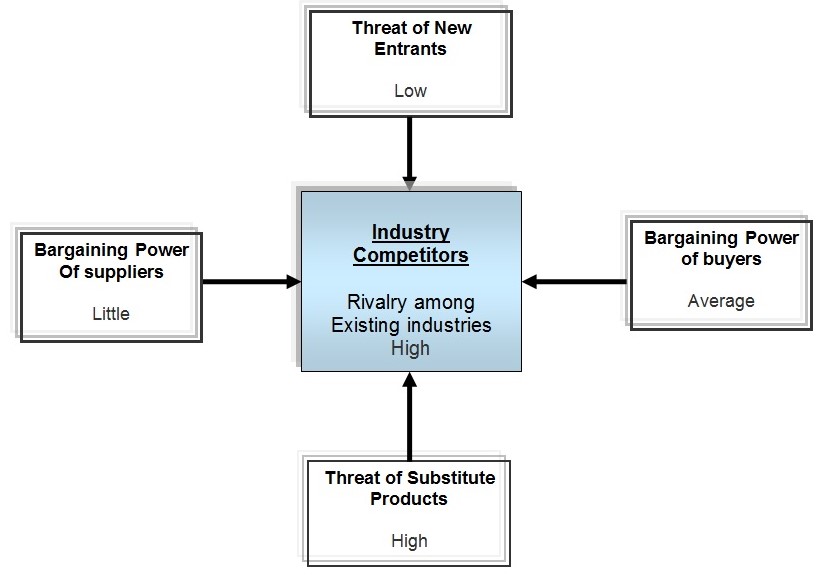
The threat of new entrants:
- In 2008/09, most of the multi-national company has suffered lose for recession so the threat of new entrants is low for this year.
- New entrants would require large capital to compete with Pernod Ricard.
- In addition, it will be difficult for this company to follow the laws like a large company.
Bargaining Power of buyers: The bargaining power of buyer is average because it offers comparatively reasonable price from customer so buyer has power over Pernod Ricard.
Threat of Substitute Products: The following diagram shows that Pernod Ricard’s is not depends on the single-product business, that means, less than 70% of revenue creates from dominant-business and in production process all businesses share materials, technology, marketing process and distribution channels so the threat of new substitute products of this company is high.
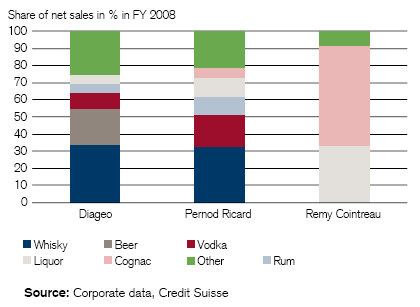
Bargaining Power of suppliers: Pernod Ricard always considers the rate of alcohol in order to gain the benefit or competitive advantage so the bargaining power of suppliers is little.
Competition among the Industry: Competition is too high in this industry and Diageo & Remy Cointreau is the main competitor of Pernod Ricard but it has different competitor in different market. Moreover, it has to compete with international rivals which sometimes difficult to control for government policy.
Methodology
Research Methodology
The foremost objective of this episode is to identify how the chosen research methodology would match with the main objective of the dissertation question and how it would be achieved. For all intents and purposes, there are two types of research methodology and they are qualitative and quantitative research. When quantitative research has been carried out in the course of obtaining primary data such as questionnaire, qualitative research is the study that is accomplished by means of interviews and observations. Thus, the method facilitates a researcher to travel around the facts of individual perceptions in excess of phenomena.
Overview
The topic of present dissertation is ‘is four strategic priorities a real source of competitive advantage: A case study of Pernod Ricard’. This paper would conduct qualitative research through interview of Pernod Ricard’s managers and executives. This method would capable to explore authentic information of Pernod Ricard.
Research Approach
The research approach to develop the methodology explicated underneath has based on descriptive research with theory and inductive way of thinking. This is essential to extend the groundwork by which the research would be purposeful, accomplished, and consequently analysed.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P., (2003) stated that first it is significant to set up the research approach in order to create a noteworthy qualitative methodology. Zikmund, W. M. (2006) added that the research approach undertakes an explicit design that would generate an overall strategy to obtaining the required information to answering the research question. This research approach would review the categories of research design and argue for data collection methods, which are built on logical relations and not just viewpoints.
Cohen, L. et al (2007) argued that the descriptive research would be applicable when the research question has been understood. Within the research approach, the data measurements are reliant on the obtainment of mandatory information as well as the quality of the information. Thus, the outcome of the research is dependent on the dimension procedures those are applied in the collection of the data and the types of data collected.
It is a significant concept of qualitative research in every phase where the description is either inductive or else deductive. Inductive research embarks on with a question and argues to describe it, when the deductive research set in motion with the predicament by functioning backwards to the answers. Thus this present research uses the inductive approach to put together the theory from the gathered data to explore promising conclusions towards four strategic priorities of Pernod Ricard is a real source of competitive advantage.
Primary Research
The selected research methodology is a descriptive interview with a manager at Pernod Ricard in London. To the authors believe the interviewer will obtain all the required information necessary to construct an entire “picture” of the impact of strategic priorities that introduce of competitive advantage. This would be a structured interview, which focuses on the strategic plan and priorities of Pernod Ricard. Secondary research is to review of published materials such as previously researched articles, which would be analysed to put on a broader perspective of the issue.
Reliability, Validity of Interviews
Why an interview with an employee of the Pernod Ricard Corporation has been given most priority in the midst of other means of data collection? The foremost reason of an interview with front line managers of Pernod Ricard has been chosen among other apparent methods is that the author has taken as true, that a dialogue which has intended to take place with one of the representatives of the organisation in this case Pernod Ricard, would be additionally fruitful than any other potential means. As these employees would be at the top consciousness of virtual to the research issues such as, what are the internal difficulties that the Pernod Ricard Corporation has to overcome and how their strategic plan to face future complications does.
The Interviews
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P. (2003) defined that an interview is a purposeful dialogue stuck between two or more people and can collect data, which would be both reliable and valid. Saunders et al (2003) also added that a structured interview as using questionnaires pedestal on predestined and standard or identical sets of questions. The semi-structured interviews would contain a list of themes and questions to be covered when an unstructured interview is an informal but used to explore in depth of the general area of interest. In this research, a semi-structured interview has been applied. The semi-structured interview has chosen because it consents to for specific data to be exposed based on the manager’s perceptions. The semi-structured interview has applied in such situations. Here the respondent’s range of replies would be estimated and necessitates to clarifying details opinions and ideas.
Contingency Plans
Within the event of the collected data from the interview may not be satisfactory enough for analysising and to drawing a conclusion. The research method would be altered and as formerly pointed out the qualitative method of a data collection for the analysis would take place. Qualitative research methodology especially non-participant observation methods such as questionnaire as well as published works would be tailored. The foremost grounds for that option are the fact that this method would set aside the author to carry out the research in shorter time employing observation.
Secondary Research
A questionnaire would be assembled and forwarded to the managers and customers of Pernod Ricard Corporation. This would provide broader insights as to a feedback from the public; the sample would include the younger layer of society, age group involving the ages of 18-36. The objective of this questionnaire is to expand an insight to customer reaction and participation in the strategic analysis, which would find out their level of competitive advantage of Pernod Ricard Corporation. The main issued that would be raised are:
- Modification in strategic analysis, necessary or not,
- The level of competitive advantage with existing systems,
- Advantages and disadvantages of the strategic priorities,
- Future trends and expectations.
Data Analysis
All through the course of the said interview all, the data would be collected and earlier than any actual analysis would take place the data should be pre-approved by the interviewer and a senior manager of the same Pernod Ricard, Middlesex branch. Once the approval has been gained, all the irrelevant data would be eradicated with viewpoint not to create any bias. The remaining data would be examined, compared, and contrasted with previous research in order to determine on the scale of time how Pernod Ricard concerning strategic priorities have been shaped and what the future trends of the organisation are.
Results / Findings
Effect and Effectiveness of the Four Strategic Priorities
Pernod Ricard (2009) supported that the Corporation get support by the implementations of the effect and effectiveness of four strategic priorities as below. Following achievements are forecast from their distribution subsidiaries in France and these are not considering the USA, Australia, Canada, and Japan. In addition, 12th May, 2009 a press release stated that the Pernod Ricard France has took up 229 % ratio.
- At first, the Pernod Ricard would increase its financial resources amounted by 1 billion € through their new rights offered at April 15 and this offer in valid until 29th April.
- Though the institutional investors are out of France, the Group Publicly offered 38,786,220 shares in France. At last, the gross profit from this was amounted by € 1,035,592,074 and from each share € 26.70.
- In a 98.3% take-up ratio, shareholder of the Pernod Ricard has 38,129,025 new shares though market demand was for about € 2.37 billion and by 2.3 times the rights offering was got an oversubscription. In order to meet the additional demand for shares allocation of the new shares were only 657,195 where 50,625,518 new shares were exercising by the right holders.
- During July 1st, 2008 the Prenod Ricard was entitled dividends for the new issued shares and their journey for the Euro next Paris (ISIN code: FR 0000120693) trading business get admitted themselves in 14th May 2008. In this time, settlement for both offering and delivery of the new issued shares right was also executed. Moreover, through this settlement the Pernod Ricard had compromised of 258,574,803 shares.
- In 2008/2009 fiscal year they like to increase their strength of balance sheet with addition of non-strategic assets amounted by 1 billion €. Thus, the implementation of their proposed dividend policy brought a well cash savings results. On the other hand, the Group could enable to access into a favorable financial stage through their strong shareholders’ equity. This feature flexible their way of future growth.
- Analysing all, of the above stages CEO (Chief Executive Officer) Pierre Pringuet has declared following issues-
- Shareholders of the Pernod Ricard serve the flow of confidence in their financial statement and it made them highly pleased.
- Strategies and modes of growth are now much easier than before so that now they are capable to expand their business more steadily and emphasis on primarily towards to touch the global leader position.
SWOT analysis with Competitor
Overall performance appraisal of the Pernod Ricard and its core rival the Diageo Plc, would easily evaluated during following SWOT analysis. Factors of the SWOT analysis in a comparison table for both the companies has outlined recent market position strengths, weaknesses, probable opportunities and threats within next fiscal years.
Within 2007/2008 fiscal year the Diageo Plc had enjoyed more competitive advantages rather than in 2008/2009. On the other hand, both the companies the Pernod Ricard and the Diageo Plc passes through a close competition since 2005 to 2009. In addition, both the companies have more than 10 strategic brands in different market and merger and acquisition record. Now the Pernod Ricard and the Diageo Plc have placed in the second and first in the global ranking respectively.
Dilemma with Business Models
The business models of Pernod Ricard limitation of Corporation needs to follow the strategic horizon when maintain the status quo and cost and quality achievement though current rivals have already enjoys that. To overcome these limits mangers of the Pernod Ricard would show their efficiency in following ways and hence improvement of the all of the organisation would be possible.
- Move forward the organisation, utilize the Western model to create generic strategies.
- Management of the strategic hierarchies.
- Drive into the entire corporation adopt strategic intent as well as competitive revitalization.
- Continue a stability over time.
- Essence of winning would be achieved by practice of strategic intent.
- A clear view of company’s vision, mission, goals and objectives.
- Continue effort and keep commitment individually.
- Assessment of the success along with the firms objectives would easily present the desired position of the firm and define its vision.
- Make realize the essence of winning all level of the organisation and in accordance of it active the management process.
- Beat the competition have to be the common vision for them who are under the strategic intent as well as try to be best and the market leader.
- Targeted objectives commitment have to generated from each of the team members who individually effort to execute this.
- Focus on the short term stability over time operation of the strategic intend should be matched.
In addition, the Western model is reactive rather than be proactive. Now business organisations keep them far away of the military battle since learned from the battlefield. Strategic objectives would be take hold of if tools of the strategies were properly utilized since there have no place of flexibility where strategic intent itself acts but not to take any advantage from the new opportunities.
Conclusions
Conclusion
In view of the fact that fair strategic priorities are the key component of competitive advantage. Among the myriad approaches of strategic analysis has a broader perspective for both the corporate bodies as well as investors. The four strategic priorities model of Pernod Ricard implies the way of overcoming uncertainties of the group that could be accomplished to be rehabilitated into sureness equivalents with the same time keeps it in a standard growth rate. Consequently, the value of a business or asset could be amplified upon all the equity supported starting points along with the effects of debt on top of value.
With the robust growth of assets of Pernod Ricard, the group can develop their areas in investments in core brands, infrastructure projects, and consumers’ networking. Pernod Ricard has strong growth of interest rate scenario and suitable macroeconomic environment, which are better than the crisis of global financial system. The study is given established database of proper stock price and value of the group. Finally, it can be suggested in short that, the Pernod Ricard should monitor stock market behaviour, setting policies like money supply, interest rate, and price index comparing with other competitors both in locally and globally.
Key Recommendation
The wine and spirit market acts with the regulations on international level of business for alcoholic drink sector. The regulatory framework for wine and spirit market should be matched by the market players that can differ country to country. Meanwhile local legislation regarding the use of alcoholic drinks may change in terms of duty and tax structure. Thus, it is required for the alcoholic drink operators to restructure their strategic priorities complying with the local legislation. For Pernod Ricard its four strategic priorities are positively real source of its competitive advantage but it has been recommended following aspects for the group to take into further consideration.
In recent time, the financial crisis of well-established markets, like USA and Europe is going throw the global recession and the people’s purchase power has decrease while job cut has thrown their life into serious uncertainties. Fall of US property market has collapsed the banking sector that has seriously injured all other industries. The bail out bill and rescue package could not keep any significant role to increase the customers purchase power or to lead the market upward. Thus, there are huge possibilities for the crises to stay alive for long run. When people have to straggle for home, food, and employment, they would be bound to leave their alcoholic drink habits.
At the same time, investors would suffer from uncertainty in the borrowed amount by the Pernod Ricard and would reluctant for further investment. This crisis would be in full swing and warnings for high cost of capital and lower rate of return should seriously affect Pernod Ricard group by economic meltdown (HR Guide to the Internet, 2000). Thus, it is suggested for Pernod Ricard to price cut rather than huge promotional expenditure.
As it is seen that, Pernod Ricard has emerging market in stock, so this can be recommended that, the studies have to be developed by assessing market performances, detecting undesired behaviour, monitoring continuously. The alcoholic drink sectors of US should develop their area of market efficiency, price of stocks today and next time, required return, and the value of the group by proper research and development.
Due to the recessionary impact in US, citizens are loosing confidence on their economy and banking sector. Individuals have a propensity to save money for the reason of long run threat. As the companies have driven to job cut, more panic has been spread out among the working force. Spending by browning by the unemployed should turn a wide sphere risk for the nation. Macroeconomic circle of saving and investment would be hampered and Pernod Ricard would engage its effort to research and development of this situation
Bibliography
Accenture, (2006), Pernod Ricard IT Merger Integration Propels High Performance. Web.
Auburn University, 2009, Strategic Intent. Web.
Cohen, L. Manion, L. Morrison, K., 2007, Research Methods in Education, 6th edition, London: Routledge.
Diageo Plc, Diageo Annual Report 2008. Web.
Dess, G. G., Lumpkin, G. T., & Eisner, A. B., 2008, Strategic Management: Text & Cases, Strategic Management: Creating Competitive Advantages. Web.
David, F., 2008, Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, 12th edition, Prentice Hall.
Economic Develop Commission, 2009, The Journey Forward: A 3-Year View and Guide of Economic Strategies for Brevard County. Web.
Food & Drink Business, (2007), Pernod Ricard Raises Spirits With a Collaborative Supply Chain, Logility, Rathbone House Surrey, UK. Web.
Griffin, R. W. 2006, Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York.
Hitt. A. M., Ireland. D. R. & Hoskisson. E. R, 2001, Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization, 4th Edition, Thomson Learning Publication Ltd.
HR Guide to the Internet, 2000, Job Analysis: Methods Of: Interview. Web.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L., 2006. Marketing management, 12th Edition, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Porter, M. E., 2004, Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press.
McGahan. M. A. 1994, Industry Structure and Competitive Advantages, Harvard Business review, 72 (5): 115 – 124.
Porter, M. E., & Kramer M. R., 2006, Strategy & Society: the Link between Competitive Advantage and Corporate Responsibility, Harvard Business Review. Web.
Pernod Ricard (2008), Corporate Responsibility. Web.
Pernod Ricard, (2009), Distribution of interim cash dividend, Press release – Paris. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2008, Premiumisation. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, 15 key brands. Web.
Pernod Ricard, Key financial reporting at 30 June 2008. Web.
Pernod Ricard, Annual Report 2007/2008 of Pernod Ricard. Web.
Pringuet, P., 2009, Premium brands at the heart of the new global economy, Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, 2008/09 9 month sales Confirmed guidance of double digit growth* in Group share of net profit from recurring operations, which should exceed ” 1 billion for the first time Capital increase of ” 1 billion by way of a rights issue. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, 15 strategic brands of Pernod Ricard Corporate. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, Ethics: a sincere and sustainable commitment. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, Pernod Ricard Charter: Objectives, principles, roles and responsibilities. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, 4 Major Regions. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2007, Entreprendre: Magazine for Pernod Ricard Shareholders. Web.
Pernod Ricard, 2009, Entreprendre: Magazine for Pernod Ricard Shareholders (VODCA). Web.
Porter, M. E., 2004, Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press.
Ricard, P. (2008), A winning cocktail recipe for future growth, The Entreprendre, issue no. 53., Paris.
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P., 2003, Research Methods for Business Students, 4th edition, London: FT Prentice Hall.
Schuler, R. S., Jackson, S. E., & Storey, J., 2000, Human Resource Management: A Critical Text, HRM and Its Link with Strategic Management. Web.
Sekaran, U., 2006, Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons Inc, Singapore.
Senge, P. 1990, Review of the fifth discipline: The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organisation. Web.
Senge M. P., 2009, Mental Models. Web.
Senge, P., 1994, Review of The Fifth Discipline, The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organisation. Web.
Skinner, S. J., & Ivancevich, J. M. 2003, Business for the 21st Century, Homewood, Boston.
Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., & Gilbert, D. R., 2006, Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
The Entreprendre, (2008), The magazine for Pernod Ricard shareholders, issue. Web.
Thompson, A. et al, 2007, Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.
Yahoo Finance, 2009, Basic Chart of Pernod Ricard. Web.
Zikmund, W. M., 2006, Business Research Methods, 7th edition, Orlando: Harcourt Publishers.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire has been developed in an attitude that has conserved its internal cohesiveness; special care has been provided to ensure that each question focuses on one exacting issue. Likert Scales (1-7) affords the evaluation method for the various aspects:
Table-6.
Appendix 1
List of Figures
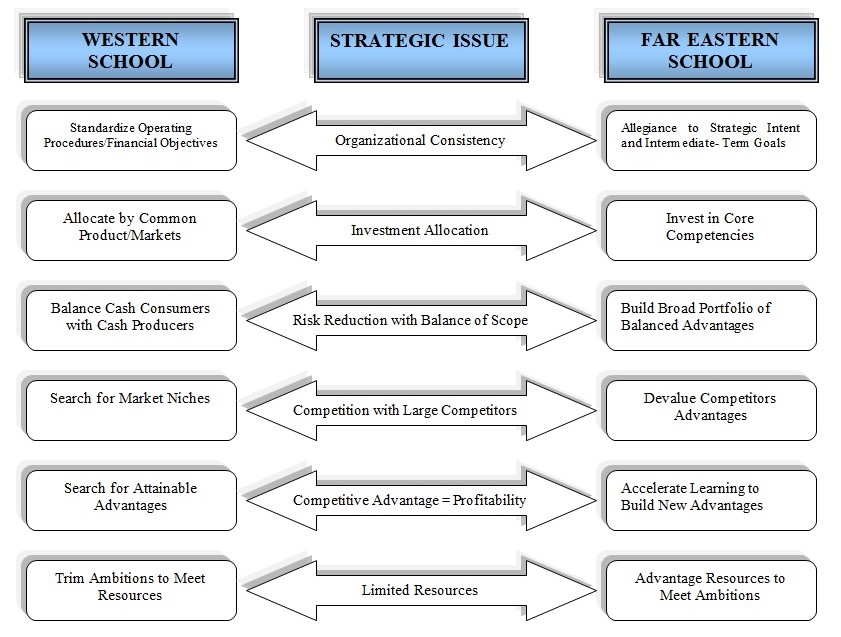
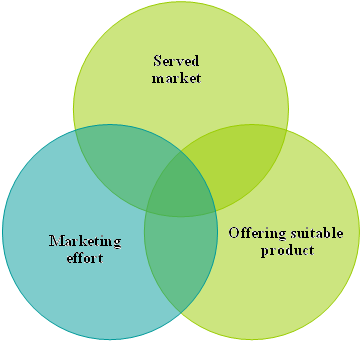
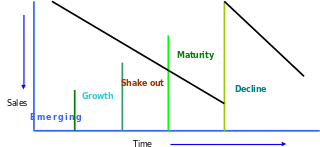
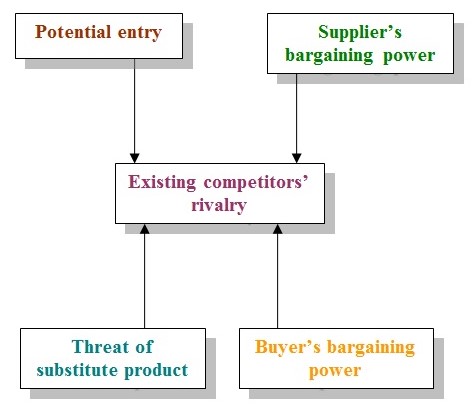
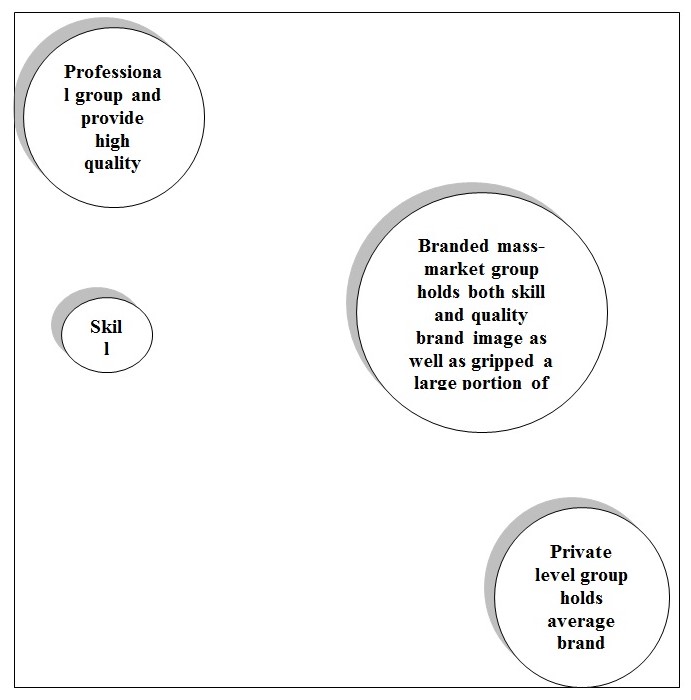
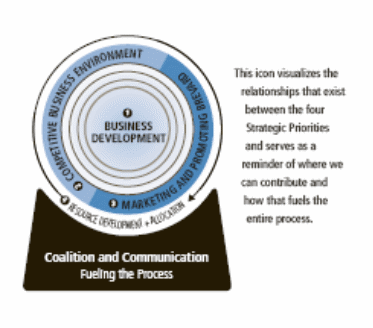
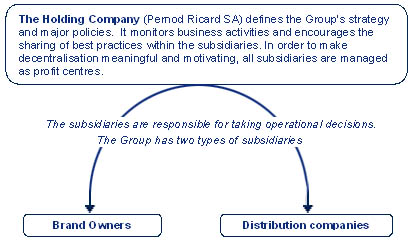
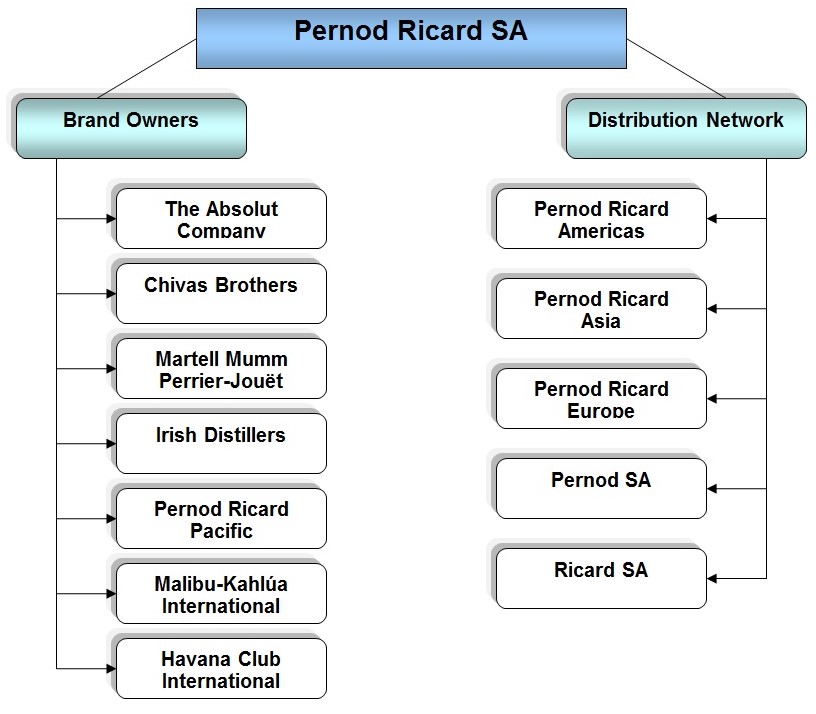
Brands
Group profits of the Pernod Ricard mostly earned from their 15 key brands. Not only in profit making are these brands also holding the potential growth strongly. Following are the key strategic brands those continue the above features: